- Как исправить синий экран смерти NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM на Windows 10?
- Устраняем NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM на Windows 10
- Исправить ошибку NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM в Windows 10
- Как исправить ошибку NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM
- 1. Проверка диска
- 2. Восстановить системные файлы
- 3. Удалит устройство
- NTFS overview
- Increased reliability
- Increased security
- Support for large volumes
- Formatting requirements for large files
- Maximum file name and path
- Flexible allocation of capacity
- Обзор файловой системы NTFS NTFS overview
- повышенная надежность; Increased reliability
- Повышенная безопасность Increased security
- Поддержка больших томов Support for large volumes
- Требования к форматированию для больших файлов Formatting requirements for large files
- Максимальная длина имени файла и пути к файлу Maximum file name and path
- Динамическое выделение емкости Flexible allocation of capacity
Как исправить синий экран смерти NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM на Windows 10?
NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM – это синий экран смерти, который способен появляться на всех версиях операционной системы Windows. Как правило, причиной, стоящей за этим критическим сбоем, являются проблемы с файловой системой жесткого диска, на котором располагается ОС Windows. Чуть реже, причиной BSoD NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM может быть какой-то драйвер в системе, который выводит ее из стабильного состояния.
Обычно, решается данный синий экран смерти с помощью такой системной утилиты, как Check Disk. Эта утилита встроена в вашу операционную систему, так что искать ее или загружать со сторонних ресурсов вам не понадобится. Применить Check Disk можно с помощью системной консоли Windows. Именно этим мы с вами и займемся в данной статье.
Устраняем NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM на Windows 10
Не каждый синий экран смерти намертво блокирует компьютер пользователя. Если вам удалось обойти NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM и войти в операционную систему, то считайте себя везунчиком, так как устранить критический сбой, вероятно, вам удастся куда быстрее. Все дело в том, что применить программу Check Disk можно только в Командной строке, доступ к которой можно получить в двух местах: ОС и Windows RE(среда восстановления).
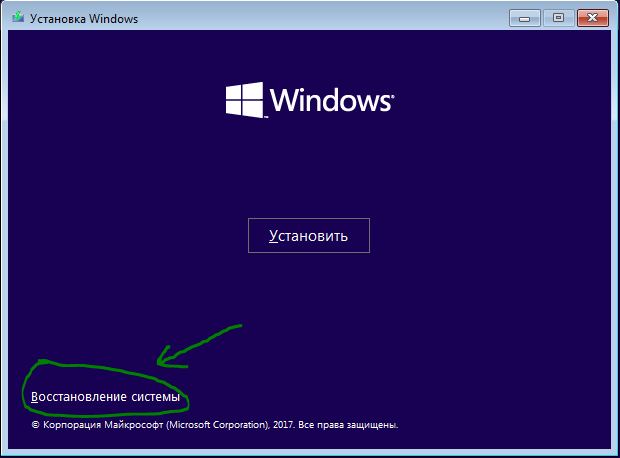
Если же синий экран смерти NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM заблокировал вашу систему, то, к сожалению, вам придется воспользоваться Средой Восстановления, доступ к которой можно получить с помощью установочного носителя Windows.
Если есть доступ к системе:
- нажмите правой кнопкой мыши на Пуск;
- выберите в контекстном меню пункт «Командная строка(администратор)»;
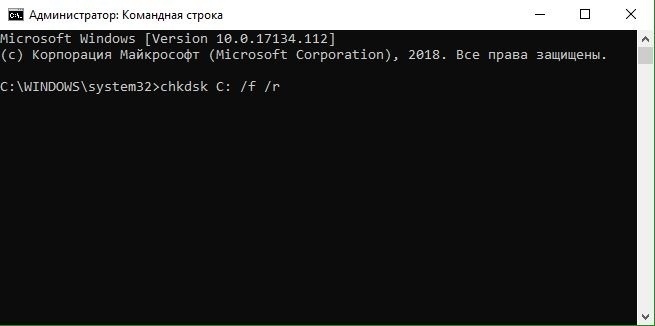
- впишите в консоль команду chkdsk /f /r и нажмите Enter;
- дождитесь окончания процедуры, а затем перезагрузите компьютер.
Если доступа к системе нет(NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM блокирует доступ):
- создайте установочный носитель Windows 10(USB-носитель или CD);
- загрузитесь через него и доберитесь до окна с кнопкой «Установить»;
- нажмите на кнопку «Восстановление системы»;
- выберите раздел «Поиск и устранение неисправностей»;
- далее откройте «Дополнительные параметры»;
- далее кликните на инструмент «Командная строка»;
- введите в консоль команду chkdsk /f /r и нажмите Enter;
- на запрос о выполнение проверки при следующей загрузке системы – нажмите «Y»;
- перезагрузитесь и подождите, пока завершиться процесс проверки вашего жесткого диска.
Обычно, использования программы Check Disk достаточно, чтобы разрешить проблему с синим экраном смерти NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM. Тем не менее бывают случаи, когда вышеуказанный метод не срабатывает. Что же, в таком случае, мы рекомендуем вам попробовать войти в Среду Восстановления Windows и испробовать некоторые опции: восстановление при загрузке и восстановление системы с помощью точки восстановления. Если и это не поможет, то можете воспользоваться опцией «Вернуть компьютер в предыдущее состояние», что, по-сути, эквивалентно переустановке Windows 10.
Исправить ошибку NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM в Windows 10
Ваш ПК или ноутбук работает вяло, или медленно реагирует на ввод с клавиатуры, а потом выдает ошибку на синем экране NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM. Также может быть код ошибки 0x00000024, который указывает на проблему с файлом ntfs.sys. Сам файл ntfs.sys отвечает за чтение и запись данных на диск.
Обычно эта ошибка связана, когда вы установили новое оборудование (драйвер), повреждением секторов на SSD или HDD дискt, отсутствует или поврежден системный файл. Давайте разберем, как исправить ошибку NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM на синем экране (BSOD) в Windows 10.
Как исправить ошибку NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM
Если вы не можете попасть в дополнительные параметры загрузки при включении ПК, то рекомендую создать установочную флешку с Windows 10, чтобы использовать восстановление и командную строку. После загрузки с установочной флешки Windows 10, дойдите до пункта установки и нажмите снизу ссылку «Восстановление системы«.
Далее Вы попадете в меню дополнительных опций. Нажмите «Поиск и устранение неисправностей» > «Дополнительные параметры» и «Восстановление при загрузке«. Если это не помогло, то запустите командную строку и следуйте указания ниже.
1. Проверка диска
Запустите командную строку от имени администратора, если загрузились с рабочего стола, но лучше запустите её через дополнительные параметры при включении ПК. В окно CMD введите следующую команду, которая исправит ошибки на диске:
2. Восстановить системные файлы
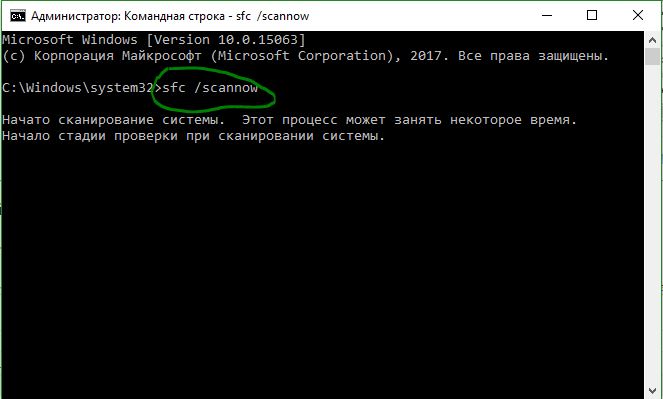
Поврежденные системные файлы могут выдавать любые сообщения об ошибках и NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM не исключение. Запустите командную строку и введите ниже команды по очереди, чтобы исправить системные файлы:
- sfc /scannow
- DISM /ONLINE /CLEANUP-IMAGE /RESTOREHEALTH
3. Удалит устройство
Если вы установили недавно какое-либо устройство, то нужно удалить его драйвер. Обычно ошибка NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM бывает из-за установки второго HDD или SSD. Тогда в этом случае, нужно удалить и обновить драйвер SATA/IDE.
NTFS overview
Applies to: Windows 10, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008
NTFS—the primary file system for recent versions of Windows and Windows Server—provides a full set of features including security descriptors, encryption, disk quotas, and rich metadata, and can be used with Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) to provide continuously available volumes that can be accessed simultaneously from multiple nodes of a failover cluster.
For additional feature information, see the Additional information section of this topic. To learn about the newer Resilient File System (ReFS), see Resilient File System (ReFS) overview.
Increased reliability
NTFS uses its log file and checkpoint information to restore the consistency of the file system when the computer is restarted after a system failure. After a bad-sector error, NTFS dynamically remaps the cluster that contains the bad sector, allocates a new cluster for the data, marks the original cluster as bad, and no longer uses the old cluster. For example, after a server crash, NTFS can recover data by replaying its log files.
NTFS continuously monitors and corrects transient corruption issues in the background without taking the volume offline (this feature is known as self-healing NTFS, introduced in Windows Server 2008). For larger corruption issues, the Chkdsk utility, in Windows Server 2012 and later, scans and analyzes the drive while the volume is online, limiting time offline to the time required to restore data consistency on the volume. When NTFS is used with Cluster Shared Volumes, no downtime is required. For more information, see NTFS Health and Chkdsk.
Increased security
Access Control List (ACL)-based security for files and folders—NTFS allows you to set permissions on a file or folder, specify the groups and users whose access you want to restrict or allow, and select access type.
Support for BitLocker Drive Encryption—BitLocker Drive Encryption provides additional security for critical system information and other data stored on NTFS volumes. Beginning in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, BitLocker provides support for device encryption on x86 and x64-based computers with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) that supports connected stand-by (previously available only on Windows RT devices). Device encryption helps protect data on Windows-based computers, and it helps block malicious users from accessing the system files they rely on to discover the user’s password, or from accessing a drive by physically removing it from the PC and installing it on a different one. For more information, see What’s new in BitLocker.
Support for large volumes
NTFS can support volumes as large as 8 petabytes on Windows Server 2019 and newer and Windows 10, version 1709 and newer (older versions support up to 256 TB). Supported volume sizes are affected by the cluster size and the number of clusters. With (2 32 – 1) clusters (the maximum number of clusters that NTFS supports), the following volume and file sizes are supported.
| Cluster size | Largest volume and file |
|---|---|
| 4 KB (default size) | 16 TB |
| 8 KB | 32 TB |
| 16 KB | 64 TB |
| 32 KB | 128 TB |
| 64 KB (earlier max) | 256 TB |
| 128 KB | 512 TB |
| 256 KB | 1 PB |
| 512 KB | 2 PB |
| 1024 KB | 4 PB |
| 2048 KB (max size) | 8 PB |
Note that if you try to mount a volume with a cluster size larger than the supported maximum of the version of Windows you’re using, you get the error STATUS_UNRECOGNIZED_VOLUME.
Services and apps might impose additional limits on file and volume sizes. For example, the volume size limit is 64 TB if you’re using the Previous Versions feature or a backup app that makes use of Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) snapshots (and you’re not using a SAN or RAID enclosure). However, you might need to use smaller volume sizes depending on your workload and the performance of your storage.
Formatting requirements for large files
To allow proper extension of large .vhdx files, there are new recommendations for formatting volumes. When formatting volumes that will be used with Data Deduplication or will host very large files, such as .vhdx files larger than 1 TB, use the Format-Volume cmdlet in Windows PowerShell with the following parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| -AllocationUnitSize 64KB | Sets a 64 KB NTFS allocation unit size. |
| -UseLargeFRS | Enables support for large file record segments (FRS). This is needed to increase the number of extents allowed per file on the volume. For large FRS records, the limit increases from about 1.5 million extents to about 6 million extents. |
For example, the following cmdlet formats drive D as an NTFS volume, with FRS enabled and an allocation unit size of 64 KB.
You also can use the format command. At a system command prompt, enter the following command, where /L formats a large FRS volume and /A:64k sets a 64 KB allocation unit size:
Maximum file name and path
NTFS supports long file names and extended-length paths, with the following maximum values:
Support for long file names, with backward compatibility—NTFS allows long file names, storing an 8.3 alias on disk (in Unicode) to provide compatibility with file systems that impose an 8.3 limit on file names and extensions. If needed (for performance reasons), you can selectively disable 8.3 aliasing on individual NTFS volumes in Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, and more recent versions of the Windows operating system. In Windows Server 2008 R2 and later systems, short names are disabled by default when a volume is formatted using the operating system. For application compatibility, short names still are enabled on the system volume.
Support for extended-length paths—Many Windows API functions have Unicode versions that allow an extended-length path of approximately 32,767 characters—beyond the 260-character path limit defined by the MAX_PATH setting. For detailed file name and path format requirements, and guidance for implementing extended-length paths, see Naming Files, Paths, and Namespaces.
Clustered storage—When used in failover clusters, NTFS supports continuously available volumes that can be accessed by multiple cluster nodes simultaneously when used in conjunction with the Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) file system. For more information, see Use Cluster Shared Volumes in a Failover Cluster.
Flexible allocation of capacity
If the space on a volume is limited, NTFS provides the following ways to work with the storage capacity of a server:
- Use disk quotas to track and control disk space usage on NTFS volumes for individual users.
- Use file system compression to maximize the amount of data that can be stored.
- Increase the size of an NTFS volume by adding unallocated space from the same disk or from a different disk.
- Mount a volume at any empty folder on a local NTFS volume if you run out of drive letters or need to create additional space that is accessible from an existing folder.
Обзор файловой системы NTFS NTFS overview
Применяется к: Windows 10, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008 Applies to: Windows 10, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008
NTFS — основная файловая система в последних версиях Windows и Windows Server — предоставляет полный набор возможностей, включая дескрипторы безопасности, шифрование, дисковые квоты и расширенные метаданные. Ее можно использовать с общими томами кластера (CSV) для предоставления томов непрерывной доступности, доступ к которым можно осуществлять одновременно с нескольких узлов отказоустойчивого кластера. NTFS—the primary file system for recent versions of Windows and Windows Server—provides a full set of features including security descriptors, encryption, disk quotas, and rich metadata, and can be used with Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) to provide continuously available volumes that can be accessed simultaneously from multiple nodes of a failover cluster.
Дополнительные сведения о функциях см. в этом разделе далее в этой статье. For additional feature information, see the Additional information section of this topic. См. сведения о новой системе Resilient File System (ReFS). To learn about the newer Resilient File System (ReFS), see Resilient File System (ReFS) overview.
повышенная надежность; Increased reliability
NTFS использует файл журнала и сведения о контрольных точках для восстановления согласованности файловой системы при перезагрузке компьютера после сбоя системы. NTFS uses its log file and checkpoint information to restore the consistency of the file system when the computer is restarted after a system failure. После ошибки поврежденного сектора NTFS динамически изменяет конфигурацию кластера, содержащего поврежденный сектор, выделяет новый кластер для данных, отмечает исходный кластер как поврежденный и больше не использует старый кластер. After a bad-sector error, NTFS dynamically remaps the cluster that contains the bad sector, allocates a new cluster for the data, marks the original cluster as bad, and no longer uses the old cluster. Например, после сбоя сервера NTFS может восстановить данные путем воспроизведения файлов журнала. For example, after a server crash, NTFS can recover data by replaying its log files.
NTFS непрерывно отслеживает и исправляет временные проблемы повреждения в фоновом режиме, не переводя том в автономный режим (эта функция, введенная в Windows Server 2008, известна как NTFS с самовосстановлением). NTFS continuously monitors and corrects transient corruption issues in the background without taking the volume offline (this feature is known as self-healing NTFS, introduced in Windows Server 2008). При значительных проблемах с повреждением программа Chkdsk в Windows Server 2012 и более поздних версиях сканирует и анализирует диск, пока том подключен, ограничивая время автономной работы временем, необходимым для восстановления целостности данных в томе. For larger corruption issues, the Chkdsk utility, in Windows Server 2012 and later, scans and analyzes the drive while the volume is online, limiting time offline to the time required to restore data consistency on the volume. Когда NTFS используется с CSV, простои не требуются. When NTFS is used with Cluster Shared Volumes, no downtime is required. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье NTFS Health and Chkdsk (Работоспособность NTFS и Chkdsk). For more information, see NTFS Health and Chkdsk.
Повышенная безопасность Increased security
Безопасность на основе списка управления доступом (ACL) для файлов и папок. NTFS позволяет устанавливать разрешения для файла или папки, указывать группы и пользователей, чей доступ требуется ограничить или разрешить, и выбрать тип доступа. Access Control List (ACL)-based security for files and folders—NTFS allows you to set permissions on a file or folder, specify the groups and users whose access you want to restrict or allow, and select access type.
Поддержка шифрования диска BitLocker. Шифрование диска BitLocker обеспечивает дополнительную безопасность важных системных сведений и других данных, хранящихся на томах NTFS. Support for BitLocker Drive Encryption—BitLocker Drive Encryption provides additional security for critical system information and other data stored on NTFS volumes. Начиная с Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows 8.1, BitLocker поддерживает шифрование устройств на компьютерах с архитектурой x86 и x64 с доверенным платформенным модулем, который поддерживает режим ожидания с подключением (ранее доступный только на устройствах Windows RT). Beginning in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, BitLocker provides support for device encryption on x86 and x64-based computers with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) that supports connected stand-by (previously available only on Windows RT devices). Шифрование устройств помогает защитить данные на компьютерах под управлением Windows и помогает предотвратить доступ пользователей-злоумышленников к системным файлам, которые они используют для обнаружения пароля, или к диску путем физического удаления его с компьютера и установки в другой компьютер. Device encryption helps protect data on Windows-based computers, and it helps block malicious users from accessing the system files they rely on to discover the user’s password, or from accessing a drive by physically removing it from the PC and installing it on a different one. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье What’s New in BitLocker (Новые возможности BitLocker). For more information, see What’s new in BitLocker.
Поддержка больших томов Support for large volumes
NTFS может поддерживать тома размером до 8 ПБ в версии Windows Server 2019 и выше и Windows 10 версии 1709 и выше (более ранние версии поддерживают до 256 ТБ). NTFS can support volumes as large as 8 petabytes on Windows Server 2019 and newer and Windows 10, version 1709 and newer (older versions support up to 256 TB). Поддерживаемые размеры томов зависят от размера кластеров и их количества. Supported volume sizes are affected by the cluster size and the number of clusters. Для кластеров (2 32 –1) (максимальное число кластеров, поддерживаемое NTFS) поддерживаются следующие размеры томов и файлов. With (2 32 – 1) clusters (the maximum number of clusters that NTFS supports), the following volume and file sizes are supported.
| Размер кластера Cluster size | Самый крупный том и файл Largest volume and file |
|---|---|
| 4 КБ (размер по умолчанию) 4 KB (default size) | 16 ТБ 16 TB |
| 8 КБ 8 KB | 32 ТБ 32 TB |
| 16 КБ 16 KB | 64 ТБ 64 TB |
| 32 КБ 32 KB | 128 ТБ 128 TB |
| 64 КБ (предыдущий максимальный размер) 64 KB (earlier max) | 256 ТБ 256 TB |
| 128 КБ 128 KB | 512 ТБ 512 TB |
| 256 KB 256 KB | 1 ПБ 1 PB |
| 512 КБ 512 KB | 2 ПБ 2 PB |
| 1024 КБ 1024 KB | 4 ПБ 4 PB |
| 2048 КБ (максимальный размер) 2048 KB (max size) | 8 ПБ 8 PB |
Обратите внимание, что при попытке подключить том с размером кластера, который превышает поддерживаемый максимум используемой версии Windows, вы получите ошибку STATUS_UNRECOGNIZED_VOLUME. Note that if you try to mount a volume with a cluster size larger than the supported maximum of the version of Windows you’re using, you get the error STATUS_UNRECOGNIZED_VOLUME.
Службы и приложения могут накладывать дополнительные ограничения на размер файлов и томов. Services and apps might impose additional limits on file and volume sizes. Например, ограничение размера тома составляет 64 ТБ, если вы используете функцию предыдущих версий или приложение резервного копирования, которое использует моментальные снимки службы теневого копирования томов (и не используете сеть SAN или RAID). For example, the volume size limit is 64 TB if you’re using the Previous Versions feature or a backup app that makes use of Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) snapshots (and you’re not using a SAN or RAID enclosure). Тем не менее, может потребоваться использовать тома меньшего размера в зависимости от рабочей нагрузки и производительности хранилища. However, you might need to use smaller volume sizes depending on your workload and the performance of your storage.
Требования к форматированию для больших файлов Formatting requirements for large files
Есть новые рекомендации по форматированию томов в отношении правильного расширения больших файлов VHDX. To allow proper extension of large .vhdx files, there are new recommendations for formatting volumes. В ходе форматирования томов, которые будут использоваться при дедупликации данных, или при размещении очень больших файлов, таких как файлы VHDX размером больше 1 ТБ, используйте в Windows PowerShell командлет Format-Volume со следующими параметрами. When formatting volumes that will be used with Data Deduplication or will host very large files, such as .vhdx files larger than 1 TB, use the Format-Volume cmdlet in Windows PowerShell with the following parameters.
| Параметр Parameter | Описание Description |
|---|---|
| -AllocationUnitSize 64KB -AllocationUnitSize 64KB | Задает размер единицы распределения NTFS 64 КБ. Sets a 64 KB NTFS allocation unit size. |
| -UseLargeFRS -UseLargeFRS | Включает поддержку сегментов записей больших файлов (FRS). Enables support for large file record segments (FRS). Это необходимо для увеличения количества экстентов, допустимых для каждого файла в томе. This is needed to increase the number of extents allowed per file on the volume. Для больших записей FRS ограничение увеличивается с примерно 1 500 000 до 6 000 000 экстентов. For large FRS records, the limit increases from about 1.5 million extents to about 6 million extents. |
Например, следующий командлет форматирует диск D как том NTFS с включенными FRS и размером единицы распределения 64 КБ. For example, the following cmdlet formats drive D as an NTFS volume, with FRS enabled and an allocation unit size of 64 KB.
Можно также использовать команду format. You also can use the format command. В системной командной строке введите следующую команду, где /L форматирует большой том FRS, а /A:64k задает размер единицы распределения 64 КБ: At a system command prompt, enter the following command, where /L formats a large FRS volume and /A:64k sets a 64 KB allocation unit size:
Максимальная длина имени файла и пути к файлу Maximum file name and path
NTFS поддерживает длинные имена файлов и пути увеличенной длины со следующими максимальными значениями: NTFS supports long file names and extended-length paths, with the following maximum values:
Поддержка длинных имен файлов с обратной совместимостью. NTFS допускает длинные имена файлов, сохраняя псевдоним 8.3 на диске (в кодировке Юникод), чтобы обеспечить совместимость с файловыми системами, которые накладывают ограничение 8.3 на имена и расширения файлов. Support for long file names, with backward compatibility—NTFS allows long file names, storing an 8.3 alias on disk (in Unicode) to provide compatibility with file systems that impose an 8.3 limit on file names and extensions. При необходимости (по соображениям производительности) можно выборочно отключить именование 8.3 на отдельных томах NTFS в Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8 и более поздних версиях операционной системы Windows. If needed (for performance reasons), you can selectively disable 8.3 aliasing on individual NTFS volumes in Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, and more recent versions of the Windows operating system. В Windows Server 2008 R2 и более поздних версий короткие имена по умолчанию отключены при форматировании тома с помощью операционной системы. In Windows Server 2008 R2 and later systems, short names are disabled by default when a volume is formatted using the operating system. Для совместимости приложений на системном томе все еще включены короткие имена. For application compatibility, short names still are enabled on the system volume.
Поддержка путей увеличенной длины. Многие функции API Windows поддерживают версии Юникода, позволяющие использовать расширенный путь длиной приблизительно 32 767 символов, а не ограниченный по длине в 260 символов, что определяется параметром MAX_PATH. Support for extended-length paths—Many Windows API functions have Unicode versions that allow an extended-length path of approximately 32,767 characters—beyond the 260-character path limit defined by the MAX_PATH setting. Подробные требования к именам файлов и формату путей, а также рекомендации по реализации путей увеличенной длины см. в статье Naming Files, Paths, and Namespaces (Имена файлов, пути и пространства имен). For detailed file name and path format requirements, and guidance for implementing extended-length paths, see Naming Files, Paths, and Namespaces.
Кластерное хранилище. При использовании в отказоустойчивых кластерах NTFS поддерживает постоянно доступные тома, к которым могут одновременно обращаться несколько узлов кластера при использовании совместно с файловой системой CSV. Clustered storage—When used in failover clusters, NTFS supports continuously available volumes that can be accessed by multiple cluster nodes simultaneously when used in conjunction with the Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) file system. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье Use Cluster Shared Volumes in a Failover Cluster (Использование общих томов кластера в отказоустойчивом кластере). For more information, see Use Cluster Shared Volumes in a Failover Cluster.
Динамическое выделение емкости Flexible allocation of capacity
Если пространство тома ограничено, NTFS предоставляет следующие возможности для работы с емкостью хранилища сервера: If the space on a volume is limited, NTFS provides the following ways to work with the storage capacity of a server:
- применение дисковых квот для отслеживания и контроля использования дискового пространства в томах NTFS для отдельных пользователей; Use disk quotas to track and control disk space usage on NTFS volumes for individual users.
- сжатие файловой системы, чтобы максимально увеличить объем хранимых данных; Use file system compression to maximize the amount of data that can be stored.
- увеличение размера тома NTFS возможно путем добавления нераспределенного пространства с того же или с другого диска; Increase the size of an NTFS volume by adding unallocated space from the same disk or from a different disk.
- подключение тома к любой пустой папке на локальном томе NTFS, если использованы все буквы диска или необходимо создать дополнительное пространство, доступное из существующей папки. Mount a volume at any empty folder on a local NTFS volume if you run out of drive letters or need to create additional space that is accessible from an existing folder.