- Как установить Node.js и проверить его работу
- Установка Node.js
- Проверяем работу Node.js
- How to check whether a script is running under Node.js?
- 22 Answers 22
- Identify Node.js only
- Identify Node (>= 3.0.0) or io.js
- Identify Node (>= 0.10.0) or io.js
- Установка Node.js на Windows 7
- Решение
- Проверка работы Node.js и npm
- Настройка среды разработки Node.js напрямую в Windows Set up your Node.js development environment directly on Windows
- Установка nvm-windows, Node.js и npm Install nvm-windows, node.js, and npm
- Альтернативные диспетчеры версий Alternative version managers
- Установка предпочтительного редактора кода Install your favorite code editor
- Установка Git (необязательно) Install Git (optional)
Как установить Node.js и проверить его работу
Привет! В этой статье расскажу, как установить Node.js. Причем не важно, какая у вас система — Windows или macOS.
Node.js — это технология, программная платформа, позволяющая писать серверный код на языке JаvaScript. Она представляет из себя компилятор, построенный на движке V8, зашитый в Google Chrome.
V8 — это высокопроизводительный движок JavaScript и WebAssembly от Google с открытым исходным кодом, написанный на C ++.
Он используется в Chrome и Node.js и других; реализует ECMAScript и WebAssembly, работает в системах от Windows 7 и более новых, macOS 10.12+ и Linux, использующих процессоры x64, IA-32, ARM или MIPS.
V8 может работать автономно или может быть встроен в любое приложение C ++.
Установка Node.js
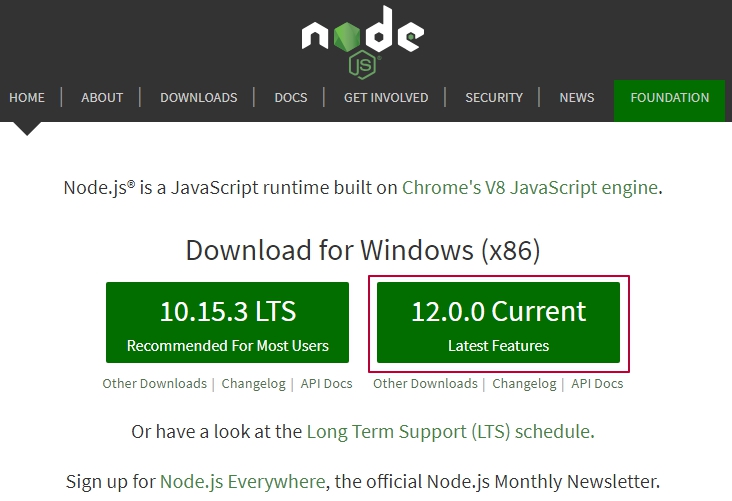
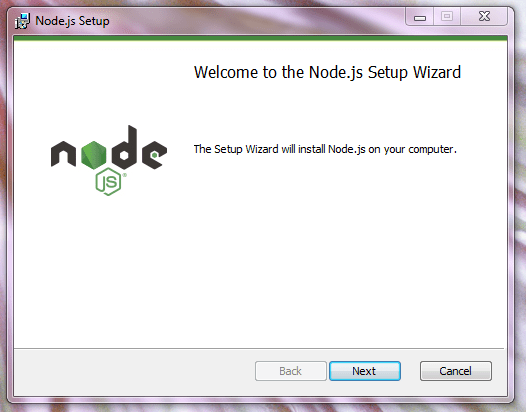
Ваша система определяется автоматически. Выбираем Current (текущую версию). Это обычный exe файл, который устанавливается как и любая другая программа.
2. Следуйте всем настройкам по умолчанию, нажимая Next для продолжения:
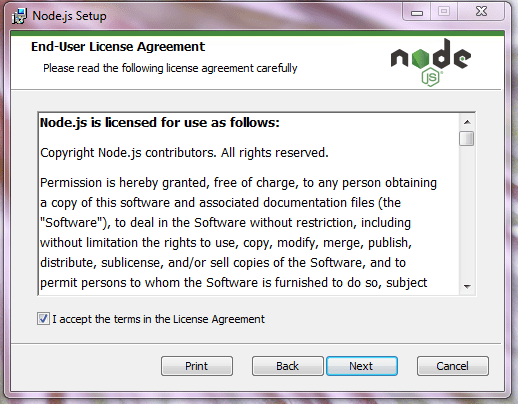
Принимаем условия использования, ставим галочку:
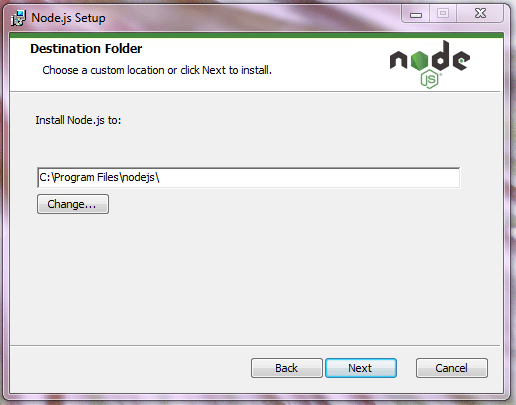
Папка назначения, куда будет установлен Node.js. По умолчанию, это Program Files на диске C:
Настройки по умолчанию. Модули, которые установятся, здесь важно наличие npm modules:
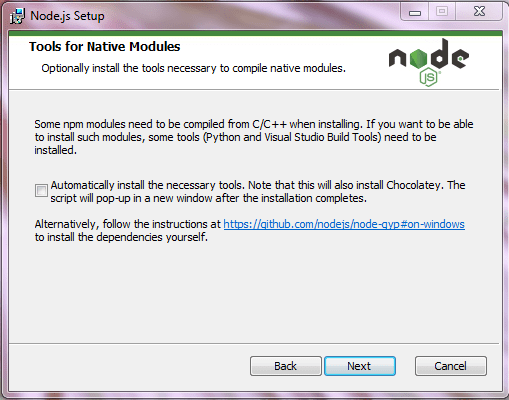
Предлагают установить дополнительные инструменты — здесь галочку не ставим:
Install — нажимаем для запуска инсталляции или Back, чтобы вернуться и изменить настройки:
После успешной установки нажимаем Finish:
Проверяем работу Node.js
1. На вашем виртуальном сервере, у меня это OpenServer/domains:
- Создаем папку node
- В папке node создаем файл index.js с содержимым:
2. Запускаем командную строку. Если не знаете, как её запустить, то перейдите Пуск -> Стандартные программы -> Выполнить
2.1. Напишите в этой строке: npm -v
-v — version — версия
Если видим версию (на скрине у меня 6.7.0), значит всё ОК!
2.2. Здесь же, в консоли, переходим к папке node: cd node и командой dir проверяем содержимое папки. Наблюдаем наличие нашего index.js
2.3. Делаем компиляцию командой: node index
node index это сокращенная команда — аналог записи node ./index.js (выше на скрине). Т.е. можно не указывать путь к файлу, Node.js по умолчанию сам ищет в корне индексный файл index.js.
2.4. И вот он, долгожданный результат: Hello, World!
Всё работает! Поздравляю! 🙂 Или нет? Пишите.
How to check whether a script is running under Node.js?
I have a script I am requiring from a Node.js script, which I want to keep JavaScript engine independent.
For example, I want to do exports.x = y; only if it’s running under Node.js. How can I perform this test?
When posting this question, I didn’t know the Node.js modules feature is based on CommonJS.
For the specific example I gave, a more accurate question would’ve been:
How can a script tell whether it has been required as a CommonJS module?
22 Answers 22
By looking for CommonJS support, this is how the Underscore.js library does it:
Edit: to your updated question:
Example here retains the Module pattern.
Well there’s no reliable way to detect running in Node.js since every website could easily declare the same variables, yet, since there’s no window object in Node.js by default you can go the other way around and check whether you’re running inside a Browser.
This is what I use for libs that should work both in a Browser and under Node.js:
It might still explode in case that window is defined in Node.js but there’s no good reason for someone do this, since you would explicitly need to leave out var or set the property on the global object.
EDIT
For detecting whether your script has been required as a CommonJS module, that’s again not easy. Only thing commonJS specifies is that A: The modules will be included via a call to the function require and B: The modules exports things via properties on the exports object. Now how that is implement is left to the underlying system. Node.js wraps the module’s content in an anonymous function:
But don’t try to detect that via some crazy arguments.callee.toString() stuff, instead just use my example code above which checks for the Browser. Node.js is a way cleaner environment so it’s unlikely that window will be declared there.
I currently stumbled over a wrong detection of Node which is not aware of the Node-environment in Electron due to a misleading feature-detection. The following solutions identify the process-environment explicitly.
Identify Node.js only
This will discover if you’re running in a Node-process, since process.release contains the «metadata related to the current [Node-]release».
After the spawn of io.js the value of process.release.name may also become io.js (see the process-doc). To proper detect a Node-ready environment i guess you should check as follows:
Identify Node (>= 3.0.0) or io.js
This statement was tested with Node 5.5.0, Electron 0.36.9 (with Node 5.1.1) and Chrome 48.0.2564.116.
Identify Node (>= 0.10.0) or io.js
@daluege’s comment inspired me to think about a more general proof. This should working from Node.js >= 0.10. I didn’t find a unique identifier for prior versions.
P.s.: I am posting that answer here since the question lead me here, although the OP was searching for an answer to a different question.
The problem with trying to figure out what environment your code is running in is that any object can be modified and declared making it close to impossible to figure out which objects are native to the environment, and which have been modified by the program.
However, there are a few tricks we can use to figure out for sure what environment you are in.
Lets start out with the generally accepted solution that’s used in the underscore library:
typeof module !== ‘undefined’ && module.exports
This technique is actually perfectly fine for the server side, as when the require function is called, it resets the this object to an empty object, and redefines module for you again, meaning you don’t have to worry about any outside tampering. As long as your code is loaded in with require , you are safe.
However, this falls apart on the browser, as anyone can easily define module to make it seem like it’s the object you are looking for. On one hand this might be the behavior you want, but it also dictates what variables the library user can use in the global scope. Maybe someone wants to use a variable with the name module that has exports inside of it for another use. It’s unlikely, but who are we to judge what variables someone else can use, just because another environment uses that variable name?
The trick however, is that if we are assuming that your script is being loaded in the global scope (which it will be if it’s loaded via a script tag) a variable cannot be reserved in an outer closure, because the browser does not allow that. Now remember in node, the this object is an empty object, yet, the module variable is still available. That is because it’s declared in an outer closure. So we can then fix underscore’s check by adding an extra check:
With this, if someone declares module in the global scope in the browser, it will be placed in the this object, which will cause the test to fail, because this.module , will be the same object as module. On node, this.module does not exist, and module exists within an outer closure, so the test will succeed, as they are not equivalent.
Thus, the final test is:
typeof module !== ‘undefined’ && this.module !== module
Note: While this now allows the module variable to be used freely in the global scope, it is still possible to bypass this on the browser by creating a new closure and declaring module within that, then loading the script within that closure. At that point the user is fully replicating the node environment and hopefully knows what they are doing and is trying to do a node style require. If the code is called in a script tag, it will still be safe from any new outer closures.
Установка Node.js на Windows 7
Привет! Рассмотрим установку Node.js на Windows 7 и протестируем его работу.
При попытке установить на Windows 7 последнюю версию v14.15.4 LTS [ссылка], возникает ошибка о том, что приложение поддерживается на Windows 8.1. и выше:
Решение
1. Находим более раннюю версию, которая подойдёт для Windows 7, перейдем по ссылке.

2. Скачиваем версию v13.14.0 [ссылка] для вашей операционной системы.
3. Нажимаем Next:
4. Соглашаемся с условиями лицензионного соглашения, ставим галочку и нажимаем Next:
5. По умолчанию, установка Node.js происходит в папку C: \Program Files\nodejs\. Поменяйте, при необходимости, и нажимайте Next:
6. Далее идут пользовательские настройки и предлагается установить дополнительные инструменты. Оставляем по умолчанию и нажимаем кнопку Next:
7. Успешная установка, нажимаем Finish:
Мои поздравления 🙂 Node.js установлен.
Проверка работы Node.js и npm
Осталось проверить, для этого:
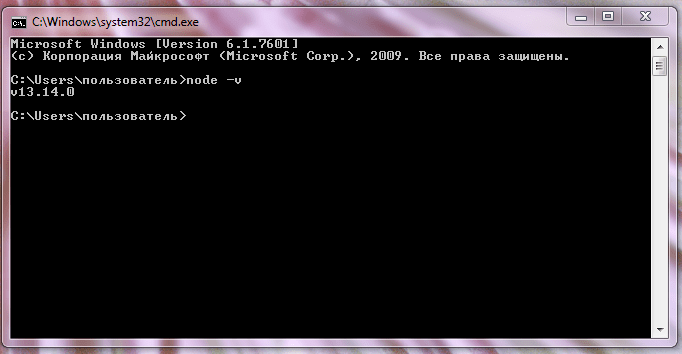
1. Запускаем консоль в стандартной программе Windows командой cmd:
2. Командой node -v (выводится v13.14.0) проверяем работу Node.js:
3. Командой npm -v проверяем npm и видим установленную версию 6.14.4
Настройка среды разработки Node.js напрямую в Windows Set up your Node.js development environment directly on Windows
Ниже приведено пошаговое руководство по началу работы с Node.js в собственной среде разработки Windows. The following is a step-by-step guide to get you started using Node.js in a native Windows development environment.
Установка nvm-windows, Node.js и npm Install nvm-windows, node.js, and npm
Существует несколько способов установки Node.js. There are multiple ways to install Node.js. Мы рекомендуем использовать диспетчер версий, так как версии меняются достаточно быстро. We recommend using a version manager as versions change very quickly. Вероятно, вам придется переключаться между несколькими версиями в зависимости от потребностей для различных проектов, над которыми вы работаете. You will likely need to switch between multiple versions based on the needs of different projects you’re working on. Диспетчер версий Node Version Manager, чаще называемый nvm, является наиболее популярным средством установки нескольких версий Node.js, но он доступен только для Mac и Linux и не поддерживается в Windows. Node Version Manager, more commonly called nvm, is the most popular way to install multiple versions of Node.js, but is only available for Mac/Linux and not supported on Windows. Вместо этого выполним шаги ниже, чтобы установить nvm-windows, а затем используем его для установки Node.js и диспетчера пакетов Node Package Manager (npm). Instead, we will walk through the steps to install nvm-windows and then use it to install Node.js and Node Package Manager (npm). Существуют также альтернативные диспетчеры версий, которые описаны в следующем разделе. There are alternative version managers to consider as well covered in the next section.
Рекомендуем всегда удалять любые имеющиеся установки Node.js или npm из операционной системы перед установкой диспетчера версий, так как эти установки могут создавать необычные и запутанные конфликты. It is always recommended to remove any existing installations of Node.js or npm from your operating system before installing a version manager as the different types of installation can lead to strange and confusing conflicts. Сюда относится удаление всех существующих каталогов установки Node.js (например, C:\Program Files\nodejs), которые могут остаться. This includes deleting any existing nodejs installation directories (e.g., «C:\Program Files\nodejs») that might remain. Созданная символьная ссылка NVM не будет перезаписывать существующий (даже пустой) каталог установки. NVM’s generated symlink will not overwrite an existing (even empty) installation directory. Справку по полному удалению предыдущих установок см. здесь. For help with removing previous installations, see How to completely remove node.js from Windows.)
Откройте репозиторий windows-nvm в Интернет-браузере и щелкните ссылку Загрузить сейчас. Open the windows-nvm repository in your internet browser and select the Download Now link.
Скачайте последний выпуск файла nvm-setup.zip. Download the nvm-setup.zip file for the most recent release.
После скачивания откройте ZIP-файл, а затем запустите файл nvm-setup.exe. Once downloaded, open the zip file, then open the nvm-setup.exe file.
Мастер установки Setup-NVM-for-Windows поможет выполнить все этапы установки, в том числе выбрать каталог, в котором будут установлены репозиторий nvm-windows и Node.js. The Setup-NVM-for-Windows installation wizard will walk you through the setup steps, including choosing the directory where both nvm-windows and Node.js will be installed.
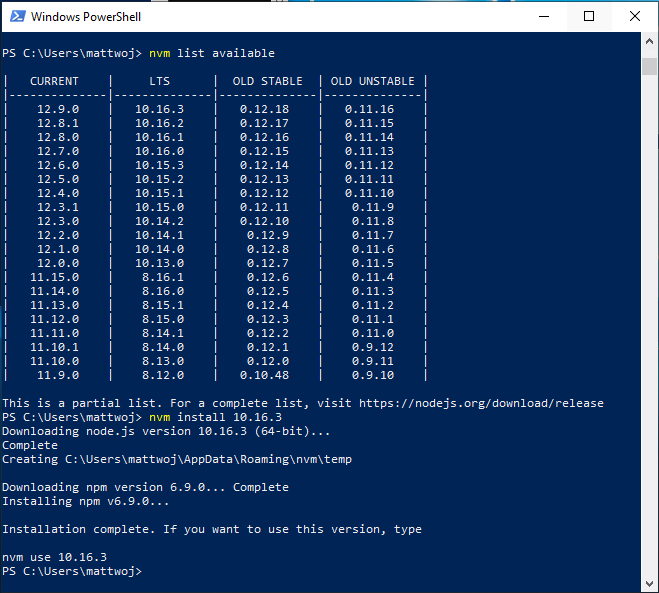
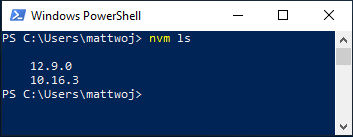
Установка завершится. Once the installation is complete. откройте PowerShell и попробуйте использовать windows-nvm, чтобы просмотреть список установленных версий Node (на этом этапе их еще не должно быть): nvm ls Open PowerShell and try using windows-nvm to list which versions of Node are currently installed (should be none at this point): nvm ls
Установите текущий выпуск Node.js (в нем вы сможете протестировать новейшие улучшенные возможности, но вероятность возникновения проблем при этом будет больше, чем при использовании версии LTS) с помощью команды nvm install latest . Install the current release of Node.js (for testing the newest feature improvements, but more likely to have issues than the LTS version): nvm install latest
Установите последний стабильный выпуск LTS Node.js (рекомендуется). Для этого сначала выполните поиск номера текущей версии LTS с помощью команды nvm list available , а затем установите версию LTS по номеру с помощью команды nvm install (замените номером, например: nvm install 12.14.0 ). Install the latest stable LTS release of Node.js (recommended) by first looking up what the current LTS version number is with: nvm list available , then installing the LTS version number with: nvm install (replacing with the number, ie: nvm install 12.14.0 ).
Вызовите список установленных версий Node, выполнив команду nvm ls . Теперь в нем должны отображаться две недавно установленные версии. List what versions of Node are installed: nvm ls . now you should see the two versions that you just installed listed.
После установки требуемых версий Node.js выберите нужную версию, введя nvm use (замените нужным номером, например nvm use 12.9.0 ). After installing the Node.js version numbers you need, select the version that you would like to use by entering: nvm use (replacing with the number, ie: nvm use 12.9.0 ).
Чтобы изменить версию Node.js на ту, которую вы хотите использовать для проекта, создайте каталог проекта с помощью команды mkdir NodeTest и укажите каталог, выполнив команду cd NodeTest . Затем введите nvm use , заменив номером версии, который вы хотите использовать (т. е. версии 10.16.3). To change the version of Node.js you would like to use for a project, create a new project directory mkdir NodeTest , and enter the directory cd NodeTest , then enter nvm use replacing with the version number you’d like to use (ie v10.16.3`).
Проверьте, какая версия npm установлена, с помощью npm —version . Этот номер версии автоматически изменится на номер той версии npm, которая связана с вашей текущей версией Node.js. Verify which version of npm is installed with: npm —version , this version number will automatically change to whichever npm version is associated with your current version of Node.js.
Альтернативные диспетчеры версий Alternative version managers
Несмотря на то что windows-nvm сейчас является самым популярным менеджером версий для Node, есть несколько альтернативных вариантов: While windows-nvm is currently the most popular version manager for node, there are alternatives to consider:
nvs (Node Version Switcher) — это кроссплатформенный вариант nvm с возможностью интеграции с VS Code. nvs (Node Version Switcher) is a cross-platform nvm alternative with the ability to integrate with VS Code.
Volta — это новый диспетчер версий, созданный командой LinkedIn. Заявлено, что он отличается увеличенной скоростью и межплатформенной поддержкой. Volta is a new version manager from the LinkedIn team that claims improved speed and cross-platform support.
Чтобы установить Volta в качестве диспетчера версий (вместо windows-nvm), перейдите в раздел Установка Windows руководства Начало работы, затем скачайте и запустите установщик Windows, следуя инструкциям. To install Volta as your version manager (rather than windows-nvm), go to the Windows Installation section of their Getting Started guide, then download and run their Windows installer, following the setup instructions.
Перед установкой Volta необходимо убедиться, что на компьютере с Windows включен режим разработчика. You must ensure that Developer Mode is enabled on your Windows machine before installing Volta.
Дополнительные сведения об использовании Volta для установки нескольких версий Node.js в Windows см. в документации по работе с Volta. To learn more about using Volta to install multiple versions of Node.js on Windows, see the Volta Docs.
Установка предпочтительного редактора кода Install your favorite code editor
Для разработки с помощью Node.js в Windows рекомендуется установить VS Code, а также пакет расширений Node.js. We recommend you install VS Code, as well as the Node.js Extension Pack, for developing with Node.js on Windows. Установите их все или выберите наиболее полезные для вас. Install them all or pick and choose which seem the most useful to you.
Чтобы установить пакет расширений Node.js, сделайте следующее: To install the Node.js extension pack:
- Откройте в VS Code окно Расширения (нажав клавиши CTRL+SHIFT+X). Open the Extensions window (Ctrl+Shift+X) in VS Code.
- В поле поиска в верхней части окна расширений введите: Node Extension Pack (Пакет расширений Node) (или имя любого расширения, которое необходимо найти). In the search box at the top of the Extensions window, enter: «Node Extension Pack» (or the name of whatever extension you are looking for).
- Выберите пункт Установить. Select Install. После установки расширение появится в папке «Включено» в окне Расширения. Once installed, your extension will appear in the «Enabled» folder of your Extensions window. Вы можете отключить, удалить или настроить параметры, выбрав значок шестеренки рядом с описанием вашего нового расширения. You can disable, uninstall, or configure settings by selecting the gear icon next to the description of your new extension.
К дополнительным рекомендуемым расширениям относятся следующие: A few additional extensions you may want to consider include:
- Отладчик для Chrome — после завершения разработки на стороне сервера с помощью Node.js вам нужно будет выполнить разработку и тестирование на стороне клиента. Debugger for Chrome: Once you finish developing on the server side with Node.js, you’ll need to develop and test the client side. Это расширение интегрирует редактор VS Code со службой отладки браузера Chrome, что увеличивает эффективность выполнения операций. This extension integrates your VS Code editor with your Chrome browser debugging service, making things a bit more efficient.
- Раскладки клавиатуры других редакторов — эти расширения позволят использовать необходимую раскладку при переходе в другой текстовый редактор (например, Atom, Sublime, Vim, eMacs, Notepad++ и т. п.). Keymaps from other editors: These extensions can help your environment feel right at home if you’re transitioning from another text editor (like Atom, Sublime, Vim, eMacs, Notepad++, etc).
- Расширение синхронизации параметров — позволяет синхронизировать параметры VS Code в разных установках, используя GitHub. Settings Sync: Enables you to synchronize your VS Code settings across different installations using GitHub. Если вы работаете на разных компьютерах, это обеспечит согласованность среды между ними. If you work on different machines, this helps keep your environment consistent across them.
Установка Git (необязательно) Install Git (optional)
Если вы планируете работать совместно с другими пользователями или размещать проект на сайте с открытым исходным кодом (например, GitHub), примите во внимание, что VS Code поддерживает управление версиями с помощью Git. If you plan to collaborate with others, or host your project on an open-source site (like GitHub), VS Code supports version control with Git. Вкладка системы управления версиями в VS Code отслеживает все изменения и содержит общие команды Git (добавление, фиксация, принудительная отправка, извлечение) прямо в пользовательском интерфейсе. The Source Control tab in VS Code tracks all of your changes and has common Git commands (add, commit, push, pull) built right into the UI. Сначала необходимо установить Git для включения панели управления версиями. You first need to install Git to power the Source Control panel.
Скачайте и установите Git для Windows с веб-сайта git-scm. Download and install Git for Windows from the git-scm website.
В комплект входит мастер установки, который задает вам ряд вопросов о параметрах установки Git. An Install Wizard is included that will ask you a series of questions about settings for your Git installation. Рекомендуется использовать все параметры по умолчанию, если у вас нет конкретной причины изменить какой-либо из них. We recommend using all of the default settings, unless you have a specific reason for changing something.
Если вы никогда не использовали Git, обратитесь к руководствам по GitHub. Они помогут вам приступить к работе. If you’ve never worked with Git before, GitHub Guides can help you get started.