- Файловая система NTFS – хитрости и секреты для пользователя Windows
- Альтернативный поток данных (ADS)
- Жесткие ссылки и символические ссылки
- Управление квотами
- How to open NTFS files
- Replies (2)
- NTFS overview
- Increased reliability
- Increased security
- Support for large volumes
- Formatting requirements for large files
- Maximum file name and path
- Flexible allocation of capacity
Файловая система NTFS – хитрости и секреты для пользователя Windows
В Windows файловая система NTFS отвечает за управление файлами, папками и дисковым пространством. Очевидно, что существует не только файловая система NTFS, но именно New Technology File System, уже не являющаяся такой «новой», так как была задумана Microsoft ещё в 1993 году, – до сих пор является наиболее широко используемой в среде Windows. Её преемником считается ReFS, но NTFS продолжает оставаться предпочтительным выбором в большинстве случаев.
Многие говорят о файловых системах, которые в будущем могли бы занять их место, но до сих пор многие не знают о продвинутой (и скрытой) функциональности NTFS. Фактически файловая система NTFS позволяет сохранять и восстанавливать «скрытые данные» (называемые альтернативным потоком данных), при необходимости экономить место на диске, сохранять файл таким образом, чтобы он находился в нескольких папках и многое другое.
Альтернативный поток данных (ADS)
ADS – это дополнительная скрытая информация, которая может быть указана в качестве дополнительного атрибута любого файла. ADS имеют не очень обнадеживающую репутацию, поскольку часто связаны с активностью некоторых вредоносных программ. В прошлом некоторые вредоносные компоненты использовали ADS для сокрытия информации, необходимой для их работы.
Тем не менее, основные решения для защиты от вредоносных программ стали намного умнее и способны выполнять полное сканирование системы, также проверяя содержимое любой ADS. В действительности, ADS используется в абсолютно законных целях: браузер и операционная система, например, отмечают происхождение файлов, чтобы предупредить пользователя, когда их открытие может скрывать ловушку.
Откройте командную строку с правами администратора и введите dir /r, чтобы получить список ADS, используемых в текущей папке.
Следующая команда, например, позволит вам получить список ADS, используемых на всём устройстве C: (выполнение операции может занять несколько минут): dir C:\ /r /s | find «:$DATA» > %userprofile%\ads.txt && notepad %userprofile%\ads.txt Затем файл ads.txt можно удалить из папки %userprofile%.
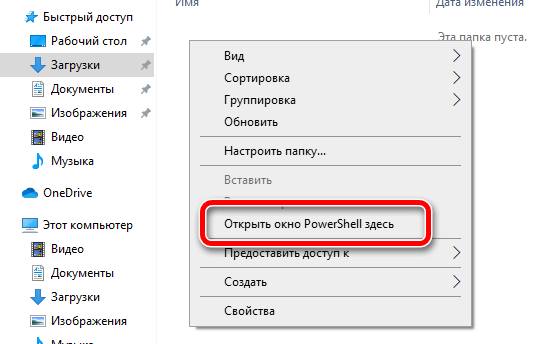
Например, мы предлагаем вам перейти в папку «Загрузки Windows», затем, удерживая клавишу Shift , щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши свободную область и выбрать Открыть окно PowerShell.
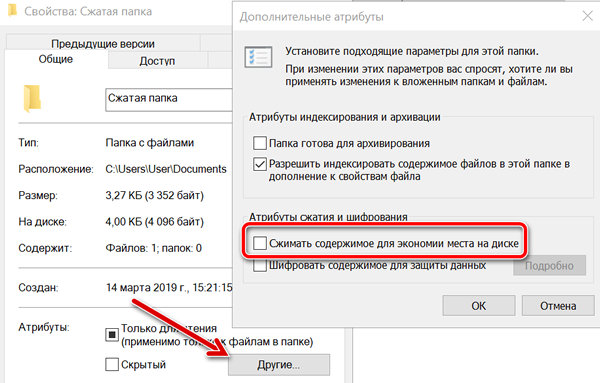
Попробуйте ввести cmd, а затем dir /r. Вы найдете несколько файлов с суффиксом :Zone.Identifier:$DATA. Это просто файлы с ADS. Например, при вводе more Сжать содержимое, чтобы сэкономить место на диске .
Из командной строки вы можете использовать команду compact для запроса сжатия содержимого папки. Введите compact /? чтобы получить полный список используемых ключей.
Жесткие ссылки и символические ссылки
Один и тот же файл может быть доступен на диске NTFS с несколькими именами и даже в нескольких папках, не занимая дополнительного места.
Жесткие ссылки доступны только для файлов (не для папок) и всегда должны ссылаться на файлы одного и того же тома. Механизм прост и включает создание новой записи уровня файловой системы для файла, который уже существует. Кроме того, могут быть использованы следующие команды для создания жесткой ссылки. Первые две работают из обычной командной строки Windows, последняя – из PowerShell:
В примере мы ссылались на гипотетический файл с расширением .exe, но, очевидно, можно ссылаться на любой тип файла; более того, filesist.exe – это имя файла, который уже существует (с относительным путём), а hardlink.exe – это имя ссылки, которая ссылается на этот файл.
Наконец, следует отметить, что жесткие ссылки работают хорошо только для файлов, которые никогда не изменяются: если приложение вмешивается в файл, например, удаляя его и затем воссоздая его, «трюк» больше не будет работать.
Microsoft интенсивно использует жесткие ссылки во время установки Windows: многие системные файлы изначально попадают в подпапки Windows\WinSxS и оттуда они сортируются в реальные системные папки, такие как Windows и System32, используя иллюстрированный метод.
Мягкие или символические ссылки являются ещё одним инструментом, который иногда может быть очень полезен в системах Windows. Символические ссылки могут относиться как к файлам, так и к папкам. Кроме того, в отличие от жестких ссылок, пункт назначения, на который она ссылается, не обязательно должен находиться на том же диске, на котором создана ссылка. Кроме того, вы можете ссылаться на ресурсы, хранящиеся на диске, подключенном к локальной сети.
Символьные ссылки могут быть созданы с помощью следующих команд:
Управление квотами
Ещё одна малоизвестная особенность NTFS – это возможность управлять квотами или определять максимальное пространство, которое могут использовать различные учетные записи пользователей, настроенные на машине Windows.
Для этого просто нажмите комбинацию клавиш Win + E , щелкните правой кнопкой мыши диск и выберите Свойства. Перейдите на вкладку Квота и нажмите кнопку Показать параметры квоты , чтобы определить пространство, которое каждый пользователь сможет использовать.
Используя соответствующие галочки, вы также можете попросить Windows записывать в журнал события каждый раз, когда пользователь приближается к определенной квоте или когда выделяемое пространство заканчивается.
How to open NTFS files
Replies (2)
NTFS is a windows file structure its not a file, like a doc
Whilst one care has been discontinued unless you deleted the program it will still be on your PC
2 people found this reply helpful
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback.
On Sun, 11 Jul 2010 16:26:16 +0000, mc trucker wrote:
My one care anti-virus was discontinued and it had backed my files in NTFS on My Book external hard drive. Now that one care is deleted i can not open those NTFS files.
Sorry, but your message is very confusing, and I don’t understand it.
NTFS is a file system, and either your external drive is all NTFS or
not. The backup can’t be NTFS and everything else FAT32.
NTFS is a file system that Windows XP can read without a problem.
Whether One Care is installed or not has nothing to do with whether
you can access a file on an NTFS drive.
I know next to nothing about One Care, but your saying that an
anti-virus program backed up your files sounds very strange. Are you
sure that’s correct? Anti-virus programs don’t normally do any
backups.
What are the names of these backup files? In particular, what are
their extensions (the part of the file name after the dot at the end)?
How have you tried to open them? What happens when you try? If you get
an error message, please quote it verbatim.
NTFS overview
Applies to: Windows 10, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008
NTFS—the primary file system for recent versions of Windows and Windows Server—provides a full set of features including security descriptors, encryption, disk quotas, and rich metadata, and can be used with Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) to provide continuously available volumes that can be accessed simultaneously from multiple nodes of a failover cluster.
For additional feature information, see the Additional information section of this topic. To learn about the newer Resilient File System (ReFS), see Resilient File System (ReFS) overview.
Increased reliability
NTFS uses its log file and checkpoint information to restore the consistency of the file system when the computer is restarted after a system failure. After a bad-sector error, NTFS dynamically remaps the cluster that contains the bad sector, allocates a new cluster for the data, marks the original cluster as bad, and no longer uses the old cluster. For example, after a server crash, NTFS can recover data by replaying its log files.
NTFS continuously monitors and corrects transient corruption issues in the background without taking the volume offline (this feature is known as self-healing NTFS, introduced in Windows Server 2008). For larger corruption issues, the Chkdsk utility, in Windows Server 2012 and later, scans and analyzes the drive while the volume is online, limiting time offline to the time required to restore data consistency on the volume. When NTFS is used with Cluster Shared Volumes, no downtime is required. For more information, see NTFS Health and Chkdsk.
Increased security
Access Control List (ACL)-based security for files and folders—NTFS allows you to set permissions on a file or folder, specify the groups and users whose access you want to restrict or allow, and select access type.
Support for BitLocker Drive Encryption—BitLocker Drive Encryption provides additional security for critical system information and other data stored on NTFS volumes. Beginning in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, BitLocker provides support for device encryption on x86 and x64-based computers with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) that supports connected stand-by (previously available only on Windows RT devices). Device encryption helps protect data on Windows-based computers, and it helps block malicious users from accessing the system files they rely on to discover the user’s password, or from accessing a drive by physically removing it from the PC and installing it on a different one. For more information, see What’s new in BitLocker.
Support for large volumes
NTFS can support volumes as large as 8 petabytes on Windows Server 2019 and newer and Windows 10, version 1709 and newer (older versions support up to 256 TB). Supported volume sizes are affected by the cluster size and the number of clusters. With (2 32 – 1) clusters (the maximum number of clusters that NTFS supports), the following volume and file sizes are supported.
| Cluster size | Largest volume and file |
|---|---|
| 4 KB (default size) | 16 TB |
| 8 KB | 32 TB |
| 16 KB | 64 TB |
| 32 KB | 128 TB |
| 64 KB (earlier max) | 256 TB |
| 128 KB | 512 TB |
| 256 KB | 1 PB |
| 512 KB | 2 PB |
| 1024 KB | 4 PB |
| 2048 KB (max size) | 8 PB |
Note that if you try to mount a volume with a cluster size larger than the supported maximum of the version of Windows you’re using, you get the error STATUS_UNRECOGNIZED_VOLUME.
Services and apps might impose additional limits on file and volume sizes. For example, the volume size limit is 64 TB if you’re using the Previous Versions feature or a backup app that makes use of Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) snapshots (and you’re not using a SAN or RAID enclosure). However, you might need to use smaller volume sizes depending on your workload and the performance of your storage.
Formatting requirements for large files
To allow proper extension of large .vhdx files, there are new recommendations for formatting volumes. When formatting volumes that will be used with Data Deduplication or will host very large files, such as .vhdx files larger than 1 TB, use the Format-Volume cmdlet in Windows PowerShell with the following parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| -AllocationUnitSize 64KB | Sets a 64 KB NTFS allocation unit size. |
| -UseLargeFRS | Enables support for large file record segments (FRS). This is needed to increase the number of extents allowed per file on the volume. For large FRS records, the limit increases from about 1.5 million extents to about 6 million extents. |
For example, the following cmdlet formats drive D as an NTFS volume, with FRS enabled and an allocation unit size of 64 KB.
You also can use the format command. At a system command prompt, enter the following command, where /L formats a large FRS volume and /A:64k sets a 64 KB allocation unit size:
Maximum file name and path
NTFS supports long file names and extended-length paths, with the following maximum values:
Support for long file names, with backward compatibility—NTFS allows long file names, storing an 8.3 alias on disk (in Unicode) to provide compatibility with file systems that impose an 8.3 limit on file names and extensions. If needed (for performance reasons), you can selectively disable 8.3 aliasing on individual NTFS volumes in Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, and more recent versions of the Windows operating system. In Windows Server 2008 R2 and later systems, short names are disabled by default when a volume is formatted using the operating system. For application compatibility, short names still are enabled on the system volume.
Support for extended-length paths—Many Windows API functions have Unicode versions that allow an extended-length path of approximately 32,767 characters—beyond the 260-character path limit defined by the MAX_PATH setting. For detailed file name and path format requirements, and guidance for implementing extended-length paths, see Naming Files, Paths, and Namespaces.
Clustered storage—When used in failover clusters, NTFS supports continuously available volumes that can be accessed by multiple cluster nodes simultaneously when used in conjunction with the Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) file system. For more information, see Use Cluster Shared Volumes in a Failover Cluster.
Flexible allocation of capacity
If the space on a volume is limited, NTFS provides the following ways to work with the storage capacity of a server:
- Use disk quotas to track and control disk space usage on NTFS volumes for individual users.
- Use file system compression to maximize the amount of data that can be stored.
- Increase the size of an NTFS volume by adding unallocated space from the same disk or from a different disk.
- Mount a volume at any empty folder on a local NTFS volume if you run out of drive letters or need to create additional space that is accessible from an existing folder.