- How to share files between a Linux and Windows computer
- Create a shared folder on Windows
- Access a Windows shared folder from Linux, using Konqueror
- Access a Windows shared folder from Linux, using Nautilus
- Access a Windows shared folder from Linux, using the command line
- Как подключиться к Linux из Windows
- Удалённый доступ к Linux с помощью VNC
- Шаг 1. Установка рабочей среды XFCE
- Шаг 2. Установка TightVNC
- Шаг 3. Настройка пароля
- Шаг 4. Настройка скрипта запуска
- Шаг 5. Запуск VNC сервера
- Шаг 6. Подключение из Windows
- Шаг 8. Настройка systemd
- Использование RDP для удалённого подключения
- Подключение к Linux из Windows по SSH
- Использование Putty для подключения к Linux
- Выводы
- How to Access Shares on Windows 11 from Ubuntu
- Enable Network Discovery in Windows 11
- Turn on Public Folder Sharing in Windows 11
- Access shares on Windows 11 from Ubuntu
- How to access Ubuntu files from Windows
How to share files between a Linux and Windows computer
The easiest and most reliable way to share files between a Linux and Windows computer on the same local area network is to use the Samba file sharing protocol. All modern versions of Windows come with Samba installed, and Samba is installed by default on most distributions of Linux.
Create a shared folder on Windows
First, create a shared folder on your Windows machine.
- Open the Control Panel.
- Go to Network and Sharing Options.
- Go to Change Advanced Sharing Settings.
- Select Turn on Network Discovery and Turn on File and Print Sharing.
Now, create a new folder to share or choose an existing folder that you’d like to share.
- Right-click the folder and select Properties.
- Go to the Sharing tab.
- Above the Share button is the network name of the share you are creating. It should look like \\YOURCOMPUTERNAME\Users\YourUserName\ShareFolderName. Make a note of this network name to use later on your Linux machine.
- Click Share.
Access a Windows shared folder from Linux, using Konqueror
Many Linux distributions use the KDE desktop environment and the Konqueror file manager/browser. If this is what you are using, you can follow these steps to access your Windows shared folder:
- Click the K menu icon.
- Select Internet ->Konqueror.
- In the Konqueror window that opens, click the Network Folders link, or type remote:/ in the address bar and press Enter .
- Click the Samba Shares icon.
- Click the icon of your Windows Home workgroup.
- Click the Workgroup icon.
- Click the icon for your computer.
- When prompted, enter the username and password for the Windows account that created the share.
- Click OK.
Access a Windows shared folder from Linux, using Nautilus
Many Linux distributions, especially those that use the GNOME desktop environment, use the Nautilus file manager. If this is what you’re using, you can follow these steps to access your Windows shared folder:
- Open Nautilus.
- From the File menu, select Connect to Server.
- In the Service type drop-down box, select Windows share.
- In the Server field, enter the name of your computer.
- Click Connect.
Alternatively, in the Nautilus address bar, you can type smb://ComputerName/ShareName and press Enter . For instance, when you created your Windows Share, if the share name was listed as:
Type smb://YOURCOMPUTERNAME/Users/YourUserName/ShareFolderName and press Enter . Note the smb: at the beginning; in Linux, use forward slashes instead of backslashes.
Access a Windows shared folder from Linux, using the command line
You can also access your Windows share from the Linux command line using the smbclient program.
- Open a terminal.
- Type smbclient at the command prompt.
- If you receive a «Usage:» message, this means smbclient is installed, and you can skip to the next step. If the command is not found, however, you need to install smbclient. Follow these steps to install it.
Источник
Как подключиться к Linux из Windows
В мире ИТ существует уже довольно широкий спектр операционных систем, начиная с серверных, заканчивая операционными системами для мобильных устройств. В обычных пользовательских компьютерах и в серверах довольно часто используются две ОС — Linux и Windows. Поэтому очень часто возникают ситуации, когда приходится подключаться по сети из одной операционной системы к другой для выполнения разнообразных операций.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим варианты подключения к Linux из Windows. Существуют бесплатные и условно бесплатные утилиты вроде AnyDesk или TeamViewer, но установка их довольно тривиальна и не нуждается в дополнительном пояснении. Утилиты подобного рода обладают рядом ограничений при бесплатном некоммерческом использовании, либо их функциональность не удовлетворяет тем или иным потребностям пользователя. Мы рассмотрим полностью бесплатные способы как подключится к Linux из Windows.
Удалённый доступ к Linux с помощью VNC
На сегодняшний день самое популярное удаленное подключение к Linux из Windows, с использованием привычный в Windows графического интерфейса, является VNC (Virtual Network Computing) — утилита, использующая протокол RFB (Remote FrameBuffer — удалённый кадровый буфер). Управление осуществляется путём передачи нажатий клавиш на клавиатуре и движений мыши с одного компьютера на другой и ретрансляции содержимого экрана через компьютерную сеть.
В качестве сервера VNC в данном примере будет использоваться TightVNC, установленный в Ubuntu 20.04. Для установки сервера VNC необходимо выполнить ряд действий:
Шаг 1. Установка рабочей среды XFCE
Xfce — одна из самых легковесных рабочих сред, используемых в Linux, она будет быстро работать даже при слабом и нестабильном сетевом подключении. Установите её с помощью команд:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies
Шаг 2. Установка TightVNC
Далее установите TightVNC:
sudo apt install tightvncserver
Шаг 3. Настройка пароля
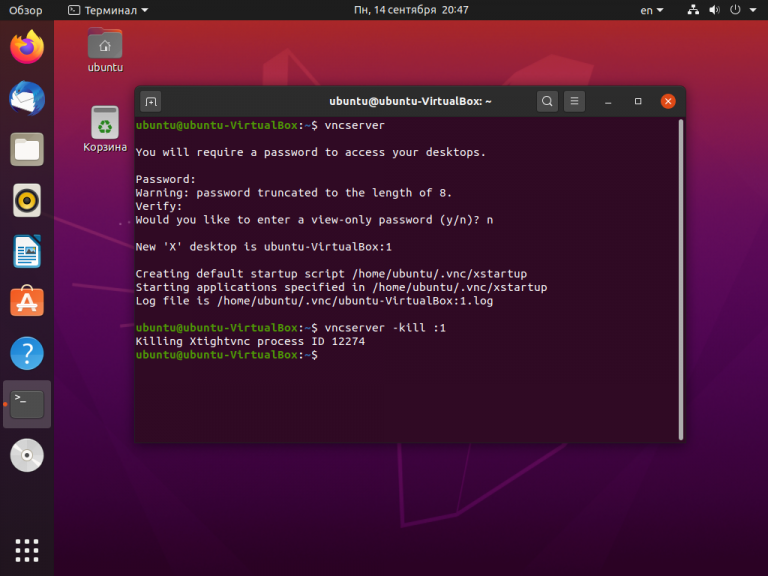
Перед началом выполнения всех действий необходимо задать пароль пользователя VNC. Выполните команду:
Вам будет предложено создать новый пароль, а также пароль только для просмотра. Откажитесь от второй опции:
Завершите процесс vncserver:
vncserver -kill :1
Шаг 4. Настройка скрипта запуска
Отредактируйте скрипт, который выполняется после запуска VNC-сервера:
Он должен содержать такой текст:
#!/bin/sh
unset SESSION_MANAGER
unset DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS
startxfce4 &
Сделайте файл исполняемым:
Шаг 5. Запуск VNC сервера
На этом этапе уже можно запустить VNC-сервер с помощью команды:
Шаг 6. Подключение из Windows
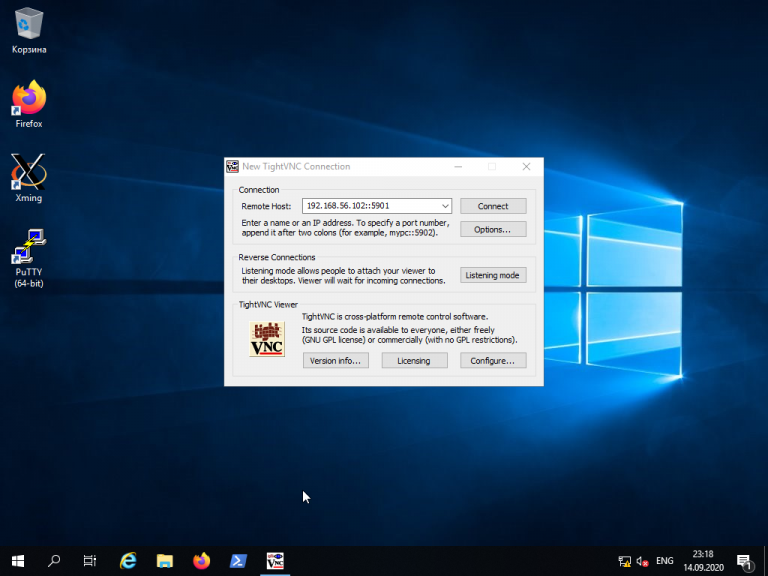
Для того, чтобы подключиться из Windows к вашему Linux-серверу, используйте TightVNC Viewer.
Укажите IP-адрес компьютера, к которому нужно подключиться, и номер порта в поле Remote Host. В данном примере — 192.168.56.102::5901:
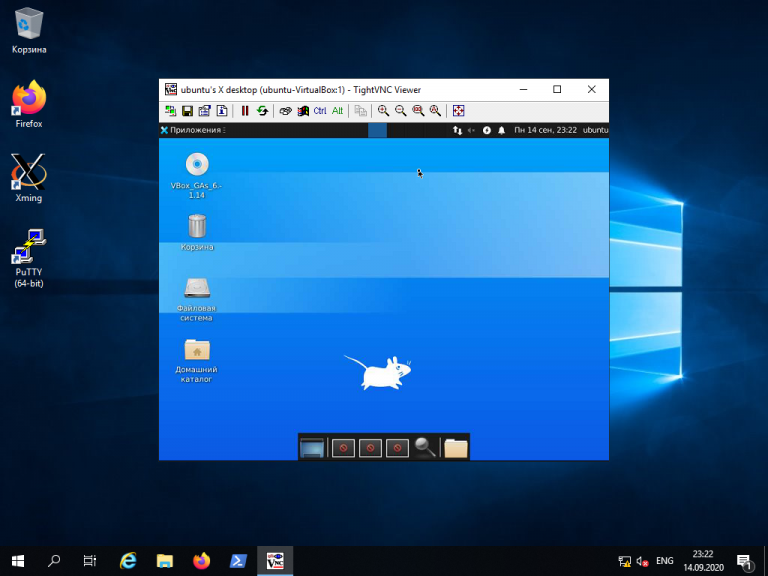
После того, как будет введён пароль, вы должны увидеть рабочий стол Xfce:
Шаг 8. Настройка systemd
Для того, чтобы запуск вашего VNC-сервера добавить в автозагрузку надо использовать systemd. Создайте новый файл сервиса systemd:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@.service
Его содержимое должно быть следующим:
[Unit]
Description=Systemd VNC server startup script for Ubuntu 20.04
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
User=ubuntu
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/vncserver -kill :%i &> /dev/null
ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver -depth 24 -geometry 800×600 :%i
PIDFile=/home/ubuntu/.vnc/%H:%i.pid
ExecStop=/usr/bin/vncserver -kill :%i
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Измените имя пользователя ubuntu и рабочего каталога ubuntu на нужные вам значения. Если у вас запущен VNC-сервер, остановите его:
vncserver -kill :1
Сообщите systemd о появлении нового сервиса:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Добавьте запуск вашего нового сервиса в список автозагрузки:
sudo systemctl enable vncserver@1.service
sudo systemctl start vncserver@1
Использование RDP для удалённого подключения
Помимо VNC, для управления Linux-сервером из Windows можно воспользоваться RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol). Для этого на компьютере с Ubuntu 20.04 установите утилиту xrdp:
sudo apt install xrdp
Для корректной работы сервиса необходимо добавить пользователя xrdp в группу ssl-cert:
sudo adduser xrdp ssl-cert
sudo apt-get install xfce4
Добавьте Xfce в сессии RDP в качестве рабочего стола по умолчанию:
Перезапустите сервис xrdp:
sudo systemctl restart xrdp.service
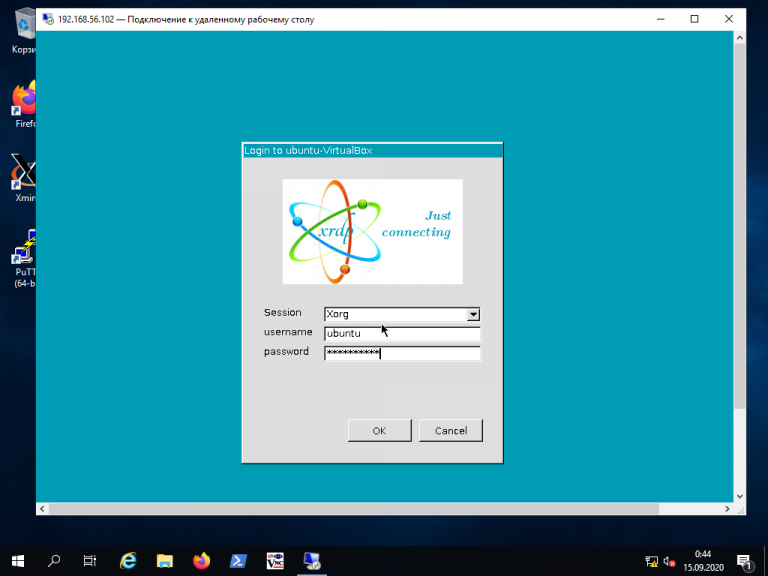
Процедура подключения из Windows к Linux-серверу по протоколу RDP почти ничем не отличается от подключения к удалённым Windows-серверам. Введите IP-адрес сервера, логин и пароль пользователя в Linux:
Если всё сделано правильно, вы увидите рабочий стол Xfce:
Подключение к Linux из Windows по SSH
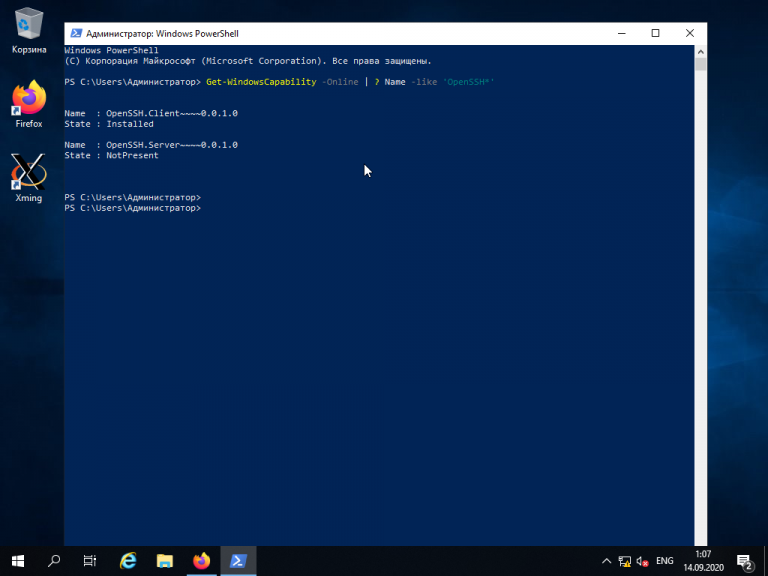
Для подключения к компьютеру под управлением Linux по протоколу SSH из Windows можно воспользоваться PowerShell. Сначала становите OpenSSH Client, если ещё не установлен. Запустите на вашем компьютере PowerShell от имени администратора системы и выполните следующую команду:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like ‘OpenSSH*’
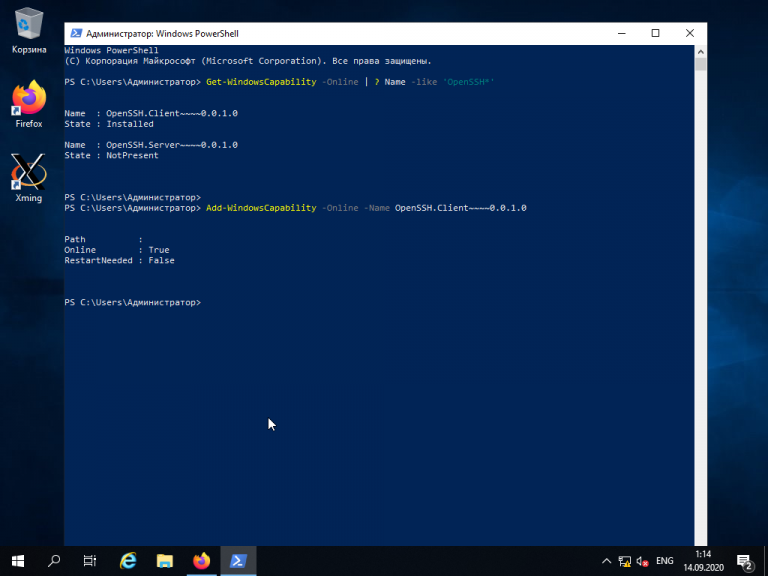
Это необходимо для того, чтобы узнать текущую версию SSH-клиента. В данном примере доступна версия OpenSSH.Client-0.0.1.0. Установите OpenSSH.Client с помощью команды:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Client
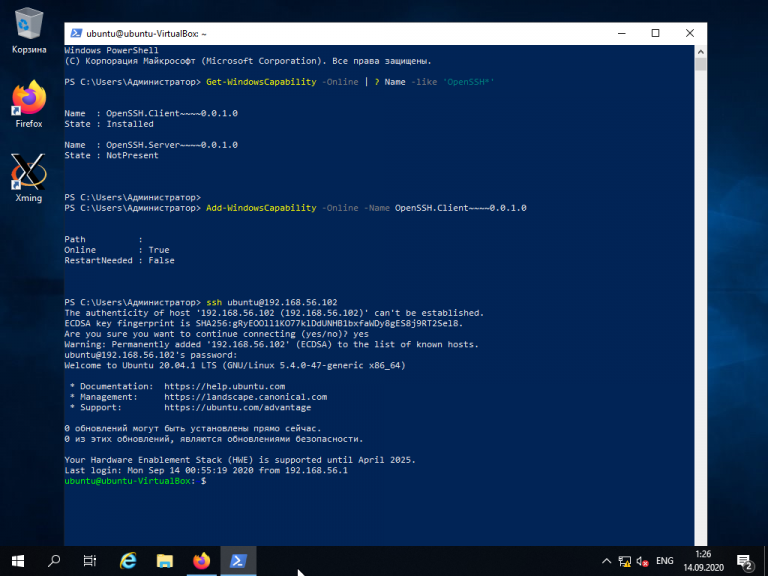
Для того, чтобы подключиться к устройству, на котором запущен SSH-сервер, необходимо ввести имя пользователя и IP-адрес. Команда для подключения по SSH используя PowerShell выглядит так:
Здесь ubuntu — имя пользователя на удалённом компьютере, а 192.168.56.1 — IP-адрес Linux-сервера, на котором запущен демон SSH.
При первом подключении необходимо подтвердить использование специального персонального ключа для шифрованного соединения по SSH-протоколу (введите слово Yes), затем введите пароль пользователя (в данном случае для пользователя ubuntu):
Как видите, соединение прошло успешно. Теперь можно выполнять все команды так же, как если бы вы их выполняли используя стандартный Linux SSH-клиент:
Для завершения терминальной сессии на удалённом компьютере введите команду exit. Теперь вы знаете как выполняется подключение к Linux из Windows по SSH.
Использование Putty для подключения к Linux
Пожалуй, одним из самых популярных способов подключения к Linux из Windows является кроссплатформенная утилита Putty — небольшая по размерам, но очень часто незаменима для подключения по таким протоколам как SSH, Telnet, rlogin и даже с помощью последовательных портов.
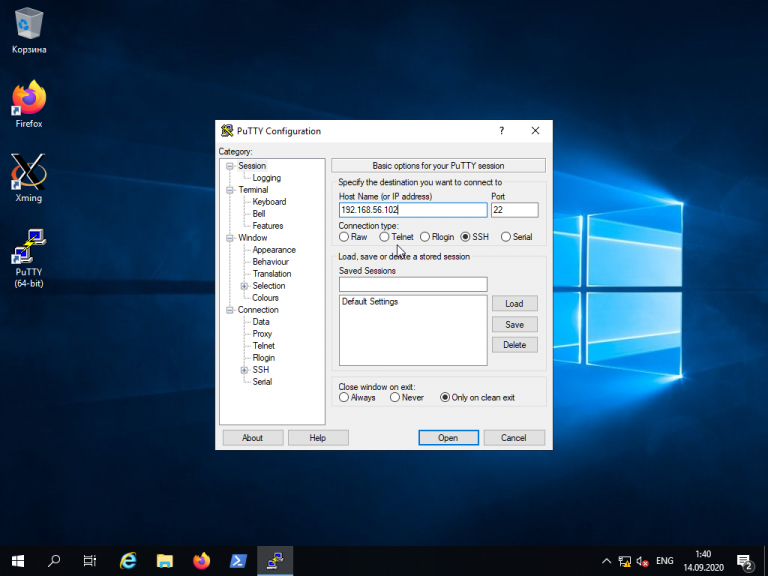
Для обычного подключения к Linux-серверу по протоколу SSH достаточно в поле Host Name (or IP—address) указать его IP-адрес и нажать кнопку Open (в данном примере Linux-сервер имеет IP-адрес: 192.168.56.102):
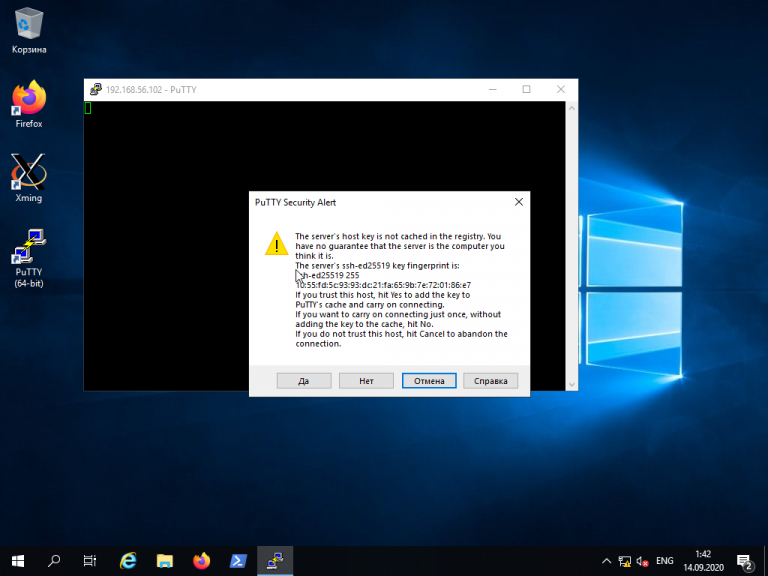
При первом подключении Putty предупредит, что используется специальный ключ безопасности и его нужно добавить в доверенные хосты. Нажмите кнопку Да:
Далее нужно будет ввести логин и пароль. Если всё сделано правильно, запустится удалённая сессия терминала Linux:
Мало кто знает, что Putty позволяет запустить почти любое приложение, установленное на компьютере с Linux, по сети в Windows. Для этого на компьютере с Windows нужно установить собственный X-сервер. В данном примере воспользуемся Xming.
Скачайте Xming с официального сайта. Установка довольно тривиальная, поэтому не будем на ней останавливаться. Ничего не меняйте в процессе установки. Просто нажимайте кнопку Next до тех пор, пока программа не установится и не запустится:
Когда установка Xming завершится, откройте Putty и в настройках сессии для вашего подключения в разделе SSH -> X11 включите флажок напротив опции Enable X11 forwarding, а также, в строке Отображение дисплея X впишите значение localhost:0, после чего откройте сессию подключения с помощью кнопки Open:
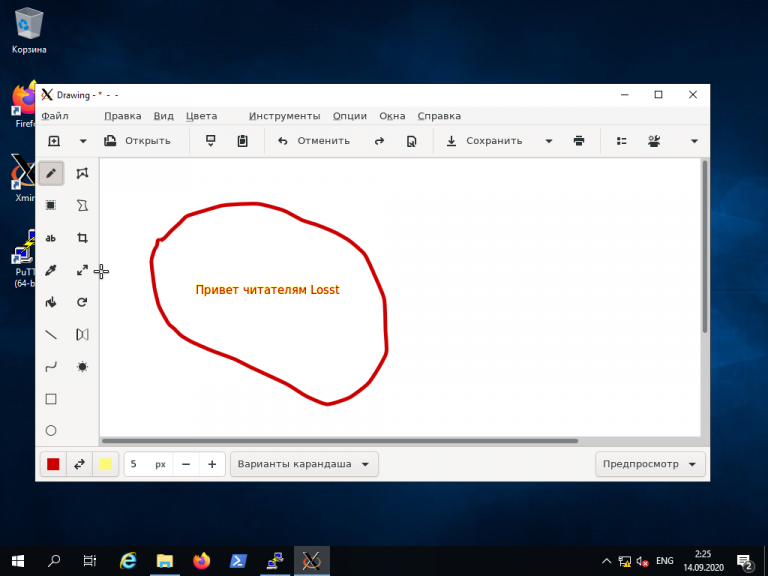
В открывшемся терминале Putty введите консольное название программы, обладающей графическим интерфейсом. В данном примере введено название графического редактора drawing:
(Знак & позволит запустить программу в фоновом режиме, в этом случае в окне Putty можно будет выполнять и другие команды):
Как видите, Linux-приложение drawing успешно запустилось по сети на X-сервере, установленном в Windows. С ним можно работать так же, как и с локальным приложением.
Выводы
Сегодня не существует слишком уж больших проблем для подключения к Linux из Windows. Способов существует довольно много. Каждый из них обладает своими достоинствами и недостатками, например, скорость работы VNC, да и других тоже, существенно зависит от скорости сетевого соединения. Существуют также программные средства, позволяющие подключаться к Linux-серверам используя мессенджеры или браузеры.
Источник
How to Access Shares on Windows 11 from Ubuntu
This post shows students and new users how to connect to shares on Windows 11 from Ubuntu desktop.
By default when you open Ubuntu file manager, it should find network shares that are automatically advertise across the local network. Similar to Windows systems, Ubuntu uses SMB protocol to connect to Windows shares that are advertised and shared.
Remote users can connect over the network and access shared files and folders as if they were directly connected to the local machines. This is a convenient way to make files and folders available to other people on your local network.
When shares are advertised Ubuntu and other desktop computers should be able to view and connect to the shared resources. However, if the shares are not advertised, users on the same network will have to manually connect to the shares by typing the resource network address. The steps below will show you how to do that.
Ubuntu and Windows 11 should work seamlessly when it comes to file sharing since both will still use SMB protocol. The new Windows 11, which will probably be generally available later this year, will come with many new features and enhancements that may confuse some students and new users right away. Some things and settings have changed so much that folks will have to learn new ways of using Windows.
Despite all these new changes in Windows 11, filesharing between Windows and Ubuntu should still work.
Enable Network Discovery in Windows 11
As we mentions above, shares must be advertised in order for other devices to view or access. In Windows, Network Discovery needs to be turned for advertising of shares to be viewed from other devices.
If your Windows devices are not able to see or discovery each other on your private network, it might likely be that Network Discovery is disabled.
To enable Network Discovery, continue below.
Windows 11 has a centralized location for majority of its settings. From system configurations to creating new users and updating Windows, all can be done from its System Settings pane.
To get to System Settings, you can use the Windows key + i shortcut or click on Start ==> Settings as shown in the image below:
Alternatively, you can use the search box on the taskbar and search for Settings. Then select to open it.
Windows Settings pane should look similar to the image below. In Windows Settings, click Network & internet , then select Ethernet on the right pane of your screen shown in the image below.
In Ethernet settings pane, under Network profile type, choose Private. This profile will allow devices in your network to be discovered. This profile should also be selected if you need file sharing or use apps that communicate over this network.
The private profile is suitable for home, work places and network that are trusted.
If you have other networks like Wi-Fi (if you’re connected to a wireless network) or Ethernet (if you’re connected to a network using a network cable), you can also set the profile type to be Private.
When you’re done, exit and network discovery should be enabled.
Turn on Public Folder Sharing in Windows 11
Use the steps below to setup file sharing.
Windows 11 has a centralized location for majority of its settings. From system configurations to creating new users and updating Windows, all can be done from its System Settings pane.
However, change account username is still done in the old Control Panel. To get to Control Panel, you can click on Start and start typing Control Panel as shown in the image below:
In the Control Panel, select Network and Internet as highlighted in the image below.
On the next pane, select Network and Sharing Center as highlighted below.
Next, select Change advanced sharing settings as highlighted below.
In the Advanced sharing center, select the Private (current profile) and Turn on file and printer sharing.
Save your changes and exit.
On the same Advance sharing options page, scroll down All networks.
There you should see settings for Public folder sharing, Media streaming, File sharing connections and Password protected sharing. Windows should automatically turn on file and printer sharing in private networks. However, in some instances, this will not be enabled.
If you can not automatically find printers and shared resources in your private network, then File sharing option may be disabled.
If you enable password protected sharing, only people who have accounts on the local computer or in domain environment will be able to access shared files and printers.
Make your changes and save, then exit.
The settings above can easily be done using the commands below when run as administrator.
You must open the command prompt as administrator to run the commands above.
Access shares on Windows 11 from Ubuntu
Now that Network Discovery and file sharing is enabled, you can now connect to Ubuntu and view shares on Windows devices.
To browse Windows files over the network, open File Manager application from the Activities overview (top left corner) or click File Manager on the dock and click Other Locations in the sidebar.
If Network Discovery is enabled and file sharing enable, you should see shared file and folders in the Windows Network folder above.
If not, run the commands below to install Samba.
In the file manager, click Other Locations in the sidebar. In Connect to Server, enter the address of the server, in the form of a URL. Details on supported URLs are listed below If you have connected to the server before, you can select it from the Recent Servers list.
Then click the Connect button when you’re ready to connect.
Another format with multiple shared folders:
Windows computers use a proprietary protocol to share files over a local area network. Computers on a Windows network are sometimes grouped into domains for organization and to better control access. If you have the right permissions on the remote computer, you can connect to a Windows share from the file manager.
You should see Windows shares if you have access to them.
If accessing the shares and you’re prompted for login name and password, type in the Windows account login info. This account must have access to view the shared content.
How to access Ubuntu files from Windows
On the Ubuntu machine, we’ll want to create a folder to share with Windows systems. Run the commands below to create a folder called samba in the system root directory.
After that, set the group ownership to sambashare and permission to allow member of the group to access the folder.
After changing the folder permission to allow sharing, run the commands below to add your Ubuntu account to allow access via Samba.
Replace yourusername with your Ubuntu account.
Next, set Samba password and enable your Ubuntu account to access Samba shares.
Next, add your user account to sambashare group.
After that, open Samba configuration file by running the commands below.
Then add these lines at the bottom of the file and save.
After saving the file, restart Samba by running the commands below.
At this point you should be able to access the /samba folder on Ubuntu system using your account. When prompted, type in your Ubuntu username and password.
That should do it!
Conclusion:
This post showed you how to enable Windows Network Discovery and enable file sharing to access shared content from Ubuntu. If you find any error above, please use the comment form below to report.
Источник