- How to Change Windows 10 Display Language Without Reinstalling the Operating System?
- Introduction
- How to change the default display language in Windows 10?
- Disable language synchronization
- The steps to take if you want to change the display language
- Changing region settings
- Conclusion
- Paging in windows operating system
- Paging in windows operating system
How to Change Windows 10 Display Language Without Reinstalling the Operating System?
Read this article to find out how to change the language of Windows 10 interface without having to reinstall it, what system languages can be installed and what settings should be modified for that purpose.

Introduction
In Windows 10, people usually choose the preferred language for the entire operating system when they install it. However, if the language settings were wrong, or people have to use computing devices with certain language preferences, there are some settings to be modified in order to bring them in line with your personal likings.
So if you ever need to change language preferences in Windows 10, this can be done in a quick and easy way with the help of the Settings app and without having to reinstall the operating system.
In today’s article, we will show you how to change the default display language into any other, including doing it for new and existing user accounts.
How to change the default display language in Windows 10?
If you have to move to a different region or you need to use a display language different from the default choice, or the initial language settings for the computing device have been wrong, there is absolutely no point in reinstalling Windows 10. All you need is to modify a couple of system settings to enjoy the experience of using your operating system in the right language.
Disable language synchronization
If you are using a Microsoft account, the language settings will apply to all devices linked to such account. If you plan to change regional and language settings for one computer only, you need to disable synchronization of such settings before you proceed.
This is how you disable language sync in Windows 10.
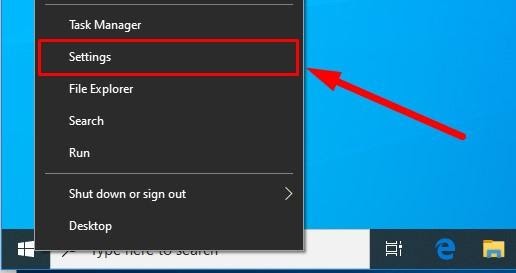
Open the main system application, Settings. You can do it in any way you prefer. For example, click on the Start button in the lower left corner of your desktop, on the Taskbar, and open the main Windows menu. Use the scroll bar or the mouse wheel to search the list of all programs and applications installed on this computer and find the line Settings, or click on the Settings button in the left side of the user menu, and the application will open.
In the main Settings window, scroll down if necessary and choose the tab Accounts.
In the left panel, go to Sync your settings.
In the right panel, find the section Individual sync settings and the line Language preferences, then set the slider to the Off position (disabled).
When these steps are taken, you can start changing language settings for the copy of Windows 10 installed on this computer, without worrying that this can affect similar settings in other linked devices.
The steps to take if you want to change the display language
To change the display language of your Windows 10, you should close all running applications and do what is described below.
Use any method you prefer to open the Settings application. For example, right-click on the Start button that you can find on the Taskbar, in the left lower corner of the desktop, or press the key sequence Windows + X instead to open the context menu, and select the line Settings. The application will start immediately.
Use the scroll bar or the mouse wheel to navigate the Settings window, and find the tab Time and language.
In the left panel, go to Language.
Now look to the right and find the section Preferred languages, where you can prioritize language settings, and click on the button Add a preferred language, with a + (plus) symbol on it.
In the new window Choose a language to install use the scroll bar or the mouse wheel to find the language you need, or start typing its name in the search field above.
Choose the language pack you are planning to use in Windows 10 from the list.
When the language is chosen, hit Next.
In the next page Install language features check the box for Install language pack to confirm your choice (the box with the tick will become blue, i.e. active).
Click Install below.
Changes will take effect after the language package is installed, which usually takes several minutes only. In some cases, restarting your Windows 10 may be required, and then the corresponding language settings will apply to all system elements. The changes will affect the sign-in screen, the Settings app, Windows Explorer, desktop, all applications, preferred browsers and websites you visit. From now on, they will use the new language by default. Besides, Windows 10 may suggest reviewing your current privacy settings.
Changing region settings
If you change the display language for Windows 10 because you move to a different region, then regional settings should be modified too.
Changing them in Windows 10 is easy enough: just follow the steps below.
Open the main system application, Settings, using any way you prefer. For example, press the keyboard shortcut Windows + I to access the app directly.
In the main window of the Settings app, find and select the tab Time and language.
In the left panel, select Region.
In the right panel, find the section Region and use the nested menu Country or region to specify your new location if it differs from the current settings.
In the section Regional format use another nested menu to select proper formats to display date and time in Windows, if these differ for your time and region.
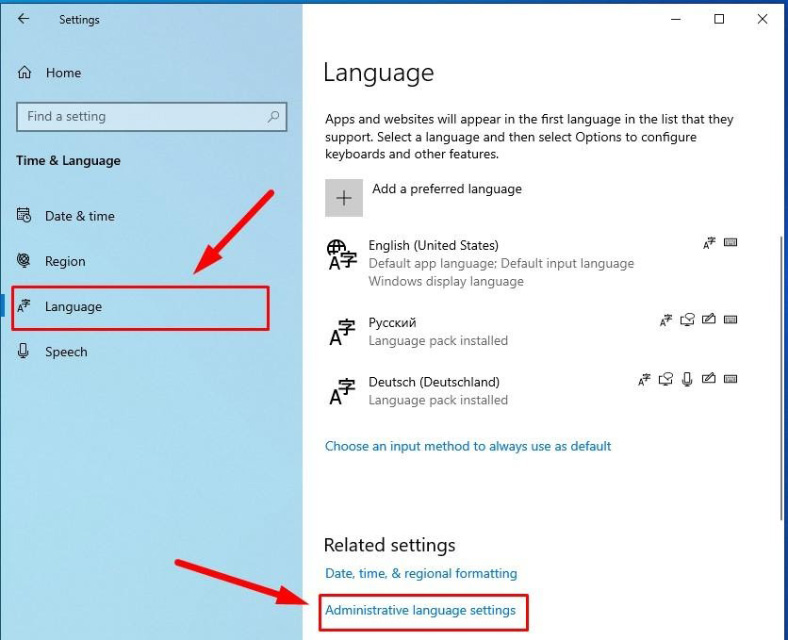
Now look at the left panel and jump to the tab Language again.
Use the scroll bar or the mouse wheel to find the section Related settings and click on the link Administrative language settings.
In the new pop-up Region window, jump to the tab Administrative and in the section Welcome screen and new user accounts hit the button Copy settings.
The new window will show you corresponding screen and account settings. In the section Copy your current settings to check the boxes for each option: Welcome screen and system accounts and New user accounts.
Click ОК one more time, and then restart the computer.
After all these steps, your computer will display proper regional settings specified according to your physical location.
Most of the time, people don’t change or install additional languages regularly for their personal needs. This opportunity to change language packs quickly is more often required in small or large companies that need to deal with customers having various language preferences.
Besides, this option would be useful for people who have to move to a different region and would like their regional settings to comply. Another scenario is buying a computer from another country when the required configuration is not available locally.
Also, you should remember that modifying language settings may disable some functions like Cortana because this service is not supported in certain regions.
Conclusion
Preferred display language is one of the easily customizable things in the operating system. If you ever need to change the language settings, use one of the methods described here to replace the language pack currently used by Windows 10 without having to reinstall it.
See the full article with all additional video tutorials. If you still have any questions, please ask in a comments. Also visit our Youtube channel, there are over 400 video tutorials.
Paging in windows operating system
Paging is a memory management scheme that eliminates the need for contiguous allocation of physical memory. This scheme permits the physical address space of a process to be non – contiguous.
- Logical Address or Virtual Address (represented in bits): An address generated by the CPU
- Logical Address Space or Virtual Address Space( represented in words or bytes): The set of all logical addresses generated by a program
- Physical Address (represented in bits): An address actually available on memory unit
- Physical Address Space (represented in words or bytes): The set of all physical addresses corresponding to the logical addresses
Example:
- If Logical Address = 31 bit, then Logical Address Space = 2 31 words = 2 G words (1 G = 2 30 )
- If Logical Address Space = 128 M words = 2 7 * 2 20 words, then Logical Address = log2 2 27 = 27 bits
- If Physical Address = 22 bit, then Physical Address Space = 2 22 words = 4 M words (1 M = 2 20 )
- If Physical Address Space = 16 M words = 2 4 * 2 20 words, then Physical Address = log2 2 24 = 24 bits
The mapping from virtual to physical address is done by the memory management unit (MMU) which is a hardware device and this mapping is known as paging technique.
- The Physical Address Space is conceptually divided into a number of fixed-size blocks, called frames.
- The Logical address Space is also splitted into fixed-size blocks, called pages.
- Page Size = Frame Size
Let us consider an example:
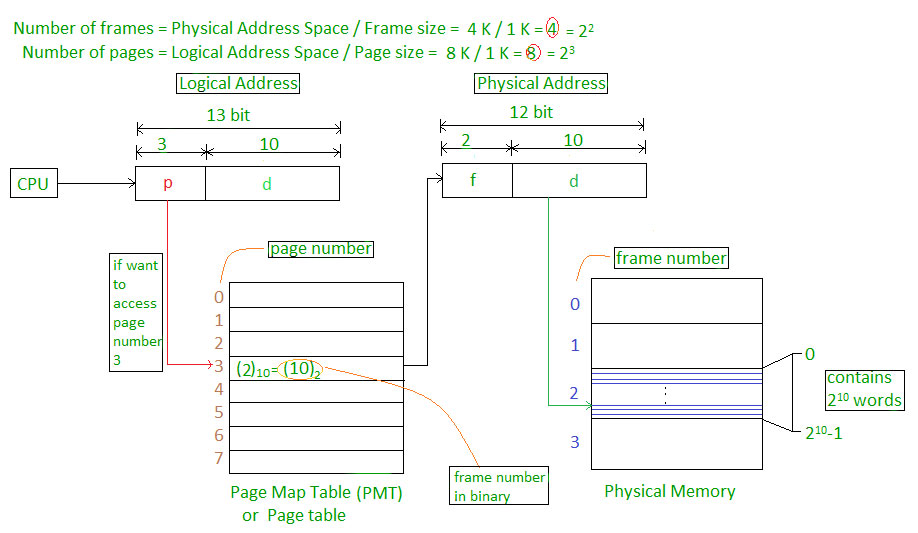
- Physical Address = 12 bits, then Physical Address Space = 4 K words
- Logical Address = 13 bits, then Logical Address Space = 8 K words
- Page size = frame size = 1 K words (assumption)
Address generated by CPU is divided into
- Page number(p): Number of bits required to represent the pages in Logical Address Space or Page number
- Page offset(d): Number of bits required to represent particular word in a page or page size of Logical Address Space or word number of a page or page offset.
Physical Address is divided into
- Frame number(f): Number of bits required to represent the frame of Physical Address Space or Frame number.
- Frame offset(d): Number of bits required to represent particular word in a frame or frame size of Physical Address Space or word number of a frame or frame offset.
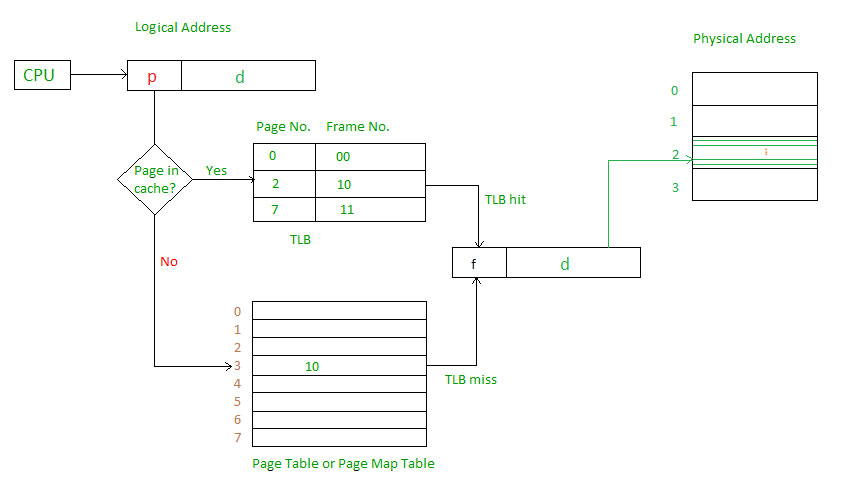
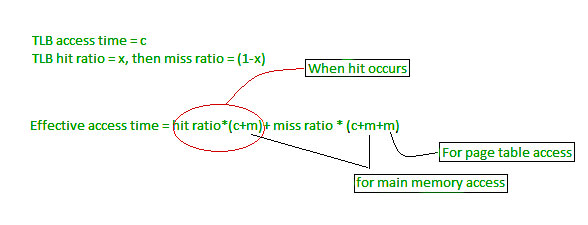
The hardware implementation of page table can be done by using dedicated registers. But the usage of register for the page table is satisfactory only if page table is small. If page table contain large number of entries then we can use TLB(translation Look-aside buffer), a special, small, fast look up hardware cache.
- The TLB is associative, high speed memory.
- Each entry in TLB consists of two parts: a tag and a value.
- When this memory is used, then an item is compared with all tags simultaneously.If the item is found, then corresponding value is returned.
Main memory access time = m
If page table are kept in main memory,
Effective access time = m(for page table) + m(for particular page in page table)
Questions asked in GATE on Paging:
GATE CS 2001 Question 46
This article has been contributed by Vikash Kumar. Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important CS Theory concepts for SDE interviews with the CS Theory Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready.
Paging in windows operating system
An operating system acts as an intermediary between the user of a computer and computer hardware. The purpose of an operating system is to provide an environment in which a user can execute programs in a convenient and efficient manner.
An operating system is software that manages computer hardware. The hardware must provide appropriate mechanisms to ensure the correct operation of the computer system and to prevent user programs from interfering with the proper operation of the system.
Operating System – Definition:
- An operating system is a program that controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface between the user of a computer and the computer hardware.
- A more common definition is that the operating system is the one program running at all times on the computer (usually called the kernel), with all else being application programs.
- An operating system is concerned with the allocation of resources and services, such as memory, processors, devices, and information. The operating system correspondingly includes programs to manage these resources, such as a traffic controller, a scheduler, a memory management module, I/O programs, and a file system.
Functions of Operating system – Operating system performs three functions:
- Convenience: An OS makes a computer more convenient to use.
- Efficiency: An OS allows the computer system resources to be used efficiently.
- Ability to Evolve: An OS should be constructed in such a way as to permit the effective development, testing, and introduction of new system functions at the same time without interfering with service.
The operating system as User Interface –
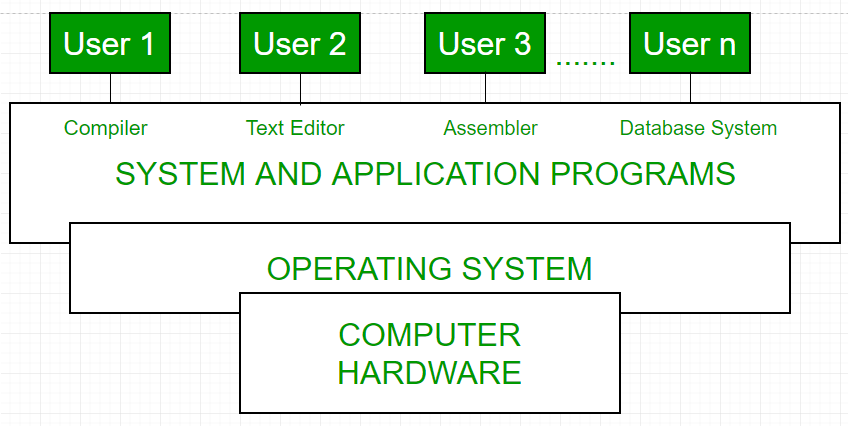
Every general-purpose computer consists of the hardware, operating system, system programs, and application programs. The hardware consists of memory, CPU, ALU, and I/O devices, peripheral devices, and storage devices. System program consists of compilers, loaders, editors, OS, etc. The application program consists of business programs, database programs.
Fig1: Conceptual view of a computer system
Every computer must have an operating system to run other programs. The operating system coordinates the use of the hardware among the various system programs and application programs for various users. It simply provides an environment within which other programs can do useful work.
The operating system is a set of special programs that run on a computer system that allows it to work properly. It performs basic tasks such as recognizing input from the keyboard, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, sending output to the display screen, and controlling peripheral devices.
OS is designed to serve two basic purposes:
- It controls the allocation and use of the computing System’s resources among the various user and tasks.
- It provides an interface between the computer hardware and the programmer that simplifies and makes it feasible for coding, creation, debugging of application programs.
The Operating system must support the following tasks. The task are:
- Provides the facilities to create, modification of programs and data files using an editor.
- Access to the compiler for translating the user program from high-level language to machine language.
- Provide a loader program to move the compiled program code to the computer’s memory for execution.
- Provide routines that handle the details of I/O programming.
I/O System Management –
The module that keeps track of the status of devices is called the I/O traffic controller. Each I/O device has a device handler that resides in a separate process associated with that device.
The I/O subsystem consists of
Drivers for specific hardware devices.
Assembler –
The input to an assembler is an assembly language program. The output is an object program plus information that enables the loader to prepare the object program for execution. At one time, the computer programmer had at his disposal a basic machine that interpreted, through hardware, certain fundamental instructions. He would program this computer by writing a series of ones and Zeros (Machine language), place them into the memory of the machine.
Compiler –
The High-level languages- examples are FORTRAN, COBOL, ALGOL, and PL/I are processed by compilers and interpreters. A compiler is a program that accepts a source program in a “high-level language “and produces a corresponding object program. An interpreter is a program that appears to execute a source program as if it was machine language. The same name (FORTRAN, COBOL, etc.) is often used to designate both a compiler and its associated language.
Loader –
A Loader is a routine that loads an object program and prepares it for execution. There are various loading schemes: absolute, relocating, and direct-linking. In general, the loader must load, relocate and link the object program. The loader is a program that places programs into memory and prepares them for execution. In a simple loading scheme, the assembler outputs the machine language translation of a program on a secondary device and a loader places it in the core. The loader places into memory the machine language version of the user’s program and transfers control to it. Since the loader program is much smaller than the assembler, those make more core available to the user’s program.
History of Operating system –
The operating system has been evolving through the years. The following table shows the history of OS.
| Generation | Year | Electronic device used | Types of OS Device |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | 1945-55 | Vacuum Tubes | Plug Boards |
| Second | 1955-65 | Transistors | Batch Systems |
| Third | 1965-80 | Integrated Circuits(IC) | Multiprogramming |
| Fourth | Since 1980 | Large Scale Integration | PC |
Types of Operating System–
- Batch Operating System- Sequence of jobs in a program on a computer without manual interventions.
- Time-sharing operating System- allows many users to share the computer resources. (Max utilization of the resources).
- Distributed operating System- Manages a group of different computers and makes appear to be a single computer.
- Network operating system- computers running in different operating systems can participate in a common network (It is used for security purposes).
- Real-time operating system – meant applications to fix the deadlines.
Examples of Operating System are –
- Windows (GUI based, PC)
- GNU/Linux (Personal, Workstations, ISP, File and print server, Three-tier client/Server)
- macOS (Macintosh), used for Apple’s personal computers and workstations (MacBook, iMac).
- Android (Google’s Operating System for smartphones/tablets/smartwatches)
- iOS (Apple’s OS for iPhone, iPad, and iPod Touch)
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important DSA concepts with the DSA Self Paced Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready.