- Arch Linux User Repository
- Search Criteria
- Package Details: pamac-aur 10.2.0-2
- Package Actions
- Dependencies (27)
- Required by (5)
- Sources (1)
- Latest Comments
- bassam commented on 2021-10-04 23:28
- Hanabishi commented on 2021-10-01 16:19
- kanehekili commented on 2021-09-30 17:19
- bxabi commented on 2021-09-29 09:39
- Gotit commented on 2021-06-20 18:50
- Zeph commented on 2021-06-14 10:16
- tigr72 commented on 2021-06-14 10:03
- theone77 commented on 2021-06-13 07:08
- marcos.lcog commented on 2021-06-11 20:26
- darklyn3r commented on 2021-06-11 18:57
- Pamac не видит пакеты из AUR
- Pamac
- Содержание
- Installing Software
- Removing Software
- Preferences
- Locating and Installing Packages
- Removing Packages
- Identifying Installed Packages
- Displaying Detailed Package Information
- Updating the System
- Dealing with Orphaned Packages
- Cleaning the Cache
- Other Useful Pamac Functions
Arch Linux User Repository
Search Criteria
Package Details: pamac-aur 10.2.0-2
Package Actions
| Git Clone URL: | https://aur.archlinux.org/pamac-aur.git (read-only, click to copy) |
|---|---|
| Package Base: | pamac-aur |
| Description: | A Gtk3 frontend, Package Manager based on libalpm with AUR and Appstream support |
| Upstream URL: | https://gitlab.manjaro.org/applications/pamac |
| Keywords: | gui installer libalpm package pacman yay |
| Licenses: | GPL3 |
| Conflicts: | pamac, pamac-tray-appindicator |
| Provides: | pamac=10.2.0-2 |
| Submitter: | Zeph |
| Maintainer: | Zeph |
| Last Packager: | Zeph |
| Votes: | 347 |
| Popularity: | 4.94 |
| First Submitted: | 2013-12-05 12:57 |
| Last Updated: | 2021-10-03 21:21 |
Dependencies (27)
- archlinux-appstream-data (archlinux-appstream-data-pamac)
- dbus-glib (dbus-glib-git)
- desktop-file-utils (desktop-file-utils-git)
- git (git-git, git-vfs)
- json-glib (json-glib-git)
- libhandy (libhandy-git, libhandy-glade-catalog-disabled-git)
- libnotify (libnotify-gtk2, libnotify-id-git, libnotify-id)
- libsoup (libsoup-gnome-git, libsoup-gnome)
- polkit (polkit-no-script-git, polkit-git, polkit-consolekit, polkit-duktape)
- vte3>=0.38 (vte3-ng-emoji-terminix-zsh-notify, vte3-ng-fullwidth-emoji, vte3-git, vte3-tilix, vte3-ng, vte3-kinetic, vte3-nohang, vte3-selectall, vte3-notification)
- appstream-glib>=0.7.18-1 (appstream-glib-git)
- libpamac-aur>=11.1
- glib2>=2.42 (glib2-clear, glib2-quiet, glib2-selinux, glib2-nodocs-git, glib2-git, glib2-patched-thumbnailer)
- gtk3>=3.22 (gtk3-adwaita-3-32-git, gtk3-git, gtk3-ubuntu, gtk3-no_deadkeys_underline, gtk3-classic, gtk3-patched-filechooser-icon-view, gtk3-typeahead)
- gnutls>=3.4 (gnutls-tiny-git, gnutls-git, gnutls-next, gnutls-openssl, gnutls-nodocs-git)
- asciidoc (asciidoc-git) (make)
- gettext (gettext-git) (make)
- gobject-introspection (gobject-introspection-git) (make)
- itstool(make)
- libappindicator-gtk3 (libappindicator-gtk3-ubuntu, libappindicator-bzr) (make)
- meson (meson-git) (make)
- ninja (ninja-git, ninja-samurai, ninja-mem, ninja-kitware, ninja-bin) (make)
- xorgproto (xorgproto-git) (make)
- vala>=0.46 (vala0.42, vala0.44, vala-git) (make)
- gtk3>=3.22 (gtk3-adwaita-3-32-git, gtk3-git, gtk3-ubuntu, gtk3-no_deadkeys_underline, gtk3-classic, gtk3-patched-filechooser-icon-view, gtk3-typeahead) (make)
- lxsession (lxsession-git) (optional) – needed for authentification in Xfce, LXDE etc.
- polkit-gnome (polkit-gnome-gtk2, xfce-polkit-git, xfce-polkit, polkit-gnome-git) (optional) – needed for authentification in Cinnamon, Gnome
Required by (5)
- bootsplash-manager-bin (requires pamac)
- mintmenu (requires pamac) (optional)
- pamac-tray-icon-plasma (requires pamac)
- pamac-zsh-completions (requires pamac)
- update-notifier (requires pamac) (optional)
Sources (1)
Latest Comments
bassam commented on 2021-10-04 23:28
Getting an error
Hanabishi commented on 2021-10-01 16:19
kanehekili commented on 2021-09-30 17:19
Same problem on Arch linux:
bxabi commented on 2021-09-29 09:39
I’m getting this error:
Gotit commented on 2021-06-20 18:50
@Zeph I tried your fix dated 6/10/21 but can’t remove pamac as I get:
error while loading shared libraries: libalpm.so.12: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
Had to grab the libalpm.so.12 files from a 5.x version of pacman and drop them in usr/lib. Then I could:
Zeph commented on 2021-06-14 10:16
tigr72 commented on 2021-06-14 10:03
In the settings, the cache size always shows 0 files, 0 bytes and the button for clearing the cache is not active
theone77 commented on 2021-06-13 07:08
Thank you Zeph, I did as you said: yay -Rncs pamac-aur yay -S pamac-aur All good now.
marcos.lcog commented on 2021-06-11 20:26
pamac-alll is working perfectly with libpamac-full!! I just had to remove pamac-aur before getting the new packs.
darklyn3r commented on 2021-06-11 18:57
Thanks @Zeph .. I already removed and reinstalled pacman and now everything works very well for me
Copyright © 2004-2021 aurweb Development Team.
AUR packages are user produced content. Any use of the provided files is at your own risk.
Источник
Pamac не видит пакеты из AUR
Доброго времени суток! Начал осваивать Archlinux и столкнулся с такой проблемой. Pamac не видит пакеты AUR я уже побывал и Aurman и Pacaur сами по себе они работают но когда захожу Pamac и переключать на AUR «пакет не найден». Подскажите где искать причину проблемы или решение.
P.S. Перед установкой Pamac удалял ненужные пакеты Gnome. Хотя все зависимости Pamac-a на месте.
А в настройках включёно? Preferences->AUR->Enable AUR support. Или в /etc/pamac.conf EnableAUR
ничего что сам разработчик aurman советует перейти на yay?
From a pure technical point of view, there is no need to switch, if you are happy with aurman as of now. Since I need an AUR helper myself, aurman development will continue. Do not expect frequent updates however, because current aurman fulfills all of my needs.
Да все включено, но не работает.
Тогда не в курсе. Поставил себе pamac-aur, включил aur в настройках и всё заработало. Никаких дополнительных действий не делал. А из терминала оно не запускается? Может что пишет?
Удалил полностью Pacaur Pamac. Попробую установить заново. Может не использовать Pacaur?
Источник
Pamac
Содержание
Pamac is Manjaro’s Package Manager. It is based on libalpm with AUR and Appstream support. It focuses on providing an easy to use interface while still providing a powerful set of features.
Pamac is pre-installed on many Manjaro Editions but if your system does not have it can be easily installed. Pamac comes in several different packages:
- pamac-gtk — The GTK version of pamac. Includes a tray icon for many desktops.
- pamac-qt — The Qt version of pamac. Experimental.
- pamac-cli — The command line version of pamac.
- pamac-tray-appindicator — A tray icon for KDE plasma
These packages can be installed using pacman. For example, to install the GTK version, you can use the command:
Installing Software
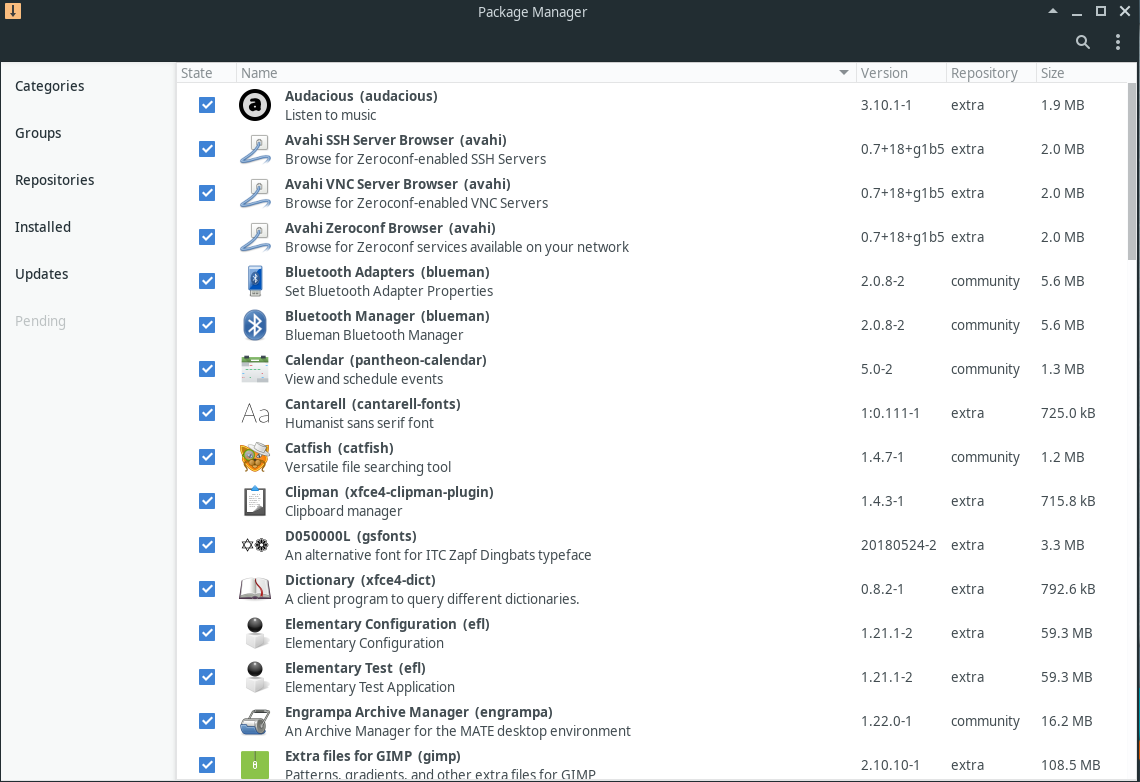
To install packages simply check check the box next to the packages. Once you have selected all the packages all the packages you want to install, click the Apply button at the bottom of the page.
If any of the packages have optional dependencies(packages that enable additional functionality) you will see a window like the one to the left which allows to select the ones you would like to install.
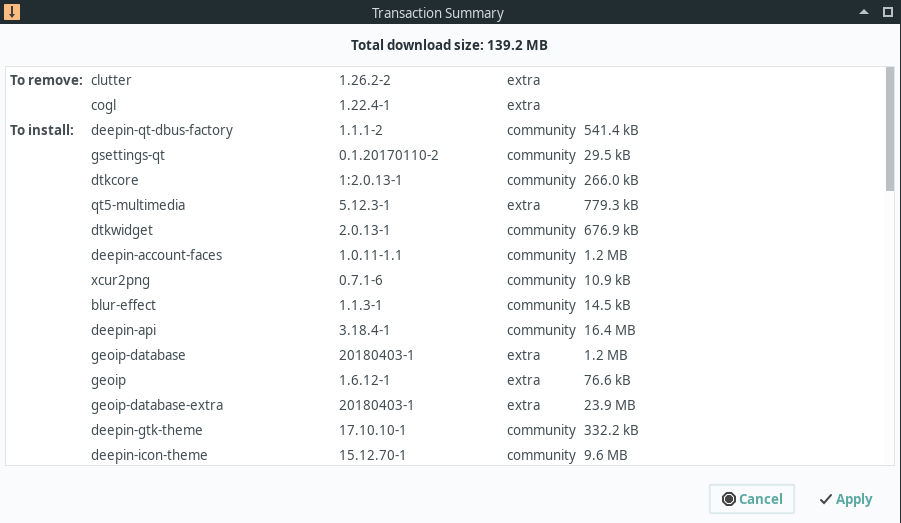
After you have selected optional dependencies, you should see a windows similar to the one pictured on the left. This lists all the packages that will be installed, upgraded or removed by the action. Once you have reviewed the list, press the Apply button to install the packages.
You may notice this list has more packages than you selected in the GUI. This is because many packages also have dependencies which are packages that must be installed in order for the software you selected to function properly. You may also notice that packages are being removed even though you didn’t select any packages to remove. This is happening in the example to the left where you can see clutter and cogl are being removed. They are being removed because they conflict with deepin-clutter and deepin-cogl which provide the same functionality.
Removing Software
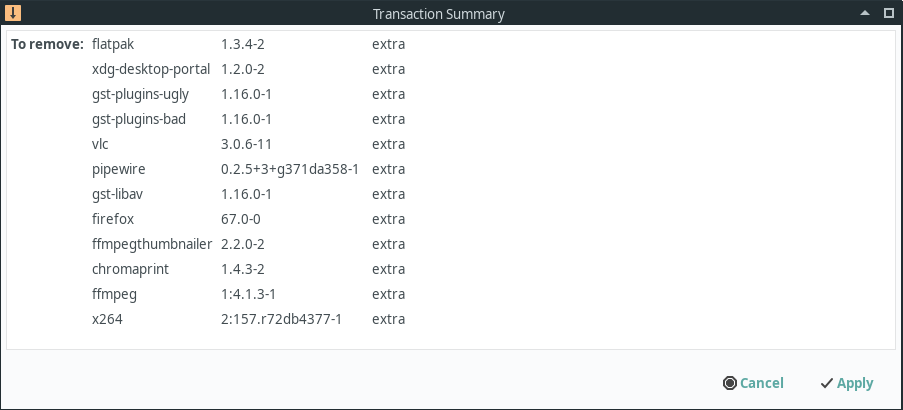
Removing software is as simple as unchecking the packages you want to remove and clicking the Apply button at the bottom of the page.
Once you do you should see a screen similar to the one on the left which lists all the packages that are about to be removed. You may notice this list contains more packages than you selected. This is because when you remove a package that other packages depend on, those packages are also removed.
Preferences
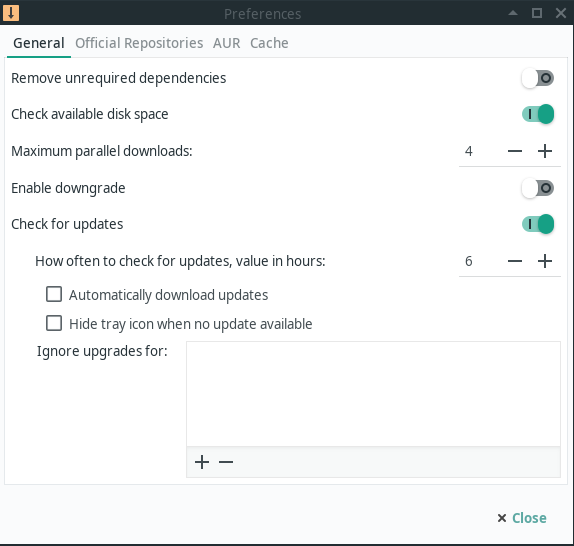
You can access the preferences by clicking on the three dots in the upper right corner and selecting preferences.
The General tab of preferences contains several settings, most of which are self explanatory.
- Remove unrequired dependencies — This removes dependencies which are no longer required by any package
- Check available disk space — Checks to ensure you have sufficient disk space available before downloading and installing packages
- Maximum parallel downloads — The number of concurrent downloads allowed
- Enable downgrade — This allows packages to be downgraded as well as upgraded. This is important when switching branches.
- Check for updates — Disabling this will stop Pamac from looking for updates. In most cases, turning this off on a rolling release distro like Manjaro is a bad idea.
- Ignore updates for — This is a list of packages that you don’t want to be upgraded. This is inherently dangerous practice and should only be used by advanced users.
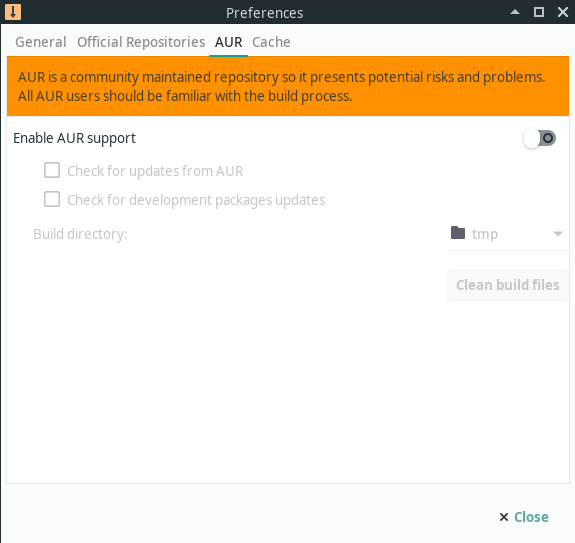
Pamac is also capable of installing and upgrading packages from the Arch User Repository(AUR). Please carefully read the considerations in the linked page prior to enabling support for AUR.
If you enable AUR support, it is usually wise to also select, «Check for updates from AUR» so software you install from AUR won’t become outdated.
Checking for «development package» updates will allow updates on *-git packages which are built from the latest source code to also be updated.
The «Build directory» is where AUR packages will be built. Using «tmp» usually will provide the best performance but very large packages may fail to build. In this case, select somewhere with more available space.
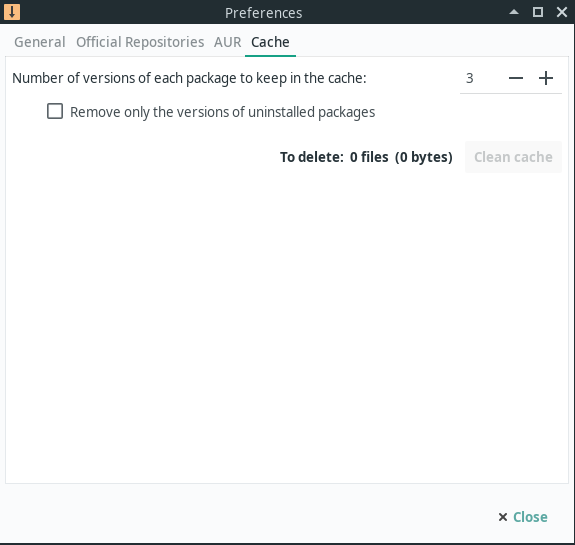
When Pamac installs packages, it keeps a copy of all the old packages you have downloaded. This cache can be very useful if you have to download packages in an emergency. However, left unchecked, this cache will grow very large over time. These preferences allow your cache to be automatically managed based on your preferences.
The first option allows you to set a number for how many copies of each package are retained. In other words, if you have downloaded 25 versions of firefox over the life of your install and you set this number to «3», only the most recent 3 versions will be retained. Unless you are very short on disk space, it is recommended to set this to at least 2.
By selecting «Remove only the versions of uninstalled packages» pamac will retain all versions of packages you still have installed.
Pamac also includes a fully functional CLI for when you don’t have a functional GUI or for those that prefer to manager packages that way.
Locating and Installing Packages
To search for available packages you can use the command pamac search . For example, to search the repos for packages containing the word smplayer:
As you can see, this will also show you which packages are already installed. If you would like to search both the repos and AUR you add -a like this:
Once you have identified the packages you wish to install you can install them with command pamac install . For example, if we wanted to install smplayer and smplayer-themes we could use the command:
If you want to install packages from AUR you use the command pamac build . Sticking with the above example, if you decided you wanted to install umplayer instead you could the command:
Removing Packages
The command pamac remove can be used to uninstall packages installed from the repos or AUR. For example if you wanted to remove all the packages installed above you could use the command:
Identifying Installed Packages
To display a list of all installed packages you can use the command:
Displaying Detailed Package Information
To display detailed information on a package that is in the repos or installed on your system use the command pamac info . Keeping with our example:
If you also would like to check packages in AUR you could use:
Updating the System
To check if updates are available you can use the command:
To update all installed packages installed from the repos or AUR you can use the command:
Dealing with Orphaned Packages
To check to see if there any orphaned packages(packages which are no longer needed) installed you can use:
To remove all orphans use the command:
Cleaning the Cache
When pamac installs packages, it keeps a copy of all the old packages you have downloaded. This cache can be very useful if you have to install older packages in an emergency. However, left unchecked, this cache will grow very large over time.
Otherwise, to clear the cache completely, enter the following command (and use with care):
A safer way to remove old package cache files is to remove all packages except for the latest three package versions using:
Other Useful Pamac Functions
To see which package owns a certain file on your system, use the command pamac search -f . For example:
To force a package to be installed even if it is already installed use pamac reinstall . For example:
Источник