- How to Use the mkdir Command in Linux
- Absolute Path and Relative Path:
- Creating a Directory with mkdir:
- Creating a Directory along with Parent Directories with mkdir:
- Creating Multiple Directories with mkdir:
- Verbose Mode of mkdir:
- Create Folder in Linux Create Directory in Linux [mkdir Command]
- mkdir command [Make Directory Command]
- Make directory command options
- How to Create Directory in Linux
- Creating multiple directories
- Creating a parent directory
- Setting permission for directory while creating the directory
- Verifying the directories
- How to Create Folder in Linux? [Step By Step Guide]
- rmdir command/rm command to Remove the Directory/Folder in Linux
- Conclusion
How to Use the mkdir Command in Linux
The mkdir command is used to make new directories in Linux. In this article, I am going to show you how to use the mkdir command to create directories from the command line in Linux. I am going to use Ubuntu 18.04 LTS for the demonstration, but any Linux distribution should be fine to try out the examples given here. So, let’s get started.
Absolute Path and Relative Path:
There are 2 types of path in Linux. Absolute path and relative path. Having clear concepts of these terms are essential to working with the mkdir command.
Absolute path: It is the full path to your desired directory or file. An absolute path contains the / (root) directory first and then moves downward the directories hierarchy (tree) until your desired directory or file is reached.
For example, /db/mysql/data is an absolute directory path. /etc/fstab is an absolute file path.
Relative path: Relative path is calculated from the current working directory. It may start with or without ./ but it can’t start with /
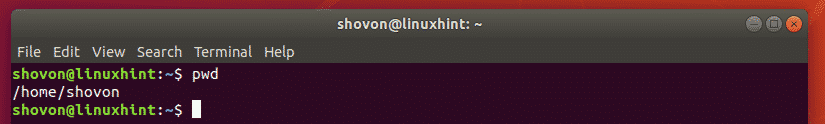
You can print the current working directory path with the pwd command as follows:
Now, if the directory path is ./db/mysql/data or simply db/mysql/data then, it’s actually inside the parent directory /home/shovon. Notice how we don’t have to type in the full or absolute path /home/shovon/db/mysql/data.
Absolute paths make working with mkdir command a lot easier.
Creating a Directory with mkdir:
This is the simplest and the most common usage of mkdir. You can create a new directory with mkdir very easily.
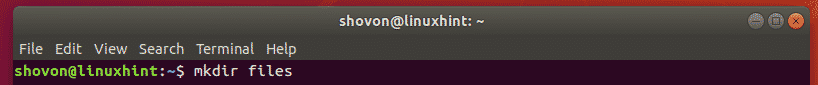
To create a new directory files/ (let’s say) in your current working directory, run the following command:
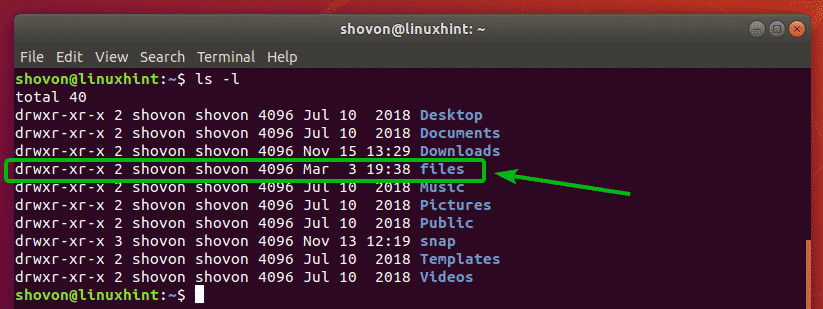
As you can see, a new directory files/ is created.
If you don’t want to create a directory in your current working directory, you can of course navigate to the parent directory (inside where you want to create the new directory) and create a new directory as shown above. But there is a better solution.
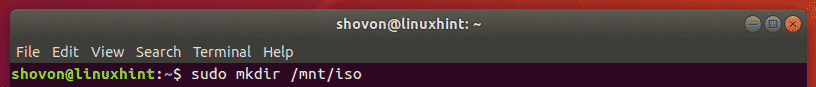
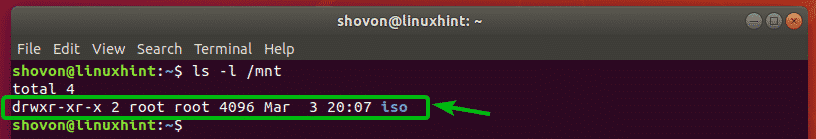
To create a new directory without navigating to the parent directory, you can specify the directory path as follows:
This command creates a new directory iso/ inside the /mnt directory. I didn’t have to navigate to the /mnt directory as you can see.
Creating a Directory along with Parent Directories with mkdir:
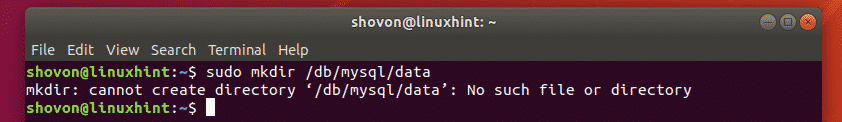
In the earlier section, I showed you how to create a new directory using the absolute path. But, if the parent directory does not exist, then you won’t be able to create a new directory this way. mkdir would throw an error. You will have to create the parent directory first and then create the desired directory.
Luckly, mkdir has a -p or –parents flag which will create the necessary parent directories if they do not exist.
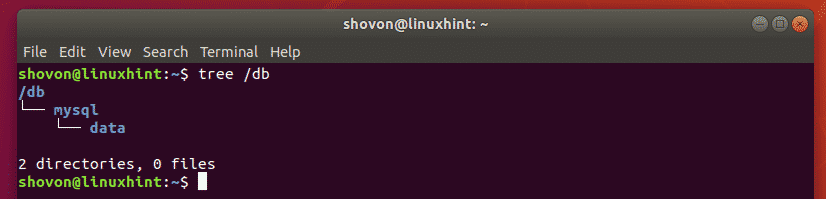
For example, let’s say, you want to move the MySQL data directory to /db/mysql/data. But none of the parent directories exist at the moment. So, instead of using 3 mkdir command, you can run a single command to tell mkdir to create the parent directories as needed.
As you can see, the parent directories are created as required.
The mkdir with the -o flag can also create parent directories automatically for relative paths as well.
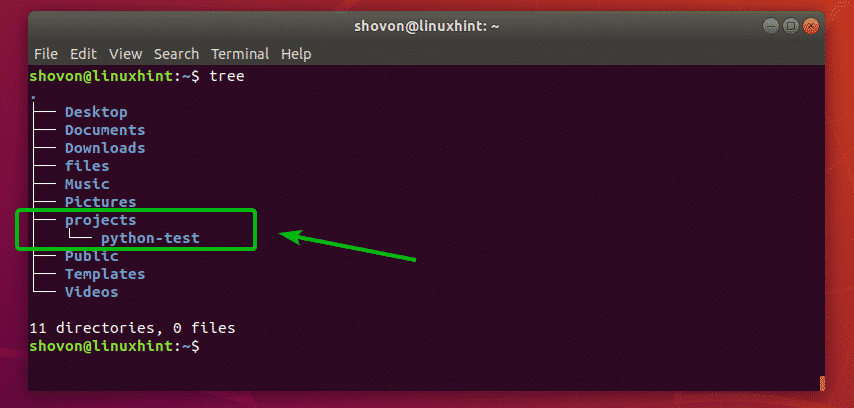
For example, let’s say, you want to create a new directory projects/python-test in your current working directory. To do that, run mkdir as follows:
As you can see, the projects/python-test directory is created inside the current working directory.
Creating Multiple Directories with mkdir:
You can create multiple directories with a single mkdir command if you want.
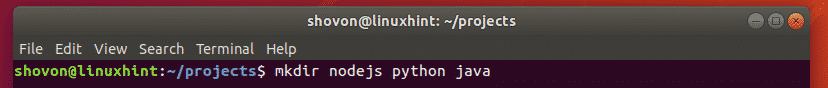
Let’s say, you want to create 3 directories nodejs/, python/, java/ inside your current working directory
/projects. To create all these directories, run mkdir as follows:
As you can see, the required directories are created.
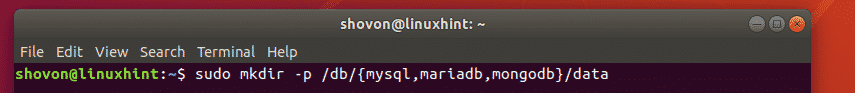
Again, let’s say, you want to create multiple directories for the mysql, mariadb, mongodb databases using absolute path. You also want to create any parent directories as required. To do that, run mkdir command as follows:
As you can see, the required directories are created all at once.
Here, the directory paths are /db/mysql/data, /db/mariadb/data, /db/mongodb/data. What changes in each directory path? Well, the second level directory mysql, mariadb, mongodb. So, we can put it inside curly braces without any whitespace as /db/
Verbose Mode of mkdir:
By default, mkdir does not print any message on the screen if the command runs successfully. Only error messages are printed. If you want mkdir to print messages on the screen, then you can use the -v flag or the –verbose flag.
The same command in the earlier section can be written as follows as well.
As you can see, mkdir now prints message as directories are created.
So, that’s how you use the mkdir command in Linux. Thanks for reading this article.
Источник
Create Folder in Linux Create Directory in Linux [mkdir Command]
Looking to create folder in Linux/create directory in Linux? Then this post will give you detailed insights on the mkdir command and to execute this process.
List of content you will read in this article:
Everyone who is a beginner or advanced Linux administrator somehow is looking to create folder in Linux/create directory in Linux.
Linux is widely adopted and used due to its stability and flexibility in carrying out various tasks in an easier way. One of the key features of Linux is the terminal where you can run any command to run various tasks from making changes to the system to download any required software.
In this article, we will be highlighting the commands with various options for creating directories or folders in the Linux system. Linux offers an easy command for that- mkdir command that stands for “make directory”. Also, the “mkdir” command will allow you to set permissions, create multiple directories using the single command, and do many other tasks.
Before you run the mkdir command, make sure to complete the prerequisites such as-
- Linux or Unix-like OS.
- Access to the command-line terminal for executing the commands.
- The user should be having the right access to creating the directory.
mkdir command [Make Directory Command]
If you want to create a new directory, you can make use of the “mkdir” command for creating single or multiple directories within the Linux system. You can use this command along with various options for applying various functionality. The syntax can you can use for the “mkdir” command is as follows-
mkdir [option] dir_name
Make directory command options
Option / Syntax
Description
This command will create a directory within the current directory location
This command will help in creating multiple directories in the current directory location. Make sure that you do not use the spaces inside the <>
mkdir –p dir/path/new_dir
This command will allow you to create a directory structure with the missing parent directories (if there is any)
mkdir –m777 dir_name
This command will help in creating a directory and allow you to provide full read, write, execute permissions for every user
mkdir –v dir_name(s)
This command will help in creating a directory in the current location along with the details of the mkdir command.
How to Create Directory in Linux
To run the “mkdir” command, go to the terminal and open it with the admin access if you have, otherwise, you just need to have the right and appropriate access to execute the “mkdir” command.
Always, remember that the options in Linux are case-sensitive so use them correctly else the meaning will change. As per the below example, we have created a directory “Sam”.
mkdir Sam
This command will result in the creation of the directory in the current working directory. If the directory has been created successfully then you will get an empty line on the terminal. If you want to verify the result of the creation of the directory, you can use the “ls” command.
Creating multiple directories
If you want to create several directories in the same directory, you can use the “mkdir” for creating them separately. But it will take time to run individual commands. So to save your time by running separate commands, you can use a single “mkdir” command along with the directory names separated by a comma.
Consider the following example for creating multiple directories at once.
mkdir
There is no need to add space between the directory names in the brackets. But, if you add the space then the name will take an extra character.
Creating a parent directory
If you want to create a structure with multiple subdirectories, then you can use the “mkdir” command along with the “-p: option. Using this option will make sure that the missing parent directory will be added in the process.
Here, we are considering the example where we want to add the “dirtest2” directory within the “dirtest1” directory in the Linux directory, then we have to provide the complete path with the “mkdir” command as shown below.
mkdir –p Linux/dirtest1/dirtest2

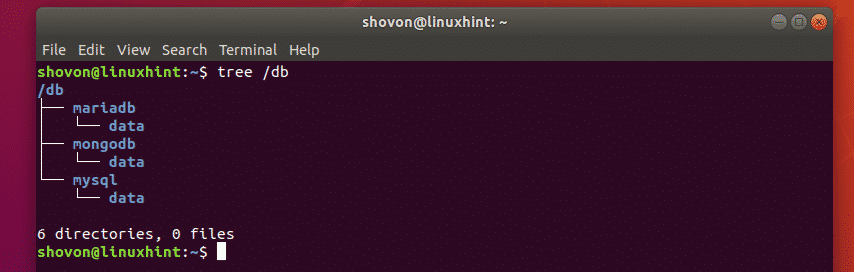
Once you run the “mkdir” command with the complete path, then to confirm the creation of the directory, you can run the “ls” command along with the “-R” option. This option will help in showing the recursive directory tree that will display the contents of each directory present in the provided path.
But, if you miss the “-p” option, the terminal will display an error that the directory that you have provided does not exist. You can see the below example. 
In the above example, the terminal will show an error that the dirtest3 does not exist rather than creating the parent directory.
Setting permission for directory while creating the directory
If you create any directory in the Linux system, then by default the directory will get the “rwx” permission but only for the user who created that directory. If you want to change the permission for the directory for all the users, then you can use the “-m” option along with the “mkdir” command.
In the below example, we are providing the permission to the directory as “777” that is any user will be able to read, write, or execute that file if required.
mkdir -m
mkdir -m 777 alpha
ls -l

If you want to check the details of the created directory along with their permissions, then you need to get the long listing of the directories. For this, you can run the “ls” command along with the “-l” option.
Verifying the directories
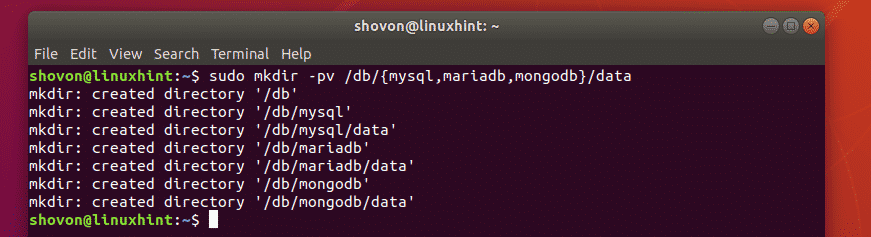
So far, you have noticed that after running the “mkdir” command, you will not get any feedback or the result showing if the creation is successful or not. If you want see the details of the “mkdir” command, then you can use the “-v” option with the “mkdir” command.
Considering the below example with the “-v” option, you will get the details of the command.
Now that you get the complete details of the creation of the directory, you do not have to run the “ls” command to creak the created directory.
How to Create Folder in Linux? [Step By Step Guide]
Follow the below-given steps to create a folder in Linux easily.
Step 1: In Linux, first open the terminal.
Step 2: then enter mkdir dir1 command to build a folder with the name dir1.
Let’s take a closer look at certain cases and other applications. The syntax to create a directory in Linux is as follows:
mkdir folder
mkdir [option] folderName
mkdir directory
By using the ls command to list the contents of the directory, you can confirm that it was created:
This will show the list of all the current directories.
mkdir’s -v (—verbose) option instructs it to print a message for each directory it creates.
mkdir: created directory ‘folder’
The file is generated in the current working directory when only the directory name is provided without the complete path. The latest working directory is the location where the commands are being executed. The cd command is used to modify the actual working directory.
To build a directory in a different region, you’ll need to specify the parent directory’s absolute or relative file direction. To construct a new directory in the /xyz directory, for example, type:
You’ll get a Permission denial error if you want to build a directory in a parent directory where the user doesn’t have enough permissions.
After executing the command you will get output like this:
mkdir: cannot create directory ‘/root/newdirectory’: Permission denied
You can create a parent folder using the following command:
mkdir -p dir11/dir12
mkdir -p parent1/child1
mkdir -p pictures1/memories1
This will list all the directories present in the parent and child folder, respectively to verify it you have to follow the below listed given command.
ls -l
ls -l pictures1
rmdir command/rm command to Remove the Directory/Folder in Linux
Here, we are removing a folder called directory1, so we will execute the below command:
rm -rf directory1
Conclusion
This is all about how to create folder in Linux by using mkdir command. With this guide, you will be able to understand the working of the “mkdir” command. You can use the “mkdir” command along with various options that we have mentioned and explained their usage, how they impact the working of the normal “mkdir” command and how it changes the output. Make sure to use the right option in the right scenario for getting the correct result. The options are case-sensitive, so make sure to use the right option else you will end up with the error
If you feel there is any other option available in Linux to create directories and folders, Please suggest with the comment box, We will try to include your suggestion.
Источник