- miglen / linux-networking-tools.md
- Top 10 Ubuntu Network Tools
- Top 10 Ubuntu Network Tools
- 1. Iftop
- 2. Vnstat
- 3. Iptraf
- 4. Hping3
- 5. Dstat
- 6. Icinga
- 7. slurm
- 8. bmon
- 9. Nmap
- 10. Tcpdump
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Shubham Aggarwal
- [в закладки] Шпаргалка системного администратора по сетевым инструментам Linux
- ▍Примеры
- Traceroute
- ▍Пример
- Telnet
- ▍Пример
- Netstat
- ▍Примеры
- Nmcli
- ▍Примеры
- Маршрутизация
- ▍Примеры
- Tcpdump и Wireshark
- ▍Примеры
- Iptables
- ▍Примеры
- Nslookup
- ▍Примеры
- Поиск неполадок
- ▍Примеры
- Итоги
miglen / linux-networking-tools.md
List of Linux networking tools
Displays contents of /proc/net files. It works with the Linux Network Subsystem, it will tell you what the status of ports are ie. open, closed, waiting, masquerade connections. It will also display various other things. It has many different options. Netstat (Network Statistic) command display connection info, routing table information etc. To displays routing table information use option as -r.
This is a sniffer, a program that captures packets off a network interface and interprets them for you. It understands all basic internet protocols, and can be used to save entire packets for later inspection.
The ping command (named after the sound of an active sonar system) sends echo requests to the host you specify on the command line, and lists the responses received their round trip time. PING (Packet INternet Groper) command is the best way to test connectivity between two nodes. Whether it is Local Area Network (LAN) or Wide Area Network (WAN). Ping use ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to communicate to other devices. You can ping host name of ip address using below command.
traceroute will show the route of a packet. It attempts to list the series of hosts through which your packets travel on their way to a given destination. Also have a look at xtraceroute (one of several graphical equivalents of this program). traceroute is a network troubleshooting utility which shows number of hops taken to reach destination also determine packets traveling path. Below we are tracing route to global DNS server IP Address and able to reach destination also shows path of that packet is traveling.
tracepath performs a very simlar function to traceroute the main difference is that tracepath doesn’t take complicated options.
“ network exploration tool and security scanner”. nmap is a very advanced network tool used to query machines (local or remote) as to whether they are up and what ports are open on these machines.
Dig (domain information groper) query DNS related information like A Record, CNAME, MX Record etc. This command mainly use to troubleshoot DNS related query.
nslookup command also use to find out DNS related query. The following examples shows A Record (IP Address) of tecmint.com.
host command to find name to IP or IP to name in IPv4 or IPv6 and also query DNS records.
hostname is to identify in a network. Execute hostname command to see the hostname of your box. You can set hostname permanently in /etc/sysconfig/network. Need to reboot box once set a proper hostname.
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is useful to view / add the contents of the kernel’s ARP tables. To see default table use the command as.
This command is used to configure network interfaces, or to display their current configuration. In addition to activating and deactivating interfaces with the “up” and “down” settings, this command is necessary for setting an interface’s address information if you don’t have the ifcfg script.
- ifup — Use ifup device-name to bring an interface up by following a script (which will contain your default networking settings). Simply type ifup and you will get help on using the script.
- ifdown — Use ifdown device-name to bring an interface down using a script (which will contain your default network settings). Simply type ifdown and you will get help on using the script.
- ifcfg — Use ifcfg to configure a particular interface. Simply type ifcfg to get help on using this script.
The route command is the tool used to display or modify the routing table. To add a gateway as the default you would type:
iwconfig command in Linux is use to configure a wireless network interface. You can see and set the basic Wi-Fi details like SSID channel and encryption. You can refer man page of iwconfig to know more.
Show / manipulate routing, devices, policy routing and tunnels.
- List interfaces with detailed info:
- List interfaces with brief network layer info:
ip -brief address
- List interfaces with brief link layer info:
- Display the routing table:
- Make an interface up/down:
ip link set <
- Add/Delete an ip address to an interface:
ip route add default via <
Источник
Top 10 Ubuntu Network Tools
Top 10 Ubuntu Network Tools
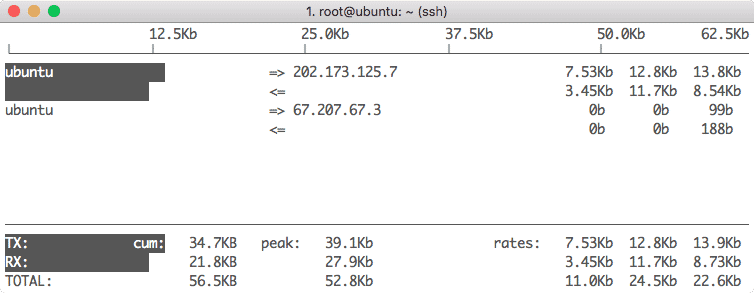
1. Iftop
This is one of the easiest tools to use for network usage and DNS operations. When it is started on Ubuntu, we get a simple screen like:
Iftop Home screen
We can press “h” and we will be shown help screen for more features:
Help screen for iftop
It is very similar to top utility but specialises in network monitoring and knowing which process is using the network at what IP and what bandwidth are they consuming.
2. Vnstat
Vnstat is another network monitoring utility which is usually included in most of the Linux distributions or can be installed very easily. Like the last utility, it allows us to control the network packets sent and received in a given interval of time which is chosen by the user itself. With vnstat help screen, we can see the following features:
$ vnstat —help
vnStat 1.18 by Teemu Toivola
-q, —query query database
-h, —hours show hours
-d, —days show days
-m, —months show months
-w, —weeks show weeks
-t, —top10 show top10
-s, —short use short output
-u, —update update database
-i, —iface select interface ( default: eth0 )
-?, —help short help
-v, —version show version
-tr, —traffic calculate traffic
-ru, —rateunit swap configured rate unit
-l, —live show transfer rate in real time
See also «—longhelp» for complete options list and «man vnstat» .
As it doesn’t have a fancy GUI, we are showing the console output here:
$ vnstat
Database updated: Mon Sep 10 09: 52 :01 2018
eth1 since 11 / 20 / 08
rx: 3.32 TiB tx: 2.81 TiB total: 6.13 TiB
monthly
rx | tx | total | avg. rate
————————+————-+————-+—————
Aug ’18 609.40 GiB | 282.21 GiB | 891.61 GiB | 2.79 Mbit/s
Sep ‘ 18 16.95 GiB | 10.46 GiB | 27.40 GiB | 2.80 Mbit / s
————————+————-+————-+—————
estimated 552.14 GiB | 340.70 GiB | 892.83 GiB |
daily
rx | tx | total | avg. rate
————————+————-+————-+—————
yesterday 19.19 GiB | 8.63 GiB | 27.82 GiB | 2.70 Mbit / s
today 16.95 GiB | 10.46 GiB | 27.40 GiB | 2.80 Mbit / s
————————+————-+————-+—————
estimated 17.81 GiB | 10.99 GiB | 28.80 GiB |
Clearly, it also provides an estimate of the data which will be used at a same rate for the month.
3. Iptraf
Iptraf is another great console-based network monitoring tool for Ubuntu or Linux in general which collects a huge amount of data in terms of IPs which passes through the network with a deep dive in detail like their ICMP flags, TCP faults and byte count. Even a basic interface for the same will look like:
Apart from the packet tracking byte count, we have many more features like:
Ubuntu iptraf features
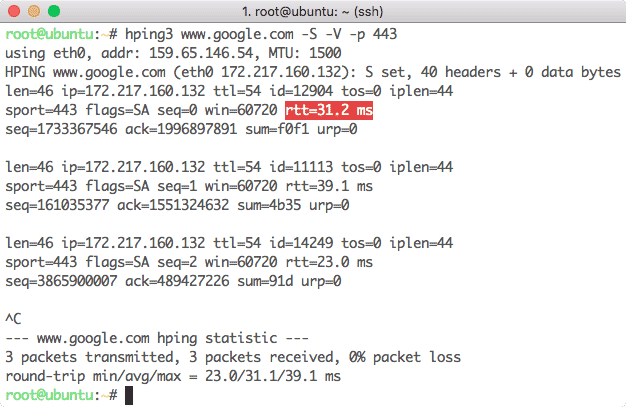
4. Hping3
Hping3 is a command line utility which is similar to Ping command with a small addition that it can use TCP, UDP, and RAW-IP as transport protocols. The main feature is that it doesn’t only check if a Port or an IP is open but it also measures the round trip time the packet took to come back. For instance, if we need to check if www.google.com has an open port 443 and calculate the round-trip time, we can use the following command:
Here is what we get back with this command:
Hping3 round trip
5. Dstat
Dstat is comparatively a less known network monitoring tool in Linux family. Dstat allows us to display all of our system resources in near real-time, we can eg. compare disk utilization in combination with interrupts from our IDE controller, or compare the network bandwidth numbers directly with the disk throughput (in the same interval).
Find more information here for this tool.
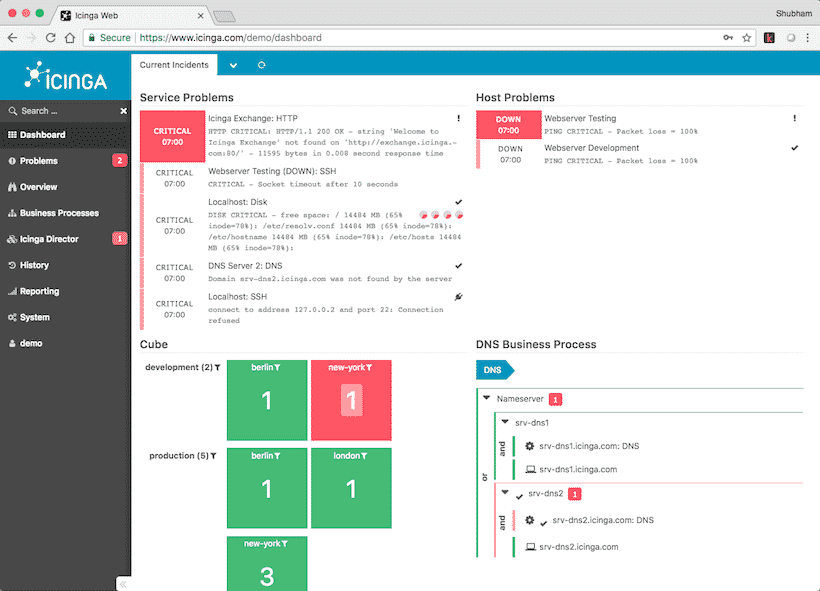
6. Icinga
Icinga is an enterprise-grade tool for network monitoring which also takes care of any suspicious activity on the server and informs configured users like admin about such activities. It has a very nice interactive dashboard which looks like:
It is even possible to try a demo dashboard for this tool. Visit this page for more information.
7. slurm
slurm is a smart and simple network load monitoring tool. It has the following features:
- It provides real-time traffic statistics
- It has three graph modes: combined RX and TX and two split views
- It can monitor any network device
- It curses ASCII graphics
- It has an ASCII theme support
It is an open-source networking tool (look here for the source code). It has a basic interface like:
8. bmon
bmon, which stands for Bandwidth Monitor, is another network monitoring tool with a speciality that it can monitor multiple interface traffic. It also provides information about packets, errors and much more data critical for monitoring. Once installed, here is the list of features it provides for monitoring:
When we start it with a network interface, we will see a simple interface like:
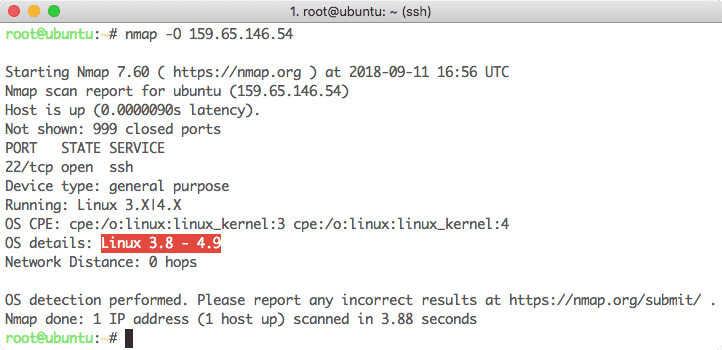
9. Nmap
Nmap is one of the most popular network scanners for common use. The information it can provide includes (but not limited to):
- It can tell what’s running on a given network hosts
- Scan and identify open TCP Ports
- Which OS is running on given IP
- Ping sweeps on an IP subnet
We can -O option for OS detection. Let’s look at an example command we used:
10. Tcpdump
Tcpdump is an excellent tool which goes beyond its scope to provide features like sniffing as well. It can analyze data which is going out of the host and also the data which is arriving on the host. It is possible to intercept the traffic between two hosts with this tool as well (of course you need to have access to those hosts). We first try a command to see what data is going out of our host:
Next, we can also try to sniff traffic going out of a particular port:
Conclusion
In this lesson, we looked at some most popular networking tools in the Ubuntu ecosystem. Even though we might have missed some good tools, please mention them to my Twitter handle which you think should have made the cut @sbmaggarwal or @linuxhint.
About the author
Shubham Aggarwal
I’m a Java EE Engineer with about 4 years of experience in building quality products. I have excellent problem-solving skills in Spring Boot, Hibernate ORM, AWS, Git, Python and I am an emerging Data Scientist.
Источник
[в закладки] Шпаргалка системного администратора по сетевым инструментам Linux
В повседневные задачи системных администраторов входит работа с сетями и с подключённым к ним оборудованием. Нередко роль рабочего места администратора играет компьютер, на котором установлен какой-нибудь дистрибутив Linux. Утилиты и команды Linux, о которых пойдёт речь в материале, перевод которого мы публикуем сегодня, включают в себя список инструментов различной сложности — от простых, до продвинутых, которые предназначены для решения широкого спектра задач по управлению сетями и по диагностике сетевых неполадок.
В некоторых из рассматриваемых здесь примеров вы столкнётесь с сокращением (fully qualified domain name, полное доменное имя). Встретив его, замените его, в зависимости от обстоятельств, на адрес интересующего вас сайта или сервера, например, на нечто вроде server-name.company.com .
Утилита ping , как можно судить по её названию, используется для проверки связи между узлами сети, между компьютером, на котором её запускают, и другой системой. Эта утилита использует протокол ICMP, отправляя эхо-запросы, на которые отвечает удалённая система, получающая их. Использование ping , кроме того — это хороший способ проверки связности сети, проводимой в качестве первого шага диагностики сети при наличии неполадок. Команду ping можно использовать с адресами IPv4 и IPv6. Тут можно почитать подробности об IP-адресах и о работе с ними.
▍Примеры
Ping, кроме того, можно использовать для выяснения IP-адресов сайтов на основе их имён. Вот как это выглядит.

Использование ping для выяснения IP-адреса сайта по его имени
Traceroute
Traceroute — это приятная утилита, которая позволяет исследовать маршруты передачи данных между компьютерами. В то время как команда ping направлена на то, чтобы выяснить, можно ли установить связь между двумя узлами сети, traceroute даёт сведения об IP-адресах маршрутизаторов, через которые проходят данные от вашей системы до конечной, например — до веб-сайта или сервера. Команда traceroute обычно применяется на втором шаге диагностики сети, после команды ping .
▍Пример
Telnet
Утилита telnet позволяет связаться с удалённым компьютером по протоколу Telnet и взаимодействовать с ним, используя соответствующие команды.
▍Пример
Для организации сеанса Telnet-связи с другим компьютером используется следующая команда:
Netstat
Эта команда позволяет собирать сведения о сети и используется в ходе поиска и исправления сетевых неполадок, применяется для проверки данных о работе интерфейсов и портов, для исследования таблиц маршрутизации, для изучения информации о работе протоколов. Эта команда непременно должна присутствовать в арсенале системного администратора.
▍Примеры
Для того чтобы получить список всех портов, находящихся в режиме прослушивания, воспользуйтесь такой командой:
Следующая команда выводит сведения обо всех портах. Для того чтобы ограничиться только TCP-портами, нужно воспользоваться ключом -at , для того, чтобы получить данные об UDP-портах, используйте ключ -au .
Для просмотра таблиц маршрутизации воспользуйтесь такой командой:
Вот как выглядит результат выполнения этой команды.

Сведения о таблице маршрутизации
Вот вариант этой команды, выводящий статистику по протоколам:

Статистика по протоколам
Следующий вариант вызова netstat позволяет узнать сведения об отправленных и полученных пакетах (transmission/receive, TX/RX) по каждому интерфейсу:

Данные об отправленных и полученных пакетах
Nmcli
Утилита nmcli отлично подходит для управления сетевыми соединениями, для выполнения настроек и для решения других подобных задач. С её помощью можно управлять программой NetworkManager и модифицировать сетевые параметры различных устройств.
▍Примеры
Вот как с помощью nmcli вывести список сетевых интерфейсов:
Так можно вывести информацию по конкретному интерфейсу:
Следующий вариант вызова команды позволяет проверить подключение устройства к сети:

Примеры использования nmcli
Эта команда позволяет отключить заданный интерфейс:
А эта позволяет включить интерфейс:
Вот пример команды, которая добавляет VLAN-интерфейс с заданным VLAN-номером, IP-адресом и шлюзом к указанному интерфейсу:
Маршрутизация
Существует множество команд, которые можно использовать для проверки правил маршрутизации и их настройки. Рассмотрим самые полезные из них.
▍Примеры
Следующая команда показывает все текущие маршруты, настроенные для соответствующих интерфейсов:

Маршруты, настроенные для интерфейсов
Эта команда позволяет добавить в таблицу маршрутизации шлюз, используемый по умолчанию:
Следующая команда добавляет в таблицу маршрутизации новый сетевой маршрут. Существует и множество других её параметров, позволяющих выполнять такие операции, как добавление маршрута и шлюза, используемых по умолчанию, и так далее.
С помощью такой команды можно удалить запись о заданном маршруте из таблицы маршрутизации:
Вот примеры использования команды route .

Использование команды route
Вот команда, которая применяется для вывода текущей таблицы соседей. Кроме того, её можно использовать для добавления, изменения или удаления сведений о соседях:
Взглянем на примеры её использования.

Данные, полученные с помощью команды ip neighbor
Вот сведения о команде ip neigh

Сведения о команде ip neigh
Команда arp (ARP — это сокращение от Address Resolution Protocol, протокол определения адреса) похожа на ip neighbor . Утилита arp выводит данные о соответствии IP-адресов MAC -адресам. Вот как её использовать:
Вот пример её вызова.

Вызов команды arp
Tcpdump и Wireshark
Linux даёт в распоряжение администратора множество инструментов для захвата и анализа пакетов. Среди них, например, tcpdump , wireshark , tshark , и другие. Они используются для захвата сетевого трафика в передаваемых системой пакетах или в пакетах, получаемых ей. Это делает их весьма ценным инструментом администратора, помогающим в деле выяснения причин различных сетевых неполадок. Тем, кто предпочитает командную строку всем остальным способам общения с компьютерами, понравится tcpdump . Тем же, кто любит графические интерфейсы, можно порекомендовать wireshark — отличный инструмент для захвата и анализа пакетов. Утилита tcpdump — это встроенное в Linux средство для захвата сетевого трафика. Его можно использовать для захвата и вывода трафика с фильтрацией по портам, протоколам, и по другим признакам.
▍Примеры
Такая команда показывает, в режиме реального времени, пакеты с заданного интерфейса:
Пакеты можно сохранять в файл, воспользовавшись флагом -w и задав имя файла:
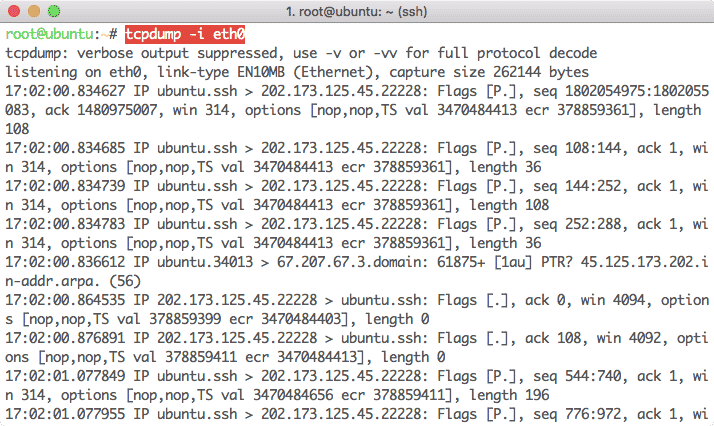
Вот пример использования tcpdump .

Использование tcpdump
Следующий вариант команды используется для захвата пакетов, приходящих с заданного IP системы-источника:
Так можно захватить пакеты, идущие на заданный адрес системы-приёмника:
Вот пример использования tcpdump для захвата пакетов для заданного номера порта, например, это может быть порт 53, 80, 8080, и так далее:
Здесь показано, как с помощью tcpdump захватывать пакеты заданного протокола, вроде TCP, UDP или других:
Iptables
Утилита iptables похожа на файрвол, она поддерживает фильтрацию пакетов, что позволяет управлять трафиком, пропуская или блокируя его. Диапазон возможностей этой утилиты огромен. Рассмотрим несколько наиболее распространённых вариантов её использования.
▍Примеры
Следующая команда позволяет вывести все существующие правила iptables :
Эта команда удаляет все существующие правила:
Следующие команды разрешают прохождение трафика с заданного номера порта к заданному интерфейсу:
Следующие команды разрешают loopback-доступ к системе:
Nslookup
Инструмент nslookup используется для получения сведений о назначении IP-адресов сетевым ресурсам. Его можно использовать и для получения сведений с DNS-серверов, например таких, как все DNS-записи для некоего веб-сайта (ниже мы рассмотрим соответствующий пример). На nslookup похожа утилита dig (Domain Information Groper).
▍Примеры
Следующая команда выводит IP-адреса вашего DNS-сервера в поле Server, и, ниже, выдаёт IP-адрес искомого сайта:
Такая команда показывает все доступные записи для заданного веб-сайта или домена:
Поиск неполадок
Вот набор команд и список важных файлов, используемых для идентификации сетевых неполадок.
▍Примеры
Итоги
В этой небольшой шпаргалке мы рассказали о сетевых инструментах Linux, предназначенных для системных администраторов. Надеемся, вам эти инструменты пригодятся.
Уважаемые читатели! Чем вы пользуетесь для администрирования сетей и для выяснения причин сетевых неполадок?
Источник