- Показать скрытые файлы в Linux
- Показ скрытых файлов в Dolphin
- Скрытые файлы в Nautilus
- Просмотр скрытых файлов в терминале
- Linux Tips: View hidden files
- how to show or display hidden files in linux
- ls command
- dir command
- KDE File Manager (dolphin)
- Gnome File Manager (files or nautilus)
- Xfce File Manager (thunar)
- Midnight Commander
- Hide Folders and Show Hidden Files in Ubuntu Linux [Beginner Trick]
- Show hidden files in Ubuntu & other Linux distributions
- How to hide files or folders in Ubuntu
- Bonus Tip: Hiding multiple files and folders without renaming all of them (valid for GUI only)
- How to Show Hidden Files in Linux
- How to Show Hidden Files
- Show Hidden Files From the Command Line
- Show Hidden Files in a Graphical Interface (GUI)
- How to Hide Files
- Hide File or Directory Using the Linux Command Line
- Hide a File in a Graphical Interface (GUI)
- How to Create Password-Protected Hidden Files
- Create Password-Protected, Hidden File From the Command Line
- Create a Hidden, Password-Protected File From the Graphical Interface
Показать скрытые файлы в Linux
В Linux как и в Windows есть скрытые файлы, правда работают они здесь немного по-другому. В файловых системах Linux нет никакого атрибута скрытности, просто разработчики договорились, что файлы с точкой перед названием будут считаться скрытыми.
Это, как правило, различные файлы настроек, файлы кэша, и временные данные приложений. Как вы поняли, в этой инструкции мы рассмотрим как посмотреть скрытые файлы в Linux, а именно в файловых менеджерах Dolphin и Nautilus а также в терминале.
Показ скрытых файлов в Dolphin
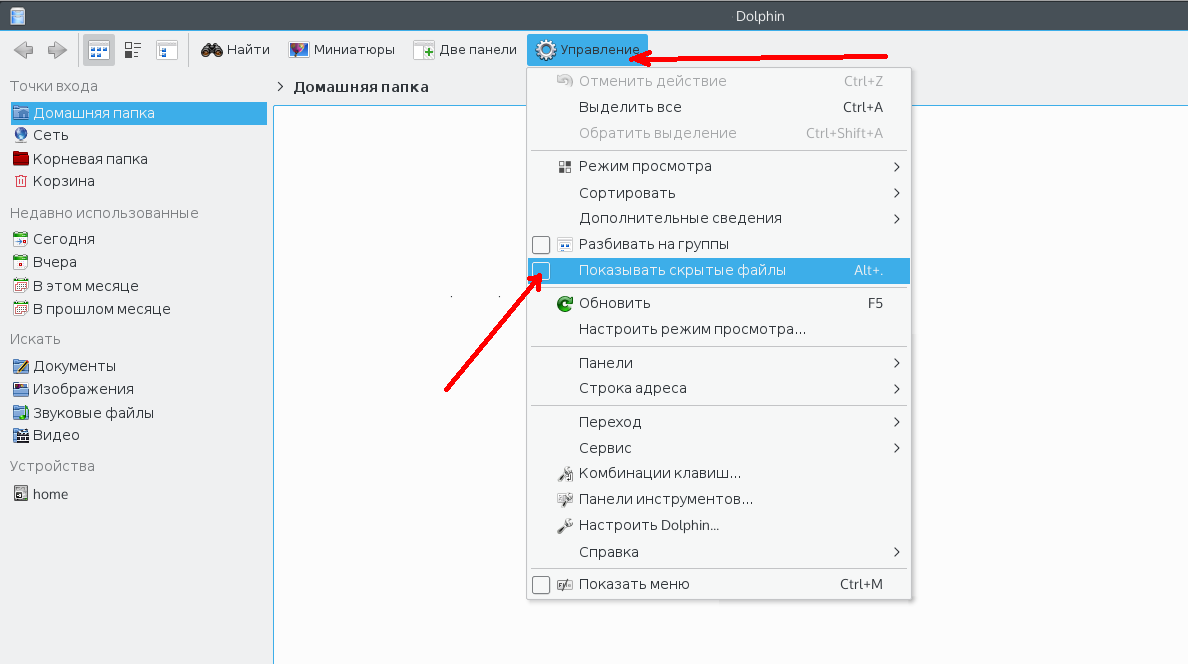
В стандартном файловом менеджере KDE скрытые файлы можно посмотреть отметив флажок показать скрытые файлы в меню управление:
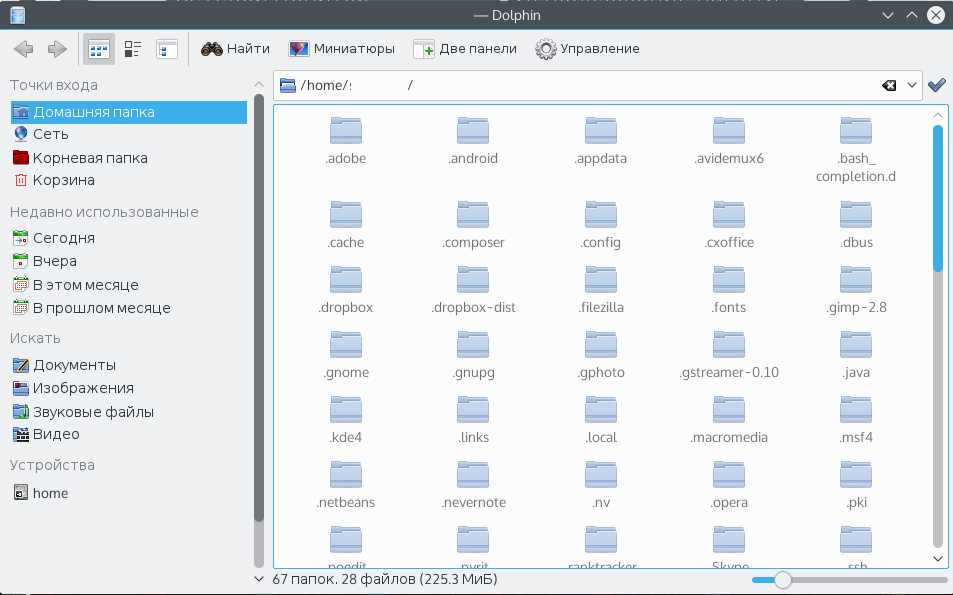
Вот они будут выглядеть немного светлее обычных:
Того же эффекта можно добиться нажав сочетание клавиш Alt+. (Alt + точка) Чтобы вернуть все как было нажмите эти же клавиши еще раз или снимите флажок в меню.
Скрытые файлы в Nautilus
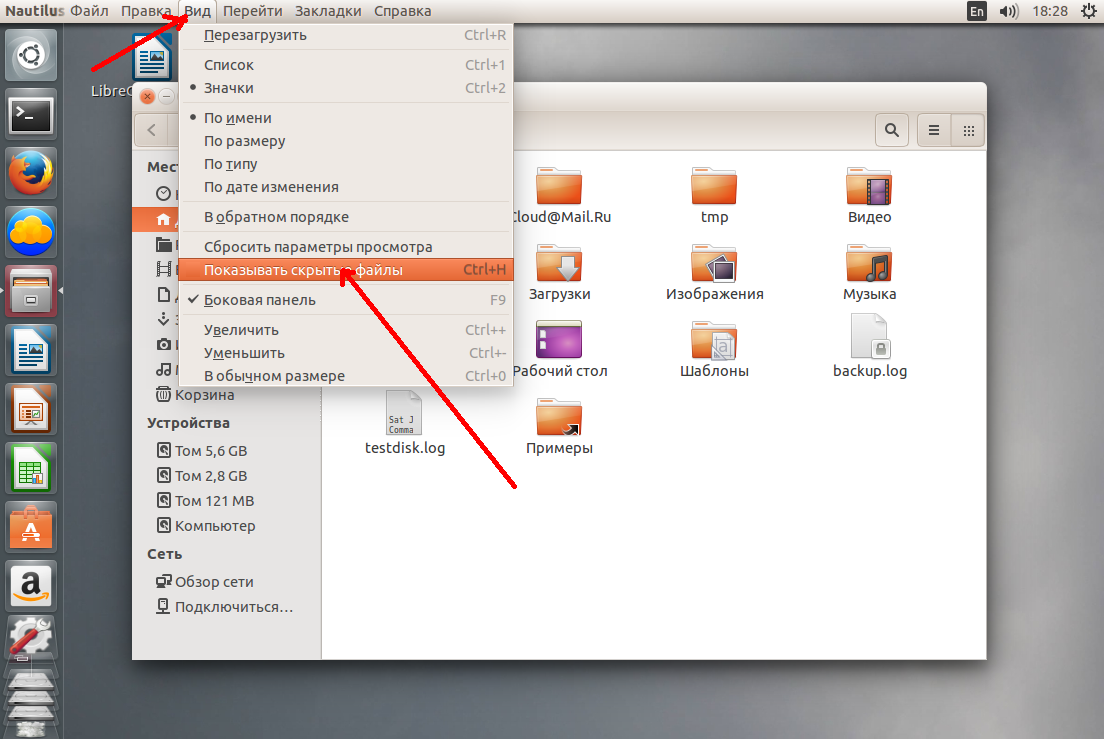
В Nautilus все почти так же. Откройте меню Вид и установите галочку Показать скрытые файлы:
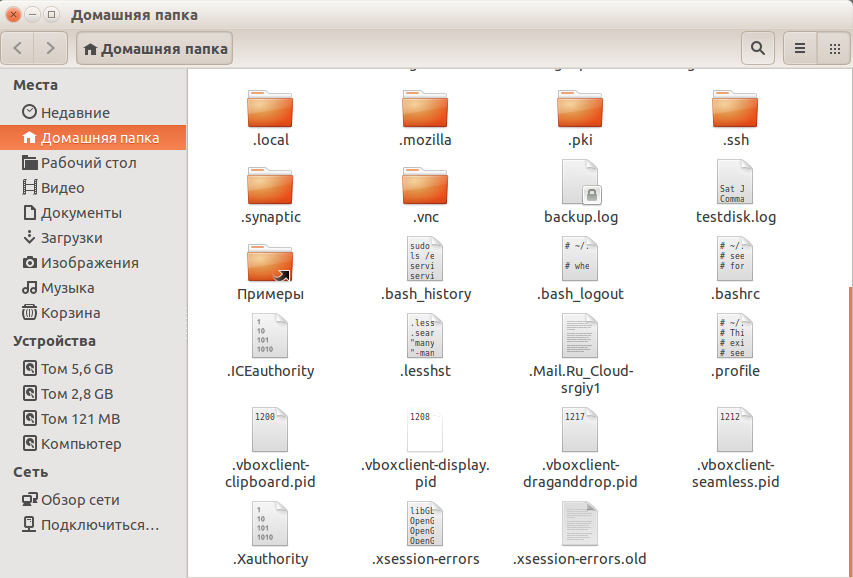
Выглядят они здесь так же как и все, только с точкой в имени:
И здесь тоже есть горячие клавиши Ctrl+H, H означает Hidden, что переводиться как скрытый.
Просмотр скрытых файлов в терминале
В терминале для просмотра списка файлов в директории используется утилита ls. Передав в ей опцию -a мы увидим все файлы, в том числе скрытые. Например, для домашней папки текущего пользователя:
Чтобы просматривать скрытые файлы было удобнее можно добавить опцию -l:
Теперь вы знаете как включается просмотр скрытых файлов и папок в Linux. Как видите, это очень просто. Намного проще чем в Windows, так как вам не надо заходить ни в какие настройки и можно сделать всё прямо в файловом менеджере. Что примечательно, файловый менеджер запоминает какая настройка выбрана между перезагрузками, поэтому вам не придется менять настройки каждый раз.
Источник
Linux Tips: View hidden files
In the Linux operating system, a hidden file is any file that begins with a «.». When a file is hidden it can not been seen with the bare ls command or an un-configured file manager. In most cases you won’t need to see those hidden files as much of them are configuration files/directories for your desktop. There are times, however, that you will need to see them in order to edit them or even navigate through the directory structure.To do this you will need to know the correct options (for ls) or how to see them in your file manager of choice.
In this Linux Tips article I will show you how to view hidden files with ls, Thunar, Nautilus, and Dolphin.
LS
If you need to see hidden files using the ls command you need to add the -a switch. But if you just add the -a switch most likely your files will fly by you and you will miss what you are looking for. To avoid this pipe the command through the less command like so:
The above command will allow you to page through the contents so you can actually see what is there. You can scroll either up or down using the arrow keys or you can scroll down one page at a time with the space bar.
Thunar
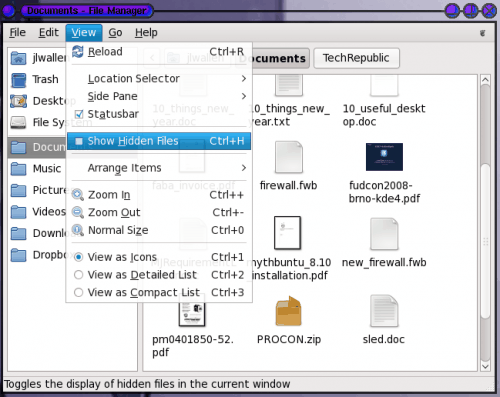
If you don’t know, Thunar is the file manager for the Enlightenment desktop. In order to see hidden files in Thunar click the View menu and check the Show Hidden Files box (as shown in Figure 1.) Or you can hit the key combination Ctrl-H.
If you use the key combination you must make sure you are focused on the Thunar window. When you set Thunar to view hidden files it will always do so until you unset this option.
Nautlius
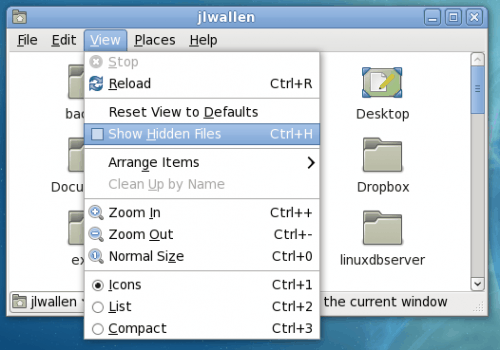
Nautilus is the file manager for the GNOME desktop. With the Nautilus file manager viewing hidden files is done in the same way. From the View menu select the Show Hidden Files option (see Figure 2) or hit the key combination Ctrl-H. Like Thunar, if you use the key combination you must be focused on the Nautilus window.
And like Thunar, the hidden file option will stick until it is unset.
Dolphin
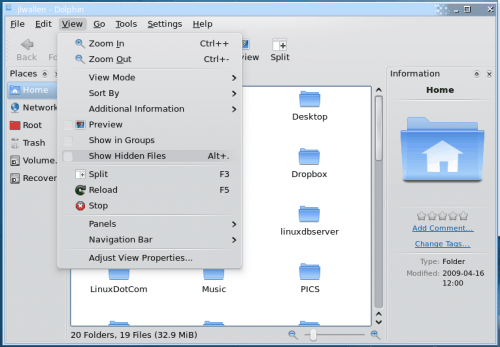
Dolphin is the KDE file manager that replaced Konqueror. In order to view hidden files in this file manager you select the View Hidden Files option from the View menu. You can also enable this action by hitting the Ctrl-. key combination. And like both Thunar and Nautilus, in order to use the key combination Dolphin must be in focus or the combination will not work.
Again, like the other graphical file managers, this option will remain until unset.
Final Thoughts
Hidden files are an important part of the Linux operating system. Although you can go your entire Linux lifetime without ever having to view a single hidden file, on that one occasion that you will need to do so, it’s good to know how.
Источник
This post and this website contains affiliate links. See my disclosure about affiliate links.
how to show or display hidden files in linux
In Linux, as you should already know, there is the concept of hidden files and hidden folders. It is not exactly hidden in the literal sense, but all that means is that the file managers and file system utilities will not display these types of files (or folders) by default.
The hidden file concept is not a security feature and it does not provide any extra protection compared to other files. However, there are a couple of reasons (or benefits) for these kind of files.
- These files are usually a mechanism to store user preference or system files that are not modified by user regularly.
- They are also used by different utilities to store configuration and state of the programs. As these files are not actively used by user on a normal day-to-day basis, it makes sense to hide them in most cases.
- It also allows the file manager utilities to prevent cluttering up the user interface and provide a soft division between user files and user specific configuration files.
Any file or folder whose name start with a dot (.) is a hidden file, also known as dot file. These files will not be displayed by default when listing the contents of a folder. These files can be referenced just as any file, by using the name of the file (including the dot).
We will see how you can view these files using the most popular directory listing commands and file managers.
ls command
The ls command is probably the most used command line utility and it lists the contents of the specified directory. In order to display all files, including the hidden files in the folder, use the -a or –all option with ls.
This will display all the files, including the two implied folders: . (current directory) and .. (parent folder). If you want to omit the display of these two folders, then use the -A or –almost-all option.
This is quite useful, if you are using the output of the command as input to some other script. You probably do not the script to loop in the current folder (depending on the script).
If you want to display only the hidden files, then you will need to specify a regular expression with the ls command., the following will display just the hidden file and folders.
The -d option is to ensure that the directory contents are not printed out for each directory in the list.
dir command
Another popular command used to display directory contents is dir. Almost all options for dir is the same as ls, which means everything that was shown for ls in the previous section will work for dir as well.
will display all files, hidden files and the implied folders (. and ..).
will display all files, folders including the hidden folders but excluding both . and ..
will display just the hidden files and hidden folders.
KDE File Manager (dolphin)
The default file manager in KDE is Dolphin. The default setting in Dolphin is not to display hidden or dot files. There are couple of different ways you can enable the option here.
The easiest is probably the keyboard shortcut Alt+. (Alt and dot). You can easily enable the display and disable it again using the same shortcut.
The other option is using the menu option. Click on the Hamburger icon on the menu bar (for Settings/Configuration). In the drop down menu, you will see the option named Show Hidden Files. Click and select it on it to enable the display of hidden files.
You can leave that option selected, if you want to always display the hidden files. The other commonly used file manager is Konqueror, which uses embedded dolphin to display the file system, as well.
Gnome File Manager (files or nautilus)
The default file manager in Gnome on most distros is Gnome Files. It was formerly known as Nautilus. The keyboard shortcut to display hidden files in Nautilus is Ctrl+H. This shortcut can be used to toggle the display of dot files.
The other option is to change it in the configuration. Open Edit -> Preferences and navigate to the Views tab. Select the option Shown hidden and backup files. In modern or latest versions, this option is in Files -> Preferences menu.
Xfce File Manager (thunar)
Xfce is a popular light weight desktop environment, and the default file manager is thunar. The keyboard shortcut is display hidden files is again Ctrl+H just as with Gnome File Manager.
You can find the option with in the menu as well, as with other file managers. Click on View in the menu bar, and select Show Hidden Files option.
Midnight Commander
Midnight Commander is a command line based file manager which has a loyal following. The keyboard shortcut to display dot files here is Alt + . (Alt-Period).
There is also a configuration setting with in Panel Options. Open Options from the menu and then Panel Options. Select the option Show Hidden Files.
No matter which file manager you are using, there should be an option to display hidden files. Most times, it is disabled by default and as it should be. You can try first by right clicking and checking the context menu. The next place to check is either the Settings or Preferences dialog which is often in the Edit or View menu.
Источник
Hide Folders and Show Hidden Files in Ubuntu Linux [Beginner Trick]
Last updated October 29, 2020 By Abhishek Prakash 16 Comments
Your are probably familiar with the concept of “hiding” a folder or file in Windows. Hiding a folder or file just “removes” the folder from the normal view and then you can choose to display “hidden files” to see it.
So how do you see the hidden files in Linux then? Let me show you that.
Show hidden files in Ubuntu & other Linux distributions
If you are in a terminal, you can use the ls command to display the all the files, including the hidden ones:
You can recognize the hidden files and folders with the dot (.) before their names.
If you use desktop Linux, you can still see hidden files easily. Let’s see how.
Keyboard Shortcut in GUI
If you are in the file manager, you can use the Ctrl+H keyboard shortcut in Ubuntu and I presume other distributions to display all the files including the hidden ones.
Pressing Ctrl+H again will hide the files.
If you are not a fan of keyboard shortcuts, you can use the file manager GUI to display the hidden folders and files.
To see a hidden file or hidden folder in Ubuntu, go to the file manager (default is Nautilus). File Manager is Ubuntu’s counter part of Windows Explorer.
Now go to the top menu->Show hidden files:
How to hide files or folders in Ubuntu
Now that you have learned to see hidden files in Ubuntu, let’s now see how you can hide a folder or files.
Unfortunately/interestingly, there is no similar way as in Windows to hide a folder. In Windows, you right click on a file and choose the option of making it hidden. But this option is not available in Ubuntu.
So, how can you hide a folder in Ubuntu then? Very simple! Using the Linux property of hiding a file/folder. In Linux, if a file name starts with . (dot), it is considered as a hidden file.
Now if you want to hide a file or folder, lets say MyFolder, just rename it to .MyFolder and it will be taken as a hidden file or folder.
If you are using Linux desktop, just right click and choose the rename option and add the dot before the name.
Bonus Tip: Hiding multiple files and folders without renaming all of them (valid for GUI only)
This is a neat little trick that will let you hide several files and folders from the normal view in your desktop Linux’s file manager.
Traditionally, if you create a .hidden file and add the name of the folders in this file, those folders will be hidden from normal view when you close your file manager and open it again.
Keep in mind that this trick works with only the current directory you are in. It won’t work for nested directories. You can create the .hidden file in any directory to hide files and folders in it.
This was about hiding files in Linux. There are separate methods for locking a folder in Linux. I hope you like this little bit of Linux knowledge.
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник
How to Show Hidden Files in Linux
Home » SysAdmin » How to Show Hidden Files in Linux
Linux, by default, hides many of the sensitive system files. Hidden files are usually system or application files, concealed to prevent accidental changes.
This guide will show you how to display and work with hidden files in Linux.
- A system running Linux
- Access to a terminal window / command line (optional)
Note: Some directories require administrator, root, or sudo privileges to access. Depending on the files you want to access, you may need to switch users or use the sudo command.
How to Show Hidden Files
Show Hidden Files From the Command Line
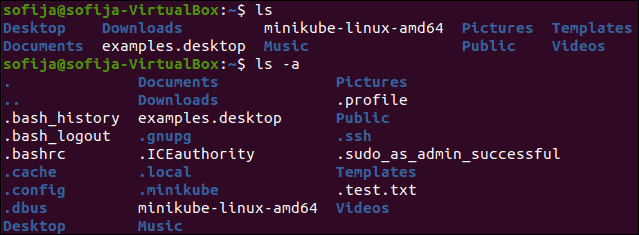
To display all the files in a directory, including hidden files, enter the following command:
The ls command lists the contents of the current directory. The –a switch lists all files – including hidden files.
To list regular and hidden files in a different directory than your current working location:
Replace /etc with any other directory.
Show Hidden Files in a Graphical Interface (GUI)
There’s a simple method to show hidden files if you’re more comfortable working in Gnome (or any other graphical interface).
1. First, browse to the directory you want to view.
2. Then, press Ctrl+h .
If Ctrl+h doesn’t work, click the View menu, then check the box to Show hidden files.
Note: Ctrl+h works in newer Ubuntu and CentOS environments. If you’re running an older or different version, it may not work.
How to Hide Files
Hide File or Directory Using the Linux Command Line
To mark a file as hidden, use the mv (move) command.
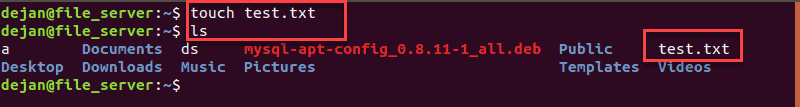
1. First, create a test file. Use the touch command to create an empty test.txt file:
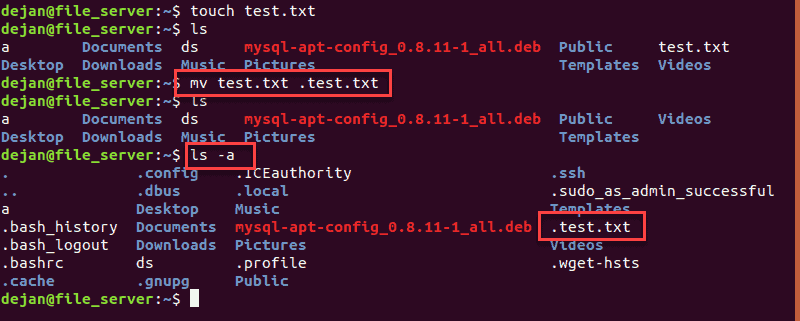
2. Then, hide the file by moving it under a new filename. The period (.) at the beginning of the new filename indicates that it’s hidden:
3. To verify the file is now hidden, display the contents of the current directory:
4. Now, list the contents, including hidden files:
You should see test.txt in the second listing.
Note: The process is entirely the same for directories. Use the mv command with a period (.) at the beginning of the new directory name.
Hide a File in a Graphical Interface (GUI)
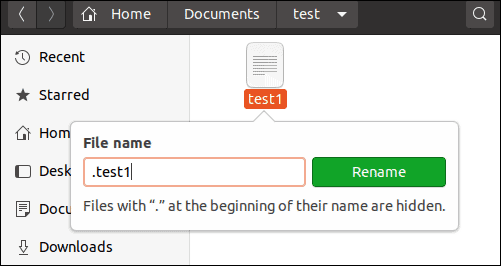
You can also mark a file as hidden using a graphical interface.
1. Right-click the file you want to hide.
2. Then, select Rename.
3. Make the file hidden by placing a period at the beginning of the filename.
Use the same process to hide a directory.
How to Create Password-Protected Hidden Files
Create Password-Protected, Hidden File From the Command Line
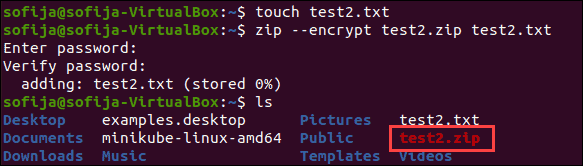
1. To create a hidden and password-protected archive file from the command line, start by creating a new text file:
2. Next, compress and encrypt that file:
3. You’ll be asked to enter and confirm a password for the file.
4. Then, use the ls command – you should see test2.zip in the file list.
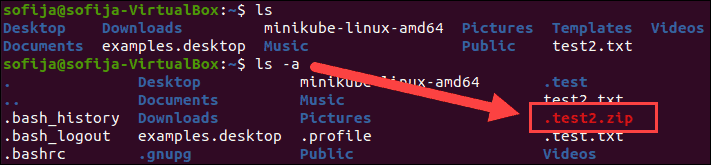
5. Next, set the .zip file to hidden by entering:
6. Finally, use ls and ls –a to confirm and verify the file is hidden.
Create a Hidden, Password-Protected File From the Graphical Interface
Encrypting a file requires more steps in the graphical version of Linux.
1. Start by opening the File Manager to your home directory.
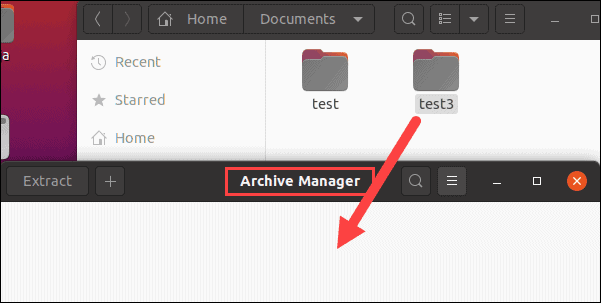
2. Right-click an empty area, then click New Folder (a folder and a directory are the same things).
3. Name the folder test3 and click Create.
4. Next, click Activities > Search > type archive manager > launch the Archive Manager.
5. Drag and drop the new test3 folder into the Archive Manager window.
6. The system will ask: Do you want to create an archive with these files? Click Create Archive.
7. In the Create Archive dialog box, the filename should be test3. Just to the right, click the drop-down and select the .zip format.
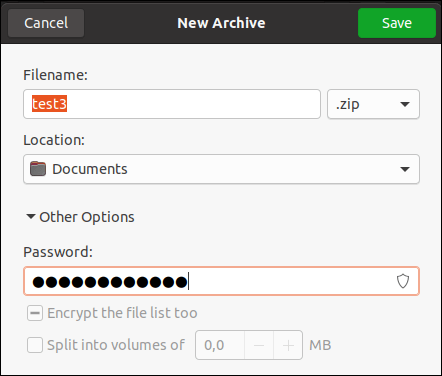
8. Click Other options near the bottom. Type a password to use for your archive, then click Save.
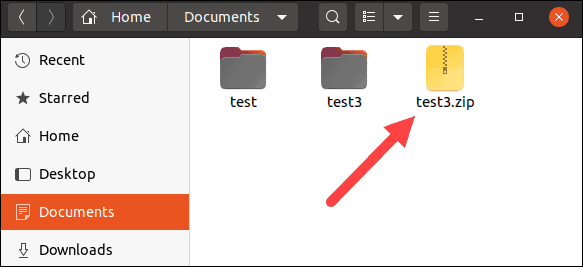
9. Close the Archive Manager. You should now see a test3.zip file in the home directory.
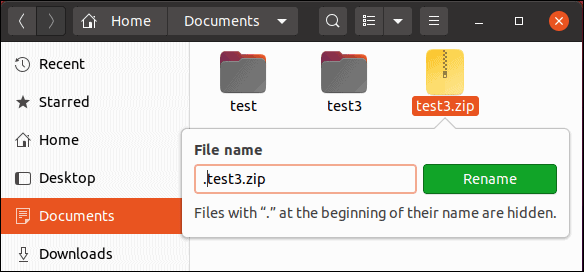
10. Right-click the test3.zip file, click Rename, and add a period at the beginning of the filename.
You should now be able to show and hide hidden files in Linux. These commands can be especially useful if you need to find configuration files.
Also, you can find web browser data, certain application caches, and logs stored in hidden files.
Источник