- Создание загрузочной флешки Windows 10 в Linux
- Загрузочная флешка Windows 10 с помощью WoeUSB
- Создание загрузочной флешки Windows 10 в Linux без программ
- Make bootable usb from iso linux windows
- 2. Requirements
- 3. USB selection
- 4. Boot selection and Partition scheme
- 5. Select the Ubuntu ISO file
- 6. Write the ISO
- 7. Additional downloads
- 8. Write warnings
- 9. Writing the ISO
- 10. Installation complete
- How to Easily Create Windows 10 Bootable USB on Ubuntu or Any Linux Distro
- What you need
- Download Windows 10 ISO
- Creating a Windows 10 Bootable USB for UEFI Firmware
- Boot Windows 10 ISO Installer without USB (BIOS & UEFI)
- Creating a Windows 10 Bootable USB for Legacy BIOS Using WoeUSB
- How to Use WoeUSB From the Command Line
Создание загрузочной флешки Windows 10 в Linux

В этой инструкции пошагово о двух способах создать загрузочную флешку Windows 10 из Linux, которые подойдут как для установки на UEFI-системе, так и для того, чтобы установить ОС в Legacy режиме. Также могут пригодиться материалы: Лучшие программы для создания загрузочной флешки, Загрузочная флешка Windows 10.
Загрузочная флешка Windows 10 с помощью WoeUSB
Первый способ создания загрузочной флешки Windows 10 в Linux — использование бесплатной программы WoeUSB. Созданный с её помощью накопитель работает и в UEFI и в Legacy режиме.
Для установки программы используйте следующие команды в терминале
После установки порядок действий будет следующим:
- Запустите программу.
- Выберите ISO образ диска в разделе «From a disk image» (также, при желании, можно сделать загрузочную флешку с оптического диска или смонтированного образа).
- В разделе «Target device» укажите флешку, на которую будет записан образ (данные с неё будут удалены).
- Нажмите кнопку Install и дождитесь завершения записи загрузочной флешки.
- При появлении ошибки с кодом 256 «Source media is currently mounted», размонтируйте образ ISO с Windows 10.
- При ошибке «Target device is currently busy», размонтируйте и отключите флешку, затем снова подключите её, обычно помогает. Если не сработало, попробуйте предварительно отформатировать её.
На этом процесс записи завершен, можно использовать созданный USB накопитель для установки системы.
Создание загрузочной флешки Windows 10 в Linux без программ
Этот способ, пожалуй, ещё проще, но подойдет только в том случае, если вы планируете загружаться с созданного накопителя на UEFI-системе и устанавливать Windows 10 на GPT диск.
- Отформатируйте флешку в FAT32, например, в приложении «Диски» в Ubuntu.
- Смонтируйте образ ISO с Windows 10 и просто скопируйте всё его содержимое на отформатированную флешку.
Загрузочная флешка Windows 10 для UEFI готова и с неё можно без проблем загрузиться в EFI-режиме.
Источник
Make bootable usb from iso linux windows
With a bootable Ubuntu USB stick, you can:
- Install or upgrade Ubuntu
- Test out the Ubuntu desktop experience without touching your PC configuration
- Boot into Ubuntu on a borrowed machine or from an internet cafe
- Use tools installed by default on the USB stick to repair or fix a broken configuration
Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB stick from Microsoft Windows is very simple and we’re going to cover the process in the next few steps.
Alternatively, we also have tutorials to help you create a bootable USB stick from both Ubuntu and Apple macOS.
2. Requirements
- A 4GB or larger USB stick/flash drive
- Microsoft Windows XP or later
- Rufus, a free and open source USB stick writing tool
- An Ubuntu ISO file. See Get Ubuntu for download links
Take note of where your browser saves downloads: this is normally a directory called ‘Downloads’ on your Windows PC. Don’t download the ISO image directly to the USB stick! If using Windows XP or Vista, download version 2.18 of Rufus.
3. USB selection
Perform the following to configure your USB device in Rufus:
- Launch Rufus
- Insert your USB stick
- Rufus will update to set the device within the Device field
- If the Device selected is incorrect (perhaps you have multiple USB storage devices), select the correct one from the device field’s drop-down menu
You can avoid the hassle of selecting from a list of USB devices by ensuring no other devices are connected.
4. Boot selection and Partition scheme
Now choose the Boot selection. Choices will be Non bootable and FreeDOS. Since you are creating a bootable Ubuntu device select FreeDOS.
The default selections for Partition scheme (MBR) and Target system (BIOS (or UEFI-CSM)) are appropriate (and are the only options available).
5. Select the Ubuntu ISO file
To select the Ubuntu ISO file you downloaded previously, click the SELECT to the right of “Boot selection”. If this is the only ISO file present in the Downloads folder you will only see one file listed.
Select the appropriate ISO file and click on Open.
6. Write the ISO
The Volume label will be updated to reflect the ISO selected.
Leave all other parameters with their default values and click START to initiate the write process.
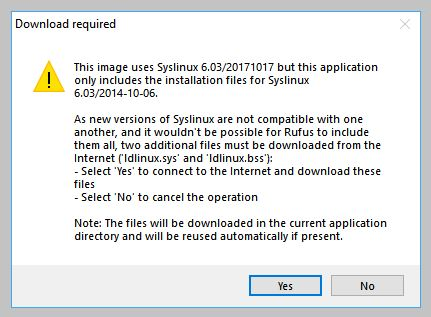
7. Additional downloads
You may be alerted that Rufus requires additional files to complete writing the ISO. If this dialog box appears, select Yes to continue.
8. Write warnings
You will then be alerted that Rufus has detected that the Ubuntu ISO is an ISOHybrid image. This means the same image file can be used as the source for both a DVD and a USB stick without requiring conversion.
Keep Write in ISO Image mode selected and click on OK to continue.
Rufus will also warn you that all data on your selected USB device is about to be destroyed. This is a good moment to double check you’ve selected the correct device before clicking OK when you’re confident you have.
If your USB stick contains multiple partitions Rufus will warn you in a separate pane that these will also be destroyed.
9. Writing the ISO
The ISO will now be written to your USB stick, and the progress bar in Rufus will give you some indication of where you are in the process. With a reasonably modern machine, this should take around 10 minutes. Total elapsed time is shown in the lower right corner of the Rufus window.
10. Installation complete
When Rufus has finished writing the USB device, the Status bar will be green filled and the word READY will appear in the center. Select CLOSE to complete the write process.
Congratulations! You now have Ubuntu on a USB stick, bootable and ready to go.
If you want to install Ubuntu, take a look at our install Ubuntu desktop tutorial.
Источник
How to Easily Create Windows 10 Bootable USB on Ubuntu or Any Linux Distro
This tutorial is going to show you an easy way to create a Windows 10 bootable USB on Linux. I use Ubuntu 20.04 as an example. The method applies to any Linux distribution. I use Windows to do online banking because my bank doesn’t support Linux and sometimes play games that can’t run on Linux.
What you need
- A computer running Linux
- A USB flash drive at least 8GB
- Windows 10 ISO
Download Windows 10 ISO
First, you should download Windows 10 ISO from Microsoft official download link. Note that you might not be able to download the ISO from this link on a Windows computer. This download link is visible to users on Linux computer. Once downloaded, follow the instructions below.
Note: It’s recommended to download the Windows 10 April 2018 update ISO, because the October Update ISO contains a file that is larger than 4GB, which can not be copied to a FAT32 partition.
Update: Microsoft doesn’t allow you to download the Windows 10 April 2018 Update ISO from their website anymore. You can download the ISO via this link: Win10 1803 English x64 ISO
Creating a Windows 10 Bootable USB for UEFI Firmware
This method works for UEFI firmware and is very simple. You create a GUID partition table on your USB stick, create a FAT32 file system on it, and then mount Windows 10 ISO image and copy those Windows 10 files to your USB stick and you are done. The following is a step-by-step guide.
First, install GParted partition editor on your Linux distribution. Ubuntu users run the following command.
Then insert your USB stick to your computer. Make sure you back up important files in your USB stick if there’s any. Next, launch Gparted. You will need to enter your password in order to use GParted.
Select your USB stick from the drop-down menu on the upper-right corner. My USB stick is /dev/sdb . Yours may be different.
If there’s a key icon after the partition name, that means the partition is mounted. Make sure all partitions on your USB stick are unmounted. To unmount a partition, simply right-click on it and select unmount.
Next, on the menu bar, select Device > Create partition table.
Choose GPT as the partition table type and click Apply.
Then right-click on the unallocated space and select New to create a new partition.
Change file system type from ext4 to fat32 and click Add.
Note: The install.wim file in Windows 10 October 2018 update ISO is 4.1G, so if you downloaded this ISO image, you need to change ext4 to ntfs . If you downloaded Windows 10 April 2018 Update ISO, which contains a 3.9G size install.wim file, you can change ext4 to fat32
Update: It is my observation that my NTFS formatted USB stick isn’t bootable on my old laptop, which was bought in 2012. However, it is bootable on my desktop computer, which was bought in 2017. It has a graphical UEFI firware (I can use my mouse to configure firmware settings).
Next, click the green check button on the toolbar to apply this operation. Once that’s done, close GParted (This is important), then find your Windows 10 ISO in file manager. Open it with disk image mounter.
Open the mounted file system. Select all files and folders and copy them to your USB stick.
Sometimes the file manager on Ubuntu hangs and it seems that the copy operation has stopped. Actually it’s working, just be patient. When you see a check mark, it means the copy operation has finished.
If your file manager doesn’t have the Disk image mounter in the context menu, then you can use the following commands to mount. The first command will create a mount point for Windows 10 ISO and the second command will mount Windows 10 ISO under that mount point.
Now in your file manager, go to /mnt/windows10/ and copy all files and folders to your USB stick.
Once the file and folders are copied, your windows 10 bootable USB is created! You can shut down your computer, boot it from this USB stick and install Windows 10 in UEFI mode. Keep in mind that you may need to disable compatibility support module (CSM) in the firmware in order to boot in UEFI mode. You may also need to remove USB stick from your computer and insert it back in order for the firmware to detect the boot loader on your USB stick.
Boot Windows 10 ISO Installer without USB (BIOS & UEFI)
Ever wondered if you can boot Windows 10 ISO installer without a USB flash drive? Yes, you can do it with GRUB2, which is the standard boot loader on Linux.
GRUB2 can not boot Windows 10 ISO directly. You need to create a separate NTFS partition on your hard disk or SSD with a partition editor like GParted and extract the Windows 10 ISO to that partition. Download the Windows 10 ISO file. The latest Windows 10 ISO file is 5.8G. The new NTFS partition should be at least 7G and it should not be used to store any other files.
Then find your Windows 10 ISO in file manager. Open it with disk image mounter.
Open the mounted file system. Select all files and folders and copy them to the NTFS partition.
Sometimes the file manager on Ubuntu hangs and it seems that the copy operation has stopped. Actually, it’s working. Just be patient. When you see a checkmark, it means the copy operation has finished.
Next, open up a terminal window and edit the /etc/grub.d/40_custom file with a text editor such as Nano.
In this file, we can add custom entries to the GRUB boot menu. In this case, we want to add an entry to boot the Windows 10 installer. If your computer still uses the traditional BIOS firmware, then add the following lines in this file.
My NTFS partition is the 6th partition on my first disk, so I use (hd0,6) as the root. You can run sudo parted -l command to check your NTFS partition number. If your computer has multiple hard drives, use the drivemap command to set the partition (hd0,6) as the first hard disk, so Windows will be able to boot.
If your computer uses UEFI firmware, then add the following text in this file.
Save and close the file. (Press Ctrl+O , then press Enter to save a file in Nano text editor. Press Ctrl+X to exit.)
Then update GRUB boot menu.
Next, set GRUB to boot the Windows 10 installer for the next boot with the following command.
Unplug all your external USB storage devices, then reboot your computer. GRUB will choose the Windows 10 installer.
GRUB2 can also boot Linux ISO files stored on the hard drive, so you don’t need to create Linux live USB.
Creating a Windows 10 Bootable USB for Legacy BIOS Using WoeUSB
WoeUSB is a fork of WinUSB. Both of them are open-source software (licensed in GPL) for making Windows bootable USB sticks on Linux platform, but the latter hasn’t been updated since 2012. You may be wondering why it’s named WoeUSB. The author said it’s a GNU convention to abbreviate software that support Windows to “woe”.
To install WoeUSB on Ubuntu 14.04/16.04/17.04, you can use the following PPA. Simply open up a terminal window and run the following commands one by one. Other Linux distro users can compile this software by following the instructions on the Github project page.
This PPA contains many other software. If you don’t need them, you can now remove this PPA from your system.
You can launch WoeUSB from Unity Dash or your application menu.
You can also start it from command line with:
It’s very easy to use the WoeUSB GUI. Select Windows ISO image and your target USB device. Make sure your data on the USB device is backed up before hitting the Install button.
Then wait for the installation to complete.
Once done, you can use the bootable USB to install Windows 10 on your computer.
How to Use WoeUSB From the Command Line
First, find the device name of your USB stick using the following command.
Mine is /dev/sdb . Make sure your USB is unmounted with the following command. Replace /dev/sdb1 with your own partition name.
Then create a bootable Windows 10 USB like below. Red texts shoudl be adapted to your own ISO file name and USB device name. The -v (—verbose) option will give more detailed output.
In my test, the Windows 10 USB created with WoeUSB can boot in both legacy and UEFI mode on my old computer. On my new computer, it can boot in legacy mode but failed in UEFI mode. I don’t know the exact reason, but it’s probably because of bug in this software.
That’s it! I hope this tutorial helped you create windows 10 bootable USB on Ubuntu or any Linux distribution. As always, if you found this post useful, then subscribe to our free newsletter to get new tutorials.
Источник