- Operating System Version
- Which version of Windows operating system am I running?
- Find operating system info in Windows 10
- Related links
- Find operating system info in Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1
- Related links
- Find operating system info in Windows 7
- Related links
- Identify Windows version for enrollment
- Get Company Portal
- Supported versions
- Find Windows 10 version number
- Windows 10 desktop devices
- Windows 10 mobile devices
- Enroll other Windows devices
- IT administrator support
- Next steps
- Windows Version Numbers
- A list of Windows version numbers & major Windows builds
- Windows Version Numbers
- How to Update Windows
- Major Changes in Windows 10
- Windows Version Numbers
Operating System Version
The Version API Helper functions are used to determine the version of the operating system that is currently running. For more information, see Getting the System Version.
The following table summarizes the most recent operating system version numbers.
| Operating system | Version number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 | 10.0* |
| Windows Server 2019 | 10.0* |
| Windows Server 2016 | 10.0* |
| Windows 8.1 | 6.3* |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 6.3* |
| Windows 8 | 6.2 |
| Windows Server 2012 | 6.2 |
| Windows 7 | 6.1 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 6.1 |
| Windows Server 2008 | 6.0 |
| Windows Vista | 6.0 |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 5.2 |
| Windows Server 2003 | 5.2 |
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition | 5.2 |
| Windows XP | 5.1 |
| Windows 2000 | 5.0 |
* For applications that have been manifested for Windows 8.1 or Windows 10. Applications not manifested for Windows 8.1 or Windows 10 will return the Windows 8 OS version value (6.2). To manifest your applications for Windows 8.1 or Windows 10, refer to Targeting your application for Windows.
Identifying the current operating system is usually not the best way to determine whether a particular operating system feature is present. This is because the operating system may have had new features added in a redistributable DLL. Rather than using the Version API Helper functions to determine the operating system platform or version number, test for the presence of the feature itself.
To determine the best way to test for a feature, refer to the documentation for the feature of interest. The following list discusses some common techniques for feature detection:
- You can test for the presence of the functions associated with a feature. To test for the presence of a function in a system DLL, call the LoadLibrary function to load the DLL. Then call the GetProcAddress function to determine whether the function of interest is present in the DLL. Use the pointer returned by GetProcAddress to call the function. Note that even if the function is present, it may be a stub that just returns an error code such as ERROR_CALL_NOT_IMPLEMENTED.
- You can determine the presence of some features by using the GetSystemMetrics function. For example, you can detect multiple display monitors by calling GetSystemMetrics(SM_CMONITORS).
- There are several versions of the redistributable DLLs that implement shell and common control features. For information about determining which versions are present on the system your application is running on, see the topic Shell and Common Controls Versions.
If you must require a particular operating system, be sure to use it as a minimum supported version, rather than design the test for the one operating system. This way, your detection code will continue to work on future versions of Windows.
Note that a 32-bit application can detect whether it is running under WOW64 by calling the IsWow64Process function. It can obtain additional processor information by calling the GetNativeSystemInfo function.
Which version of Windows operating system am I running?
Find operating system info in Windows 10
To find out which version of Windows your device is running, press the Windows logo key + R, type winver in the Open box, and then select OK.
Here’s how to learn more:
Select the Start button > Settings > System > About .
Under Device specifications > System type, see if you’re running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
Under Windows specifications, check which edition and version of Windows your device is running.
Related links
If you’re having a problem with activation, see Activate in Windows 10.
If you forgot the password you use to sign in to Windows devices or email, see How to reset your Microsoft password.
For info about updating Windows, see Windows Update: FAQ.
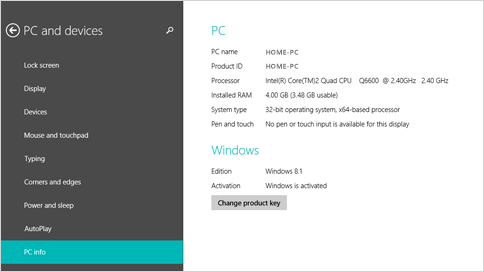
Find operating system info in Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1
To find out which version of Windows your device is running, press the Windows logo key + R, type winver in the Open box, and then select OK.
If your device is running Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1, here’s how to learn more:
If you’re using a touch device, swipe in from the right edge of the screen, tap Settings, and then tap Change PC settings. Continue to step 3.
If you’re using a mouse, point to the lower-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer up, click Settings, and then click Change PC settings.
Select PC and devices > PC info.
Under Windows you’ll see which edition and version of Windows your device is running.
Under PC > System type you’ll see if you’re running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
Related links
If you’re having a problem with activation, see Activate Windows 7 or Windows 8.1
If you forgot the password you use to sign in to Windows devices or email, see How to reset your Microsoft password.
For info about updating Windows, see Windows Update: FAQ.
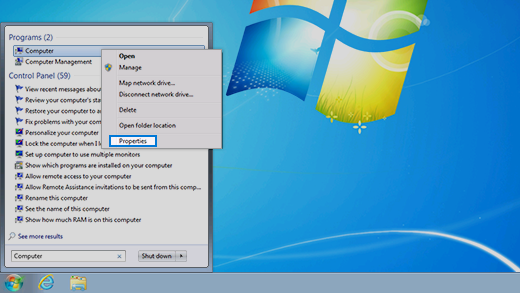
Find operating system info in Windows 7
Select the Start 
Under Windows edition, you’ll see the version and edition of Windows that your device is running.
Support for Windows 7 ended on January 14, 2020
We recommend you move to a Windows 10 PC to continue to receive security updates from Microsoft.
Related links
If you’re having a problem with activation, see Activate Windows 7 or Windows 8.1.
If you forgot the password you use to sign in to Windows devices or email, see How to reset your Microsoft password.
For info about updating Windows, see Windows Update: FAQ.
Identify Windows version for enrollment
Find out which enrollment steps you need to take to set up your device for work or school. This article will help you identify which version of Windows you’re running and point you to the appropriate enrollment steps. It also provides information about how to access Company Portal.
Get Company Portal
You can enroll Windows 10 devices through the Company Portal website or app. If you’re enrolling a device with an earlier version of Windows, you must enroll the device through the Company Portal website.
If you have any trouble signing in to the app or website, see Sign in to the Company Portal.
Supported versions
Company Portal currently supports devices running the following versions of Windows:
- Windows 10 (Home, Pro, Education, S mode, and Enterprise versions)
- Windows 8.1 RT
- Windows 8.1
Other versions of Windows, such as Windows 10 Holographic, are supported in the Company Portal. However, these versions are not covered in this article because they are for very specific uses.
Find Windows 10 version number
Enrollment steps differ for different versions of Windows 10 devices. The following steps describe how to find the version number on Windows 10 desktop and mobile devices. After you know your version, continue to the recommended enrollment steps.
Windows 10 desktop devices
Go to Start.
In the search bar, type the phrase «about your PC.» Select About your PC from the results.
Scroll down to Windows specifications to find the Version of Windows 10 that’s installed on your PC.
If your version is
Windows 10 mobile devices
Go to All apps and select the Settings app.
Select System > About.
Under Device information, find the Version.
If your version is
Enroll other Windows devices
You can enroll Windows 8.1. or Windows RT 8.1 devices via the Company Portal website.
IT administrator support
If you’re an IT administrator and run in to problems while enrolling devices, see Troubleshooting Windows device enrollment problems in Microsoft Intune. This article lists common errors, their causes, and steps to resolve them.
Next steps
Now that you know the supported devices, and your Windows 10 version number, proceed to the recommended enrollment article.
For more information about device management, Company Portal, and how both are used in schools and at work, see the following articles:
Need help? Contact your company support. Go to the Company Portal website to find your organization’s IT contact information.
Windows Version Numbers
A list of Windows version numbers & major Windows builds
Each Microsoft Windows operating system has a familiar name, like Windows 10 or Windows Vista, but behind each common name is an actual Windows version number 1 .
You can determine your Windows version a number of ways if you want to check which build number you’re currently running.
Windows Version Numbers
Below is a list of major Windows versions and their associated version numbers:
| Reference Table for Windows Version Numbers | ||
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Version Details | Version Number |
| Windows 10 | Windows 10 (20H2) | 10.0.19042 |
| Windows 10 (2004) | 10.0.19041 | |
| Windows 10 (1909) | 10.0.18363 | |
| Windows 10 (1903) | 10.0.18362 | |
| Windows 10 (1809) | 10.0.17763 | |
| Windows 10 (1803) | 10.0.17134 | |
| Windows 10 (1709) | 10.0.16299 | |
| Windows 10 (1703) | 10.0.15063 | |
| Windows 10 (1607) | 10.0.14393 | |
| Windows 10 (1511) | 10.0.10586 | |
| Windows 10 | 10.0.10240 | |
| Windows 8 | Windows 8.1 (Update 1) | 6.3.9600 |
| Windows 8.1 | 6.3.9200 | |
| Windows 8 | 6.2.9200 | |
| Windows 7 | Windows 7 SP1 | 6.1.7601 |
| Windows 7 | 6.1.7600 | |
| Windows Vista | Windows Vista SP2 | 6.0.6002 |
| Windows Vista SP1 | 6.0.6001 | |
| Windows Vista | 6.0.6000 | |
| Windows XP | Windows XP 2 | 5.1.2600 3 |
[1] More specific than a version number, at least in Windows, is a build number, often indicating exactly what major update or service pack has been applied to that Windows version. This is the last number shown in the version number column, like 7600 for Windows 7. Some sources note the build number in parenthesis, like 6.1 (7600).
[2] Windows XP Professional 64-bit had its own version number of 5.2. As far as we know, that’s the only time Microsoft has designated a special version number for a specific edition and architecture-type of a Windows operating system.
[3] Service pack updates to Windows XP did update the build number but in a very minor and long-winded way. For example, Windows XP with SP3 and other small updates is listed as having a version number of 5.1 (Build 2600.xpsp_sp3_qfe.130704-0421 : Service Pack 3).
How to Update Windows
To update Windows to the newest build number, use Windows Update. Using the built-in Windows Update utility is the easiest way to check for and install Windows updates.
If your version of Windows isn’t currently set up to install updates automatically, you can change the Windows Update settings so that new updates are downloaded and applied automatically. This is the simplest way to keep Windows updated to the latest version number.
Major Changes in Windows 10
Microsoft introduced several changes to the Windows operating system with the release of Windows 10. These are some of the biggest differences between Windows 10 and Windows 8 (and older versions of Windows):
Windows Version Numbers
Did you like my page, one of my freeware applications or online tools?
Donate via PayPal and support the publishing of this free content with any amount you want quickly and easily.
Allow for the domain Gaijin.at the display of advertising in your ad-blocker and help in this way to preserve this page!
| Name / Description | Version | Build Number | Public Release | RTM Release |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 3.10 | 511 | 1993-07-27 | |
| Windows NT 3.5 | 3.50 | 807 | 1994-09-21 | |
| Windows NT 3.1, Service Pack 3 | 3.10 | 528 | 1994-11 | |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 3.51 | 1057 | 1995-05-30 | |
| Windows 95 | 4.00 | 950 | 1995-08-24 | |
| Windows 95 OEM Service Release 1 | 4.00 | 950 A | 1996-02-14 | |
| Windows 95 OEM Service Release 2 | 4.00 | 950 B | 1996-08-24 | |
| Windows NT 4.0 | 4.0 | 1381 | 1996-08-24 | 1996-07-31 |
| Windows 95 OEM Service Release 2.1 | 4.00 | 950 B | 1997-08-27 | |
| Windows 95 OEM Service Release 2.5 | 4.00 | 950 C | 1997-11-26 | |
| Windows 98 | 4.10 | 1998 | 1998-05-15 | |
| Windows 98 Second Edition (SE) | 4.10 | 2222 | 1999-05-05 | |
| Windows 2000 | 5.0 | 2195 | 2000-02-17 | 1999-12-15 |
| Windows Me | 4.90 | 3000 | 2000-09-14 | 2000-06-19 |
| Windows XP | 5.1 | 2600 | 2001-10-25 | 2001-08-24 |
| Windows XP, Service Pack 1 | 5.1 | 2600.1105-1106 | 2002-09-09 | |
| Windows Server 2003 | 5.2 | 3790 | 2003-04-24 | |
| Windows XP, Service Pack 2 | 5.1 | 2600.2180 | 2004-08-25 | |
| Windows Server 2003, Service Pack 1 | 5.2 | 3790.1180 | 2005-03-30 | |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 5.2 | 3790 | 2005-12-06 | 2005-12-06 |
| Windows Vista | 6.0 | 6000 | 2007-01-30 | 2006-11-08 |
| Windows Server 2003, Service Pack 2 | 5.2 | 3790 | 2007-03-13 | |
| Windows Home Server | 5.2 | 4500 | 2007-11-04 | 2007-07-16 |
| Windows Vista, Service Pack 1 | 6.0 | 6001 | 2008-02-04 | |
| Windows Server 2008 | 6.0 | 6001 | 2008-02-27 | 2008-02-04 |
| Windows XP, Service Pack 3 | 5.1 | 2600 | 2008-04-21 | |
| Windows Vista, Service Pack 2 | 6.0 | 6002 | 2009-05-26 | 2009-04-28 |
| Windows Server 2008, Service Pack 2 | 6.0 | 6002 | 2009-05-26 | |
| Windows 7 | 6.1 | 7600 | 2009-10-22 | 2009-07-22 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 6.1 | 7600 | 2009-10-22 | 2009-07-22 |
| Windows 7, Service Pack 1 | 6.1 | 7601 | 2011-02-22 | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2, Service Pack 1 | 6.1 | 7601 | 2011-02-22 | 2011-02-09 |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | 6.1 | 8400 | 2011-04-06 | 2011-04-06 |
| Windows Server 2012 | 6.2 | 9200 | 2012-09-04 | 2012-08-01 |
| Windows 8 | 6.2 | 9200 | 2012-10-26 | 2012-08-01 |
| Windows 8.1 | 6.3 | 9600 | 2013-08-27 | 2013-10-17 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 6.3 | 9600 | 2013-10-18 | 2013-08-27 |
| Windows 10, Version 1507 | 10.0 | 10240 | 2015-07-29 | 2015-07-15 |
| Windows 10, Version 1511 | 10.0 | 10586 | 2015-11-10 | |
| Windows 10, Version 1607 | 10.0 | 14393 | 2016-08-02 | |
| Windows Server 2016, Version 1607 | 10.0 | 14393 | 2016-08-02 | |
| Windows 10, Version 1703 | 10.0 | 15063 | 2017-04-05 | |
| Windows 10, Version 1709 | 10.0 | 16299 | 2017-10-17 | |
| Windows Server 2016, Version 1709 | 10.0 | 16299 | 2017-10-17 | |
| Windows 10, Version 1803 | 10.0 | 17134 | 2018-04-30 | |
| Windows Server 2019, Version 1809 | 10.0 | 17763 | 2018-10-02 | |
| Windows 10, Version 1809 | 10.0 | 17763 | 2018-11-13 | |
| Windows Server 2008, Service Pack 2, Rollup KB4489887 | 6.0 | 6003 | 2019-03-19 | |
| Windows 10, Version 1903 | 10.0 | 18362 | 2019-05-21 | |
| Windows 10, Version 1909 | 10.0 | 18363 | 2019-11-12 | |
| Windows 10, Version 2004 | 10.0 | 19041 | 2020-05-27 | |
| Windows 10, Version 20H2 | 10.0 | 19042 | 2020-10-20 |
Did you like my page, one of my freeware applications or online tools?
Donate via PayPal and support the publishing of this free content with any amount you want quickly and easily.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tim-fisher-5820c8345f9b581c0b5a63cf.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WorkBadgePhoto-61c0b98ef5a74e4a85851a8f706dbd65.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ECCFABA3-2C6D-4E4B-B339-39CC928CAED3-0519147fe72c4150aa94ee4299c7531d.jpeg)



