- Netstat and pid windows
- Команды netstat
- Популярные Похожие записи:
- 6 Responses to Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть
- 7 netstat Command Usage on Windows with Example
- Show all connections
- Show only established connection
- Show PID used by port number
- Show statistics of all protocols
- Show routing information
- Show Interface Statistics
- Show Fully Qualified Domain Name of foreign address (remote host)
- netstat
- Syntax
- Parameters
- Remarks
- Examples
Netstat and pid windows
Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть-01
Всем привет ранее я начал рассказ про сетевые утилиты системного администратора в статье «Утилита pathping или как диагностировать проблему на маршруте до сайта. Сетевые утилиты 3 часть», движемся дальше и разбираем еще одну утилиту netstat или, как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Данная программка, будет не заменимым инструментом в багаже софта, любого системного инженера, поможет ему провести быструю диагностику ситуации и обнаружить ряд всевозможных проблем с сервисами и их доступностью.
Команды netstat
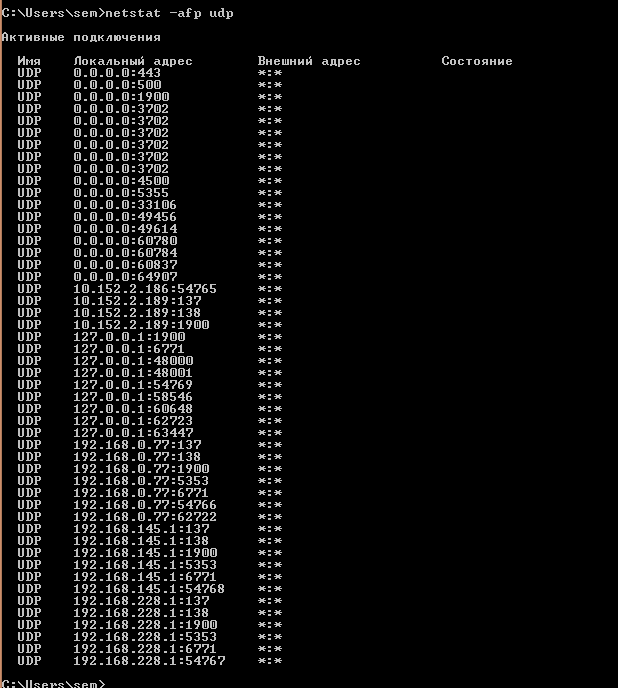
Netstat — Отображение активных подключений TCP, портов, прослушиваемых компьютером, статистики Ethernet, таблицы маршрутизации IP, статистики IPv4 (для протоколов IP, ICMP, TCP и UDP) и IPv6 (для протоколов IPv6, ICMPv6, TCP через IPv6 и UDP через IPv6)
Представим ситуацию вы установили например MSM LSI утилиту для просмотра параметров RAID контроллера, запускаете утилиту, но ничего она не находит, потому что закрыт порт а какой вы не в курсе, и не всегда в инете можно быстро найти информацию об этом, для этого вы и может запустить netstat и посмотреть какой порт слушает ваш сервер с MSM процессом.
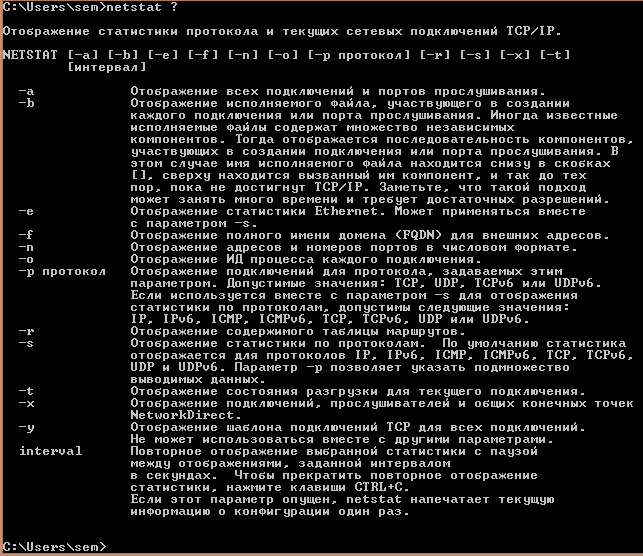
Открываем командную строку Windows и вводим netstat ?. У вас выскочит справка утилиты.
Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть-02
Отображение статистики протокола и текущих сетевых подключений TCP/IP.
NETSTAT [-a] [-b] [-e] [-f] [-n] [-o] [-p протокол] [-r] [-s] [-x] [-t]
[интервал]
- -a Отображение всех подключений и портов прослушивания.
- -b Отображение исполняемого файла, участвующего в создании
- каждого подключения или порта прослушивания. Иногда известные исполняемые файлы содержат множество независимых компонентов. Тогда отображается последовательность компонентов, участвующих в создании подключения или порта прослушивания. В этом случае имя исполняемого файла находится снизу в скобках [], сверху находится вызванный им компонент, и так до тех пор, пока не достигнут TCP/IP. Заметьте, что такой подход может занять много времени и требует достаточных разрешений.
- -e Отображение статистики Ethernet. Может применяться вместе с параметром -s.
- -f Отображение полного имени домена (FQDN) для внешних адресов.
- -n Отображение адресов и номеров портов в числовом формате.
- -o Отображение ИД процесса каждого подключения.
- -p протокол Отображение подключений для протокола, задаваемых этим параметром. Допустимые значения: TCP, UDP, TCPv6 или UDPv6. Если используется вместе с параметром -s для отображения статистики по протоколам, допустимы следующие значения: IP, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, TCP, TCPv6, UDP или UDPv6.
- -r Отображение содержимого таблицы маршрутов.
- -s Отображение статистики по протоколам. По умолчанию статистика отображается для протоколов IP, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, TCP, TCPv6, UDP и UDPv6. Параметр -p позволяет указать подмножество выводимых данных.
- -t Отображение состояния разгрузки для текущего подключения.
- -x Отображение подключений, прослушивателей и общих конечных точек NetworkDirect.
- -y Отображение шаблона подключений TCP для всех подключений. Не может использоваться вместе с другими параметрами. interval Повторное отображение выбранной статистики с паузой между отображениями, заданной интервалом в секундах. Чтобы прекратить повторное отображение статистики, нажмите клавиши CTRL+C. Если этот параметр опущен, netstat напечатает текущую информацию о конфигурации один раз.
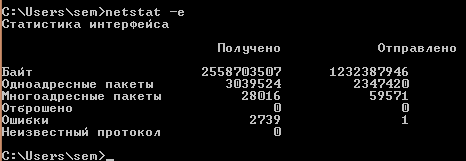
Давайте посмотрим интересные ключи утилиты netstat. Первое что вводим
и у нас на экране появится статистика сетевых пакетов ethernet.
Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть-03
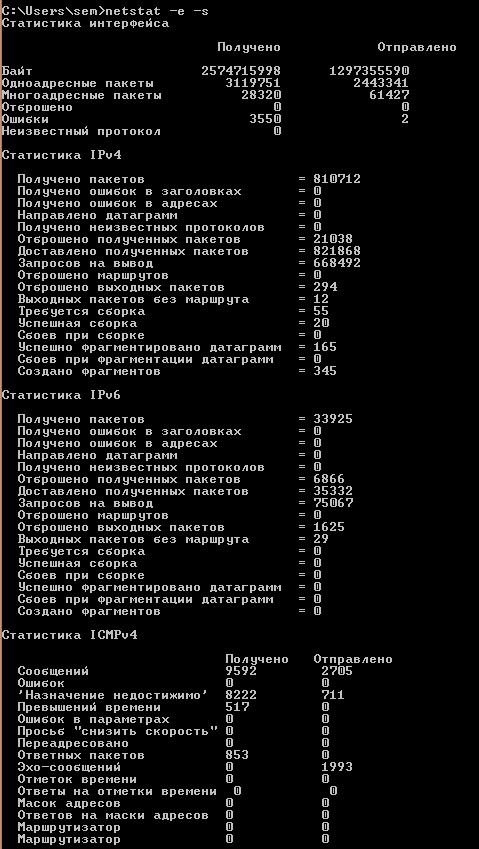
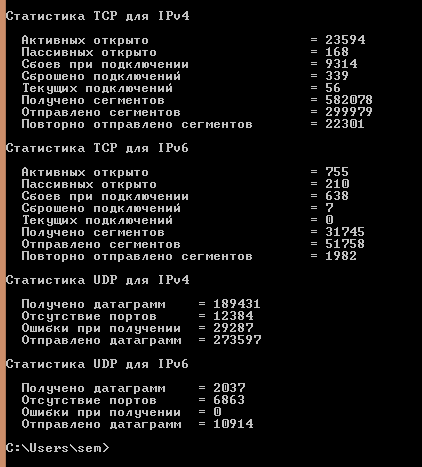
Если добавим ключ -s то получим статистику по протоколам.
Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть-04
Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть-05
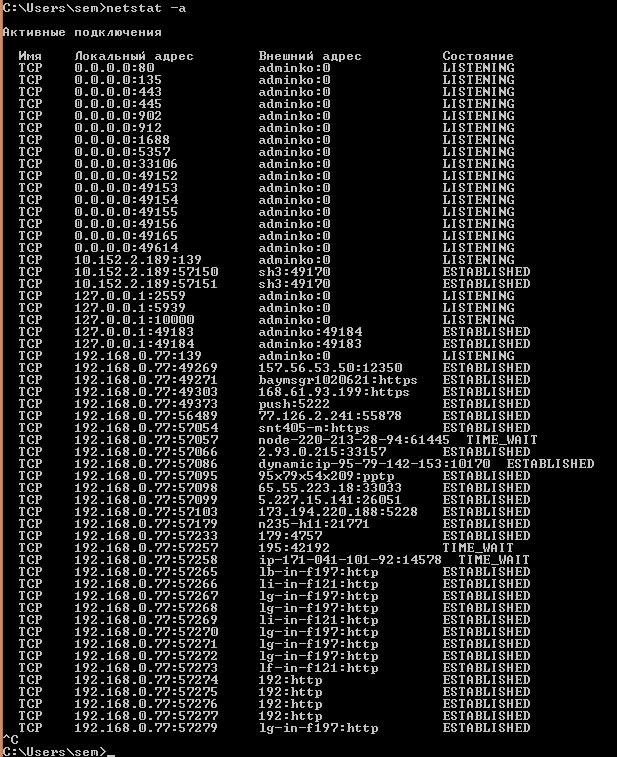
Очень полезно посмотреть все что слушает ваш хост для этого пишем
Вывод команды содержит Тип протокола либо TCP либо UDP, локальный адрес с портом который слушается и внешний адрес с портом и состояние действия.
Для полного понимания информации, предоставляемой этой командой, необходимо понять принципы установки соединения в протоколе TCP/IP. Вот основные этапы процесса установки соединения TCP/IP:
1. При попытке установить соединение клиент отправляет сообщение SYN серверу.
2. Сервер отвечает собственным сообщением SYN и подтверждением (ACK).
Процесс разрыва соединения состоит из следующих этапов:
1. Клиент сообщает «Я закончил», отправляя сообщение FIN серверу. На этом этапе клиент только принимает данные от сервера, но сам ничего не отправляет.
2. После этого сервер отправляет сообщение ACK и отправляет собственное сообщение FIN клиенту.
3. После этого клиент отправляет сообщение ACK серверу, подтверждая запрос сервера FIN.
4. При получении сообщения ACK от клиента сервер закрывает соединение.
Понимание этапов процесса установки и разрыва соединения позволяет более прозрачно интерпретировать состояния соединений в выводе команды netstat. Соединения в списке могут находиться в следующих состояниях.
- CLOSE_WAIT — указывает на пассивную фазу закрытия соединения, которая начинается после получения сервером сообщения FIN от клиента.
- CLOSED — соединение прервано и закрыто сервером.
- ESTABLISHED — клиент установил соединение с сервером, получив от сервера сообщение SYN.
- FIN_WAIT_1 — клиент инициировал закрытие соединения (отправил сообщение FIN).
- FIN_WAIT_2 — клиент получил сообщения ACK и FIN от сервера.
- LAST_ACK — сервер отправил сообщение FIN клиенту.
- LISTEN — сервер готов принимать входящие соединения.
- SYN_RECEIVED — сервер получил сообщение SYN от клиента и отправил ему ответ.
- TIMED_WAIT — клиент отправил сообщение FIN серверу и ожидает ответа на это сообщение.
- YN_SEND — указанное соединение активно и открыто.
Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть-06
Если добавить ключ -f то будут разрешаться имена удаленных внешних ресурсов
Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть-07
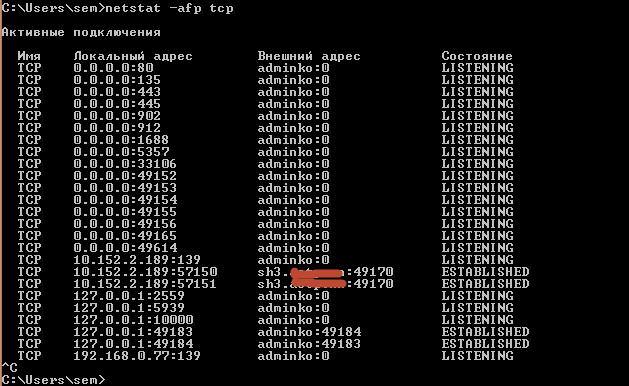
также можно вывести только TCP порты
Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть-08
Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть-09
Вот такая вот полезная утилиты с которой вы всегда будите знать по каким портам общаются службы на хосте. Читайте далее Утилита TCPView. Как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 5 часть
Популярные Похожие записи:
6 Responses to Утилита netstat или как определить какие порты слушает ваш компьютер. Сетевые утилиты 4 часть
thank you very much, would you weird area for any designers to hide this setting up. i had been possessing a number of difficulties with a new Dreamhost machine and i had not been guaranteed the reason why works out which they modify demonstrating invisible documents automagically, whereas different hosting space we connect to together with Filezilla appear to indicate invisible documents automagically. your own personal article allowed me to figure it available, i really appreciate it.
Уважаемый Иван, большое спасибо, это отличная получилась статья! У меня все получилось.
Очень рад, что смог вам помочь!
Добрый день. А как узнать какая программа занимает 80 порт?
Очень просто вы через netstat или tcpView смотрите PID процесса, который висит на порту, далее по PID вычисляете исполняемый файл.
>Добрый день. А как узнать какая программа занимает 80 порт?
Для Linux:
netstat -nl4p | grep :80
Для *BSD:
sockstat -l -4 | grep :80
Для Windows NT:
netstat -bnap TCP
(без фильтра, требуется права встроенного администратора для командной оболочки)
7 netstat Command Usage on Windows with Example
netstat is a command-line network tool that is a handy troubleshooting command. Its cross-platform utility means you can use it on Linux, macOS, or Windows.
netstat can be very handy in the following.
- Display incoming and outgoing network connections
- Display routing tables
- Display number of network interfaces
- Display network protocol statistics
Let’s get it started…
Show all connections
To start with netstat, let’s see the command that displays all connections.
Type the above command and hit enter. You will see all the active connections from different states as shown below.
You will see a header with Proto, Local Address, Foreign Address, and State. Let’s see brief info about them.
- Proto – defined the protocol type (TCP, UDP, etc. ) of the socket.
- Local Address – displays your computer IP address and port, local end of the socket.
- Foreign Address – displays remote computer that your computer is connected to, the remote end of the socket.
- State – defines the state of the socket (LISTENING, ESTABLISHED, CLOSE_WAIT, TIME_WAIT).
We can filter the connections in different ways. Let’s see them.
Show only established connection
We have seen the state in the connection information. You can use below syntax to view all established connections from/to your Windows server.
Note: to view LISTEN, CLOSE_WAIT, TIME_WAIT you can just use as follows.
To see the connections that are in LISTENING state change ESTABLISHED keyword in the previous command to LISTENING. You will get the information about connections that are in the listening state as follows.
Similarly, run the following command to see all the connections that are in CLOSE_WAIT state.
Finally, use the TIME_WAIT flag to get information about all the connections that are in TIME_WAIT state.
Show PID used by port number
Every connection is a process internally. And every process has an ID, and its called PID. We can see the PID of every socket connection using the following command.
The above command displays all the connections with PID. Let’s run the command and see how we get the result.
We got an extra column called PID. And its the process identifier.
A very handy when you have to find out which PID is using the particular port number.
You can see the following info if you use the above command.
Show statistics of all protocols
Useful when you have to find out for any received header error, received address error, discarded packet, etc. It will list out statistics from IPv4, IPv6, ICMPv4, ICMPv6, TCP, UDP, etc.
You will see the statistics of all protocols as shown below.
To find out any errors quickly you can use syntax.
The above command filters all the errors from statistics of all protocols.
Show routing information
To display Route Table, you can use the below syntax. The following syntax will also list all interfaces.
If you use the above command, then you see the info about routing as shown below.
Show Interface Statistics
To view the status of all interface, you can use the following syntax. This will display Received & Sent details.
Show Fully Qualified Domain Name of foreign address (remote host)
If you are tracking some issues and would like to know FQDN of the remote host, then you can use the following syntax.
If you run the above command, then you will see a similar result as follows.
Note: you can combine findstr syntax to show precise results like below.
The above command will filter the connections and displays only established connections. Let’s see an example.
We can filter the connections using the domain with the following command.
Specify the domain in the command and you will see the filtered connections as follows.
I hope this helps you get familiar with netstat command usage on Windows. If you are interested in learning Windows administration then I would suggest checking out this course.
netstat
Applies to: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
Displays active TCP connections, ports on which the computer is listening, Ethernet statistics, the IP routing table, IPv4 statistics (for the IP, ICMP, TCP, and UDP protocols), and IPv6 statistics (for the IPv6, ICMPv6, TCP over IPv6, and UDP over IPv6 protocols). Used without parameters, this command displays active TCP connections.
This command is available only if the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol is installed as a component in the properties of a network adapter in Network Connections.
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| -a | Displays all active TCP connections and the TCP and UDP ports on which the computer is listening. |
| -b | Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or listening port. In some cases well-known executables host multiple independent components, and in these cases the sequence of components involved in creating the connection or listening port is displayed. In this case the executable name is in [] at the bottom, on top is the component it called, and so forth until TCP/IP was reached. Note that this option can be time-consuming and will fail unless you have sufficient permissions. |
| -e | Displays Ethernet statistics, such as the number of bytes and packets sent and received. This parameter can be combined with -s. |
| -n | Displays active TCP connections, however, addresses and port numbers are expressed numerically and no attempt is made to determine names. |
| -o | Displays active TCP connections and includes the process ID (PID) for each connection. You can find the application based on the PID on the Processes tab in Windows Task Manager. This parameter can be combined with -a, -n, and -p. |
| -p |
Remarks
The netstat command provides statistics for the following:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Proto | The name of the protocol (TCP or UDP). |
| Local address | The IP address of the local computer and the port number being used. The name of the local computer that corresponds to the IP address and the name of the port is shown unless the -n parameter is specified. If the port is not yet established, the port number is shown as an asterisk (*). |
| Foreign address | The IP address and port number of the remote computer to which the socket is connected. The names that corresponds to the IP address and the port are shown unless the -n parameter is specified. If the port is not yet established, the port number is shown as an asterisk (*). |
| State | Indicates the state of a TCP connection, including:
|
Examples
To display both the Ethernet statistics and the statistics for all protocols, type:
To display the statistics for only the TCP and UDP protocols, type:
To display active TCP connections and the process IDs every 5 seconds, type:
To display active TCP connections and the process IDs using numerical form, type: