- How To Install MySQL On Ubuntu, Debian, Mint Kali?
- Update Repository Information
- Install MySQL Server From Apt Repository
- Download MySQL Server Binary
- Install MySQL Binary Deb Package
- Secure MySQL Server Installation
- Show MySQL Service or Daemon Status
- Start MySQL Service/Daemon/Server
- Stop MySQL Service/Daemon/Server
- Test MySQL Server By Logging In
- Как установить MySQL 8.0 на Kali Linux
- Как установить MySQL 8.0 на Kali Linux
- Установите MySQL 8.0 в Kali Linux
- Проверка функциональности базы данных MySQL 8.0
- Ethical hacking and penetration testing
- InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
- Installing and configuring MySQL and phpMyAdmin on Kali Linux
- Table of contents
- What is MySQL for
- MySQL client and server
- Installing MySQL on Kali Linux
- Kali Linux replaced MySQL with MariaDB
- Setting up MySQL on Kali Linux
- Starting and enabling MySQL autorun
- Setting and changing the MySQL password. Reset forgotten MySQL/MariaDB password
- How to connect to MySQL server
- How to change MySQL user password in Kali Linux
- No password and empty MySQL password
- How to install phpMyAdmin on Kali Linux
- How to change phpMyAdmin URL. How to enable and disable phpMyAdmin
- Error “Login without a password is forbidden by configuration (see AllowNoPassword)”
- How to use phpMyAdmin on Kali Linux
- phpMyAdmin alternative
- Additional MySQL Resources
How To Install MySQL On Ubuntu, Debian, Mint Kali?
MySQL is a free and opensource database server which is very popular in the opensource community. MySQL is used by a lot of applications and companies like Facebook, Google, etc. In this tutorial, we will learn how to install MySQL into deb or apt-based distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, and Kali. This guide can be used for other deb or apt based distributions too.
Update Repository Information
It is not a requirement but a best practice to update repository information which will provide us the newest information about MySQL.
Install MySQL Server From Apt Repository
MySQL Server application is named as mysql-server as package name. We can use apt or apt-get in order to install mysql-server package like below. We can also use -y option in order to automatically accept conformation.
Download MySQL Server Binary
Another way to install MySQL is from a binary installation file. We can download MySQL binary from official download site mysql.com. But keep in mind that different versions of MySQL Server are provided with different licenses and costs. We will use community version for Ubuntu which can be listed from the following link.
and we will download the deb package with wget .
Install MySQL Binary Deb Package
After the download is completed we will first extract the tar archive like below.
and we will install the mysql-community-server_8.0.11-1ubuntu18.04_amd64.deb package with dpkg like below.
Secure MySQL Server Installation
Security is an important part of today’s IT systems. We can make MySQL more secure by using mysql_secure_installation hardening script. This will run some commands which will change MySQL configuration and harden it. This script will start by asking root password and then ask some questions about security.
Show MySQL Service or Daemon Status
After the installation is completed and secured we can list the status of the MySQL server. We will use systemctl command with status option to list whether the MySQL daemon is working or not.
As we can see the daemon is running properly.
Start MySQL Service/Daemon/Server
If the MySQL service is not started or stopped with a reason we can start MySQL service with start option like below.
Stop MySQL Service/Daemon/Server
If we need to stop the MySQL daemon we can use stop option. This can be useful to apply a new configuration by stopping and starting the service.
Test MySQL Server By Logging In
We can test the MySQL server by connecting to the service console with mysql command. We also need to provide the username and the password like below.
Источник
Как установить MySQL 8.0 на Kali Linux
Как установить MySQL 8.0 на Kali Linux
MySQL 8.0 — это последняя стабильная версия системы управления реляционными базами данных MySQL. MySQL — это бесплатная система управления базами данных (СУБД), в которой используется язык структурированных запросов (SQL). MySQL разработан, чтобы быть стабильным, надежным и гибким в использовании.
Мы будем использовать доступный репозиторий MySQL APT для установки MySQL 8.0 на Kali Linux. Убедитесь, что этот репозиторий добавлен в вашу систему, выполнив команду ниже.
Поскольку Kali Linux не является официально поддерживаемой версией, выберите выпуск Ubuntu Bionic.
Выберите и нажмите клавишу , чтобы подтвердить установку версии.
Установите MySQL 8.0 в Kali Linux
После добавления репо обновите индекс apt и установите mysql-server:
Примите лицензионное соглашение на следующих экранах, чтобы начать установку.
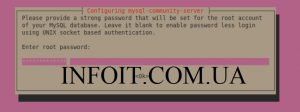
Установите пароль root для вашего сервера базы данных MySQL.
Подтвердите свой пароль root.
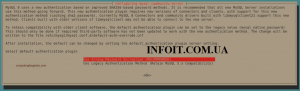
Выберите плагин аутентификации по умолчанию.
При запросе пароля root укажите пароль и подтвердите его установку.
Проверить статус с помощью:
Проверка функциональности базы данных MySQL 8.0
Вы можете проверить, нормально ли работает сервер базы данных, создав тестовую базу данных:
Источник
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
Installing and configuring MySQL and phpMyAdmin on Kali Linux
Table of contents
What is MySQL for
MySQL is a database management system that allows you to create, store, modify databases. It is often used in conjunction with PHP to store website databases. It can also be used as a data store for any program or tool.
phpMyAdmin is a web application written in PHP that is a graphical interface for MySQL that allows you to work with data, including viewing, modifying, importing and exporting data in a web interface. phpMyAdmin requires a web server (Apache), as well as PHP and MySQL.
This tutorial will help you better understand MySQL and use it to work with databases. We will also install and configure phpMyAdmin to get a graphical database management interface. Using this knowledge, you can, for example, run a site on a local computer, deploy a site using a database from a backup.
MySQL client and server
MySQL has two main components: server and client.
The MySQL server is the DBMS that powers the databases. The server is required for the database to work.
MySQL client is a utility for connecting to a server. The client is needed if you want to connect to the MySQL server on the command line.
Installing MySQL on Kali Linux
If you have already worked with Debian derivatives (Linux Mint, Ubuntu), then there are two packages in them:
- mysql-server — MySQL server
- mysql-client — MySQL client
By default, MySQL is already preinstalled in Kali Linux, but if you have a minimal build, then you may need to install the DBMS manually. If you try to install the mysql-server package, you will receive the following error:
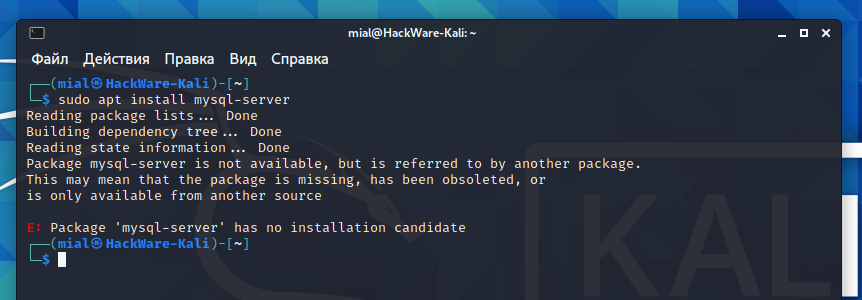
The fact is that in Kali Linux (and apparently in fresh Debian, as well as in all its derivatives), this package is called differently:
- default-mysql-server (DBMS executables and system database setup)
- default-mysql-server-core (only DBMS executables)
Therefore, use the following command to install MySQL:
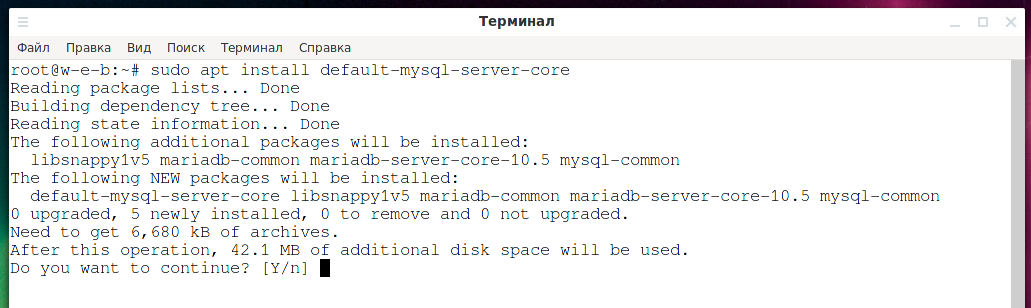
Kali Linux replaced MySQL with MariaDB
We say MySQL, but MySQL is completely absent from the Kali Linux repositories. Regardless of whether this DBMS was preinstalled on your system or you installed it manually, MariaDB is installed instead.
You can verify this yourself with the command:
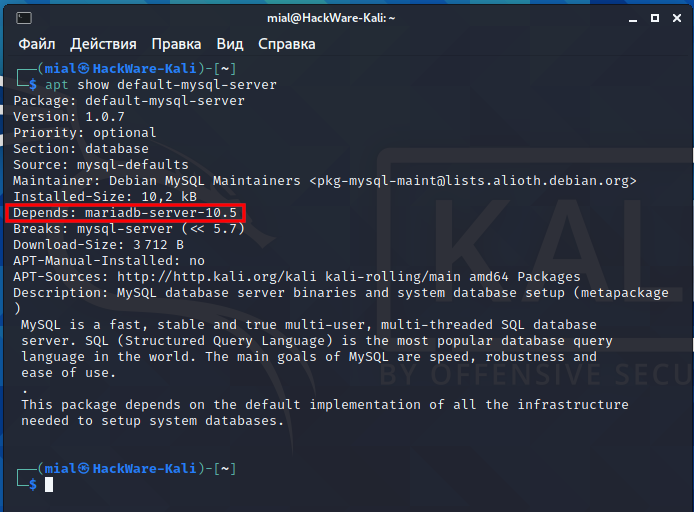
Again, MySQL is absent in the Kali Linux repositories, and if you need exactly MySQL, and not MariaDB, then you will have to decide this either by connecting an additional repository, or by manually installing the downloaded file.
MariaDB is also a database management system. It is forked from MySQL. MariaDB’s job is to perform all the functions of MySQL, but to be better. The service name, the name of the configuration files have not changed. Just out of habit, I will continue to say “MySQL” in this tutorial, but we will work exclusively with MariaDB.
Setting up MySQL on Kali Linux
MySQL config files:
- /etc/mysql/my.cnf (link to /etc/alternatives/my.cnf)
- /etc/mysql/debian.cnf (obsolete file will be removed in future versions)
- /etc/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf
- /etc/mysql/conf.d/mysqldump.cnf
- /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-client.cnf
- /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-mysqld_safe.cnf
- /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/60-galera.cnf
- /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-mysql-clients.cnf
- /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
Most of the settings are collected in the 50-server.cnf file. By default, the MySQL service listens for incoming connections only on localhost (connections from other computers are not possible).
Starting and enabling MySQL autorun
To start the service, run the command:
To enable MySQL autorun every time you turn on your computer, run the command:
Setting and changing the MySQL password. Reset forgotten MySQL/MariaDB password
For a newly installed MySQL, the root password is empty. To change it, run and follow the instructions:
For a detailed description of the steps and translation of instructions, see the article “What is the MySQL root password in Kali Linux. How to change/reset MySQL root password in Kali Linux”. In the same article, see how to reset your password if you’ve forgotten it.
How to connect to MySQL server
When the MySQL server service is running, you need to use a command like this to connect to it:
All three arguments are optional.
If the -u option is omitted, the current OS username will be used as the MySQL username.
The -p option means that you are logged in with a password. After this option, you do not need to write a password — it will be requested at the command line prompt.
If you do not specify the -h option, then an attempt will be made to connect to the local server.
Attempting to connect when no user password is set:
This will throw an error:
The essence of the problem is that unix_socket authentication is used by default, that is, when the OS username coincides with the username in MySQL/MariaDB, then the password does not need to be entered at all. But other users cannot log in as another user, so you need to use sudo to log in as root. See the article “Password and unix_socket authentication in MySQL and MariaDB” for details.
You can choose one of the options:
1. Always use sudo:
2. Make changes to the MySQL settings so that ordinary users can connect to the DBMS.
3. Create a new MySQL user. If this is a user with the same name as your name in the OS, then you can use unix_socket authentication and not enter a password when connecting. Alternatively, you can choose password authentication and use any name.
To access the MariaDB database as a regular user without using sudo privileges (this will also set the root user password), go to the MySQL command line prompt
and run the following SQL commands:
Please note that you need to enter the PASSWORD.
Then try logging into the database without sudo as shown below.
How to change MySQL user password in Kali Linux
The method shown above was used to change the authentication types, but it can also be used to change the password.
Go to the MySQL command line prompt (use either sudo or the -u option to log in as root):
and run the following commands:
Please note that you need to enter a NEW PASSWORD.
Also note that this method changes the root user’s password. If you want to change the password of another MySQL user, then in the previous SQL query specify the name of this user, for example:
No password and empty MySQL password
If you work exclusively on localhost and you do not care about security problems, then for convenience you can set an empty password (do not do this if you do not fully understand the possible risks):
In this case, when connecting, you do not need to use the -p option:
How to install phpMyAdmin on Kali Linux
By default phpMyAdmin is not installed on Kali Linux.
Installation can be done in two ways:
- Since phpMyAdmin is a PHP web application, you can simply download the archive with the source code (scripts) and unpack it to any folder on the server.
- Most distributions have a phpMyAdmin installation package in the standard repositories. The advantage of this approach is that you do not need to keep track of new phpMyAdmin releases and do manual updates.
I prefer to install phpMyAdmin from the standard repositories (while WordPress, on the contrary, I prefer to install by simply copying the folder with the WordPress files to the web server folder; thanks to this I control the update process; if you really need to update, then all this is done in the convenient web interface of WordPress itself).
You should already have Apache, MySQL, PHP installed. By default, they are already available in Kali Linux, but if you have a version with a minimum number of packages, then install them:
Install phpMyAdmin with the following command:
Answer No to the configuration prompt with dbconfig-common:
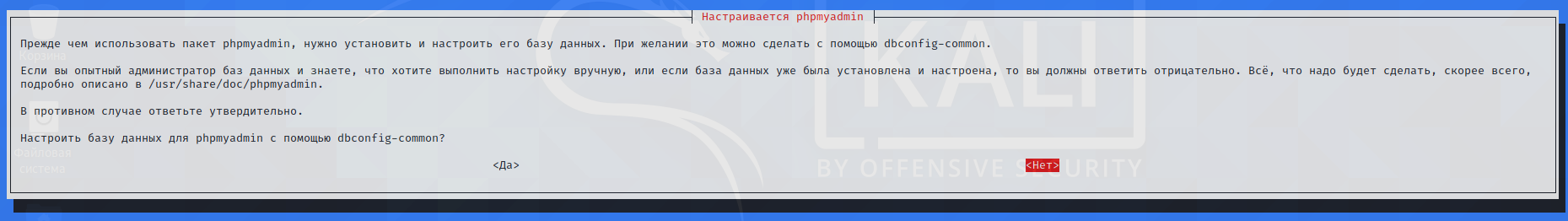
Use the Tab key to move between items and Enter to press.
Select “apache2”.
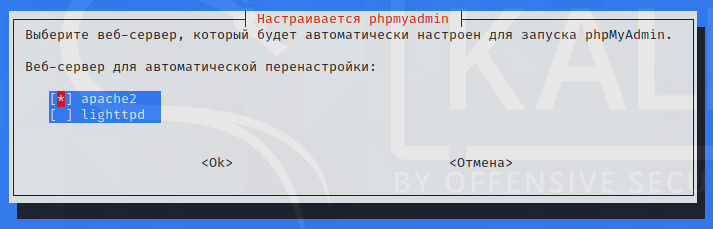
Use the Space key to select items, use the Tab key to move between items, and press Enter to finish.
Now, after enabling the web server, phpMyAdmin will be available at http://your_server_IP/phpmyadmin/
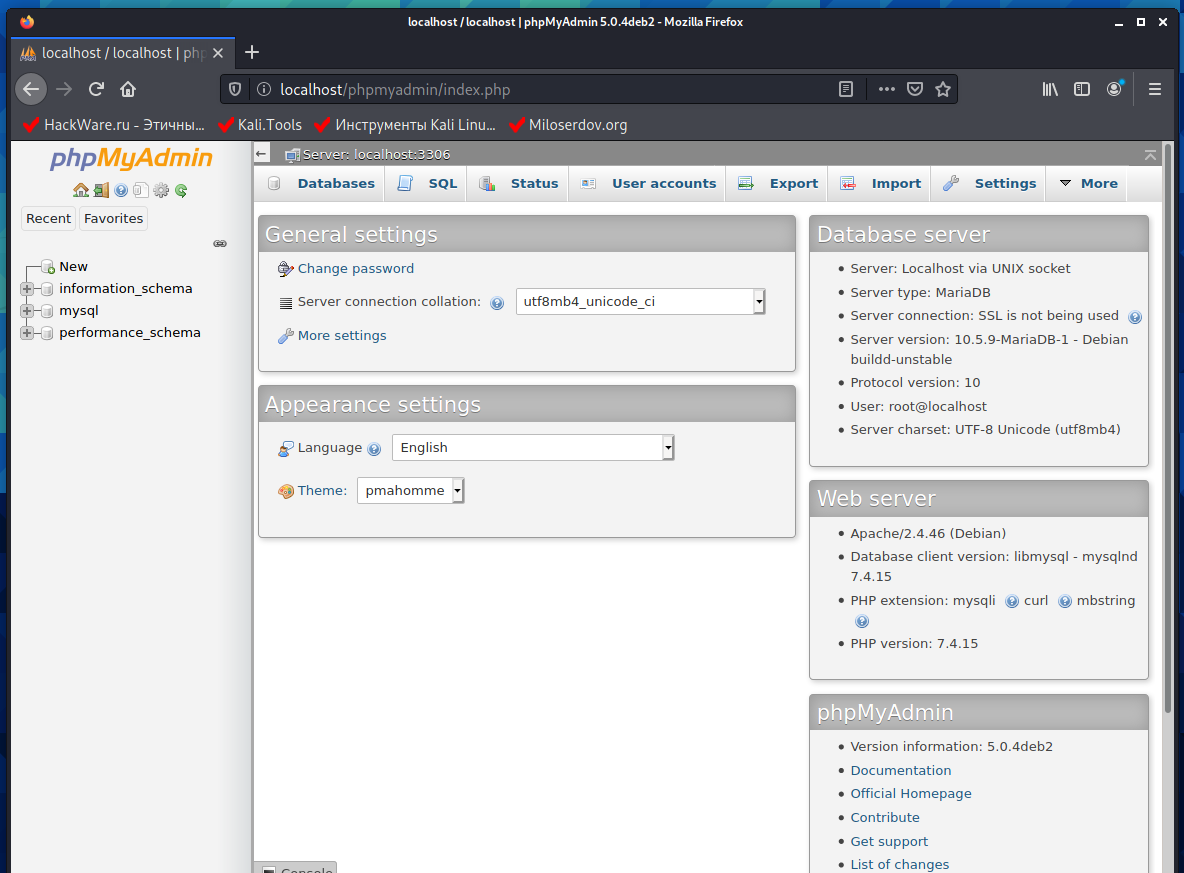
Don’t forget to start the services:
At the bottom of the phpMyAdmin page, you can see the messages with a red background:
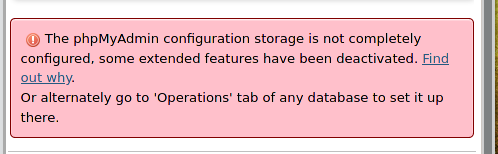
If you only want to enable them, then follow the link http://localhost/phpmyadmin/chk_rel.php and click “Create Database”.
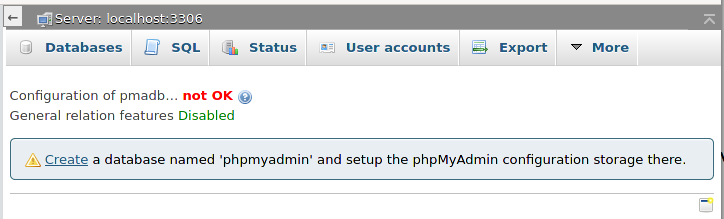
After that, all new functions will be activated.
How to change phpMyAdmin URL. How to enable and disable phpMyAdmin
If during the installation of phpMyAdmin you chose not to configure it for use with the Apache web server, use the command to enable phpMyAdmin:
Restart the web server for the changes to take effect.
To disable phpMyAdmin use the command:
Restart the web server for the changes to take effect.
There is an important line in the /etc/phpmyadmin/apache.conf file:
Its essence is that the URL /phpmyadmin (for example, http://localhost/phpmyadmin) begins to correspond to the /usr/share/phpmyadmin folder. That is, the phpMyAdmin files (scripts) are physically located in /usr/share/phpmyadmin, and not in the web server directory (for example, /var/www/html/).
Many automatic scanners of “hidden” files and folders of the web server and sites must check the directories “phpmyadmin”, “pma” and others like that. You can hide your phpMyAdmin nicely by changing the Alias. For instance:
PhpMyAdmin will now be available at http://localhost/lkjgler94345 — not easy to find.
Error “Login without a password is forbidden by configuration (see AllowNoPassword)”
When you try to log into phpMyAdmin with a blank password, you may receive an error:
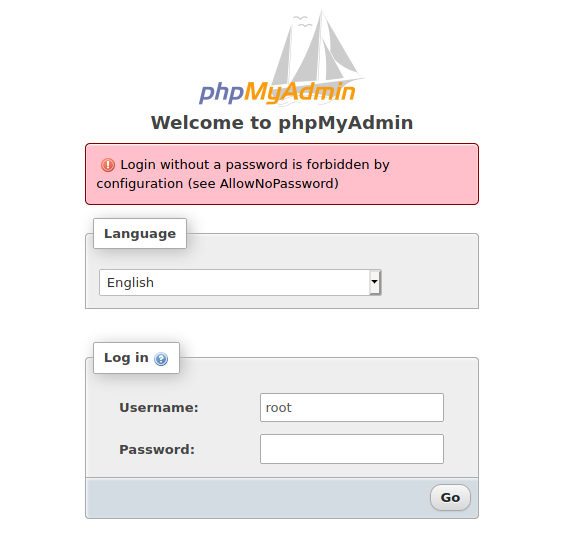
The bottom line is that login as root or another user without a password is prohibited by the phpMyAdmin configuration.
Two ways to fix it:
- set MySQL password
- allow passwordless login in phpMyAdmin config
To enable passwordless login in phpMyAdmin, open the /etc/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php file:
Find the second (there are two) line:
uncomment it to get:
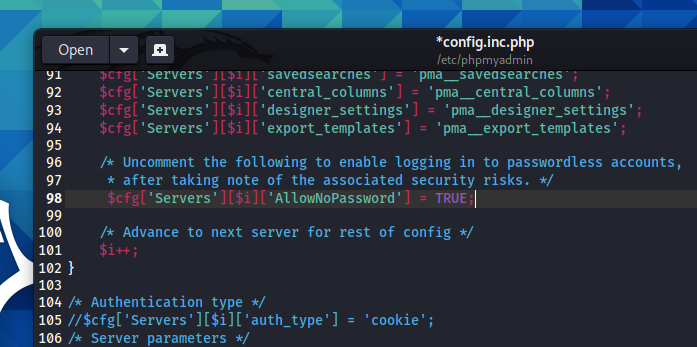
Save and close the config.inc.php file.
How to use phpMyAdmin on Kali Linux
Working in phpMyAdmin is intuitive, so there shouldn’t be any difficulties.
But by default PHP has very small limits on the size of the processed file, so if you import or export a large database, you may encounter phpMyAdmin’s “Incorrect format parameter”. The error occurs due to PHP restrictions on the size of uploaded files and files transferred by the POST method.
It is necessary to increase the value of these two variables in the php.ini (to find it locate php.ini) configuration file. Open the php.ini file and set a larger value for the following variables:
By default, the values there are:
Of course, this is too little for almost any task.
Restart the web server for the changes to take effect.
If you work a lot with phpMyAdmin, then you can customize it for yourself, including setting default settings for import and export. An example of how to do this in the article “How to change default export settings in phpMyAdmin”.
phpMyAdmin alternative
Note that phpMyAdmin is a shim that uses PHP to manipulate databases. Therefore, there is a loss in speed when processing very large databases, and you can also encounter the PHP limits set in its configuration file.
Importing and exporting large databases into MySQL can be performed using MySQL itself — auxiliary utilities are supplied with the DBMS that allow you to perform various actions. To export databases, you can use mysqldump utility.
To export a database, use the following command
- username is the username with which you can log into the database
- database_name is the name of the database to export
- data-dump.sql is a file in the current directory where the output will be saved
Database import
To import an existing database file into MySQL or MariaDB, you need to create a new database into which the contents of the dump file will be imported.
Start by logging into the database as root or another user with sufficient privileges to create a new database.
This will give you a prompt to the MySQL shell. Next, create a new database called new_database.
A confirmation will be displayed about creation.
Now exit the MySQL shell by pressing CTRL+D. On a regular command line, you can import the file with the following command:
- username is the username with which you can log into the database
- newdatabase is the name of the newly created database
- data-dump.sql — dump file with data for import located in the current directory
Successful execution of the command will not display any messages. If errors occur during this process, mysql will print them in the terminal. You can verify that the database has been imported by logging into the MySQL shell again and analyzing the data. This can be done by selecting a new database with the command
and then send a SQL query:
or a similar command to view the data.
How do I backup multiple MySQL databases?
If you want to back up multiple databases, run the following command. The following example will backup the structure and data of the rsyslog, syslog databases into a single file called rsyslog_syslog.sql.
How do I back up all databases?
If you want to back up all databases, then use the following command with the —all-database option. The following command will back up all databases, their structure and information, to a file called all-databases.sql.
How to backup only the MySQL database structure?
If you want to make a backup copy of the database structure without information, then use the —no-data option in the command. The following command will export the rsyslog database structure to the rsyslog_structure.sql file.
How to backup only information from MySQL database?
To create a backup of only information from a database without a structure, use the —no-create-info option with the command. This command will take data from the rsyslog database and copy it to the rsyslog_data.sql file.
How do I backup one table from a database?
With the next command you can make a backup copy of one table or certain tables from your database. For example, the following command will only make a backup of the wp_posts table from the wordpress database.
How do I backup multiple tables?
If you want to back up several or specific tables from the database, separate each table with a space.
How do I back up a remote MySQL database?
The following command will back up the “gallery” database from the remote server 185.117.153.79 to the local server.
You can edit databases, add new records, delete records, etc. from the command line using SQL queries.
Additional MySQL Resources
You may also be interested in the following articles:
Источник