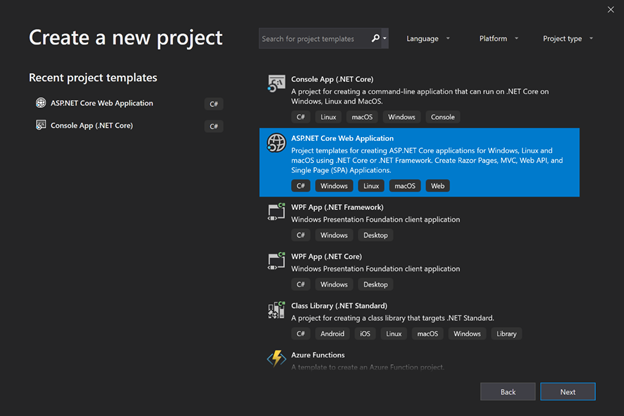
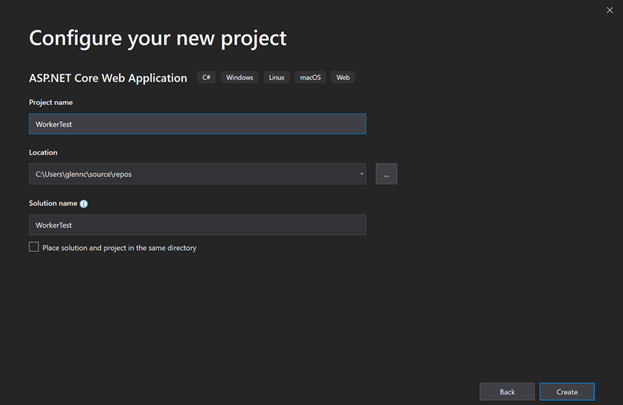
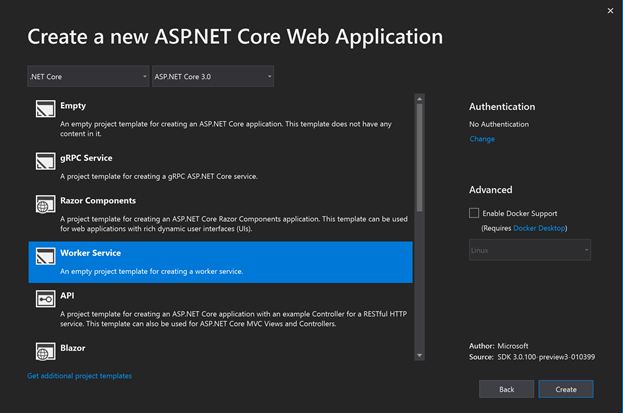
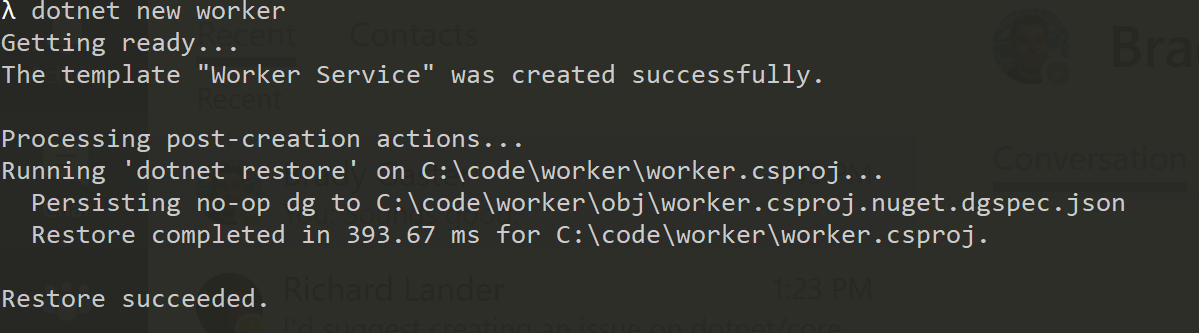
- Windows System Resource Manager Overview
- Role/Feature description
- Practical applications
- Methods of resource management
- Built-in resource management policies
- Custom resource management
- Removed or deprecated functionality
- Application. Find Resource(Object) Метод
- Определение
- Параметры
- Возвращаемое значение
- Исключения
- Примеры
- Комментарии
- .NET Core Workers как службы Windows
- Создание worker
- Создание Worker в Visual Studio
- Создание Worker в командной строке
- Запуск в виде службы Windows
- Установка Worker
- Логирование
- Дальнейшая работа
Windows System Resource Manager Overview
Applies To: Windows Server 2012
You can use Windows System Resource Manager to allocate processor and memory resources to applications, users, Remote Desktop Services sessions, and Internet Information Services (IIS) application pools.
With Windows System Resource Manager for the Windows ServerВ® 2012 operating system, you can manage server processor and memory usage with standard or custom resource policies. Managing your resources can help ensure that all the services provided by a single server are available on an equal basis or that your resources will always be available to high-priority applications, services, or users.
Windows System Resource Manager only manages processor resources when the combined processor load is greater than 70 percent. This means that it does not actively limit the resources that can be used by each consumer when processor load is low. When there is contention for processor resources, resource allocation policies help ensure minimum resource availability based on the management profile that you define.
Role/Feature description
You can use Windows System Resource Manager to:
Manage system resources (processor and memory) with preconfigured policies, or create custom policies that allocate resources per process, per user, per Remote Desktop Services session, or per Internet Information Services (IIS) application pool.
Use calendar rules to apply different policies at different times without manual intervention or reconfiguration.
Automatically select resource policies that are based on server properties and events (such as cluster events or conditions) or changes to installed physical memory or number of processors.
Collect resource usage data locally or in a custom SQL database. Resource usage data from multiple servers can be consolidated on a single computer running Windows System Resource Manager.
Create a computer group to help organize Remote Desktop Session Host servers that you want to manage. Policies can easily be exported or modified for an entire computer group.
Practical applications
Because Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 is designed to give as many resources as possible to non-operating system tasks, a server running a single role usually does not require resource management. However, when multiple applications and services are installed on a single server, they are not aware of competing processes. An unmanaged application or service will typically use all available resources to complete a task. Thus, it is important to use a tool such as Windows System Resource Manager to manage system resources on multipurpose servers. Using Windows System Resource Manager provides two key benefits:
More services can run on a single server because service availability can be improved through dynamically managed resources.
High-priority users or system administrators can access the system even during times of maximum resource load.
Methods of resource management
Windows System Resource Manager includes five built-in resource management policies that you can use to quickly implement management. In addition, you can create custom resource management policies to meet your specific needs.
Built-in resource management policies
You can enable built-in resource management policies by selecting the type of policy to use. No further configuration is required.
Equal per process
When the Equal_Per_Process resource allocation policy is managing the system, each running process is given equal treatment. For example, if a server that is running ten processes reaches 70 percent processor utilization, Windows System Resource Manager will limit each process to using 10 percent of the processor resources while they are in contention. Note that resources not used by low utilization processes will be allocated to other processes.
When the Equal_Per_User resource allocation policy is managing the system, processes are grouped according to the user account that is running them, and each of these process groups is given equal treatment. For example, if four users are running processes on the server, each user will be allocated 25 percent of the system resources to complete those processes. A user running a single application is allocated the same resources as a user running several applications. This policy is especially useful for application servers.
Equal per session
When the Equal_Per_Session resource allocation policy is managing the system, resources are allocated on an equal basis for each session connected to the system. This policy is for use with RD Session Host servers.
Equal per IIS application pool
When the Equal_Per_IISAppPool resource allocation policy is managing the system, each running IIS application pool is given equal treatment, and applications that are not in an IIS application pool can only use resources that are not being consumed by IIS application pools.
Weighted Remote Sessions
When the Weighted_Remote_Sessions resource allocation policy is managing the system, the processes are grouped according to the priority assigned with the user account. For example, if three users are remotely connected, the user assigned Premium priority will receive highest priority access to the CPU, the user assigned Standard priority will receive second priority to the CPU, and the user assigned Basic priority will receive lowest priority to the CPU. This policy is for use with RD Session Host servers.
.jpeg) Note Note |
|---|
.jpeg) Note Note |
|---|