- How to Setup NFS (Network File System) on RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Debian/Ubuntu
- Setup and Configure NFS Mounts on Linux Server
- Setting Up the NFS Server
- Setting Up the NFS Client
- Test the Working of NFS Setup
- Removing the NFS Mount
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- Настройка NFS в Ubuntu
- Немного теории
- Установка компонентов NFS
- Настройка сервера NFS в Ubuntu
- Подключение NFS
- Выводы
How to Setup NFS (Network File System) on RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Debian/Ubuntu
NFS (Network File System) is basically developed for sharing of files and folders between Linux/Unix systems by Sun Microsystems in 1980. It allows you to mount your local file systems over a network and remote hosts to interact with them as they are mounted locally on the same system. With the help of NFS, we can set up file sharing between Unix to Linux system and Linux to Unix system.

Benefits of NFS
- NFS allows local access to remote files.
- It uses standard client/server architecture for file sharing between all *nix based machines.
- With NFS it is not necessary that both machines run on the same OS.
- With the help of NFS we can configure centralized storage solutions.
- Users get their data irrespective of physical location.
- No manual refresh needed for new files.
- Newer version of NFS also supports acl, pseudo root mounts.
- Can be secured with Firewalls and Kerberos.
NFS Services
Its a System V-launched service. The NFS server package includes three facilities, included in the portmap and nfs-utils packages.
- portmap : It maps calls made from other machines to the correct RPC service (not required with NFSv4).
- nfs: It translates remote file sharing requests into requests on the local file system.
- rpc.mountd: This service is responsible for mounting and unmounting of file systems.
Important Files for NFS Configuration
- /etc/exports : Its a main configuration file of NFS, all exported files and directories are defined in this file at the NFS Server end.
- /etc/fstab : To mount a NFS directory on your system across the reboots, we need to make an entry in /etc/fstab.
- /etc/sysconfig/nfs : Configuration file of NFS to control on which port rpc and other services are listening.
Setup and Configure NFS Mounts on Linux Server
To setup NFS mounts, we’ll be needing at least two Linux/Unix machines. Here in this tutorial, I’ll be using two servers.
- NFS Server: nfsserver.example.com with IP-192.168.0.100
- NFS Client : nfsclient.example.com with IP-192.168.0.101
Installing NFS Server and NFS Client
We need to install NFS packages on our NFS Server as well as on NFS Client machine. We can install it via “yum” (Red Hat Linux) and “apt-get” (Debian and Ubuntu) package installers.
Now start the services on both machines.
After installing packages and starting services on both the machines, we need to configure both the machines for file sharing.
Setting Up the NFS Server
First we will be configuring the NFS server.
Configure Export directory
For sharing a directory with NFS, we need to make an entry in “/etc/exports” configuration file. Here I’ll be creating a new directory named “nfsshare” in “/” partition to share with client server, you can also share an already existing directory with NFS.
Now we need to make an entry in “/etc/exports” and restart the services to make our directory shareable in the network.
In the above example, there is a directory in / partition named “nfsshare” is being shared with client IP “192.168.0.101” with read and write (rw) privilege, you can also use hostname of the client in the place of IP in above example.
NFS Options
Some other options we can use in “/etc/exports” file for file sharing is as follows.
- ro: With the help of this option we can provide read only access to the shared files i.e client will only be able to read.
- rw: This option allows the client server to both read and write access within the shared directory.
- sync: Sync confirms requests to the shared directory only once the changes have been committed.
- no_subtree_check: This option prevents the subtree checking. When a shared directory is the subdirectory of a larger file system, nfs performs scans of every directory above it, in order to verify its permissions and details. Disabling the subtree check may increase the reliability of NFS, but reduce security.
- no_root_squash: This phrase allows root to connect to the designated directory.
For more options with “/etc/exports“, you are recommended to read the man pages for export.
Setting Up the NFS Client
After configuring the NFS server, we need to mount that shared directory or partition in the client server.
Mount Shared Directories on NFS Client
Now at the NFS client end, we need to mount that directory in our server to access it locally. To do so, first we need to find out that shares available on the remote server or NFS Server.
Above command shows that a directory named “nfsshare” is available at “192.168.0.100” to share with your server.
Mount Shared NFS Directory
To mount that shared NFS directory we can use following mount command.
The above command will mount that shared directory in “/mnt/nfsshare” on the client server. You can verify it following command.
The above mount command mounted the nfs shared directory on to nfs client temporarily, to mount an NFS directory permanently on your system across the reboots, we need to make an entry in “/etc/fstab“.
Add the following new line as shown below.
Test the Working of NFS Setup
We can test our NFS server setup by creating a test file on the server end and check its availability at nfs client side or vice-versa.
At the nfsserver end
I have created a new text file named “nfstest.txt’ in that shared directory.
At the nfsclient end
Go to that shared directory in client server and you’ll find that shared file without any manual refresh or service restart.
Removing the NFS Mount
If you want to unmount that shared directory from your server after you are done with the file sharing, you can simply unmount that particular directory with “umount” command. See this example below.
You can see that the mounts were removed by then looking at the filesystem again.
You’ll see that those shared directories are not available any more.
Important commands for NFS
Some more important commands for NFS.
- showmount -e : Shows the available shares on your local machine
- showmount -e: Lists the available shares at the remote server
- showmount -d : Lists all the sub directories
- exportfs -v : Displays a list of shares files and options on a server
- exportfs -a : Exports all shares listed in /etc/exports, or given name
- exportfs -u : Unexports all shares listed in /etc/exports, or given name
- exportfs -r : Refresh the server’s list after modifying /etc/exports
This is it with NFS mounts for now, this was just a start, I’ll come up with more option and features of NFS in our future articles. Till then, Stay connected with Tecmint.com for more exciting and interesting tutorials in future. Do leave your comments and suggestions below in the comment box.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
Настройка NFS в Ubuntu
Сетевая файловая система NFS или Network File System, это популярный протокол сетевой файловой системы, который позволяет пользователям подключать удаленные сетевые каталоги на своей машине и передавать файлы между серверами. Вы можете использовать дисковое пространство на другой машине для своих файлов и работать с файлами, расположенными на других серверах. По сути, это альтернатива общего доступа Windows для Linux, в отличие от Samba реализована на уровне ядра и работает более стабильно.
В этой статье будет рассмотрена установка NFS в Ubuntu. Мы разберем установку всех необходимых компонентов, настройку общей папки, а также подключение сетевых папок.
Немного теории
Как уже было сказано, NFS, это сетевая файловая система. Для работы необходим сервер, на котором будет размещена общая папка и клиенты, которые могут монтировать сетевую папку как обычный диск в системе. В отличие от других протоколов NFS предоставляет прозрачный доступ к удаленным файлам. Программы будут видеть файлы как в обычной файловой системе и работать с ними как с локальными файлами, nfs возвращает только запрашиваемую часть файла, вместо файла целиком, поэтому эта файловая система будет отлично работать в системах с быстрым интернетом или в локальной сети.
Установка компонентов NFS
Перед тем как мы сможем работать с NFS, нам придется установить несколько программ. На машину, которая будет сервером нужно установить пакет nfs-kernel-server, с помощью которого будет выполнено открытие шары nfs в ubuntu 16.04. Для этого выполните:
sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server
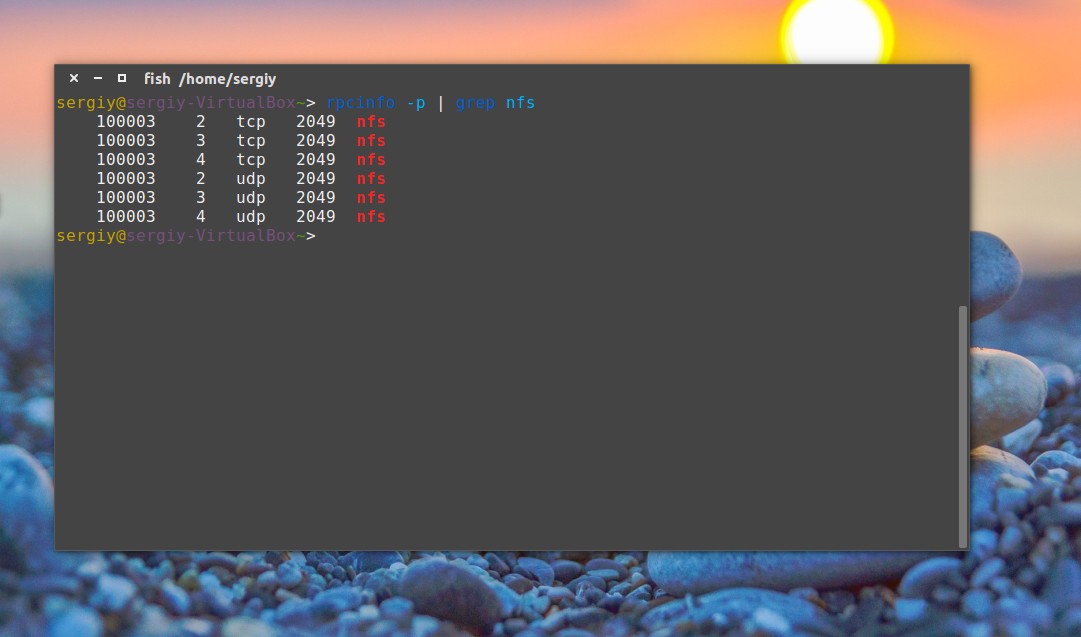
Теперь давайте проверим правильно ли установился сервер. Сервис NFS слушает соединения как для TCP, так и для UDP на порту 2049. Посмотреть действительно ли сейчас используются эти порты можно командой:
rpcinfo -p | grep nfs
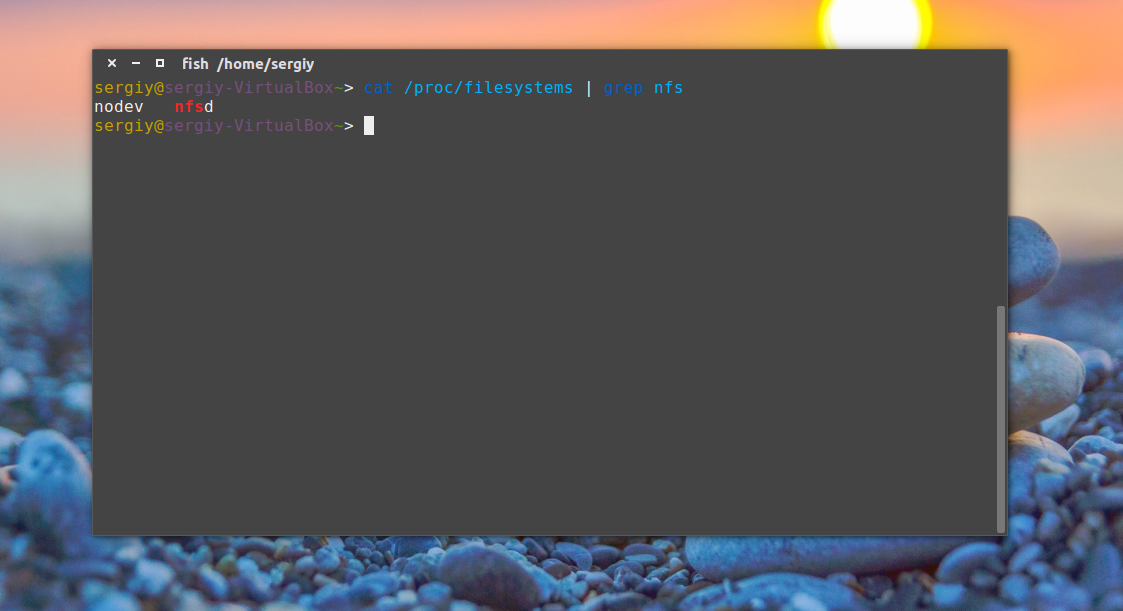
Также важно проверить поддерживается ли NFS на уровне ядра:
cat /proc/filesystems | grep nfs
Видим, что работает, но если нет, нужно вручную загрузить модуль ядра nfs:
Давайте еще добавим NFS в автозагрузку:
sudo systemctl enable nfs-server
На клиентском компьютере вам нужно установить пакет nfs-common, чтобы иметь возможность работать с этой файловой системой. Вам необязательно устанавливать компоненты сервера, достаточно будет только этого пакета:
sudo apt install nfs-common
Вот и все, дальше настройка NFS в Ubuntu.
Настройка сервера NFS в Ubuntu
Мы можем открыть NFS доступ к любой папке, но давайте создадим для этих целей новую:
sudo mkdir /var/nfs
Дальше нас интересует настройка ubuntu nfs server. Все общие папки и другие настройки nfs находятся в файле /etc/exports. Синтаксис записи папки такой:
адрес_папки клиент (опции)
Адрес папки — это та папка, которую нужно сделать доступной по сети. Клиент — ip адрес или адрес сети, из которой могут получить доступ к этой папке. А вот с опциями немного сложнее. Рассмотрим некоторые из них:
- rw — разрешить чтение и запись в этой папке;
- ro — разрешить только чтение;
- sync — отвечать на следующие запросы только тогда, когда данные будут сохранены на диск (по умолчанию);
- async — не блокировать подключения пока данные записываются на диск;
- secure — использовать для соединения только порты ниже 1024;
- insecure — использовать любые порты;
- nohide — не скрывать поддиректории при, открытии доступа к нескольким директориям;
- root_squash — подменять запросы от root на анонимные, используется по умолчанию;
- no_root_squash — не подменять запросы от root на анонимные;
- all_squash — превращать все запросы в анонимные;
- subtree_check — проверять не пытается ли пользователь выйти за пределы экспортированной папки;
- no_subtree_check — отключить проверку обращения к экспортированной папке, улучшает производительность, но снижает безопасность, можно использовать когда экспортируется раздел диска;
- anonuid и anongid — указывает uid и gid для анонимного пользователя.
Например, для нашей папки, если вы хотите разрешить к ней подключаться только с определённого IP адреса, эта строка может выглядеть вот так:
sudo vi /etc/exports
Можно разрешить только нужную подсеть, например:
Для того чтобы разрешить все адреса используйте подсеть 0.0.0.0/0 или символ *.
Открытие шары NFS в Ubuntu почти завершено. Осталось разобраться с правами. Кроме ограничений IP адреса работает обычная система полномочий UNIX, поэтому если вы хотите чтобы определённый пользователь мог получить доступ к папке, то на сервере должен существовать пользователь с таким же UID и эта папка должна принадлежать ему или группе в которой он состоит.
Кроме того, обратите внимание на то, что все подключения от имени пользователя root считаются по умолчанию анонимными (nfsnobody), чтобы это отключить добавьте опцию монтирования no_root_squash, но это не безопасно, потому что любой root пользователь сможет получить доступ на запись ко всем файлам. Теперь попытаемся настроем клиента и попытаемся ее примонтировать.
Для того чтобы все пользователи могли получить доступ ко всем файлам можно создать пользователя с UID 1001 и попросить NFS все запросы считать запросами от анонимного пользователя, а анонимному пользователю присвоить UID 1001. Это делается такими опциями:
Когда все будет настроено, останется только обновить таблицу экспорта NFS:
sudo exportfs -a
Если на вашем сервере используется брандмауэр, то следует открыть порты 111 и 2049:
sudo ufw allow 111
sudo ufw allow 2049
Подключение NFS
Мы не будем подробно останавливаться на этом вопросе в сегодняшней статье. Это довольно большая тема, заслуживающая отдельной статьи. Но пару слов я все же скажу. Чтобы подключить сетевую папку вам не нужен никакой nfs клиент ubuntu, достаточно использовать команду mount:
sudo mount 127.0.0.1:/var/nfs/ /mnt/
Теперь вы можете попытаться создать файл в подключенной директории:
Также мы посмотрите подключенные файловые системы с помощью df:
127.0.0.1:/var/nfs 30G 6,7G 22G 24% /mnt
Чтобы отключить эту файловую систему достаточно использовать стандартный umount:
sudo umount /mnt/
Выводы
В этой статье была рассмотрена настройка NFS в Ubuntu 20.04, как видите, все делается очень просто и прозрачно. Подключение NFS шары выполняется в несколько кликов, с помощью стандартных команд, а открытие шары NFS ненамного сложнее подключения. Если у вас остались вопросы, пишите в комментариях!
Источник