- How to download and install prebuilt OpenJDK packages
- JDK 9 & Later
- JDK 8
- Debian, Ubuntu, etc.
- Fedora, Oracle Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, etc.
- JDK 7
- Debian, Ubuntu, etc.
- Fedora, Oracle Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, etc.
- JDK 6
- Debian, Ubuntu, etc.
- Fedora, Oracle Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, etc.
- BSD Port
- Openjdk linux ��� ���
- About
- Install the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK
- ZIP and TAR.GZ packages
- Native installers
- Install on Windows
- Install on macOS
- Uninstall on macOS
- Install on Ubuntu 18.04+
- Install on Debian 9
- Install on Debian 10
- Install on CentOS 7 (RPM)
- Set Microsoft Build of OpenJDK as the default on Linux
- Provide feedback on the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK
- Установка Java в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Что такое Java
- Какие версии Java бывают и чем отличаются
- Какую версию устанавливать
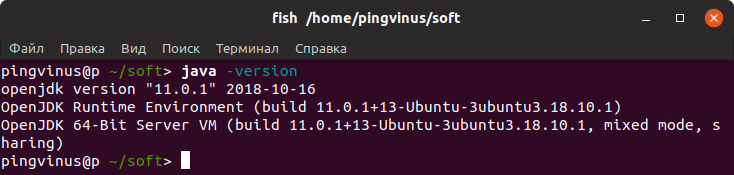
- Проверка версии Java
- Установка OpenJDK
- Установка OpenJDK JRE
- Установка OpenJDK JDK
- Установка OpenJDK определенной версии
- Установка Oracle JDK
- Установка Oracle JDK свежей версии
- Установка Oracle JDK старой версии
- Как удалить Java
- Запуск Java-программ
- Заключение
- How To Install JAVA (OpenJDK) 7/8/10/11 On Linux?
- 1) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On Arch Linux Systems?
- 2) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On RHEL7/CentOS7 Systems?
- 3) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On Ubuntu/Debian Systems?
- 4) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On Fedora Systems?
- 5) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On openSUSE Systems?
- 6) How To Setup Up JAVA Environment Variables On Linux?
- Related Posts
- How to install Oracle Java (JDK/JRE) 8/11/12 in Linux?
- How to Enable Java plugin support on Firefox on Linux
- How To Install Oracle Java 7, 8 & 9 (JDK & JRE) on Debian Via Repository
- About Magesh Maruthamuthu
- 15 Comments on “How To Install JAVA (OpenJDK) 7/8/10/11 On Linux?”
How to download and install prebuilt OpenJDK packages
JDK 9 & Later
Oracle’s OpenJDK JDK binaries for Windows, macOS, and Linux are available on release-specific pages of jdk.java.net as .tar.gz or .zip archives.
As an example, the archives for JDK 13 may be found on jdk.java.net/13 and may be extracted on the command line using
depending on the archive type.
JDK 8
Debian, Ubuntu, etc.
On the command line, type:
The openjdk-8-jre package contains just the Java Runtime Environment. If you want to develop Java programs then please install the openjdk-8-jdk package.
Fedora, Oracle Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, etc.
On the command line, type:
The java-1.8.0-openjdk package contains just the Java Runtime Environment. If you want to develop Java programs then install the java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel package.
JDK 7
Debian, Ubuntu, etc.
On the command line, type:
The openjdk-7-jre package contains just the Java Runtime Environment. If you want to develop Java programs then install the openjdk-7-jdk package.
Fedora, Oracle Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, etc.
On the command line, type:
The java-1.7.0-openjdk package contains just the Java Runtime Environment. If you want to develop Java programs then install the java-1.7.0-openjdk-devel package.
JDK 6
Debian, Ubuntu, etc.
On the command line, type:
The openjdk-6-jre package contains just the Java Runtime Environment. If you want to develop Java programs then install the openjdk-6-jdk package.
Fedora, Oracle Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, etc.
On the command line, type:
The java-1.6.0-openjdk package contains just the Java Runtime Environment. If you want to develop Java programs then install the java-1.6.0-openjdk-devel package.
BSD Port
For a list of pointers to packages of the BSD Port for DragonFly BSD, FreeBSD, Mac OS X, NetBSD and OpenBSD, please see the BSD porting Project’s wiki page.
Источник
Openjdk linux ��� ���
OpenJDK 11 for Linux x86 (IA-32)
This repository provides builds of OpenJDK 11 for Linux x86 (aka IA-32) created with the build scripts by AdoptOpenJDK. Compiled binaries are available at the release page.
Since version 11.0.3 Bell Soft provides binary packages of OpenJDK 11 for Linux x86. Therefore this repository is not necessary anymore and won’t receive any further updates on OpenJDK 11.
Unfortunately AdoptOpenJDK does not provide binaries of OpenJDK 11 for Linux x86 yet. It seems to be planned according to this issue but we don’t really know, when the package will become available on their website.
One might ask, if this old architecture is still relevant today on Linux. Of course it’s highly recommended to use x86-64, if the system supports it. But x86 is still being used and according to the philosophy of open source software, we should try to keep compatibility to older systems for as long as possible:
It was a premise of the open source movement to make software accessible to everyone everywhere. It’s unfortunate we forget sometimes it also means people running obsolete hardware. Including that “old computer,” you had thrown away a few years ago. Of course, we can question the merits of running a Pentium- or 80486-based computer in the 21st century. But merely considering the IA-32 architecture as a thing of the past would be ignoring another niche, well alive this one: embedded systems.
The provided binaries were created on a virtual machine using Debian stable for i386. Of course you might also use other build environments.
The following packages had to be installed in order to build the OpenJDK packages:
OpenJDK is compiled by calling the build.sh script. After the script was successfully executed you can find the created packages in the created package subfolder.
Build on x86-64 systems with Docker
You may build OpenJDK for Linux x86 on a x86-64 system with Docker. The openjdk-linux-x86-docker repository contains the required files and documentation.
Build on x86-64 systems natively
You may build OpenJDK for Linux x86 on a x86-64 system natively. On Debian amd64 the following steps are required:
Register the i386 architecture via:
Besides the packages mentioned above you need to install some additional packages:
Start the build script from this repository with:
After the script was successfully executed you can find the created packages in the created package subfolder.
Word of warning
We’ve tested the provided binaries with our applications. Therefore they should work. But we can’t fully guarantee, that the provided binaries work properly in any use case. Also we can’t give any support for the provided binaries.
Third party components
- build scripts provided by AdoptOpenJDK
- OpenJDK 11 source code provided by AdoptOpenJDK
- OpenJDK 10 package for Linux x86 provided by Azul Systems (used for bootstrapping)
What about OpenJDK 8 for Linux x86?
We’re not intending to provide OpenJDK 8 for Linux x86 here, because others are already covering this:
About
OpenJDK 11 / 12 binaries for Linux x86 (aka IA-32)
Источник
Install the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK
This article describes how to install the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK.
ZIP and TAR.GZ packages
For Windows, Linux, and macOS, we produce ZIP (Windows) and TAR.GZ (Linux/macOS) packages. To install, extract one of these packages in a folder of your choice, then set the JAVA_HOME environment variable to that folder.
Alternately, you can use native installers for your OS of choice, as described in the next section.
Native installers
For Windows, we produce an MSI installer with a graphical interface. For macOS, we produce a PKG installer with similar features. These installers will automatically make the JDK tools available in your PATH .
For Linux, we produce DEB and RPM packages to be used with apt and rpm .
The following sections provide instructions for these installers.
Install on Windows
To install on any version of Windows, you can use the MSI packages or the ZIP package. If you’re on Windows 10, you can use the Windows Package Manager from your Windows Terminal.
To install with the Windows Package Manager, first install winget, and then open the Windows Terminal.
Next, use the following command to search for the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK packages:
You’ll see output similar to the following:
You can now install the package by referencing the Id shown above, using the following command:
This command produces an output similar to the following:
Install on macOS
Packages for macOS are available through Homebrew or as standalone downloads in PKG or TAR.GZ formats.
To install the latest version with Homebrew:
This command produces a output similar to the following:
To install other versions with Homebrew you need to tap the cask-versions repo first:
To install on macOS with the TAR.GZ package, just extract the file into a location. The JDK will be inside /jdk- /Contents/Home .
To install using the PKG installer, open the installer and follow the instructions. By default, the JDK will be installed at /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/microsoft-17.jdk/Contents/Home .
Uninstall on macOS
To uninstall the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK installed through Homebrew or PKG, use the following commands:
To uninstall the package installed through the TAR.GZ package, simply delete the folder.
Install on Ubuntu 18.04+
To install on Ubuntu 18.04 and later versions, open a terminal and run the following commands:
After the repository is added, install the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK by running the following commands:
Note: you may have to update your default JDK, see here for details.
Install on Debian 9
To install on Debian 9, open a terminal and run the following commands:
After the repository is added, run the following commands:
Note: you may have to update your default JDK, see here for details.
Install on Debian 10
To install on Debian 10, open a terminal and run the following commands:
After the repository is added, run the following commands:
Note: you may have to update your default JDK, see here for details.
Install on CentOS 7 (RPM)
To install on CentOS 7, open a terminal and run the following command:
After the repository is added, run the following command:
Note: you may have to update your default JDK, see here for details.
Set Microsoft Build of OpenJDK as the default on Linux
If you have several versions of OpenJDK installed on your system, use the following command to set the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK as the default:
For CentOS, you can use the command alternative .
Provide feedback on the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK
Send us your comments, thoughts, and ideas to help us improve the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK. Visit our OpenJDK discussions page on GitHub to send us your feedback.
Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Источник
Установка Java в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
Что такое Java
Java — это язык программирования, разработанный компанией Sun Microsystems, которую потом купила компания Oracle.
Программы, написанные на Java обычно работают в различных операционных системах, то есть являются кроссплатформенными. Для запуска таких программ необходимо наличие в системе Виртуальной машины Java (Java Virtual Machine — JVM), то есть, проще говоря, наличие некоторых дополнительных компонентов, которые обеспечивают возможность запуска Java-программ в системе.
Обычно, когда говорят о том, что в Linux нужно установить Java, то имеют ввиду, что нужно установить Виртуальную машину Java, чтобы получить возможность запускать программы, написанные на Java.
Какие версии Java бывают и чем отличаются
Существует несколько реализаций Java для Linux. Самыми популярными являются OpenJDK и Oracle Java. В Linux обычно пользователь устанавливает одну из этих реализаций.
- Oracle Java — реализация Java для Linux от компании Oracle. В ней содержатся некоторые закрытые (проприетарные) компоненты и компоненты, которые защищены патентами.
- OpenJDK — реализация Java для Linux с открытым исходным кодом.
Обе версии вполне работоспособны и в Linux можно использовать любую из них. Но иногда, для некоторых приложений, рекомендуется использовать Oracle Java.
В Linux пакеты с Java представлены в двух редакциях:
- JRE — Java Runtime Environment — компоненты, предназначенные для запуска Java-программ в Linux.
- JDK — Java Development Kit — компоненты, предназначенные для запуска, компиляции и разработки Java-программ.
Какую версию устанавливать
Рядовому пользователю, которому нужно просто запускать Java-программы, обычно достаточно установить «OpenJDK JRE».
Если потребуется компиляция Java-программ, то нужно будет установить «OpenJDK JDK».
Рассмотрим, как установить Java в Ubuntu Linux. Абсолютно аналогично выполняется установка в Linux Mint и других дистрибутивах, основанных на Ubuntu.
Проверка версии Java
Чтобы проверить, установлена ли у вас уже в системе какая-либо версия Java, выполните в терминале команду:
Если Java установлена, то вы получите информацию о том, какие компоненты Java установлены в системе.
Установка OpenJDK
Установка OpenJDK JRE
Для установки OpenJDK JRE в Ubuntu Linux достаточно установить пакет default-jre. Для установки выполните в терминале команду:
Установка OpenJDK JDK
Если вы хотите установить OpenJDK JDK, то нужно установить пакет default-jdk (он также установит default-jre). Для установки выполните команду:
Установка OpenJDK определенной версии
Если вам нужно установить конкретную версию, то выполните одну из следующих команд. В репозиториях Ubuntu сейчас представлены OpenJDK версий 11 и 8.
После установки, можно проверить, какие компоненты Java установлены, выполнив команду:
Установка Oracle JDK
Установка Oracle JDK свежей версии
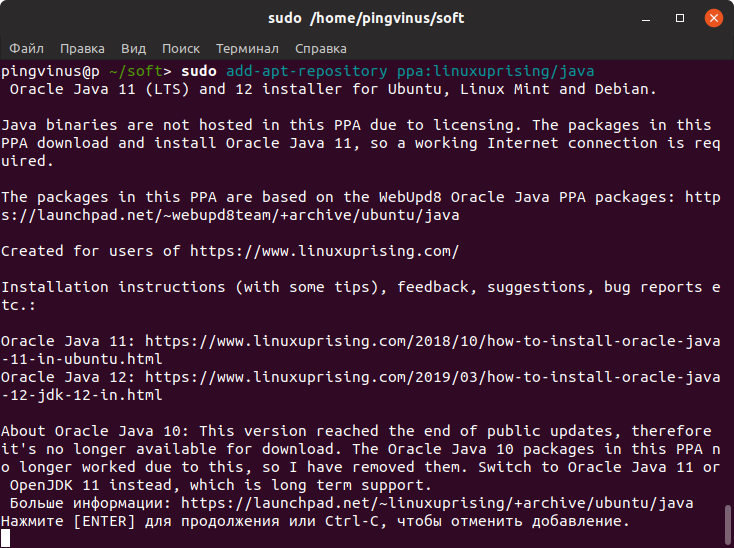
Свежую версию Oracle JDK можно установить, используя PPA-репозиторий, подготовленный проектом linuxuprising.
Сначала добавим PPA-репозиторий. Выполняем следующие команды. При выполнении первой команды появится информационное сообщение, нажмите Enter для продолжения.
Теперь выполним установку Oracle Java версии 12:
Во время установки нужно будет ознакомиться и принять лицензию:
Для установки Oracle Java версии 11 используйте команду:
Установка Oracle JDK старой версии
Если вам нужно установить Oracle JDK старой версии 8, то вы можете воспользоваться PPA-репозиторием, который подготовлен проектом webupd8. Для установки выполните в терминале следующие команды. При выполнении первой команды появится информационное сообщение, нажмите Enter для продолжения.
Как удалить Java
Если у вас установлены пакеты OpenJDK, то для их удаления используйте команду:
Или следующую команду, если требуется также удалить файлы конфигурации (полное удаление OpenJDK):
Для удаления Oracle Java используется команда:
Запуск Java-программ
Если Java установлена в Ubuntu Linux, то для запуска Java-программ обычно достаточно дважды щелкнуть по файлу программы. Он может иметь расширение .jar .
Для запуска .jar файлов из командной строки, выполните команду:
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели, какие версии Java бывают для Linux. Рассмотрели, как установить версию OpenJDK, а также версию Java от Oracle. Обычно начинающий пользователь вообще не понимает, что именно ему нужно установить. Поэтому краткое резюме: Если вам нужно просто запустить какую-нибудь Java-программу в Ubuntu Linux (Linux Mint и других подобных дистрибутивах), то устанавливайте OpenJDK JRE.
Источник
How To Install JAVA (OpenJDK) 7/8/10/11 On Linux?
JAVA is necessary to run certain applications in Linux and windows machine.
JAVA comes with two packages (JDK & JRE).
JDK stands for (Java Development Kit) which helps developers for developing, debugging, and monitoring Java applications.
JRE stands for (Java Runtime Environment) which deploys Java applications on servers.
It includes tools for JVM monitoring and tools commonly required for server applications.
Many of us needed only JRE, so make sure you have installed JRE not for JDE.
In this article we are going to explain how to install OpenJDK in Linux distributions such as RHEL, CentOS, Fedora, Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, openSUSE & Arch Linux based systems.
1) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On Arch Linux Systems?
Arch Linux is a rolling release distribution. Hence, it’s shipped with latest OpenJKD package. Use the below commands to find available OpenJDK package on Arch Linux based distributions.
Run the following command to install JRE 10 (Java Runtime Environment).
Run the following command to install JDK 10 (Java Development Kit).
2) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On RHEL7/CentOS7 Systems?
Redhat 7 based distributions also, having latest OpenJKD & JRE packages in their official repository. Use the below commands to find available OpenJDK package on Redhat 7 based distributions.
Run the following command to install JRE 11 (Java Runtime Environment).
Run the following command to install JDK 11 (Java Development Kit).
3) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On Ubuntu/Debian Systems?
Debian based systems also shipping with latest OpenJKD & JRE packages in their official repository. Use the below commands to find available OpenJDK package on Debian based distributions.
Run the following command to install JRE 8 (Java Runtime Environment).
Run the following command to install JDK 8 (Java Development Kit).
4) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On Fedora Systems?
Fedora systems also shipping with latest OpenJKD & JRE packages in their official repository. Use the below commands to find available OpenJDK package on Fedora system.
5) How To Find And Install OpenJDK/JRE On openSUSE Systems?
Use the below commands to find available OpenJDK package on openSUSE system.
6) How To Setup Up JAVA Environment Variables On Linux?
We should Setup JAVA Environment Variables for java because all the java based application uses environment variables to work.
Open your .bashrc file and add the below lines to end of the file. Make sure you need to mention your path instead of us, then Save and exit.
After saving .bashrc file, run the following command to make it work.
Now you can check the environment variables using below commands. Its clearly fetch the path of jdk and jre home.
Related Posts
How to install Oracle Java (JDK/JRE) 8/11/12 in Linux?
October 25, 2017 January 16, 2020
How to Enable Java plugin support on Firefox on Linux
March 17, 2016 April 25, 2016
How To Install Oracle Java 7, 8 & 9 (JDK & JRE) on Debian Via Repository
February 9, 2016 February 8, 2016
About Magesh Maruthamuthu
Love to play with all Linux distribution
15 Comments on “How To Install JAVA (OpenJDK) 7/8/10/11 On Linux?”
“JAVA is necessary to run most of the applications in Linux and windows machine.”
Thanks. A question: What other purposes are there for using Java these days except development?
Some corrections:
1. You should not edit your user’s local .bashrc using sudo. It belongs to your user, not the system.
2. You should not need to add java binaries to the path. They are already placed there by most distros, since they live in /usr/bin.
3. To change java version that is run when you type java, you can use:
sudo update-alternatives –config java
No need to use $PATH changing.
I am trying to install 1.8 version.
I changed this line
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:JAVA_HOME:JRE_HOME
to
PATH=$HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME:$JRE_HOME:$PATH
Previously it is giving old java version only as it will detect old java binary first because of $PATH is defined at starting.
After changing as per second line it is now working and able to detect 1.8 version in java and javac.
concise and beautiful
Thanks!! te pasaste viejo.
i’m new to Linux it was so useful i was searching around thanks
@Raghavabhargav,
Welcome to LINUX world.
Hi Magesh
Your methodology is very good but your English is a little odd for non-coder like me, which is why i am asking these questions.
In method 2 open jdk you do not give any instructions or clues for testing or checking the install.?
After my install command : echo $JAVA_HOME did not return anything.
Command: java -version , returns
java version “1.7.0_79”
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (IcedTea 2.5.5) (7u79-2.5.5-0ubuntu0.14.04.2)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.79-b02, mixed mode)
Can i assume all is OK or do i need to do more?
Regards JohnB
IT WAS VERY HELPFULL……THANKS ALOT.
@ KTEC,
Nice to hear, Always welcome.
I have CentOS 7 installed and whenever I run the command
yum search java | grep openjdk
I get only openjdk 1.6 & 1.7 not 1.8
yum search java | grep openjdk
java-1.7.0-openjdk-devel.x86_64 : OpenJDK Development Environment
java-1.6.0-openjdk-devel.x86_64 : OpenJDK Development Environment
java-1.6.0-openjdk.x86_64 : OpenJDK Runtime Environment
java-1.6.0-openjdk-demo.x86_64 : OpenJDK Demos
java-1.6.0-openjdk-javadoc.x86_64 : OpenJDK API Documentation
java-1.6.0-openjdk-src.x86_64 : OpenJDK Source Bundle
java-1.7.0-openjdk.x86_64 : OpenJDK Runtime Environment
java-1.7.0-openjdk-accessibility.x86_64 : OpenJDK accessibility connector
java-1.7.0-openjdk-demo.x86_64 : OpenJDK Demos
java-1.7.0-openjdk-headless.x86_64 : The OpenJDK runtime environment without
java-1.7.0-openjdk-javadoc.noarch : OpenJDK API Documentation
java-1.7.0-openjdk-src.x86_64 : OpenJDK Source Bundle
What repo you are using to get 1.8 in the list?
CentOS 6.x support OpenJDK 1.8 but CentOS 7 still having OpenJDK 1.7.
Источник