- Linux Increase The Maximum Number Of Open Files / File Descriptors (FD)
- Command To List Number Of Open File Descriptors
- System-wide File Descriptors (FD) Limits
- The Number Of Maximum Files Was Reached, How Do I Fix This Problem?
- User Level FD Limits
- A note about RHEL/CentOS/Fedora/Scientific Linux users
- How to Increase Number of Open Files Limit in Linux
- Find Linux Open File Limit
- Check Hard Limit in Linux
- Check Soft Limits in Linux
- How to Check System wide File Descriptors Limits in Linux
- Set User Level Open File limits in Linux
- Final thoughts
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- Исправляем ошибку “Too many open files“ в Linux
- Ошибка: Too many open files и лимиты на количество открытых файлов в Linux
- Настройки лимитов ограничения на количество одновременно открытых файлов в Linux
- Увеличить лимита открытых файловых дескрипторов для отдельного сервиса
- Увеличение максимального количества открытых файлов для Nginx и Apache
- Лимиты file-max для текущей сессии
- linux-notes.org
- Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux
- Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Linux
- Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Mac OS X
- Увеличюем nginx worker_rlimit_nofile в nginx ( на уровне Nginx)
- Включение ограничений на основе PAM в Unix/Lixux
- 3 thoughts on “ Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux ”
- Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
Linux Increase The Maximum Number Of Open Files / File Descriptors (FD)
H ow do I increase the maximum number of open files under CentOS Linux? How do I open more file descriptors under Linux?
The ulimit command provides control over the resources available to the shell and/or to processes started by it, on systems that allow such control. The maximum number of open file descriptors displayed with following command (login as the root user).
Command To List Number Of Open File Descriptors
Use the following command command to display maximum number of open file descriptors:
cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
Output:
75000 files normal user can have open in single login session. To see the hard and soft values, issue the command as follows:
# ulimit -Hn
# ulimit -Sn
To see the hard and soft values for httpd or oracle user, issue the command as follows:
# su — username
In this example, su to oracle user, enter:
# su — oracle
$ ulimit -Hn
$ ulimit -Sn
System-wide File Descriptors (FD) Limits
The number of concurrently open file descriptors throughout the system can be changed via /etc/sysctl.conf file under Linux operating systems.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
The Number Of Maximum Files Was Reached, How Do I Fix This Problem?
Many application such as Oracle database or Apache web server needs this range quite higher. So you can increase the maximum number of open files by setting a new value in kernel variable /proc/sys/fs/file-max as follows (login as the root):
# sysctl -w fs.file-max=100000
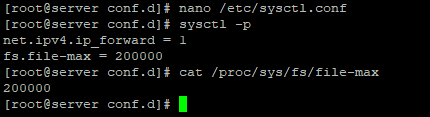
Above command forces the limit to 100000 files. You need to edit /etc/sysctl.conf file and put following line so that after reboot the setting will remain as it is:
# vi /etc/sysctl.conf
Append a config directive as follows:
fs.file-max = 100000
Save and close the file. Users need to log out and log back in again to changes take effect or just type the following command:
# sysctl -p
Verify your settings with command:
# cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
OR
# sysctl fs.file-max
User Level FD Limits
The above procedure sets system-wide file descriptors (FD) limits. However, you can limit httpd (or any other users) user to specific limits by editing /etc/security/limits.conf file, enter:
# vi /etc/security/limits.conf
Set httpd user soft and hard limits as follows:
httpd soft nofile 4096
httpd hard nofile 10240
Save and close the file. To see limits, enter:
# su — httpd
$ ulimit -Hn
$ ulimit -Sn
A note about RHEL/CentOS/Fedora/Scientific Linux users
Edit /etc/pam.d/login file and add/modify the following line (make sure you get pam_limts.so):
Save and close the file.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How to Increase Number of Open Files Limit in Linux
In Linux, you can change the maximum amount of open files. You may modify this number by using the ulimit command. It grants you the ability to control the resources available for the shell or process started by it.
In this short tutorial we will show you how to check your current limit of open files and files descriptions, but to do so, you will need to have root access to your system.
First, Lets see how we can find out the maximum number of opened file descriptors on your Linux system.
Find Linux Open File Limit
The value is stored in:
The number you will see, shows the number of files that a user can have opened per login session. The result might be different depending on your system.
For example on a CentOS server of mine, the limit was set to 818354, while on Ubuntu server that I run at home the default limit was set to 176772.
If you want to see the hard and soft limits, you can use the following commands:
Check Hard Limit in Linux
Check Soft Limits in Linux
To see the hard and soft values for different users, you can simply switch user with “su” to the user which limits you want to check.
How to Check System wide File Descriptors Limits in Linux
If you are running a server, some of your applications may require higher limits for opened file descriptors. A good example for such are MySQL/MariaDB services or Apache web server.
You can increase the limit of opened files in Linux by editing the kernel directive fs.file-max . For that purpose, you can use the sysctl utility.
For example, to increase open file limit to 500000, you can use the following command as root:
You can check the current value for opened files with the following command:
With the above command the changes you have made will only remain active until the next reboot. If you wish to apply them permanently, you will have to edit the following file:
Add the following line:
Of course, you can change the number per your needs. To verify the changes again use:
Users will need to logout and login again for the changes to take effect. If you want to apply the limit immediately, you can use the following command:
Set User Level Open File limits in Linux
The above examples, showed how to set global limits, but you may want to apply limits per user basis. For that purpose, as user root, you will need to edit the following file:
If you are a Linux administrator, I suggest you that you become very familiar with that file and what you can do to it. Read all of the comments in it as it provides great flexibility in terms of managing system resources by limiting users/groups on different levels.
The lines that you should add take the following parameters:
Here is an example of setting a soft and hard limits for user marin:
Final thoughts
This brief article showed you a basic example of how you can check and configure global and user level limits for maximum number of opened files.
While we just scratched the surface, I highly encourage you to have a more detailed look and read regarding /etc/sysctl.conf and /etc/security/limits.conf and learn how to use them. They will be of great help for you one day.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
Исправляем ошибку “Too many open files“ в Linux
Очень часто при работе на высоконагруженных Linux серверах могут возникать ошибки “too many open files». Это означает, что программа открыла слишком много файлов (читай файловых дескрипторов) и не может открыть новые. В Linux ограничения “max open file limit“ установлены по умолчанию для каждого процесса и пользователя, и они не слишком высокие.
В данной статье мы рассмотрим, как проверить текущие ограничения по количеству открытых файлов, как его изменить эту настройку для всего сервера, для отдельных сервисов и для сеанса.
Ошибка: Too many open files и лимиты на количество открытых файлов в Linux
Для начала разберемся, где мы можем наблюдать ошибку “too many open files“. Чаще всего эта ошибка встречается на серверах с установленным веб-серверов NGINX/httpd, сервером БД (MySQL/MariaDB/PostgreSQL), при чтении большого количества логов. Например, когда веб-серверу Nginx не хватает лимита для открытия файлов, вы получите ошибку:
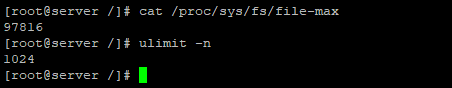
Максимально количество файловых дескрипторов, которые могут быть открыты в вашей системе можно узнать так:
Ограничение на количество открытых файлов для текущего пользователя – 1024. Можно проверить так:
Есть два типа ограничений: Hard и Soft. Пользователь может изменить лимит для soft ограничения (но значение soft не может превышать hard). Hard ограничение можно изменить только от привилегированного пользователя.
Для вывода Soft -граничения выполните:
Для вывода Hard-ограничения:
Настройки лимитов ограничения на количество одновременно открытых файлов в Linux
Чтобы разрешить всем сервисам открывать большее количество файлов, можно изменить лимиты на уровне всей ОС Linux. Чтобы новые настройки работали постоянно и не сбрасывались при перезапуске сервера или сессии, нужно поправить файл /etc/security/limits.conf. Добавьте строки:
Ели вы используете Ubuntu, нужно прописать строку:
Данный параметр добавляет возможность загрузки ограничений при авторизации пользователя.
После изменений, перезапустите терминал и проверьте значение лимита max_open_files:
Увеличить лимита открытых файловых дескрипторов для отдельного сервиса
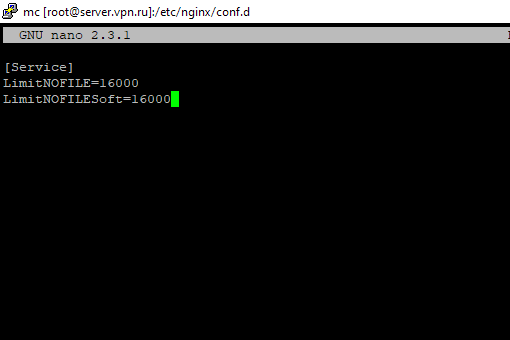
Вы можете изменить лимит на количество открытых файловых дескрипторов для конкретного сервиса, а не для всей системы. Рассмотрим на примере apache. Чтобы изменить значения, откройте настройки службы через systemctl: # systemctl edit httpd.service Добавьте необходимые лимиты, например:
После изменения, нужно обновить конфигурацию сервиса и перезапустить его:
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl restart httpd.service
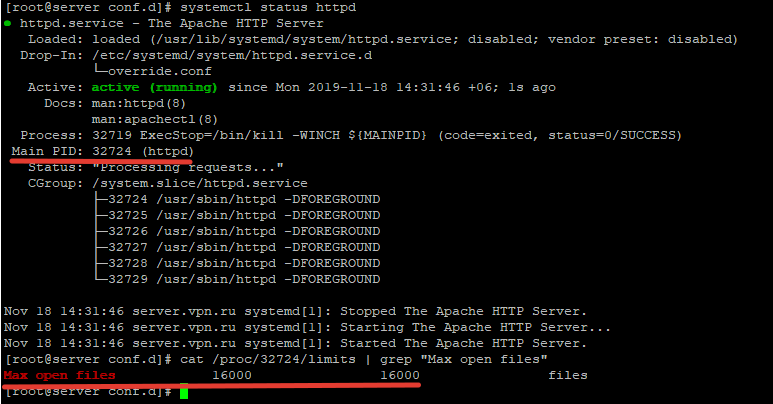
Чтобы проверить, изменились ли значения, нужно получить PID сервиса:
# systemctl status httpd.service
Например, вы определил PID сервиса 32724:
# cat /proc/32724/limits | grep «Max open files”
Так вы изменили значения Max open files для конкретного сервиса.
Увеличение максимального количества открытых файлов для Nginx и Apache
При изменении ограничения на количество открытых файлов для веб-сервера, нужно также поправить конфигурационный файл службы. Например, для Nginx в файле конфигурации /etc/nginx/nginx.conf, нужно прописать/изменить значение в директиве:
После чего выполнить рестарт Nginx.
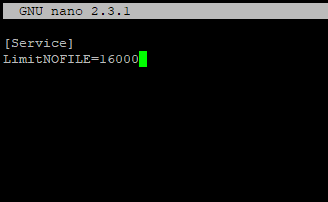
Для apache, нужно создать директорию:
После этого создайте файл limit_nofile.conf:
И добавьте в него:
Не забудьте перезапустить сервис httpd.
Лимиты file-max для текущей сессии
Чтобы изменить лимиты на открытые файлы в рамках вашей сессии терминала, выполните команду:
При закрытии терминала и создания новой сессии, лимиты вернуться к начальным значениям, указанным в файле /etc/security/limits.conf.
Чтобы изменить общее значение в системе /proc/sys/fs/file-max, измените значение fs.file-max в /etc/sysctl.conf:
В данной статье мы разобрались, как решить проблему с недостаточным лимитом для открытых файловых дескрипторов в Linux и рассмотрели несколько вариантов изменения лимитов на сервере.
Источник
linux-notes.org
Несколько раз я сталкивался с ошибкой «Too many open files»(Слишком много открытых файлов) на сервере с высокой нагрузкой. Это означает, что сервер исчерпывает ресурс на максимальный предел открытых файлов (max open file limit). Теперь вопрос в том, как я могу увеличить лимиты открытых файлов на Linux? Да все очень просто, в своей статье «Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux» покажу как это выполняется.
Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux
Приведу команды на различные Unix/Linux ОС
Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Linux
Для начала проверим какой предел установлен в ОС:
Увеличиваем данный предел в Linux
Мы можем увеличить лимиты для открытых файлов:
-===ВРЕМЕННО===-
Если есть необходимость увеличить лимит временно (для тестирования, например), то можно это сделать так:
Вот еще один пример:
-===ПОСТОЯННО===-
Если есть необходимость увеличить лимит навсегда, то можно это сделать так:
Эти настройки будут сохраняться даже после перезагрузки системы. После добавления конфигурации в файл, выполните следующую команду, чтобы изменения вступили в силу:
Настройка лимитов для каждого пользователя
Проверка установленных лимитов
Используйте следующую команду, чтобы увидеть максимальное чисто для открытых файлов:
Подключаемся от пользователя (у меня это nginx):
Проверяем параметры Hard лимитов :
В консоле, можно ввести данную команду (очень удобно отображает):
Проверяем параметры лимитов Soft :
Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Mac OS X
Выполним проверку лимитов с помощью:
- Первый аргумент — soft limit.
- Второй аргумент — hard limit.
Можно прописать в файл:
Увеличюем nginx worker_rlimit_nofile в nginx ( на уровне Nginx)
В nginx также можно увеличить лимиты с директивой worker_rlimit_nofile, которая позволяет увеличить этот лимит, если это не хватает данного ресурса на лету на уровне процесса:
И прописываем (редактируем):
После чего, проверяем конфигурацию nginx и перезапускаем его:
Save and close the file. Reload nginx web server, enter:
В комментариях писали что нельзя установить данные лимиты для Kali Linux. Вот, решил показать наглядный пример:
ulimit в Kali Linux
Включение ограничений на основе PAM в Unix/Lixux
Для Debian/Ubuntu
Редактируем файл (Debian/Ubuntu):
Открываем еще один файл:
И, приводим к виду:
И выполняем рестарт:
Для CentOS/RedHat/Fedora
Редактируем файл (Debian/Ubuntu):
Открываем еще один файл:
И, приводим к виду:
И выполняем рестарт:
У меня все! Статья «Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux», завершено.
3 thoughts on “ Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux ”
в kali linux не работает смена хард и софт лимитов. всё равно пишет 4096 и 1024 соответственно.
Можно! Что-то делаете не так. Я выложил скриншот в статье и показал что можно все сделать.
Мужикам на картинке к статье явно не повезло.
Свет приглушён, явно видно зелёный оттенок табличек аварийного освещения — либо дело за полночь, либо у них блекаут и работают от дизеля.
Сидят за консолью. По сети, оно, похоже, уже не отвечает. Плохо дело.
Стул притащили. Значит, давно не отвечает. Надо было прописать MAX OPEN FILE LIMIT заранее, а не когда уже навернулось.
Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
Этот сайт использует Akismet для борьбы со спамом. Узнайте, как обрабатываются ваши данные комментариев.
Источник