- Service Accounts
- Overview
- Standalone managed service accounts
- Software requirements
- Group managed service accounts
- Practical applications
- Software requirements
- Virtual accounts
- Software requirements
- See also
- Group Managed Service Accounts в Windows Server 2012
- Создаем KDS ключ
- Создаем учетную запись gMSA
- Установка gMSA на сервере
- «Тонкая» настройка gMSA
- Group Managed Service Accounts Overview Group Managed Service Accounts Overview
- Описание функции Feature description
- Практическое применение Practical applications
- Требования к программному обеспечению Software requirements
- Сведения о диспетчере сервера Server Manager information
- См. также See also
Service Accounts
Applies to
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016
This topic for the IT professional explains group and standalone managed service accounts, and the computer-specific virtual computer account, and it points to resources about these service accounts.
Overview
A service account is a user account that is created explicitly to provide a security context for services running on Windows Server operating systems. The security context determines the service’s ability to access local and network resources. The Windows operating systems rely on services to run various features. These services can be configured through the applications, the Services snap-in, or Task Manager, or by using Windows PowerShell.
This topic contains information about the following types of service accounts:
Standalone managed service accounts
A managed service account is designed to isolate domain accounts in crucial applications, such as Internet Information Services (IIS), and eliminate the need for an administrator to manually administer the service principal name (SPN) and credentials for the accounts.
To use managed service accounts, the server on which the application or service is installed must be running at least Windows ServerВ 2008В R2. One managed service account can be used for services on a single computer. Managed service accounts cannot be shared between multiple computers, and they cannot be used in server clusters where a service is replicated on multiple cluster nodes. For this scenario, you must use a group managed service account. For more information, see Group Managed Service Accounts Overview.
In addition to the enhanced security that is provided by having individual accounts for critical services, there are four important administrative benefits associated with managed service accounts:
You can create a class of domain accounts that can be used to manage and maintain services on local computers.
Unlike domain accounts in which administrators must reset manually passwords, the network passwords for these accounts are automatically reset.
You do not have to complete complex SPN management tasks to use managed service accounts.
Administrative tasks for managed service accounts can be delegated to non-administrators.
Software requirements
Managed service accounts apply to the Windows operating systems that are designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of this topic.
Group managed service accounts
Group managed service accounts are an extension of the standalone managed service accounts, which were introduced in Windows ServerВ 2008В R2. These are managed domain accounts that provide automatic password management and simplified service principal name (SPN) management, including delegation of management to other administrators.
The group managed service account provides the same functionality as a standalone managed service account within the domain, but it extends that functionality over multiple servers. When connecting to a service that is hosted on a server farm, such as Network Load Balancing, the authentication protocols that support mutual authentication require all instances of the services to use the same principal. When group managed service accounts are used as service principals, the Windows Server operating system manages the password for the account instead of relying on the administrator to manage the password.
The Microsoft Key Distribution Service (kdssvc.dll) provides the mechanism to securely obtain the latest key or a specific key with a key identifier for an Active Directory account. This service was introduced in Windows Server 2012, and it does not run on previous versions of the Windows Server operating system. The Key Distribution Service shares a secret, which is used to create keys for the account. These keys are periodically changed. For a group managed service account, the domain controller computes the password on the key that is provided by the Key Distribution Services, in addition to other attributes of the group managed service account.
Practical applications
Group managed service accounts provide a single identity solution for services running on a server farm, or on systems that use Network Load Balancing. By providing a group managed service account solution, services can be configured for the group managed service account principal, and the password management is handled by the operating system.
By using a group managed service account, services or service administrators do not need to manage password synchronization between service instances. The group managed service account supports hosts that are kept offline for an extended time period and the management of member hosts for all instances of a service. This means that you can deploy a server farm that supports a single identity to which existing client computers can authenticate without knowing the instance of the service to which they are connecting.
Failover clusters do not support group managed service account s. However, services that run on top of the Cluster service can use a group managed service account or a standalone managed service account if they are a Windows service, an App pool, a scheduled task, or if they natively support group managed service account or standalone managed service accounts.
Software requirements
Group managed service accounts can only be configured and administered on computers running at least Windows Server 2012, but they can be deployed as a single service identity solution in domains that still have domain controllers running operating systems earlier than Windows Server 2012. There are no domain or forest functional level requirements.
A 64-bit architecture is required to run the Windows PowerShell commands that are used to administer group managed service accounts.
A managed service account is dependent on encryption types supported by Kerberos. When a client computer authenticates to a server by using Kerberos protocol, the domain controller creates a Kerberos service ticket that is protected with encryption that the domain controller and the server support. The domain controller uses the account’s msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypes attribute to determine what encryption the server supports, and if there is no attribute, it assumes that the client computer does not support stronger encryption types. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) should always be explicitly configured for managed service accounts. If computers that host the managed service account are configured to not support RC4, authentication will always fail.
NoteВ В Introduced in WindowsВ ServerВ 2008В R2, the Data Encryption Standard (DES) is disabled by default. For more information about supported encryption types, see Changes in Kerberos Authentication.
Group managed service accounts are not applicable in Windows operating systems prior to Windows Server 2012.
Virtual accounts
Virtual accounts were introduced in Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 and WindowsВ 7, and are managed local accounts that provide the following features to simplify service administration:
The virtual account is automatically managed.
The virtual account can access the network in a domain environment.
No password management is required. For example, if the default value is used for the service accounts during SQL Server setup on Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, a virtual account that uses the instance name as the service name is established in the format NT SERVICE\ .
Services that run as virtual accounts access network resources by using the credentials of the computer account in the format \ $.
For information about how to configure and use virtual service accounts, see Service Accounts Step-by-Step Guide.
Software requirements
Virtual accounts apply to the Windows operating systems that are designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of this topic.
See also
The following table provides links to additional resources that are related to standalone managed service accounts, group managed service accounts, and virtual accounts.
Group Managed Service Accounts в Windows Server 2012
Технология управляемых служебных записей (Managed Service Accounts – MSA) впервые была представлена в Windows Server 2008 R2 и предназначена для автоматического управления (смены) паролей служебных (сервисных) учетных записей. Благодаря использованию механизма Managed Service Accounts можно существенно снизить риск компрометации системных учетных записей, из-под которых запущены системные службы(не секрет, что существует большое количество утилит, позволяющих извлечь пароли локальных пользователей из LSASS).
Для учетных записей MSA генерируется пароль длиной 240 символов, из которых половина – английские буквы, другая половина – служебные символы. Пароль такой учетной записи меняется автоматически (по-умолчанию каждые 30 дней) и не хранится на локальной системе
Основным недостатком MSA является возможность использования подобной служебной записи только на одном компьютере. Это означает, что служебные учетные записи MSA не могут работать с кластерными и NLB службами (веб-фермы), которые работают одновременно на нескольких серверах и используют одну учетную запись и пароль.
Для преодоления указанного недостатка Microsoft в Windows Server 2012 добавила функционал групповых управляемых учетных записей служб (gMSA — Group Managed Service Accounts). Такие учетные записи можно одновременно использовать на нескольких серверах, чтобы все экземпляры службы использовали одну и ту же учетную запись, например в службе балансировки нагрузки (NLB), кластерных службах и т.п.
Требования gMSA :
Чтобы воспользоваться возможностями gMSA, нужно, чтобы инфраструктура соответствовала следующим требованиям:
- Уровень схемы AD — Windows Server 2012 (как ее обновить описано здесь).
- Контроллер домена Windows Server 2012 (и выше) со службой Microsoft Key Distribution Service (служба распространения ключей) – именно это служба отвечает за генерацию паролей
- PowerShell модуль для управления Active Directory
- В качестве клиентов могут использоваться Windows Server 2012/2012 R2 и Windows 8/8.1
- Служба, использующая gMSA должна быть совместима с этим типом аккаунтов (должно быть указано в документации). На данный момент gMSA поддерживают: SQL Server 2008 R2 SP1, 2012;IIS; AD LDS; Exchange 2010/2013
Создаем KDS ключ
Прежде, чем приступить к созданию учетной записи gMSA, необходимо выполнить разовую операцию по созданию корневого ключа KDS (KDS root key). Для этого на контроллере домена с правами администратора выполните команду (служба Microsoft Key Distribution Services должна быть установлена и включена):
В этом случае ключ будет создан и доступен через 10 часов, после окончания репликации.
Проверим, что корневой ключ KDS создался успешно:
Создаем учетную запись gMSA
Создадим новую учетную запись gMSA командой:
Где, gmsa1 – имя создаваемой учетной записи gMSA
dc1.winitpro.ru – имя DNS сервера
gmsa1Group – группа Active Directory, в которую включены все системы, которые будут использовать эту групповую учетную запись (группа должна быть создана предварительно)
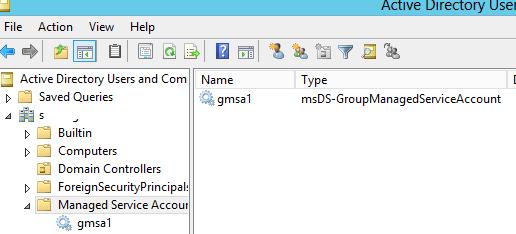
После выполнения команды нужно открыть консоль ADUC (Active Directory Users and Computers) и проверить, что в контейнере (OU) Managed Service Accounts появилась советующая учетная запись (по умолчанию этот контейнер не отображается, чтобы его увидеть, нужно в меню View оснастки включить опцию Advanced Features)
Установка gMSA на сервере
Подключим модуль Powershell для поддержки среды Active Directory:
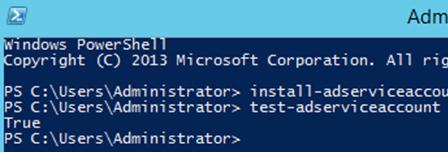
Далее нам нужно установить управляемую учетную запись на сервера, на которых она будет использоваться (из-под этой учетки в дальнейшем будет запущен некий сервис). В первую очередь нужно проверить, что этому серверу разрешено получать пароль учетной записи gMSA из Active Directory. Для этого его учетная запись должна состоять в указанной при создании доменной группе (в нашем случае gmsa1Group). Установим запись gmsa1 на данном сервере:
Проверить, что учетная групповая сервисная запись установлена корректно можно так (для Windows PowerShell 4.0):
Если команда вернет True – все настроено правильно.
Далее в свойствах службы укажем, что она будет запускаться их под учетной записи gMSA. Для этого на вкладке Log on нужно выбрать This account и указать имя сервисной учетной записи. В конце имени обязательно указывается символ $, пароль указывать не нужно. После сохранения изменений службу нужно перезапустить.
Сервисной учетной записи автоматически будут предоставлены права «Log On As a Service».
«Тонкая» настройка gMSA
Периодичность смены пароля можно изменить (по умолчанию 30 дней):
Учетную запись gMSA можно использовать и в задачах планировщика. Тонкий нюанс в том, что задание можно настроить только через PowerShell.
Аргумент «-LogonType Password» означает, что пароль для этой gMSA учетной записи будет получен с контроллера домена.
Group Managed Service Accounts Overview Group Managed Service Accounts Overview
Область применения. Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2016 Applies To: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2016
В этом разделе для ИТ Professional представлена групповая управляемая учетная запись службы с описанием практических приложений, изменений в реализации Майкрософт и требований к оборудованию и программному обеспечению. This topic for the IT professional introduces the group Managed Service Account by describing practical applications, changes in Microsoft’s implementation, and hardware and software requirements.
Описание функции Feature description
Автономная управляемая учетная запись службы (sMSA) — это управляемая Доменная учетная запись, которая обеспечивает автоматическое управление паролями, упрощенное управление именами участников-служб и возможность делегирования управления другим администраторам. A standalone Managed Service Account (sMSA) is a managed domain account that provides automatic password management, simplified service principal name (SPN) management and the ability to delegate the management to other administrators. Такой тип управляемой учетной записи службы реализован в ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7. This type of managed service account (MSA) was introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7.
Групповая управляемая учетная запись службы (gMSA) предоставляет те же функции в домене, но также расширяет эту функциональность на нескольких серверах. The group Managed Service Account (gMSA) provides the same functionality within the domain but also extends that functionality over multiple servers. При подключении к службе, размещенной в ферме серверов, такой как решение с балансировкой сетевой нагрузки, протоколы проверки подлинности, поддерживающие взаимную проверку подлинности, должны использовать один и тот же субъект для всех экземпляров служб. When connecting to a service hosted on a server farm, such as Network Load Balanced solution, the authentication protocols supporting mutual authentication require that all instances of the services use the same principal. Если в качестве субъектов-служб используется gMSA, операционная система Windows управляет паролем для учетной записи, а не полагается на администратора для управления паролем. When a gMSA is used as service principals, the Windows operating system manages the password for the account instead of relying on the administrator to manage the password.
Служба распространения ключей (Майкрософт) (kdssvc.dll) предоставляет механизм для безопасного получения последнего ключа или определенного ключа с идентификатором ключа для учетной записи Active Directory. The Microsoft Key Distribution Service (kdssvc.dll) provides the mechanism to securely obtain the latest key or a specific key with a key identifier for an Active Directory account. Служба распространения ключей использует общий секрет для создания ключей учетной записи. The Key Distribution Service shares a secret which is used to create keys for the account. Эти ключи периодически изменяются. These keys are periodically changed. Для gMSA контроллер домена определяет пароль для ключа, предоставляемого службами распространения ключей, в дополнение к другим атрибутам gMSA. For a gMSA the domain controller computes the password on the key provided by the Key Distribution Services, in addition to other attributes of the gMSA. Узлы-члены могут получить текущие и предшествующие значения пароля, обратившись к контроллеру домена. Member hosts can obtain the current and preceding password values by contacting a domain controller.
Практическое применение Practical applications
Gmsa предоставляют единое решение идентификации для служб, работающих на ферме серверов, или для систем, использующих сетевые Load Balancer. gMSAs provide a single identity solution for services running on a server farm, or on systems behind Network Load Balancer. Предоставляя решение gMSA, можно настроить службы для нового субъекта gMSA, а управление паролями будет обрабатываться Windows. By providing a gMSA solution, services can be configured for the new gMSA principal and the password management is handled by Windows.
Использование gMSA, служб или администраторов служб не требует управления синхронизацией паролей между экземплярами службы. Using a gMSA, services or service administrators do not need to manage password synchronization between service instances. GMSA поддерживает узлы, которые хранятся в автономном режиме в течение расширенного периода времени, а также Управление узлами участников для всех экземпляров службы. The gMSA supports hosts that are kept offline for an extended time period, and management of member hosts for all instances of a service. Это означает, что можно развертывать ферму серверов, поддерживающую единое удостоверение, по которому существующие клиентские компьютеры могут проверять подлинность без идентификации экземпляра службы, к которому они подключаются. This means you can deploy a server farm that supports a single identity to which existing client computers can authenticate without knowing the instance of the service to which they are connecting.
Отказоустойчивые кластеры не поддерживают групповые управляемые учетные записи служб. Failover clusters do not support gMSAs. При этом групповую или автономную учетную запись службы могут использовать службы, работающие поверх службы кластеров и представляющие собой службу Windows, пул приложений или назначенную задачу либо поддерживающие такие учетные записи изначально. However, services that run on top of the Cluster service can use a gMSA or a sMSA if they are a Windows service, an App pool, a scheduled task, or natively support gMSA or sMSA.
Требования к программному обеспечению Software requirements
-Для выполнения команд Windows PowerShell, которые используются для администрирования gmsa, требуется битовая архитектура 64. A 64-bit architecture is required to run the Windows PowerShell commands which are used to administer gMSAs.
Управляемая учетная запись службы зависит от поддерживаемых протоколом Kerberos типов шифрования. Если проверка подлинности клиентского компьютера на сервере выполняется с помощью Kerberos, контроллер домена создает билет службы Kerberos, защищенный шифром, который поддерживают и контроллер, и сервер. A managed service account is dependent upon Kerberos supported encryption types.When a client computer authenticates to a server using Kerberos the DC creates a Kerberos service ticket protected with encryption both the DC and server supports. Контроллер домена использует атрибут msDS суппортеденкриптионтипес учетной записи, — чтобы определить, какое шифрование поддерживает сервер, и, если атрибут отсутствует, предполагается, что клиентский компьютер не поддерживает более надежные типы шифрования. The DC uses the account’s msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypes attribute to determine what encryption the server supports and, if there is no attribute, it assumes the client computer does not support stronger encryption types. Если узел настроен для поддержки алгоритма RC4, проверка подлинности всегда завершится ошибкой. If the host is configured to not support RC4, then authentication will always fail. Поэтому стандарт AES всегда должен быть явным образом настроен для поддержки MSA. For this reason, AES should always be explicitly configured for MSAs.
Начиная с версии Windows Server 2008 R2, стандарт DES отключен по умолчанию. Beginning with Windows Server 2008 R2, DES is disabled by default. Дополнительные сведения о поддерживаемых типах шифрования см. в статье Изменения в проверке подлинности Kerberos. For more information about supported encryption types, see Changes in Kerberos Authentication.
Gmsa не применимы к операционным системам Windows до Windows Server 2012. gMSAs are not applicable to Windows operating systems prior to Windows Server 2012.
Сведения о диспетчере сервера Server Manager information
Нет действий по настройке, необходимых для реализации MSA и gMSA с помощью диспетчер сервера или — командлета Install WindowsFeature. There are no configuration steps necessary to implement MSA and gMSA using Server Manager or the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet.
См. также See also
В следующей таблице представлены ссылки на дополнительные ресурсы, связанные с управляемыми учетными записями служб и групповыми управляемыми учетными записями служб. The following table provides links to additional resources related to Managed Service Accounts and group Managed Service Accounts.