- Максимальный объём оперативной памяти в Windows
- Сколько оперативной памяти поддерживает Windows XP, 7, 8.1 и 10?
- Сколько оперативной памяти максимально видит разная версия Windows
- Windows XP
- Windows 7
- Windows 8 / 8.1
- Windows 10
- Устранение ошибки «Windows 10 использует не всю оперативную память»
- Устраняем проблему с неиспользуемой RAM
- Способ 1: Настройка Windows
- Способ 2: «Командная строка»
- Способ 3: Настройка BIOS
- Способ 4: Уменьшение памяти, используемой встроенной видеокартой
- Способ 5: Проверка модулей ОЗУ
- Заключение
- Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
- Memory and Address Space Limits
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Vista
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home Server
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Embedded
- How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limits
Максимальный объём оперативной памяти в Windows
Максимально поддерживаемый объём оперативной памяти для разных версий Windows. Сколько оперативной памяти поддерживает Windows XP, 7, 8.1 и 10?
Наверное многие помнят, или слышали про первые, на сегодняшний день уже древние компьютеры, такие как к примеру ZX Spectrum? Кто не помнит или забыл, то напомним, что оперативная память для этих динозавров измерялась в килобайтах. Да-да, именно в килобайтах, даже не в мегабайтах.
Сейчас любой мобильник в разы мощнее древних Спектрумов
Технология продвигается, время бежит, и оперативной памяти уже требуется не килобайты, а Гигабайты. В будущем и этого конечно будет мало, и наши сегодняшние самые мощные компьютеры, тоже будут называть динозаврами прошлого. Но вернемся в наше время.
Сколько оперативной памяти поддерживает Windows XP, 7, 8.1 и 10?
Допустим вы захотели в свой компьютер установить дополнительные линейки оперативки. Предположим было у вас 4 Гб, воткнули еще 4 Гб. Включаем комп, а в свойствах все те-же 4Гб. (Да и то это округленный показатель, на деле максимум 3.750 Гб). Почему так? О ужас.
Почему остались те-же 4 Гб. оперативы? Давайте разберемся с этим вопросом, раз и навсегда.
Все операционные системы Windows с разрядностью x86 (32 bit) не важно какая версия, все они видят только до 4 Гб. памяти. Вы хоть истыкайте памятью весь компьютер, как ежика с иголками, он будет видеть только до 4 гигабайта. Связано это с внутренними архитектурными ограничениями.
Если вы установите на компьютере 64 битную операционную систему, то все ваши линейки памяти система и увидит.
Сколько оперативной памяти максимально видит разная версия Windows
Windows XP
- Windows XP x86 (32 bit): 4 гб.
- Windows XP x64 (64 bit): 128 Гб.
Windows 7
- Windows 7 Starter x86 (32 bit): 2 Гб.
- Windows 7 Home Basic x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 7 Home Premium x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 7 Professional x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 7 Enterprise x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 7 Ultimate x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 7 Home Basic x64 (64 bit): 8 Гб.
- Windows 7 Home Premium x64 (64 bit): 16 Гб.
- Windows 7 Professional x64 (64 bit): 192 Гб.
- Windows 7 Enterprise x64 (64 bit): 192 Гб.
- Windows 7 Ultimate x64 (64 bit): 192 Гб.
Windows 8 / 8.1
- Windows 8 x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 8 Professional x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 8 Enterprise x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 8 x64 (64 bit): 128 Гб.
- Windows 8 Professional x64 (64 bit): 512 Гб.
- Windows 8 Enterprise x64 (64 bit): 512 Гб.
Windows 10
- Windows 10 Home x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 10 Home x64 (64 bit): 128 Гб.
- Windows 10 Pro x86 (32 bit): 4 Гб.
- Windows 10 Pro x64 (64 bit): 512 Гб.
Как видите, 64-битные редакции поддерживает огромный объем оперативной памяти, а вот в случае с 32-битной версией нужно быть внимательным с выбором: зачастую система не поддерживает даже указанные 4 Гб.
Максимальное количество оперативной памяти, которые способны «увидеть» 32 разрядные версии Windows — это 4 Гб. Таким образом, если у вас больший объем RAM, следует установить 64-разрядную версию, чтобы воспользоваться этой памятью.
Для того, чтобы узнать, какая версия Windows установлена на вашем компьютере, откройте пункт «Система» в панели управления (или кликните по «Мой компьютер» правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Свойства»).
Устранение ошибки «Windows 10 использует не всю оперативную память»
Устраняем проблему с неиспользуемой RAM
Причин у описываемой проблемы существует немало. В первую очередь источником является программный сбой в определении ОЗУ. Также ошибка появляется и вследствие аппаратной неисправности как модуля или модулей, так и материнской платы. Начнём с программных неполадок.
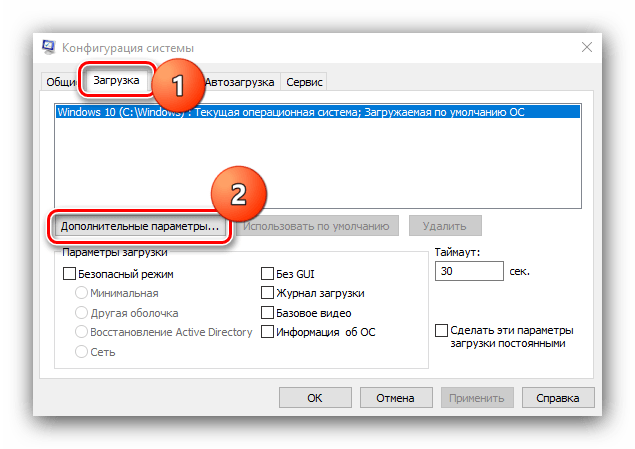
Способ 1: Настройка Windows
Первая причина проблем с использованием «оперативки» – некорректные настройки операционной системы, как правило, параметров работы с этими комплектующими.
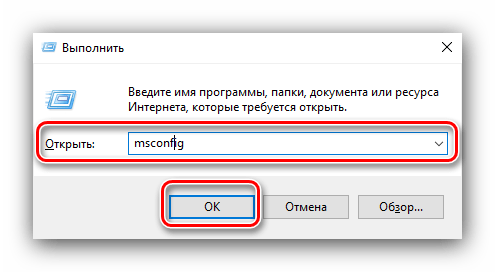
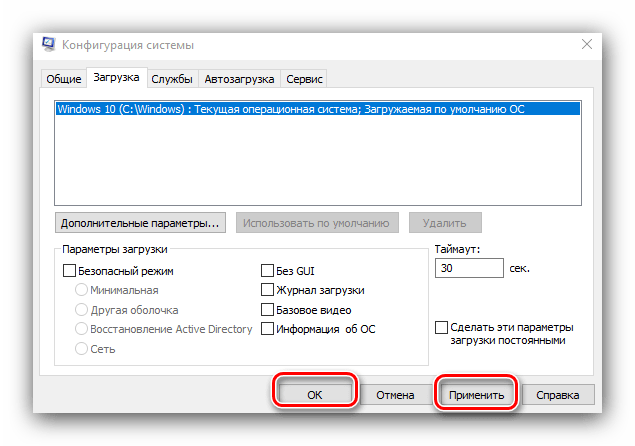
- На «Рабочем столе» нажмите сочетание клавиш Win+R. В окне «Выполнить» введите команду msconfig и кликните «ОК».
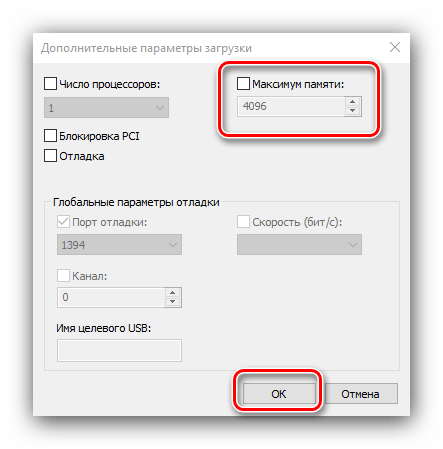
В следующем окне найдите опцию «Максимум памяти» и снимите с неё отметку, после чего нажмите «ОК».
Нажмите «Применить» и «ОК», и затем перезагрузите компьютер.
Способ 2: «Командная строка»
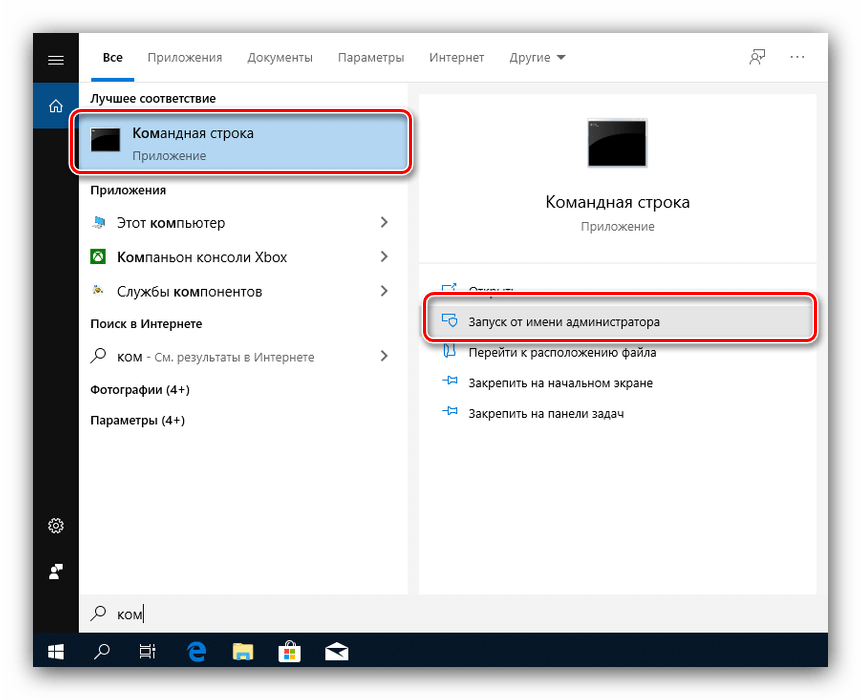
Также стоит попробовать отключить несколько опций, доступных через «Командную строку».
- Откройте «Поиск», в котором начните вводить слово командная . После обнаружения результата выделите его, затем обратитесь к меню справа и воспользуйтесь пунктом «Запуск от имени администратора».
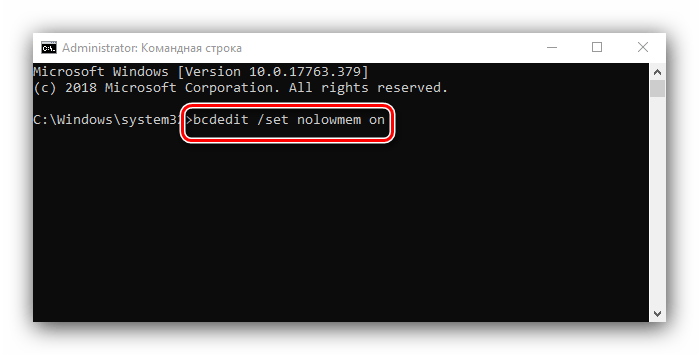
После появления интерфейса ввода команд пропишите следующее:
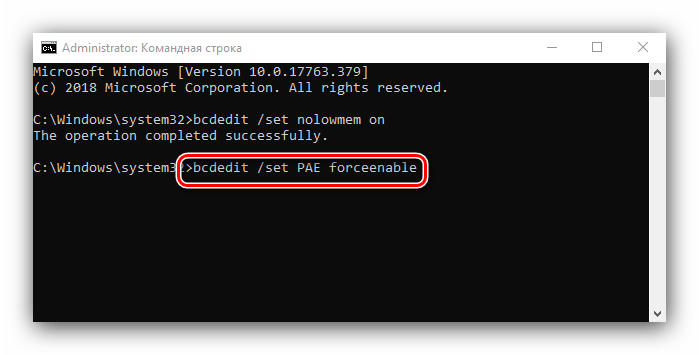
bcdedit /set nolowmem on
Нажмите Enter, затем пропишите следующую команду и снова воспользуйтесь клавишей ввода.
bcdedit /set PAE forceenable
После изменения параметров закрывайте «Командную строку» и перезагружайте компьютер.
Данный метод является более продвинутой версией первого.
Способ 3: Настройка BIOS
Не исключены также неправильные настройки микропрограммы «материнки». Параметры следует проверить и изменить.
- Войдите в БИОС любым подходящим методом.
Урок: Как войти в BIOS
- «Memory Remapping»;
- «DRAM Over 4G Remapping»;
- «H/W DRAM Over 4GB Remapping»;
- «H/W Memory Hole Remapping»;
- «Hardware Memory Hole»;
- «Memory Hole Remapping»;
- «Memory Remap Feature».
Параметры нужно включить – как правило, достаточно переместить соответствующую опцию в положение «On» или «Enabled».
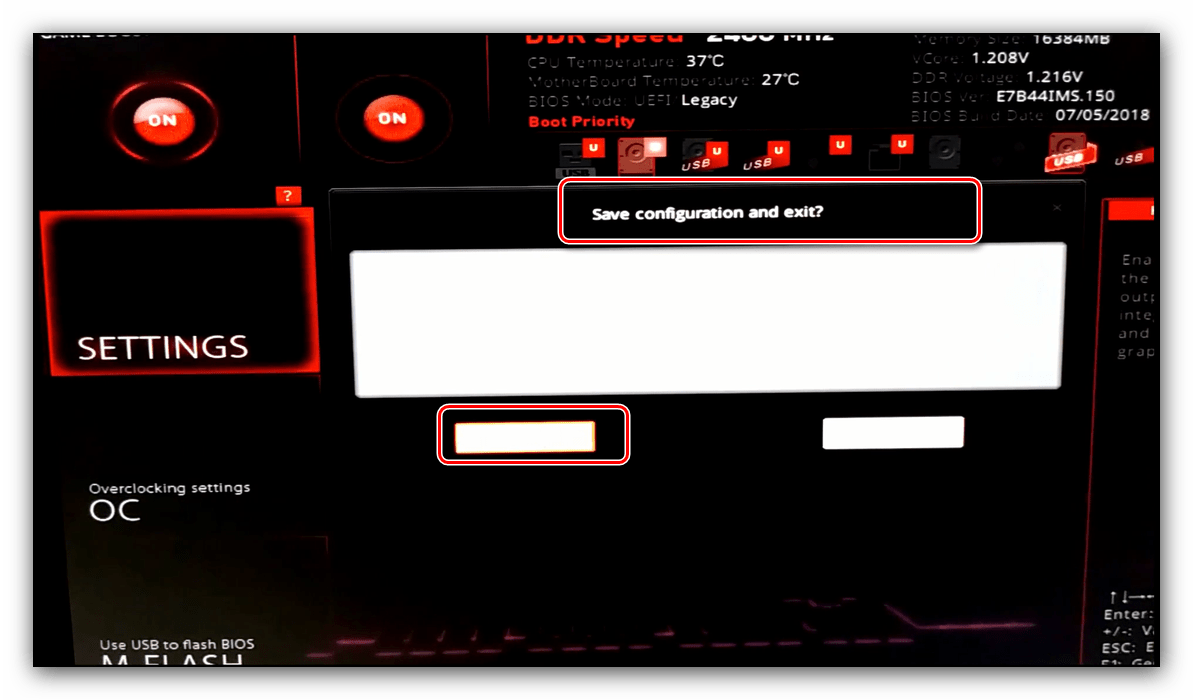
Нажмите F10 для сохранения изменений и загрузите компьютер.
Если вы не можете найти подходящие пункты, не исключено, что производитель заблокировал такую возможность на вашей модели «материнки». В этом случае поможет либо прошивка новой версии микропрограммы, либо замена системной платы.
Способ 4: Уменьшение памяти, используемой встроенной видеокартой
Пользователи ПК или ноутбуков без дискретной видеокарты часто сталкиваются с рассматриваемой проблемой, поскольку встроенные в процессор решения пользуются «оперативкой». Часть из неё закреплена за интегрированной графикой, причём объём задействованной ОЗУ можно изменить. Делается это следующим образом:
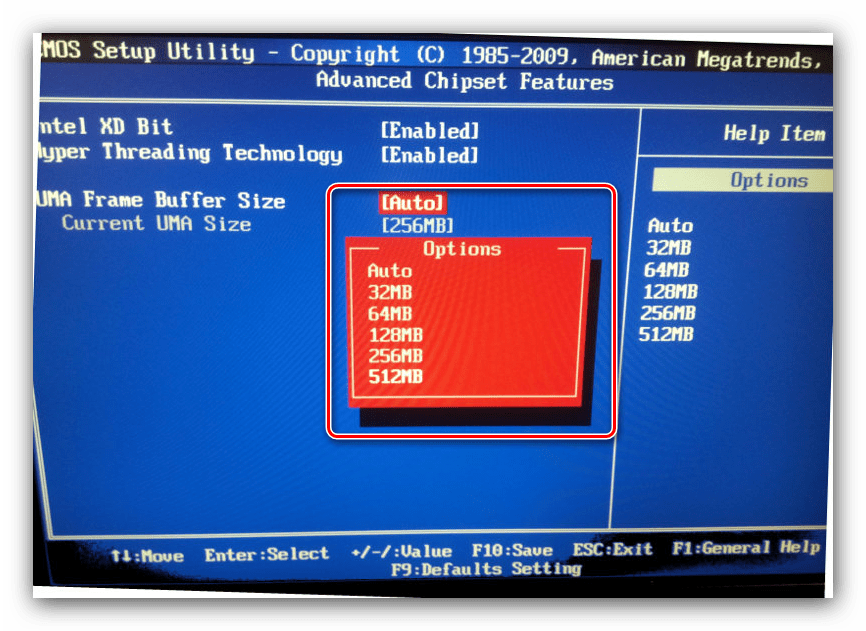
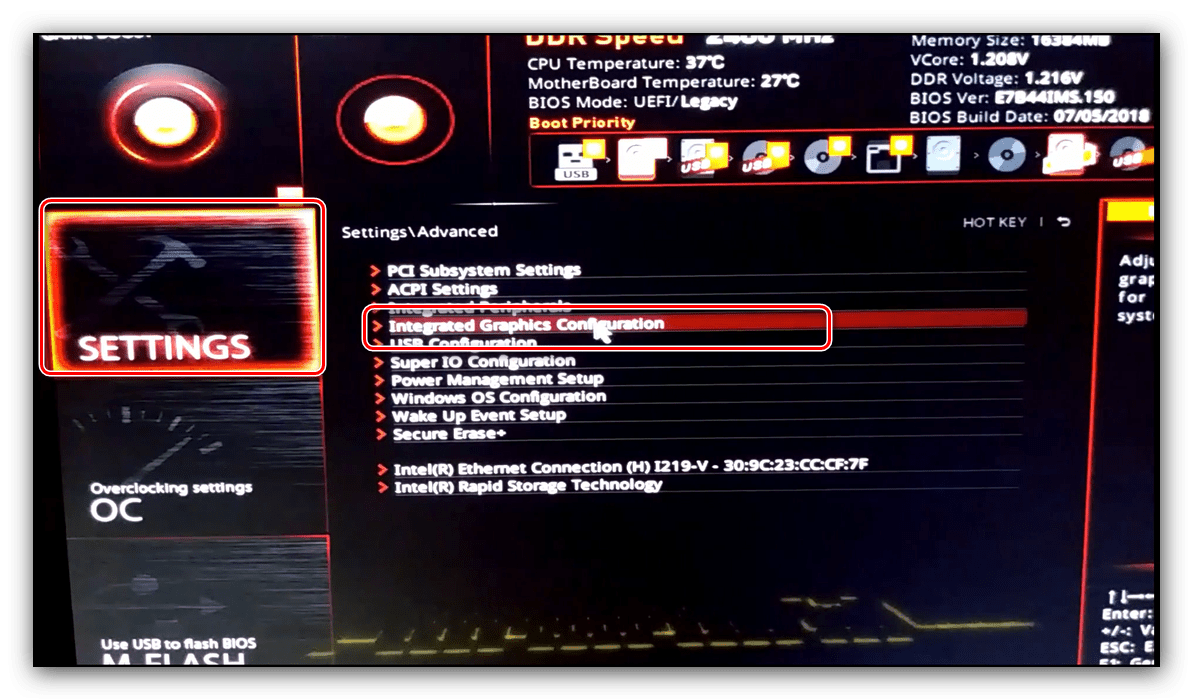
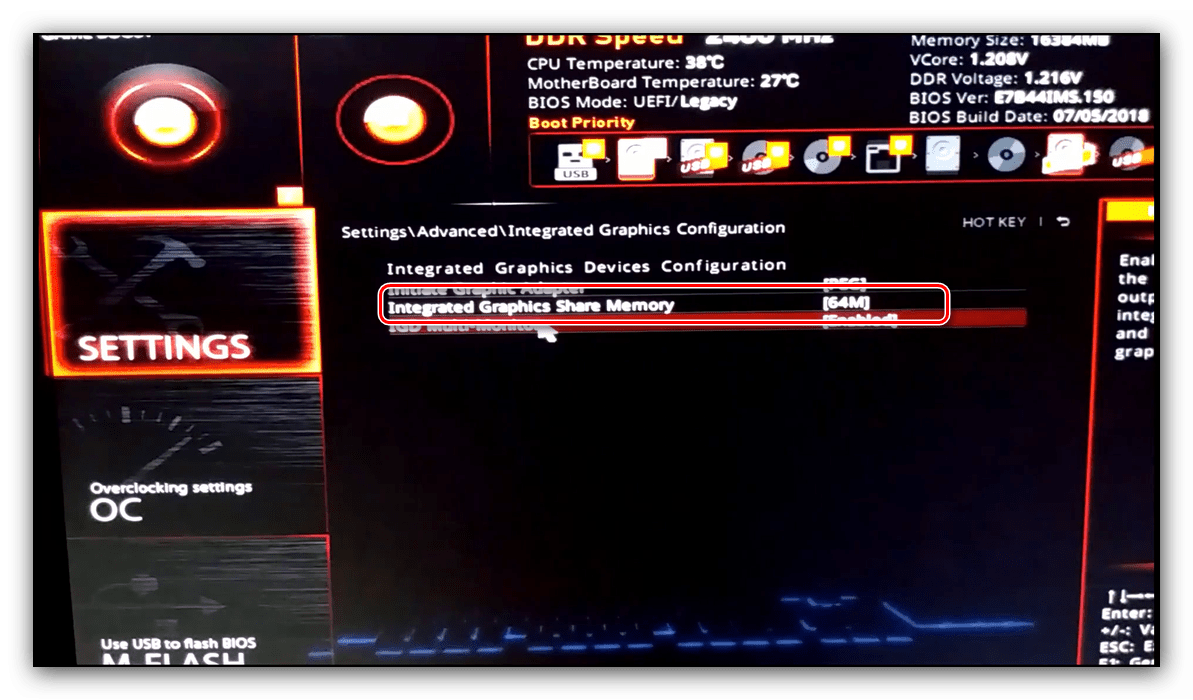
- Войдите в БИОС (шаг 1 предыдущего способа) и переключитесь на вкладку «Advanced» или же любую, где фигурирует этот термин. Далее найдите пункты, которые отвечают за работу графической подсистемы. Они могут называться «UMA Buffer Size», «Internal GPU Buffer», «iGPU Shared Memory» и в таком роде. Обычно шаги объёма фиксированы и опустить его ниже определённого порога не получится, поэтому выставьте минимально возможное значение.
В оболочке UEFI ищите разделы «Дополнительно», «System Configuration» а также просто «Memory».
Далее откройте разделы «Конфигурация системного агента», «Расширенные настройки памяти», «Integrated Graphics Configuration» либо подобное, и задайте требуемый объём по аналогии с текстовым БИОС.
Способ 5: Проверка модулей ОЗУ
Нередко источником ошибки являются неполадки с планками оперативной памяти. Проверить их и устранить возможные проблемы можно по следующему алгоритму:
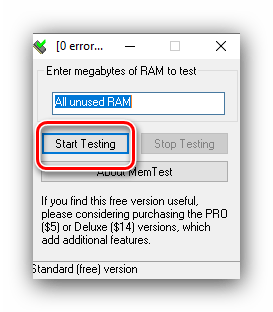
- Первым делом проверьте работоспособность «оперативки» одним из программных способов.
Если появятся ошибки, сбойный модуль нужно заменить.
Аппаратные неисправности – одна из самых редких причин описываемой проблемы, однако и самая неприятная из возможных.
Заключение
Таким образом, мы рассказали, почему в Виндовс 10 появляется сообщение о том, что используется не вся оперативная память, а также предложили варианты устранения этой ошибки.
Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
This topic describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases.
Limits on memory and address space vary by platform, operating system, and by whether the IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE value of the LOADED_IMAGE structure and 4-gigabyte tuning (4GT) are in use. IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE is set or cleared by using the /LARGEADDRESSAWARE linker option.
4-gigabyte tuning (4GT), also known as application memory tuning, or the /3GB switch, is a technology (only applicable to 32 bit systems) that alters the amount of virtual address space available to user mode applications. Enabling this technology reduces the overall size of the system virtual address space and therefore system resource maximums. For more information, see What is 4GT.
Limits on physical memory for 32-bit platforms also depend on the Physical Address Extension (PAE), which allows 32-bit Windows systems to use more than 4 GB of physical memory.
Memory and Address Space Limits
The following table specifies the limits on memory and address space for supported releases of Windows. Unless otherwise noted, the limits in this table apply to all supported releases.
| Memory type | Limit on X86 | Limit in 64-bit Windows | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User-mode virtual address space for each 32-bit process | 2 GB Up to 3 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE and 4GT | 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared (default) 4 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| User-mode virtual address space for each 64-bit process | Not applicable | With IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set (default): x64: WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2 or later: 128 TB x64: Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB Intel Itanium-based systems: 7 TB 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kernel-mode virtual address space | 2 GB From 1 GB to a maximum of 2 GB with 4GT | WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2 or later: 128 TB Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paged pool | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7, Windows ServerВ 2008 and WindowsВ Vista: Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with Service PackВ 1 (SP1), the paged pool can also be limited by the PagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server and Windows ServerВ 2003: 530 MB WindowsВ XP: 490 MB | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7, Windows ServerВ 2008 and WindowsВ Vista: 128 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonpaged pool | 75% of RAM or 2 GB, whichever is smaller. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). WindowsВ Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space and physical memory. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with SP1, the nonpaged pool can also be limited by the NonPagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: 256 MB, or 128 MB with 4GT. | RAM or 128 GB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM) WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7 and Windows ServerВ 2008: 75% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB WindowsВ Vista: 40% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB. Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| System cache virtual address space (physical size limited only by physical memory) | Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space or the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 16 TB. WindowsВ Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with SP1, system cache virtual address space can also be limited by the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: 860 MB with LargeSystemCache registry key set and without 4GT; up to 448 MB with 4GT. | Always 1 TB regardless of physical RAM WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 16 TB. Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 1 TB depending on configuration and RAM. Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 10.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2016.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 8.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2012. Windows ServerВ 2012 is available only in X64 editions.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 7.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2008В R2. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 is available only in 64-bit editions.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2008. Limits greater than 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows VistaThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ Vista.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home ServerWindows Home Server is available only in a 32-bit edition. The physical memory limit is 4 GB. Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003В R2. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003 with Service PackВ 2 (SP2). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003 with Service PackВ 1 (SP1). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows XPThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ XP.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows EmbeddedThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Embedded.
How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limitsDevices have to map their memory below 4 GB for compatibility with non-PAE-aware Windows releases. Therefore, if the system has 4GB of RAM, some of it is either disabled or is remapped above 4GB by the BIOS. If the memory is remapped, X64 Windows can use this memory. X86 client versions of Windows don’t support physical memory above the 4GB mark, so they can’t access these remapped regions. Any X64 Windows or X86 Server release can. X86 client versions with PAE enabled do have a usable 37-bit (128 GB) physical address space. The limit that these versions impose is the highest permitted physical RAM address, not the size of the IO space. That means PAE-aware drivers can actually use physical space above 4 GB if they want. For example, drivers could map the «lost» memory regions located above 4 GB and expose this memory as a RAM disk. |

 Технология продвигается, время бежит, и оперативной памяти уже требуется не килобайты, а Гигабайты. В будущем и этого конечно будет мало, и наши сегодняшние самые мощные компьютеры, тоже будут называть динозаврами прошлого. Но вернемся в наше время.
Технология продвигается, время бежит, и оперативной памяти уже требуется не килобайты, а Гигабайты. В будущем и этого конечно будет мало, и наши сегодняшние самые мощные компьютеры, тоже будут называть динозаврами прошлого. Но вернемся в наше время.