- Oracle linux yum install
- Stay Connected:
- Oracle Linux: The best Linux for your enterprise
- About Oracle Linux
- Download Oracle Linux
- Installing Software from this Yum Server
- Developing with Oracle Linux
- Oracle Instant Client: Connect your Application to Oracle Database
- Adding EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux)
- Developing Cloud Native Applications
- Browse the Repositories
- Tutorials, Hands-On Labs and Documentation
- If you need Support.
- Oracle linux yum install
- Oracle linux yum install
- Installing Software Packages (rpm, yum)
- yum Repositories
- Kernel Updates
- yum-cron
- Oracle linux yum install
Oracle linux yum install
Stay Connected:

Oracle Linux: The best Linux for your enterprise
About Oracle Linux
The Oracle Linux operating system is engineered for open cloud infrastructure. It delivers leading performance, scalability, reliability and security for enterprise SaaS and PaaS workloads as well as traditional enterprise applications. Unlike many other commercial Linux distributions, Oracle Linux is easy to download and completely free to use, distribute and update. Read on to get started.
Download Oracle Linux
Oracle Linux is available to download, for free, in various forms. Get started here.
Installing Software from this Yum Server
Developing with Oracle Linux
Interested in developing with Node.js, Python, Go or PHP? Learn how to get started below:
Oracle Instant Client: Connect your Application to Oracle Database
Learn how to install Oracle Instant Client packages from this yum server to connect your application to Oracle Database.
Adding EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux)
Oracle Linux yum server hosts packages from EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux). Read how to install them.
Developing Cloud Native Applications
Are you developing microservice-based applications? Deploying and orchestrating containers? Oracle Linux Cloud Native Environment is a fully integrated suite for the development and management of cloud-native applications. Learn how to install and use it here.
Browse the Repositories
In addition to the above, there are a wealth of other packages available on this server. Browse the repositories below.
Tutorials, Hands-On Labs and Documentation
Dig a little deeper with hand-on labs, tutorial videos, or the Oracle Linux documentation:
If you need Support.
This yum server is offered without support of any kind. Peer support is available via the Oracle Linux Community If you require support, please consider purchasing Oracle Linux Support via the Oracle Store, or via your sales representative.
Источник
Oracle linux yum install
Use this procedure to install Oracle Linux and configure your Linux installation for security errata or bug fix updates using the Oracle Linux yum server.
Obtain Oracle Linux DVDs from Oracle Store, or download Oracle Linux from the Oracle Software Delivery Cloud:
Oracle Software Delivery Cloud website:
Install Oracle Linux from the ISO or DVD image.
Download the yum repository file for your Linux distribution from the following URL using the instructions you can find on the Oracle Linux yum server website:
Ensure that the public_olrelease_latest file (for example, public_ol6_latest for Oracle Linux 6) is enabled, because this is the repository that contains the Oracle Preinstallation RPM.
(Optional) Edit the repo file to enable other repositories. For example, enable the repository public_ol6_latest by setting enabled=1 in the file with a text editor.
Run the command yum repolist to verify the registered channels.
Start a terminal session and enter the following command as root , depending on your platform. For example:
Oracle Linux 6 and Oracle Linux 7:
Use the -y option if you want yum to skip the package confirmation prompt.
You should see output indicating that you have subscribed to the Oracle Linux channel, and that packages are being installed.
Oracle Linux automatically creates a standard (not role-allocated) Oracle installation owner and groups and sets up other kernel configuration settings as required for Oracle installations. If you plan to use job-role separation, then create the extended set of database users and groups depending on your requirements.
After installation, run the command yum update as needed to obtain the most current security errata and bug fixes for your Oracle Linux installation.
Источник
Oracle linux yum install
Use this procedure to install Oracle Linux and configure your Linux installation for security errata or bug fix updates using the Oracle Linux yum server.
Obtain Oracle Linux DVDs from Oracle Store, or download Oracle Linux from the Oracle Software Delivery Cloud:
Oracle Software Delivery Cloud website:
Install Oracle Linux from the ISO or DVD image.
Download the yum repository file for your Linux distribution from the following URL using the instructions you can find on the Oracle Linux yum server website:
Ensure that the public_olrelease_latest file (for example, public_ol6_latest for Oracle Linux 6) is enabled, because this is the repository that contains the Oracle Preinstallation RPM.
(Optional) Edit the repo file to enable other repositories. For example, enable the repository public_ol6_latest by setting enabled=1 in the file with a text editor.
Run the command yum repolist to verify the registered channels.
Start a terminal session and enter the following command as root , depending on your platform. For example:
Oracle Linux 6 and Oracle Linux 7:
Use the -y option if you want yum to skip the package confirmation prompt.
You should see output indicating that you have subscribed to the Oracle Linux channel, and that packages are being installed.
Oracle Linux automatically creates a standard (not role-allocated) Oracle installation owner and groups and sets up other kernel configuration settings as required for Oracle installations. If you plan to use job-role separation, then create the extended set of database users and groups depending on your requirements.
After installation, run the command yum update as needed to obtain the most current security errata and bug fixes for your Oracle Linux installation.
Источник
Installing Software Packages (rpm, yum)
This article provides an overview of the rpm and yum commands for installing software packages on Linux, with specific reference to the information needed for the RHCSA EX200 and RHCE EX300 certification exams.
Remember, the exams are hands-on, so it doesn’t matter which method you use to achieve the result, so long as the end product is correct.
The rpm command is used to install, update, list and remove software packages. The command expects to be supplied with flags to indicate the mode of operation and one or more package files. Check out the man pages for a list of all the available options. Using the «-i» flag indicates you are attempting an install of one or more packages. The example below attempts to install a package from a CD. Notice wildcards are supported.
The «-U» option uses the supplied packages to update the system. If a package already exists on the system, but the supplied package is newer it will be applied. If the package does not already exist on the system it will be installed.
The «-q» option allows you to query installed packages. You can then erase specific packages using the «-e» option.
The big limitation of the rpm command is it does not handle dependencies for you. If there are missing dependencies, an installation will fail. It is for this reason you will probably prefer to use the yum command described below.
yum Repositories
The yum command requires a repository as the source of the packages. If you are connected to the internet, you may choose to use the repository provided by your Linux distribution. In this case I am using Oracle Linux 6.x, so I could use the repository provided by Oracle (public-yum.oracle.com). If you have paid for RHEL support, you will register your server using the rhn_register command, which will configure a yum repository.
You can also create a local repository from a distribution DVD, CD or iso file. To do this you will need to mount the DVD, CD or iso file
Next, you can do one of two things.
- Use the DVD directly as a Yum repository.
- Create a new Yum repository by copying the packages off the DVD.
To use the DVD directly, create a file called «/etc/yum.repos.d/dvd.repo» with the following contents, where the «baseurl» points to your DVD mount point.
Import the GPG key from the DVD.
You can now use the DVD as a Yum repository by referencing it using the «—enablerepo» option.
If you want to take the second option and create a new Yum repository by copying the packages off the DVD, create a local directory to hold the yum repository and copy the packages to it.
To create a repository, we need to install the createrepo package, which requires a couple of dependencies.
Now we can create a repository out of the contents of the directory.
To allow the yum command to use the repository, we must create a «.repo» file in the «/etc/yum.repos.d» directory. Create a file called «/etc/yum.repos.d/localrepo.repo» with the following contents.
Notice the «baseurl» parameter. This indicates the location of the repository. In this case I am using a local file system, so the parameter is set to «file://» followed by the path to the repository «/repo/». If this were an internet repository we would expect a baseurl with a HTTP address. For example, the Oracle Linux repository setting would be as follows.
When using internet repositories, you typically expect the «gpgkey» entry as a security precaution.
You should now be able to use the yum command to install packages.
The yum command allows you to install, update, list and remove packages.
The advantage of yum over the rpm command is it deals with all dependencies for you, prompting you with the required dependencies and the total size of the operation. If you agree, all necessary dependencies will be installed, in addition to your specified package(s).
The main Linux distribution repositories also support package groups, allowing you to install, update or remove entire feature sets using a single command. To check if any groups have been defined in the repository, issue the following command.
You can install, update or remove entire groups of packages as follows.
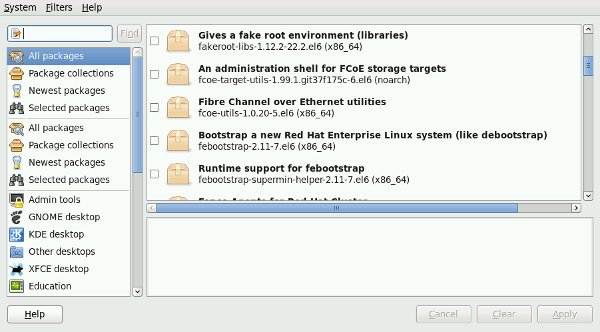
The «Add/Remove Software» dialog is available from the console menu (System > Administration > Add/Remove Software). Provided you have yum repository available, you can use this tool to install individual packages or package groups.
Kernel Updates
Updating the kernel on a system is simple using the yum command. Simply issue the following command and the kernel and all its dependencies will be updated.
The updated version of the kernel will be set as the default in the «/boot/grub/grub.conf» file, so next time the system is booted it will be used.
yum-cron
You can choose to download and apply package updates automatically using yum-cron .
If you are using Oracle Linux, you will have to enable to optional repository (ol*_optional_latest) in the «/etc/yum.repos.d/public-yum-ol*.repo» file by switching the «enabled» flag to «1».
Once installed check the «man yum-cron» page for configuration options. Most of the config files are under the «/etc/yum» directory, but depending on your version of RHEL/OL, the main config file may be placed under the same directory, or under the «/etc/sysconfig» directory.
You can choose to download-only, or download and apply the package changes. In newer versions of RHEL/OL, you also get options to specify the types of changes that will be applied, like only critical updates etc. You can also get it to email you when changes have been applied.
Remember, kernel updates will only take effect after a reboot, so you will need to schedule this where appropriate.
Источник
Oracle linux yum install
Use this procedure to install Oracle Linux and configure your Linux installation for security errata or bug fix updates using the Oracle Linux yum server.
Obtain Oracle Linux DVDs from Oracle Store, or download Oracle Linux from the Oracle Software Delivery Cloud:
Oracle Software Delivery Cloud website:
Install Oracle Linux from the ISO or DVD image.
Download the yum repository file for your Linux distribution from the following URL using the instructions you can find on the Oracle Linux yum server website:
Ensure that the public_olrelease_latest file (for example, public_ol6_latest for Oracle Linux 6) is enabled, because this is the repository that contains the Oracle Preinstallation RPM.
(Optional) Edit the repo file to enable other repositories. For example, enable the repository public_ol6_latest by setting enabled=1 in the file with a text editor.
Run the command yum repolist to verify the registered channels.
Start a terminal session and enter the following command as root , depending on your platform. For example:
Oracle Linux 6 and Oracle Linux 7:
Use the -y option if you want yum to skip the package confirmation prompt.
You should see output indicating that you have subscribed to the Oracle Linux channel, and that packages are being installed.
Oracle Linux automatically creates a standard (not role-allocated) Oracle installation owner and groups and sets up other kernel configuration settings as required for Oracle installations. If you plan to use job-role separation, then create the extended set of database users and groups depending on your requirements.
After installation, run the command yum update as needed to obtain the most current security errata and bug fixes for your Oracle Linux installation.
Источник