- Install the Microsoft ODBC driver for SQL Server (macOS)
- Microsoft ODBC 17
- Previous versions
- ODBC 13.1
- Driver files
- Resource file loading
- Troubleshooting
- Next steps
- Install SQL Server on a Mac
- Install and Configure Docker
- Now the Actual SQL Server Installation
- Pull the SQL Server Image
- Launch the SQL Server Image
- Password Strength
- Check the Docker container (optional)
- Show All Containers
- Check your Installation & Manage SQL Server
- sql-cli
- Azure Data Studio
- DBeaver
- Installing SQL Server on macOS
- Installing Docker
- Running SQL Server Container Image
- Handy Tips & Tools
- Установка Microsoft ODBC Driver for SQL Server (macOS)
- Microsoft ODBC 17
- Предыдущие версии
- ODBC 13.1
- Файлы драйвера
- Загрузка файла ресурсов
- Устранение неполадок
- Дальнейшие действия
Install the Microsoft ODBC driver for SQL Server (macOS)
This article explains how to install the Microsoft ODBC Driver for SQL Server on macOS. It also includes instructions for the optional command-line tools for SQL Server ( bcp and sqlcmd ) and the unixODBC development headers.
This article provides commands for installing the ODBC driver from the bash shell. If you want to download the packages directly, see Download ODBC Driver for SQL Server.
The Microsoft ODBC driver for SQL Server on macOS is only supported on the x64 architecture through version 17.7. The Apple M1 (ARM64) is supported starting with version 17.8. The architecture will be detected and the correct package will be automatically installed by the Homebrew formula. If your command prompt is running in x64 emulation mode on the M1, the x64 package will be installed. If you’re not running in emulation mode in your command prompt, the ARM64 package will be installed.
Microsoft ODBC 17
To install Microsoft ODBC driver 17 for SQL Server on macOS, run the following commands:
If you installed the v17 msodbcsql package that was briefly available, you should remove it before installing the msodbcsql17 package. This will avoid conflicts. The msodbcsql17 package can be installed side by side with the msodbcsql v13 package.
Previous versions
The following sections provide instructions for installing previous versions of the Microsoft ODBC driver on macOS.
ODBC 13.1
Use the following commands to install the Microsoft ODBC driver 13.1 for SQL Server on OS X 10.11 (El Capitan) and macOS 10.12 (Sierra):
Driver files
The ODBC driver on macOS consists of the following components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| libmsodbcsql.17.dylib or libmsodbcsql.13.dylib | The dynamic library ( dylib ) file that contains all of the driver’s functionality. This file is installed in /usr/local/lib/ . |
| msodbcsqlr17.rll or msodbcsqlr13.rll | The accompanying resource file for the driver library. This file is installed in [driver .dylib directory]../share/msodbcsql17/resources/en_US/ for Driver 17 and in [driver .dylib directory]../share/msodbcsql/resources/en_US/ for Driver 13. |
| msodbcsql.h | The header file that contains all of the new definitions needed to use the driver. Note: You cannot reference msodbcsql.h and odbcss.h in the same program. msodbcsql.h is installed in /usr/local/include/msodbcsql17/ for Driver 17 and in /usr/local/include/msodbcsql/ for Driver 13. |
| LICENSE.txt | The text file that contains the terms of the End-User License Agreement. This file is placed in /usr/local/share/doc/msodbcsql17/ for Driver 17 and in /usr/local/share/doc/msodbcsql/ for Driver 13. |
| RELEASE_NOTES | The text file that contains release notes. This file is placed in /usr/local/share/doc/msodbcsql17/ for Driver 17 and in /usr/local/share/doc/msodbcsql/ for Driver 13. |
Resource file loading
The driver needs to load the resource file in order to function. This file is called msodbcsqlr17.rll or msodbcsqlr13.rll depending on the driver version. The location of the .rll file is relative to the location of the driver itself ( so or dylib ), as noted in the table above. As of version 17.1 the driver will also attempt to load the .rll from the default directory if loading from the relative path fails. The default resource file path on macOS is /usr/local/share/msodbcsql17/resources/en_US/
Troubleshooting
Some users encounter an issue when trying to connect after installing the ODBC driver and receive an error like: «[01000] [unixODBC][Driver Manager]Can’t open lib ‘ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server’ : file not found (0) (SQLDriverConnect)» . It may be the case that unixODBC is not configured correctly to find registered drivers. In these cases, creating a couple symbolic links can resolve the issue.
For additional cases where you are unable to make a connection to SQL Server using the ODBC driver, see the known issues article on troubleshooting connection problems.
Next steps
After installing the driver, you can try the C++ ODBC example application. For more information about developing ODBC applications, see Developing Applications.
For more information, see the ODBC driver release notes and system requirements.
Источник
Install SQL Server on a Mac
Install SQL Server directly to your Mac — no virtual machine required!
Microsoft has made SQL Server available for macOS and Linux systems. This is made possible by running SQL Server from a Docker container. Therefore, there’s no need to install a virtual machine with Windows (which was the only way to run SQL Server on a Mac prior to SQL Server 2017).
Install and Configure Docker
This is a prerequisite for installing SQL Server on your Mac. Because the Mac runs SQL Server inside a Docker container, the first thing we need to do is download and install Docker (unless it’s already installed). Once installed, we’ll increase its memory allocation to a more suitable level for running SQL Server.
- Download Docker from the download page, extract it, and drag it into your Application folder.
- Launch Docker, and go to Preferences > Advanced and increase its memory allocation to 4GB
If I’ve confused you, don’t worry. I’ve written a tutorial with screenshots: Install Docker on a Mac and Configure for SQL Server.
OK, we’re now ready to install SQL Server on your Mac.
Now the Actual SQL Server Installation
Now that we’ve installed Docker and increased its memory allocation, we can go ahead and install SQL Server. The Mac uses the Linux image (the SQL Server for Linux Docker image).
Pull the SQL Server Image
Open a Terminal window and run the following command:*
This pulls the latest SQL Server for Linux Docker image to your computer.
* The exact command will depend on which release you download. Also, since I wrote this article, Docker has moved the repository for SQL Server. You might need to use docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2017-latest-ubuntu to download SQL Server 2017.
Also, SQL Server 2019 Preview has been available since late 2018. As of late 2019 you can download it at docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2019-CTP3.2-ubuntu .
For the latest image, see the official Microsoft repository on the Docker website.
Launch the SQL Server Image
Run the following command to launch an instance of the Docker image you just downloaded:
Replace the container name and password with your own. Also be sure to make a strong password, or you may get an error (see below).
Also, if you downloaded a different container image, replace microsoft/mssql-server-linux with your container image.
Here’s an explanation of the above parameters:
-d This is an optional parameter that launches the Docker container in daemon mode. This means that it runs in the background and doesn’t need its own Terminal window open. You can omit this parameter to have the container run in its own Terminal window. —name Homer This optional parameter provides a name for the container. This can be handy when stopping and starting the container from the Terminal. -e ‘ACCEPT_EULA=Y’ The Y shows that you agree with the EULA (End User Licence Agreement). This is required in order to install SQL Server. -e ‘SA_PASSWORD=myPassw0rd’ Required parameter that sets the sa database password. -p 1433:1433 This maps the local port 1433 to port 1433 on the container. This is the default TCP port that SQL Server uses to listen for connections. microsoft/mssql-server-linux This tells Docker which image to use. If you downloaded a different one, use that instead.
Password Strength
If you get the following error at this step, try again, but with a stronger password.
Check the Docker container (optional)
Type the following command to check that the Docker container is running.
If it’s up and running, it should return something like this:
Show All Containers
The above command only shows those containers that are currently running. To show all containers (whether they’re running or not), append the -a flag to the command (you can also use -all ):
Check your Installation & Manage SQL Server
Now that you’ve installed SQL Server on your Mac, you’ll probably want to check that you can access it and query it, etc. Then you’ll probably want to start creating databases and doing other DB-related tasks. You’ll need some sort of management tool for this.
Here are three options:
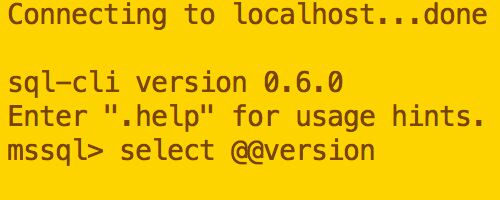
sql-cli
sql-cli is a cross platform command line tool for SQL Server. This means you can create databases and query them right from your Mac’s Terminal window.
Installation is as easy as running a single command (assuming you already have NodeJs installed).
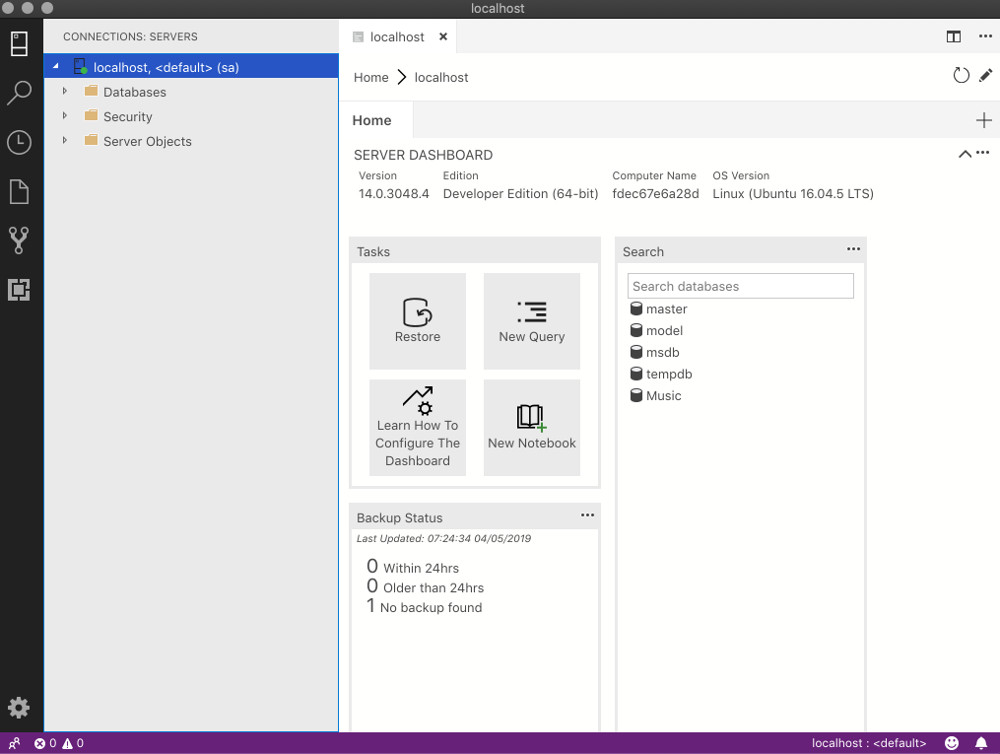
Azure Data Studio
Azure Data Studio (formerly called SQL Operations Studio) is a free GUI tool from Microsoft. It’s a bit more user friendly for those who aren’t comfortable with the command line interface.
Installation is as easy as downloading it and dragging it to your Applications folder.
DBeaver
Another GUI option is DBeaver. DBeaver is a free open source database tool that works with many different database management systems (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, SQLite, Oracle, DB2, SQL Server, Sybase, MS Access, Teradata, Firebird, Derby, etc).
You have a few options for installing DBeaver. The easiest way is to download the «installer option», and then run the installation wizard.
Источник
Installing SQL Server on macOS
It’s a bit inconvenience when working on a project that uses the Microsoft SQL Server while your dev machine is either Linux or macOS. I always ended up setting up and using a remote test database.
But now it’s no longer the case. October last year, SQL Server 2017 for Linux finally went into general availability. It’s container images are also available on Docker hub for us to use. That means we can finally install SQL Server on macOS!
Installing Docker
First, you’re going to need Docker. If you haven’t had it installed, heads up to the Docker store website and download the community edition for Mac. Just follow the instructions, it’s super easy to install.
Once it’s installed, you’ll have a new Docker icon on your menu bar. Click this icon and make sure that Docker is already.
Running SQL Server Container Image
Once you have Docker installed and running, open the terminal and run the following command to pull the latest version of SQL Server 2017 container image from Docker hub:
If you want to pull another version, just replace the 2017-latest part with the desired tag. You can check all of the available tags on Docker hub. For example, if want to pull the GA (General Availability) version instead, use the following command:
Once the image is pulled, you can run it on a new container using the following command:
- -d : Detached mode, run the container in the background.
- -p : Publish a container’s port (second value) to the host (first value). In our case, SQL server is listening on port 1433 within the container and we expose it to the same port on the host.
- —name : Assign a name to the container, we named it awesome 😎.
- -e : Set environment variables. ACCEPT_EULA=Y to confirm your acceptance of the licensing agreement. MSSQL_SA_PASSWORD=P@55word set the password for the sa user (the default system administrator username). It must be at least 8 characters and contains three of the following categories: lowercase, uppercase, digits, and symbols.
To list all of the containers, run the following command:
You should see the output similar to this:
Locate your awesome container and make sure that its STATUS column is Up . If the status is Exited , checkout the troubleshooting guide.
Handy Tips & Tools
Congratulation! 🎉 You now have Microsoft SQL Server installed on your macOS machine! Here are some common Docker commands that might come in handy for you:
It’s a bit inconvenience to run the sqlcmd from within the container in order to work with the database. Luckily there are some tools that you can use for interfacing with SQL Server:
- TablePlus: This is my favorite one. A native macOS application that works not only with MySQL and SQL Server databases but also Postgres and Redis!
- SQL Operations Studio: This one is coming from Microsoft and can be run on Windows, macOS or Linux.
- mssql for VS Code: If you’re using Visual Studio Code, this extension might come in handy.
- sql-cli for Node: If you’re a fellow Javascript developer. You can install this sql-cli for Node globally. This way you’ll have the quite similar sqlcmd feel.
Источник
Установка Microsoft ODBC Driver for SQL Server (macOS)
В этой статье объясняется, как установить Microsoft ODBC Driver for SQL Server в macOS. В ней также содержатся инструкции для необязательных средств командной строки для SQL Server ( bcp и sqlcmd ) и заголовков разработки unixODBC.
В этой статье приведены команды для установки драйвера ODBC из оболочки bash. Сведения о том, как загрузить пакеты напрямую, см. в разделе Скачивание драйвера ODBC Driver for SQL Server.
Драйвер Microsoft ODBC Driver for SQL Server в macOS поддерживается только в 64-разрядной архитектуре до версии 17.7. Apple M1 (ARM64) поддерживается начиная с версии 17.8. Будет обнаружена архитектура, и с помощью формулы Homebrew автоматически установится правильный пакет. Если командная строка работает в режиме эмуляции x64 на оборудовании M1, будет установлен пакет x64. Если командная строка не работает в режиме эмуляции, будет установлен пакет ARM64.
Microsoft ODBC 17
Чтобы установить Microsoft ODBC Driver 17 для SQL Server в macOS, выполните следующие команды:
Если вы установили пакет msodbcsql версии 17, который был доступен непродолжительное время, его следует удалить перед установкой пакета msodbcsql17 . Это позволит избежать конфликтов. Пакет msodbcsql17 можно установить параллельно с пакетом msodbcsql версии 13.
Предыдущие версии
В следующих разделах приведены инструкции по установке предыдущих версий драйвера Microsoft ODBC в macOS.
ODBC 13.1
Используйте следующие команды для установки драйвера Microsoft ODBC Driver 13.1 for SQL Server в OS X 10.11 (El Capitan) и macOS 10.12 (Sierra):
Файлы драйвера
Драйвер ODBC в macOS состоит из следующих компонентов.
| Компонент | Описание |
|---|---|
| libmsodbcsql.17.dylib или libmsodbcsql.13.dylib | Файл динамической библиотеки ( dylib ), содержащий все функциональные возможности драйвера. Этот файл устанавливается в папке /usr/local/lib/ . |
| msodbcsqlr17.rll либо msodbcsqlr13.rll | Сопутствующий файл ресурса для библиотеки драйвера. Этот файл устанавливается в папке [driver .dylib directory]../share/msodbcsql17/resources/en_US/ для версии 17 драйвера и в папке [driver .dylib directory]../share/msodbcsql/resources/en_US/ для версии 13. |
| msodbcsql.h | Файл заголовка, содержащий все новые определения, необходимые для использования драйвера. Примечание. Нельзя сочетать в одной программе ссылки на msodbcsql.h и odbcss.h. Файл msodbcsql.h устанавливается в папке /usr/local/include/msodbcsql17/ для версии 17 драйвера и в папке /usr/local/include/msodbcsql/ для версии 13. |
| LICENSE.txt | Текстовый файл с условиями лицензионного соглашения. Этот файл помещается в папку /usr/local/share/doc/msodbcsql17/ для версии 17 драйвера и в папку /usr/local/share/doc/msodbcsql/ для версии 13. |
| RELEASE_NOTES | Текстовый файл с заметками о выпуске. Этот файл помещается в папку /usr/local/share/doc/msodbcsql17/ для версии 17 драйвера и в папку /usr/local/share/doc/msodbcsql/ для версии 13. |
Загрузка файла ресурсов
Чтобы драйвер работал, он должен загрузить файл ресурсов. Этот файл имеет имя msodbcsqlr17.rll или msodbcsqlr13.rll в зависимости от версии драйвера. Файл .rll располагается по пути относительно расположения самого драйвера ( so или dylib ), указанного в таблице выше. Кроме того, начиная с версии 17.1 драйвер пытается загрузить файл .rll из каталога по умолчанию, если его не удалось загрузить по относительному пути. Путь к файлу ресурсов по умолчанию в macOS: /usr/local/share/msodbcsql17/resources/en_US/
Устранение неполадок
Некоторые пользователи столкнулись с проблемой при попытке подключения после установки драйвера ODBC и получили сообщение об ошибке следующего вида: «[01000] [unixODBC][Driver Manager]Can’t open lib ‘ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server’ : file not found (0) (SQLDriverConnect)» . Возможно, это произошло потому, что не удалось найти зарегистрированные драйверы из-за неправильной настройки unixODBC. В таких случаях проблему можно устранить, создав пару символических ссылок.
Сведения о других ситуациях, в которых не удается установить подключение к SQL Server с помощью драйвера ODBC, см. в статье, посвященной устранению известных неполадок подключения.
Дальнейшие действия
После установки драйвера можно попробовать пример приложения C++ ODBC. Подробнее о разработке приложений ODBC см. в разделе Разработка приложений.
Дополнительные сведения см. в статьях с заметками о выпуске и требованиями к системе для драйвера ODBC.
Источник