- How to create a directory or folder
- Creating a folder in Microsoft Windows
- My Computer or Windows Explorer
- Windows desktop
- Create a new folder using a shortcut key
- Windows command line
- Creating a directory in MS-DOS and the Windows command line
- Related pages
- Create a directory with a batch file
- Creating a directory in Linux, Unix, and their variants
- Creating a folder and directory in Microsoft Windows 3.X
- File Manager
- MS-DOS
- Creating a folder in macOS X
- Desktop folder
- Create a folder in a directory
- Create file from command line
- To create file using echo
- To create file using fsutil
- Limitations
- How to create an empty file at the command line in Windows?
- 33 Answers 33
- Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
- Command line syntax
- Options and commands
- Command line argument examples
- Target a specific window
- Open a new profile instance
- Target a directory
- Multiple tabs
- Multiple panes
- Multiple tabs and panes
- Tab title
- Using application title (Preview)
- Tab color
- Color scheme (Preview)
- Tab focus
- Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
- Single quoted parameters
- Escaped quotes
- Using start
How to create a directory or folder
There are multiple ways to create or add a folder, subfolder, directory, and subdirectory on a computer. The methods depend on the operating system or where the directory is being created. Select a link below for steps on how to create a directory and folder in each major operating system.
Creating a folder in Microsoft Windows
My Computer or Windows Explorer
- Open My Computer or Windows Explorer.
- Open the drive or folder where you’d like to create the new folder; for example, the C: drive. If you do not want to create a folder in the root directory, browse to the location of your choosing.
- In Windows 10 on the Home tab, click the New folder icon. In Windows 7 and earlier on the file menu bar, select File and then Folder.
In all versions of Windows, you can also right-click with your mouse on a blank portion of the folder, select New and then Folder.
If you’re using Windows 7 or earlier and do not see the file menu bar at the top of Windows Explorer, press the Alt key and it should become visible.
Windows desktop
- Navigate to the Windows desktop.
- Right-click any blank portion of the desktop.
- In the menu that appears (like that shown in the picture), click New and then Folder.
- A new folder appears. Type the name of the folder you want to use and then press Enter .
Create a new folder using a shortcut key
While in Windows Explorer, you can press Ctrl + Shift + N to create a new folder without using the mouse.
Windows command line
See the following MS-DOS and Windows command line user section for information about creating a directory in the Windows command line.
Creating a directory in MS-DOS and the Windows command line
It is more appropriate to use «directory» instead of «folder» when referring to the command line.
To create a directory in MS-DOS or the Windows command line (cmd), use the md or mkdir MS-DOS command. For example, below we are creating a new directory called «hope» in the current directory.
You can also create multiple new directories in the current directory with the md command. In the next example, we are creating three new directories, called «user1,» «user2,» and «user3,» in the current directory.
If you want to create a directory with spaces, you need to surround the directory name with quotes. In the example below, we are creating a directory called «my example directory» in the current directory.
To create a directory in the parent directory, without first moving into that directory, you can use the command below. This example moves back one directory to create the «example» directory.
To create a subdirectory in a different directory without moving it, use a command similar to the example below. This command creates a «test» directory in the hope directory.
Once a directory is created, you can use the cd command to change the directory and move into that directory.
To make a directory in another drive without moving into that drive, use a command similar to the example below. This command creates an «example» directory on the F: drive. The drive letter «f:» can be substituted from any drive letter.
Related pages
Create a directory with a batch file
A batch file is a series of commands that can be entered in the command line. Therefore, you can use any of the examples from the section above in the batch file to create a new folder.
Creating a directory in Linux, Unix, and their variants
It is more appropriate to use «directory» instead of «folder» when in a command line.
You must have the permissions to create a directory outside of your home directory.
To create a directory in Linux, Unix, or any variant, use the mkdir Linux and Unix command. For example, below we are creating a new directory called hope in the current directory.
Once the directory is created, you can use the cd command to change the directory and move into that directory.
If you want to change the permissions of a directory after its been created, use the chmod command.
Creating a folder and directory in Microsoft Windows 3.X
File Manager
- Open File Manager
- Open the folder where you’d like to place the new folder and on the top menu of File Manager, select File and then new folder.
MS-DOS
See the above MS-DOS user section for information about creating a directory in MS-DOS.
Creating a folder in macOS X
Desktop folder
- Navigate to the macOS desktop.
- Right-click (tap two fingers on the mouse) any blank space on the desktop.
- Select New Folder from the drop-down menu that appears.
- Name the folder, and then press Return .
Create a folder in a directory
- Open Finder and navigate to the directory where you’d like to create the folder.
- Click File in the upper-left corner of the screen.
- Select New Folder in the drop-down menu that appears.
- Name the folder, and then press Return .
Users may also press the shortcut key combination Command + Shift + N to create a new folder.
To create a directory in the Terminal command line, see the Linux steps.
Create file from command line
We can create files from command line in two ways. The first way is to use fsutil command and the other way is to use echo command. If you want to write any specific data in the file then use echo command. If you are not bothered about the data in the file but just want to create a file of some specific size then you can use fsutil command.
To create file using echo
To create file using fsutil
Limitations
Fsutil can be used only by administrators. For non-admin users it throws up below error.
Thank you for the quick and dirty method since windows seems to lack the “touch” command.
How can we use these commands to ‘touch’ a file. Could anyone provide the exact command that can work as linux ‘touch’ for any type of file?
Windows does not lack “touch”. It is echo. As the post describes? type: echo “” Blah.cpp
dude, this isnt working on our school’s computers, can you tell another method that works on windows 8 computers please?
lmao it works at school PC
Make sure that you are typing in the code the right way. It happened to me when I typed in “echo This is a sample text file sample.txt”.
If you want to create a file with NO text in it do this:
at the CLI type “Echo.”: Your output should look like this:
C:\Temp>echo.
To write to a file:
C:\Temp> Echo. >test.txt
This will create a file with single space in the file.
How to create an empty file at the command line in Windows?
How to create an empty file at the DOS/Windows command-line?
but it always displays that a file was copied.
Is there any other method in the standard cmd?
It should be a method that does not require the touch command from Cygwin or any other nonstandard commands. The command needs to run from a script so keystrokes cannot be used.
33 Answers 33
In the same spirit, Samuel suggests in the comments:
the shortest one I use is basically the one by Nomad:
It does give an error:
But this error is on stderr. And > only redirects stdout, where nothing have been produced.
Hence the creation of an empty file.
The error message can be disregarded here. Or, as in Rain’s answer, redirected to NUL :
(Original answer, November 2009)
( echo «» would actually put «» in the file! And echo without the ‘.’ would put » Command ECHO activated » in the file. )
Note: the resulting file is not empty but includes a return line sequence: 2 bytes.
This discussion points to a true batch solution for a real empty file:
The » » pipes a nul response to the set/p command, which will cause the variable used to remain unchanged. As usual with set/p , the string to the right of the equal sign is displayed as a prompt with no CRLF.
Since here the «string to the right of the equal sign» is empty. the result is an empty file.
The difference with cd. > filename (which is mentioned in Patrick Cuff’s answer and does also produce a 0-byte-length file) is that this «bit of redirection» (the trick) can be used to echo lines without any CR:
The dir command should indicate the file size as 11 bytes: » helloworld! «.
Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
You can use wt.exe to open a new instance of Windows Terminal from the command line. You can also use the execution alias wt instead.
If you built Windows Terminal from the source code on GitHub, you can open that build using wtd.exe or wtd .
Command line syntax
The wt command line accepts two types of values: options and commands. Options are a list of flags and other parameters that can control the behavior of the wt command line as a whole. Commands provide the action, or list of actions separated by semicolons, that should be implemented. If no command is specified, then the command is assumed to be new-tab by default.
To display a help message listing the available command line arguments, enter: wt -h , wt —help , wt -? , or wt /? .
Options and commands
Below is the full list of supported commands and options for the wt command line.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| —help , -h , -? , /? | Displays the help message. |
| —maximized , -M | Launches the terminal maximized. |
| —fullscreen , -F | Launches the terminal as full screen. |
| —focus , -f | Launches the terminal in the focus mode. Can be combined with maximized . |
| —window , -w | Launches the terminal in a specific window. |
| Command | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| new-tab , nt | —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , commandline , —title , —tabColor | Creates a new tab. |
| split-pane , sp | -H, —horizontal , -V, —vertical , —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , —title , —tabColor , —size, -s size , commandline , -D, —duplicate | Splits a new pane. |
| focus-tab , ft | —target, -t tab-index | Focuses on a specific tab. |
| move-focus , mf | direction | Move focus between panes in the given direction. Accepts one of up , down , left , right . |
When opening Windows Terminal from cmd (Command Prompt), if you want to use your custom «cmd» profile settings, you will need to use the command wt -p cmd . Otherwise, to run your default profile settings, just use wt cmd .
The -D, —duplicate parameter for split-pane is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Command line argument examples
Commands may vary slightly depending on which command line you’re using.
Target a specific window
The ability for the —window,-w parameter to accept window names is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Below are examples of how to target specific windows using the —window,-w option.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Open a new profile instance
To open a new terminal instance, in this case the command will open the profile named «Ubuntu-18.04», enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
The -p flag is used to specify the Windows Terminal profile that should be opened. Substitute «Ubuntu-18.04» with the name of any terminal profile that you have installed. This will always open a new window. Windows Terminal is not yet capable of opening new tabs or panes in an existing instance.
Target a directory
To specify the folder that should be used as the starting directory for the console, in this case the d:\ directory, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Multiple tabs
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, in this case a Command Prompt profile and a PowerShell profile, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
Multiple panes
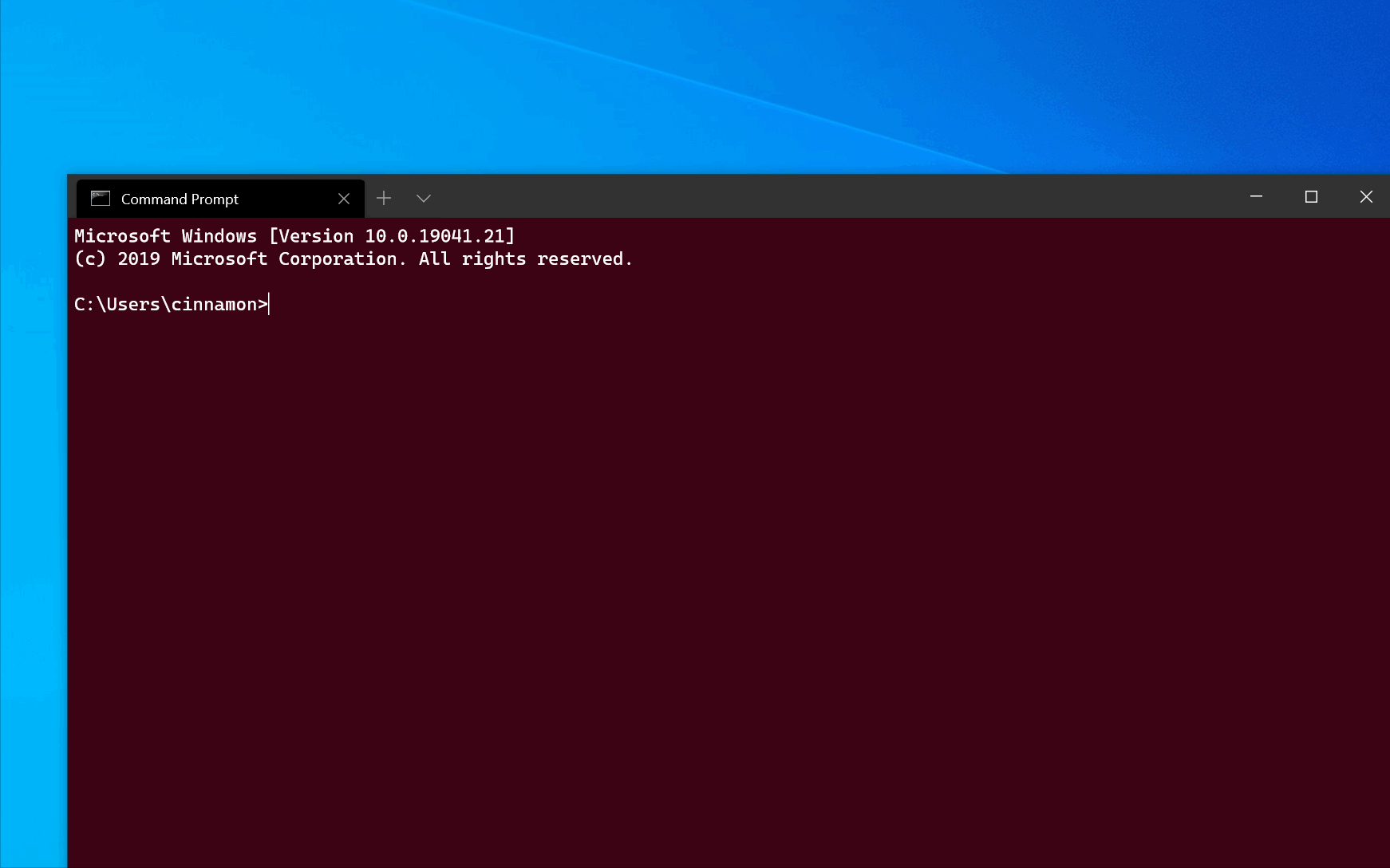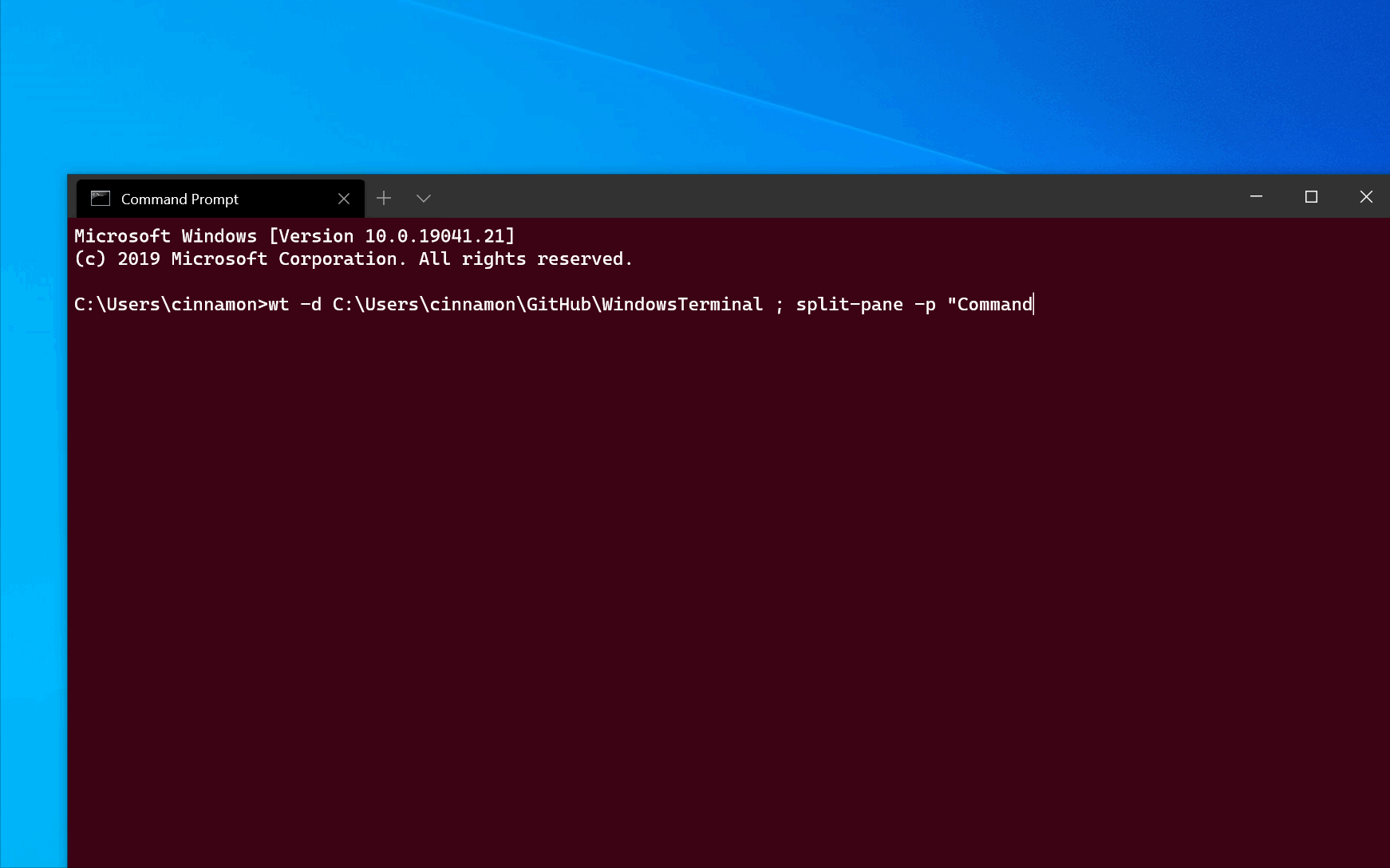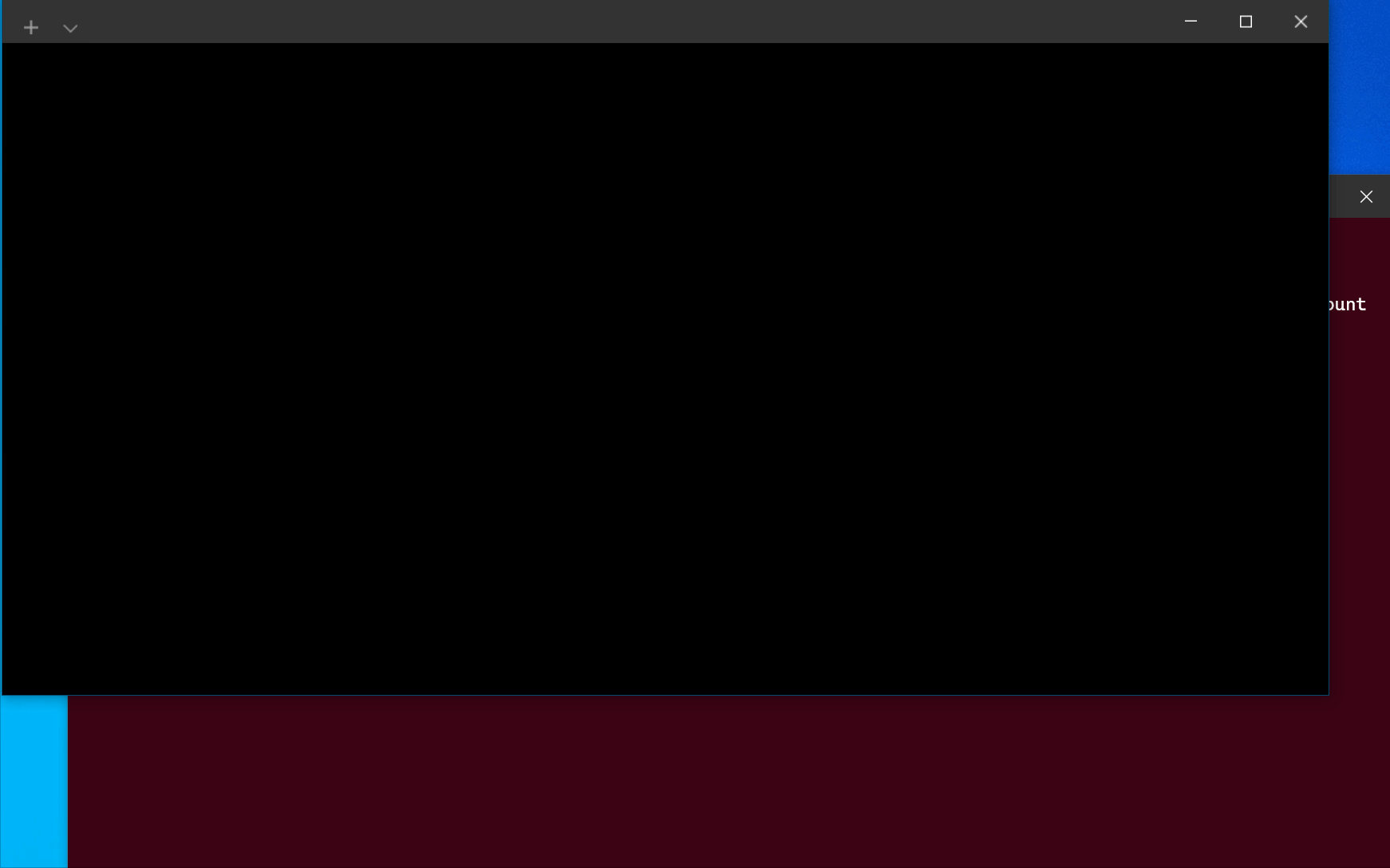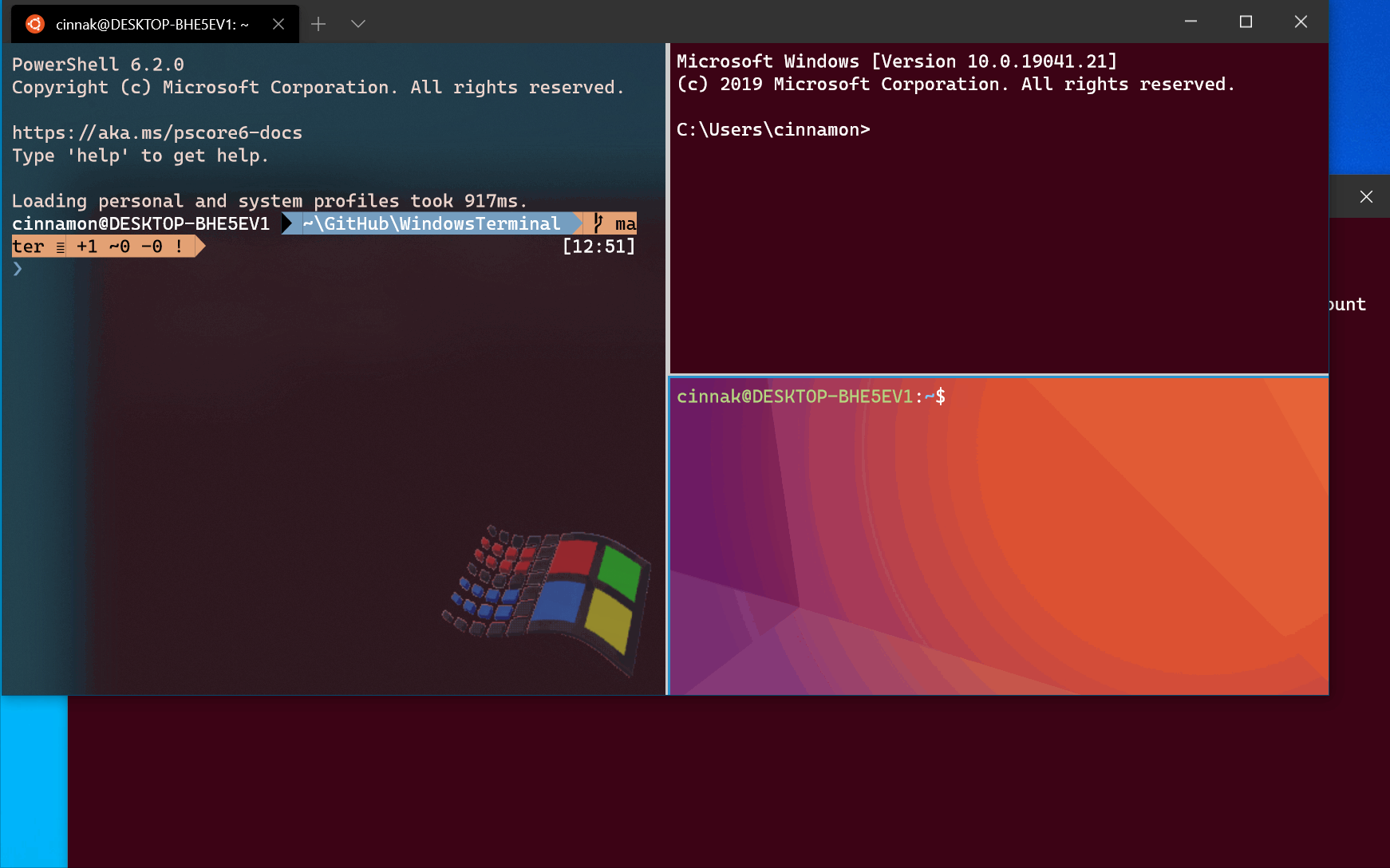
To open a new terminal instance with one tab containing three panes running a Command Prompt profile, a PowerShell profile, and your default profile running a WSL command line, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
The -H flag (or —horizontal ) indicates that you would like the panes to be split horizontally. The -V flag (or —vertical ) indicates that you would like the panes split vertically.
Multiple tabs and panes
The new-tab and split-pane commands can be sequenced to get multiple tabs, each with split panes. To open a new terminal instance with two tabs, each with two panes running a Command Prompt and a WSL command line, with each tab in a different directory, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands. Note to specify a Windows directory as the starting directory for wsl.exe that two backslashes \\ are required.
Tab title
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab titles, use the —title argument. To set the title of each tab when opening two tabs, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; forward-slash + semicolon separates commands.
Using application title (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance allowing applications within it to set the tab title by sending title change messages, use the —useApplicationTitle flag. To suppress these messages, use the —suppressApplicationTitle flag. If none of these flags are provided, the behavior is inherited from the profile’s settings. To open a tab with title tabname that will not be overridden by the application, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab color
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab colors, use the —tabColor argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile, but can be overridden as well using the tab color picker. In the following example, a new terminal is created with two tabs of different colors:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
When —tabColor is set for a tab, it is associated with the first pane of this tab. Hence in a tab with multiple panes, the color will be applied only if the first pane is in focus. To set the tab color for additional panes, you will need to add the —tabColor parameter to the split-pane subcommand as well. In the example below, a tab with two panes is created with tab colors specified for each pane:
Color scheme (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance with a specific color scheme (instead of the colorScheme set in the profile), use the —colorScheme argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab focus
To open a new terminal instance with a specific tab in focus, use the -t flag (or —target ), along with the tab-index number. To open your default profile in the first tab and the «Ubuntu-18.04» profile focused in the second tab ( -t 1 ), enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
Windows Terminal uses the semicolon character ; as a delimiter for separating commands in the wt command line. Unfortunately, PowerShell also uses ; as a command separator. To work around this, you can use the following tricks to run multiple wt commands from PowerShell. In all the following examples, a new terminal window is created with three panes — one running Command Prompt, one with PowerShell, and the last one running WSL.
The following examples use the Start-Process command to run wt . For more information on why the terminal uses Start-Process , see Using start below.
Single quoted parameters
In this example, the wt parameters are wrapped in single quotes ( ‘ ). This syntax is useful if nothing is being calculated.
Escaped quotes
When passing a value contained in a variable to the wt command line, use the following syntax:
Note the usage of ` to escape the double-quotes ( » ) around «Windows PowerShell» in the -p parameter to the split-pane parameter.
Using start
All the above examples explicitly used start to launch the terminal.
The following examples do not use start to run the command line. Instead, there are two other methods of escaping the command line:
- Only escaping the semicolons so that PowerShell will ignore them and pass them straight to wt .
- Using —% , so PowerShell will treat the rest of the command line as arguments to the application.
In both of these examples, the newly created Windows Terminal window will create the window by correctly parsing all the provided command-line arguments.
However, these methods are not recommended currently, as PowerShell will wait for the newly-created terminal window to be closed before returning control to PowerShell. By default, PowerShell will always wait for Windows Store applications (like Windows Terminal) to close before returning to the prompt. Note that this is different than the behavior of Command Prompt, which will return to the prompt immediately.