- Windows Update log files
- Generating WindowsUpdate.log
- Windows Update log components
- Windows Update log structure
- Time stamps
- Process ID and thread ID
- Component name
- Update identifiers
- Windows Setup log files analysis using SetupDiag tool
- Файлы журнала Центра обновления Windows Windows Update log files
- Создание WindowsUpdate.log Generating WindowsUpdate.log
- Компоненты журнала обновления Windows Windows Update log components
- Структура журнала обновления Windows Windows Update log structure
- Штампы времени Time stamps
- ID процесса и нить ID Process ID and thread ID
- Имя компонента Component name
- Идентификаторы обновления Update identifiers
- Анализ файлов журнала установки Windows с помощью средства SetupDiag Windows Setup log files analysis using SetupDiag tool
Windows Update log files
The following table describes the log files created by Windows Update.
| Log file | Location | Description | When to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| windowsupdate.log | C:\Windows\Logs\WindowsUpdate | Starting in Windows 8.1 and continuing in Windows 10, Windows Update client uses Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) to generate diagnostic logs. | If you receive an error message when you run Windows Update, you can use the information that is included in the Windowsupdate.log log file to troubleshoot the issue. |
| UpdateSessionOrchestration.etl | C:\ProgramData\USOShared\Logs | Starting Windows 10, the Update Orchestrator is responsible for sequence of downloading and installing various update types from Windows Update. And the events are logged to these .etl files. | When you see that the updates are available but download is not getting triggered. When Updates are downloaded but installation is not triggered. When Updates are installed but reboot is not triggered. |
| NotificationUxBroker.etl | C:\ProgramData\USOShared\Logs | Starting Windows 10, the notification toast or the banner is triggered by NotificationUxBroker.exe. | When you want to check whether the notification was triggered or not. |
| CBS.log | %systemroot%\Logs\CBS | This log provides insight on the update installation part in the servicing stack. | To troubleshoot the issues related to Windows Update installation. |
Generating WindowsUpdate.log
To merge and convert Windows Update trace files (.etl files) into a single readable WindowsUpdate.log file, see Get-WindowsUpdateLog.
When you run the Get-WindowsUpdateLog cmdlet, an copy of WindowsUpdate.log file is created as a static log file. It does not update as the old WindowsUpdate.log unless you run Get-WindowsUpdateLog again.
Windows Update log components
The Windows Update engine has different component names. The following are some of the most common components that appear in the WindowsUpdate.log file:
- AGENT- Windows Update agent
- AU — Automatic Updates is performing this task
- AUCLNT- Interaction between AU and the logged-on user
- CDM- Device Manager
- CMPRESS- Compression agent
- COMAPI- Windows Update API
- DRIVER- Device driver information
- DTASTOR- Handles database transactions
- EEHNDLER- Expression handler that’s used to evaluate update applicability
- HANDLER- Manages the update installers
- MISC- General service information
- OFFLSNC- Detects available updates without network connection
- PARSER- Parses expression information
- PT- Synchronizes updates information to the local datastore
- REPORT- Collects reporting information
- SERVICE- Startup/shutdown of the Automatic Updates service
- SETUP- Installs new versions of the Windows Update client when it is available
- SHUTDWN- Install at shutdown feature
- WUREDIR- The Windows Update redirector files
- WUWEB- The Windows Update ActiveX control
- ProtocolTalker — Client-server sync
- DownloadManager — Creates and monitors payload downloads
- Handler, Setup — Installer handlers (CBS, and so on)
- EEHandler — Evaluating update applicability rules
- DataStore — Caching update data locally
- IdleTimer — Tracking active calls, stopping a service
Many component log messages are invaluable if you are looking for problems in that specific area. However, they can be useless if you don’t filter to exclude irrelevant components so that you can focus on what’s important.
Windows Update log structure
The Windows update log structure is separated into four main identities:
- Time Stamps
- Process ID and Thread ID
- Component Name
- Update Identifiers
- Update ID and Revision Number
- Revision ID
- Local ID
- Inconsistent terminology
The WindowsUpdate.log structure is discussed in the following sections.
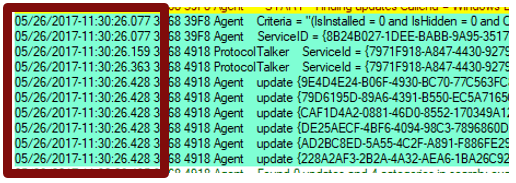
Time stamps
The time stamp indicates the time at which the logging occurs.
- Messages are usually in chronological order, but there may be exceptions.
- A pause during a sync can indicate a network problem, even if the scan succeeds.
- A long pause near the end of a scan can indicate a supersedence chain issue.
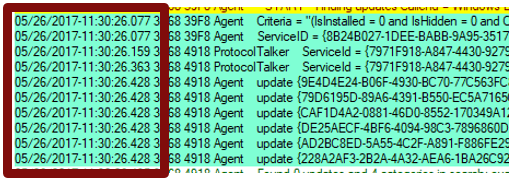
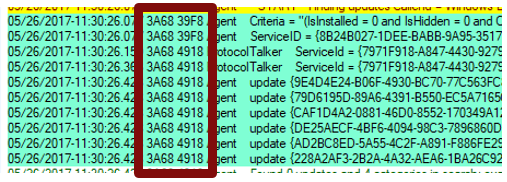
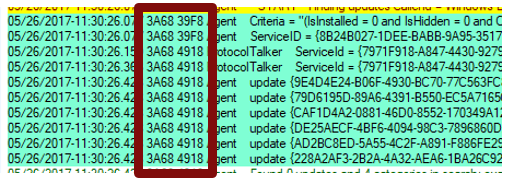
Process ID and thread ID
The Process IDs and Thread IDs are random, and they can vary from log to log and even from service session to service session within the same log.
- The first four hex digits are the process ID.
- The next four hex digits are the thread ID.
- Each component, such as the USO, Windows Update engine, COM API callers, and Windows Update installer handlers, has its own process ID.
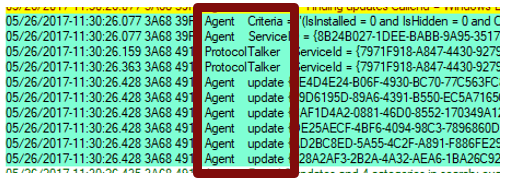
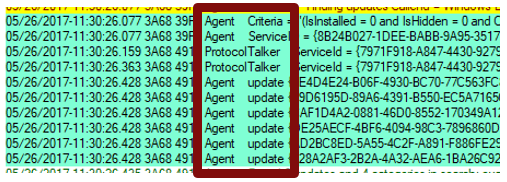
Component name
Search for and identify the components that are associated with the IDs. Different parts of the Windows Update engine have different component names. Some of them are as follows:
- ProtocolTalker — Client-server sync
- DownloadManager — Creates and monitors payload downloads
- Handler, Setup — Installer handlers (CBS, etc.)
- EEHandler — Evaluating update applicability rules
- DataStore — Caching update data locally
- IdleTimer — Tracking active calls, stopping service
Update identifiers
Update ID and revision number
There are different identifiers for the same update in different contexts. It’s important to know the identifier schemes.
- Update ID: A GUID (indicated in the previous screenshot) that’s assigned to a given update at publication time
- Revision number: A number incremented every time that a given update (that has a given update ID) is modified and republished on a service
- Revision numbers are reused from one update to another (not a unique identifier).
- The update ID and revision number are often shown together as «
.revision.»
Revision ID
- A Revision ID (don’t confuse this value with «revision number») is a serial number that’s issued when an update is initially published or revised on a given service.
- An existing update that’s revised keeps the same update ID (GUID), has its revision number incremented (for example, from 100 to 101), but gets a new revision ID that is not related to the previous ID.
- Revision IDs are unique on a given update source, but not across multiple sources.
- The same update revision might have different revision IDs on Windows Update and WSUS.
- The same revision ID might represent different updates on Windows Update and WSUS.
Local ID
- Local ID is a serial number issued when an update is received from a service by a given Windows Update client
- Typically seen in debug logs, especially involving the local cache for update info (Datastore)
- Different client PCs will assign different Local IDs to the same update
- You can find the local IDs that a client is using by getting the client’s %WINDIR%\SoftwareDistribution\Datastore\Datastore.edb file
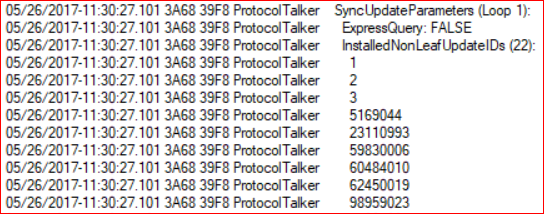
Inconsistent terminology
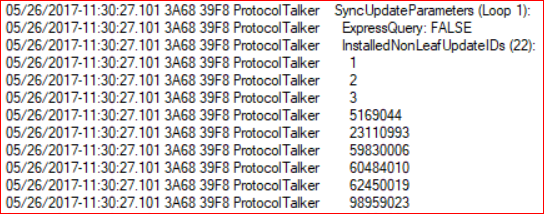
Sometimes the logs use terms inconsistently. For example, the InstalledNonLeafUpdateIDs list actually contains revision IDs, not update IDs.
Recognize IDs by form and context:
- GUIDs are update IDs
- Small integers that appear alongside an update ID are revision numbers
- Large integers are typically revision IDs
- Small integers (especially in Datastore) can be local IDs
Windows Setup log files analysis using SetupDiag tool
SetupDiag is a diagnostic tool that can be used for analysis of logs related to installation of Windows Updates. For detailed information, see SetupDiag.
Файлы журнала Центра обновления Windows Windows Update log files
Применимо к: Windows10 Applies to: Windows 10
В следующей таблице описаны файлы журналов, созданные Windows Update. The following table describes the log files created by Windows Update.
| Файл журнала Log file | Расположение Location | Описание Description | Варианты использования When to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| windowsupdate.log windowsupdate.log | C:\Windows\Logs\WindowsUpdate C:\Windows\Logs\WindowsUpdate | Начиная с Windows 8.1 и продолжая работать в Windows 10, клиент Windows Update использует трассировку событий для Windows (ETW) для создания журналов диагностики. Starting in Windows 8.1 and continuing in Windows 10, Windows Update client uses Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) to generate diagnostic logs. | Если при запуске обновления Windows вы получаете сообщение об ошибке, для устранения неполадок можно использовать сведения, включенные в файл журнала журнала Windowsupdate.log. If you receive an error message when you run Windows Update, you can use the information that is included in the Windowsupdate.log log file to troubleshoot the issue. |
| UpdateSessionOrchestration.etl UpdateSessionOrchestration.etl | C:\ProgramData\USOShared\Logs C:\ProgramData\USOShared\Logs | Начиная с Windows 10, оркестратор обновления отвечает за последовательность скачивания и установки различных типов обновлений из Windows Update. Starting Windows 10, the Update Orchestrator is responsible for sequence of downloading and installing various update types from Windows Update. И события регистрируются в эти .etl-файлы. And the events are logged to these .etl files. | Когда вы видите, что обновления доступны, но загрузка не запускается. When you see that the updates are available but download is not getting triggered. При загрузке обновлений, но установка не запускается. When Updates are downloaded but installation is not triggered. При установке обновлений, но перезагрузка не запускается. When Updates are installed but reboot is not triggered. |
| NotificationUxBroker.etl NotificationUxBroker.etl | C:\ProgramData\USOShared\Logs C:\ProgramData\USOShared\Logs | Начиная с Windows 10, всплывающее уведомление или баннер запускается NotificationUxBroker.exe. Starting Windows 10, the notification toast or the banner is triggered by NotificationUxBroker.exe. | Если вы хотите проверить, было ли вызвано уведомление или нет. When you want to check whether the notification was triggered or not. |
| CBS.log CBS.log | %systemroot%\Logs\CBS %systemroot%\Logs\CBS | В этом журнале содержится представление об установке обновления в стеке обслуживания. This log provides insight on the update installation part in the servicing stack. | Устранение неполадок, связанных с установкой обновления Windows. To troubleshoot the issues related to Windows Update installation. |
Создание WindowsUpdate.log Generating WindowsUpdate.log
Чтобы объединить и преобразовать файлы трассировки Windows Update (.etl files) в один читаемый файл WindowsUpdate.log, см. в материале Get-WindowsUpdateLog. To merge and convert Windows Update trace files (.etl files) into a single readable WindowsUpdate.log file, see Get-WindowsUpdateLog.
При запуске комлета Get-WindowsUpdateLog создается копия файла WindowsUpdate.log в виде статичного файла журнала. When you run the Get-WindowsUpdateLog cmdlet, an copy of WindowsUpdate.log file is created as a static log file. Он не обновляется как старый WindowsUpdate.log, если вы не запустите Get-WindowsUpdateLog снова. It does not update as the old WindowsUpdate.log unless you run Get-WindowsUpdateLog again.
Компоненты журнала обновления Windows Windows Update log components
В движке Обновления Windows есть разные имена компонентов. The Windows Update engine has different component names. Ниже приводится ряд наиболее распространенных компонентов, которые отображаются в файле WindowsUpdate.log: The following are some of the most common components that appear in the WindowsUpdate.log file:
- АГЕНТ- Агент обновления Windows AGENT- Windows Update agent
- AU . Автоматические обновления выполняют эту задачу AU — Automatic Updates is performing this task
- AUCLNT- Взаимодействие между AU и зарегистрированным пользователем AUCLNT- Interaction between AU and the logged-on user
- Диспетчер cdM-device CDM- Device Manager
- Агент сжатия CMPRESS- CMPRESS- Compression agent
- API обновления ДЛЯ COMAPI-Windows COMAPI- Windows Update API
- Сведения о драйвере DRIVER-Device DRIVER- Device driver information
- DTASTOR- Обрабатывает транзакции баз данных DTASTOR- Handles database transactions
- Обработитель EEHNDLER-Expression, используемый для оценки применимости обновления EEHNDLER- Expression handler that’s used to evaluate update applicability
- HANDLER- Управляет установщиками обновления HANDLER- Manages the update installers
- Сведения об общих службах MISC MISC- General service information
- OFFLSNC— обнаружение доступных обновлений без подключения к сети OFFLSNC- Detects available updates without network connection
- Сведения о выражении PARSER-Parses PARSER- Parses expression information
- PT- Синхронизирует обновления сведений в локальном магазине данных PT- Synchronizes updates information to the local datastore
- REPORT- Собирает сведения о отчетности REPORT- Collects reporting information
- SERVICE-Startup/shutdown of the Automatic Updates service SERVICE- Startup/shutdown of the Automatic Updates service
- SETUP- Устанавливает новые версии клиента обновления Windows, когда он доступен SETUP- Installs new versions of the Windows Update client when it is available
- SHUTDWN-Install at shutdown feature SHUTDWN- Install at shutdown feature
- WUREDIR— файлы перенаправления обновления Windows WUREDIR- The Windows Update redirector files
- WUWEB— управление обновлением Windows ActiveX WUWEB- The Windows Update ActiveX control
- ProtocolTalker — синхронизация с клиентом-сервером ProtocolTalker — Client-server sync
- DownloadManager — создает и отслеживает загрузки полезной нагрузки DownloadManager — Creates and monitors payload downloads
- Обработчик, установка — обработчики установки (CBS и т. п.) Handler, Setup — Installer handlers (CBS, and so on)
- EEHandler — оценка правил применимости к обновлению EEHandler — Evaluating update applicability rules
- DataStore — локальное обновление данных кэшинга DataStore — Caching update data locally
- IdleTimer — отслеживание активных вызовов, остановка службы IdleTimer — Tracking active calls, stopping a service
Многие сообщения журнала компонентов неоценимы, если вы ищете проблемы в этой области. Many component log messages are invaluable if you are looking for problems in that specific area. Однако они могут быть бесполезными, если не фильтровать, чтобы исключить нерелевантные компоненты, чтобы можно было сосредоточиться на важных компонентах. However, they can be useless if you don’t filter to exclude irrelevant components so that you can focus on what’s important.
Структура журнала обновления Windows Windows Update log structure
Структура журнала обновления Windows разделена на четыре основных удостоверения: The Windows update log structure is separated into four main identities:
- Отметки времени Time Stamps
- Process ID and Thread ID Process ID and Thread ID
- Имя компонента Component Name
- Идентификаторы обновления Update Identifiers
- Update ID and Revision Number Update ID and Revision Number
- Изменение ID Revision ID
- Локальный ID Local ID
- Несогласованная терминология Inconsistent terminology
Структура WindowsUpdate.log обсуждается в следующих разделах. The WindowsUpdate.log structure is discussed in the following sections.
Штампы времени Time stamps
Отметка времени указывает время ведения журнала. The time stamp indicates the time at which the logging occurs.
- Обычно сообщения находятся в хронологическом порядке, но могут быть исключения. Messages are usually in chronological order, but there may be exceptions.
- Пауза во время синхронизации может указывать на проблему сети, даже если проверка будет успешной. A pause during a sync can indicate a network problem, even if the scan succeeds.
- Длинная пауза в конце сканирования может указывать на проблему цепи суперсемейки. A long pause near the end of a scan can indicate a supersedence chain issue.
ID процесса и нить ID Process ID and thread ID
ID-данные процесса и потоковые ИД являются случайными, и они могут отличаться от журнала к журналу и даже от сеанса службы до сеанса службы в одном журнале. The Process IDs and Thread IDs are random, and they can vary from log to log and even from service session to service session within the same log.
- Первые четыре двузначные цифры — это код процесса. The first four hex digits are the process ID.
- Следующие четыре двузначные цифры — это код потока. The next four hex digits are the thread ID.
- Каждый компонент, например usO, двигатель обновления Windows, вызыватели API COM и обработчики установщика обновления Windows, имеет свой собственный ID процесса. Each component, such as the USO, Windows Update engine, COM API callers, and Windows Update installer handlers, has its own process ID.
Имя компонента Component name
Поиск и определение компонентов, связанных с идентификацией. Search for and identify the components that are associated with the IDs. Различные части двигателя обновления Windows имеют разные имена компонентов. Different parts of the Windows Update engine have different component names. Некоторые из них являются следующими: Some of them are as follows:
- ProtocolTalker — синхронизация с клиентом-сервером ProtocolTalker — Client-server sync
- DownloadManager — создает и отслеживает загрузки полезной нагрузки DownloadManager — Creates and monitors payload downloads
- Обработчик, установка — обработчики установки (CBS и т.д.) Handler, Setup — Installer handlers (CBS, etc.)
- EEHandler — оценка правил применимости к обновлению EEHandler — Evaluating update applicability rules
- DataStore — локальное обновление данных кэшинга DataStore — Caching update data locally
- IdleTimer — отслеживание активных вызовов, остановка службы IdleTimer — Tracking active calls, stopping service
Идентификаторы обновления Update identifiers
Update ID and revision number Update ID and revision number
Существуют различные идентификаторы для одного и того же обновления в разных контекстах. There are different identifiers for the same update in different contexts. Важно знать схемы идентификаторов. It’s important to know the identifier schemes.
- Update ID: GUID (указанный на предыдущем скриншоте), который назначен заданным обновлениям во время публикации Update ID: A GUID (indicated in the previous screenshot) that’s assigned to a given update at publication time
- Номер версии. Число, приращенное каждый раз при внесении изменения и переопубликовки данного обновления (с заданным ИД обновления) в службе. Revision number: A number incremented every time that a given update (that has a given update ID) is modified and republished on a service
- Номера версий повторно будут повторноиспользоваться из одного обновления в другое (а не уникальный идентификатор). Revision numbers are reused from one update to another (not a unique identifier).
- ID обновления и номер ревизии часто показаны вместе как «
.revision». The update ID and revision number are often shown together as « .revision.»
Изменение ID Revision ID
- Update ID (не путайте это значение с «номером ревизии») — это серийный номер, который выдается при первоначальном опубликовании или исправлении обновления в данной службе. A Revision ID (don’t confuse this value with «revision number») is a serial number that’s issued when an update is initially published or revised on a given service.
- В обновленном обновлении сохраняется один и тот же ID обновления (GUID), увеличивается число его изменений (например, от 100 до 101), но он получает новый ИД,не связанный с предыдущим ID. An existing update that’s revised keeps the same update ID (GUID), has its revision number incremented (for example, from 100 to 101), but gets a new revision ID that is not related to the previous ID.
- Коды ревизии уникальны для данного источника обновления, но не для нескольких источников. Revision IDs are unique on a given update source, but not across multiple sources.
- Один и тот же вариант обновления может иметь различные ID-версии в Windows Update и WSUS. The same update revision might have different revision IDs on Windows Update and WSUS.
- Один и тот же ID-версии может представлять различные обновления в Windows Update и WSUS. The same revision ID might represent different updates on Windows Update and WSUS.
Локальный ID Local ID
- Локальный ID — это серийный номер, выданный при получении обновления от службы заданным клиентом Обновления Windows Local ID is a serial number issued when an update is received from a service by a given Windows Update client
- Обычно в журналах отключки, особенно с использованием локального кэша для обновления информации (Datastore) Typically seen in debug logs, especially involving the local cache for update info (Datastore)
- Различные клиентские компьютеры назначят разные локальные ID-документы одному обновлению Different client PCs will assign different Local IDs to the same update
- Локальные ID,которые клиент использует, можно найти, получив файл %WINDIR%\SoftwareDistribution\Datastore\Datastore.edb You can find the local IDs that a client is using by getting the client’s %WINDIR%\SoftwareDistribution\Datastore\Datastore.edb file
Несогласованная терминология Inconsistent terminology
Иногда журналы используют термины несогласованно. Sometimes the logs use terms inconsistently. Например, в списке InstalledNonLeafUpdateIDs фактически содержатся измененные ИД, а не обновленные. For example, the InstalledNonLeafUpdateIDs list actually contains revision IDs, not update IDs.
Распознавание ID-данных по форме и контексту: Recognize IDs by form and context:
- GUID — это обновленные ID-интерфейсы GUIDs are update IDs
- Небольшие integers, которые отображаются рядом с обновлением ID являются номерами ревизии Small integers that appear alongside an update ID are revision numbers
- Крупные integers, как правило, являются ID-версии Large integers are typically revision IDs
- Небольшими наборами (особенно в Datastore) могут быть локальные ID-версии Windows Update, несовершенная
Small integers (especially in Datastore) can be local IDs
Анализ файлов журнала установки Windows с помощью средства SetupDiag Windows Setup log files analysis using SetupDiag tool
SetupDiag — это диагностический инструмент, который можно использовать для анализа журналов, связанных с установкой обновлений Windows. SetupDiag is a diagnostic tool that can be used for analysis of logs related to installation of Windows Updates. Подробные сведения см. в инструкции SetupDiag. For detailed information, see SetupDiag.


 Small integers (especially in Datastore) can be local IDs
Small integers (especially in Datastore) can be local IDs 


