- Create and format a hard disk partition
- Hard drives and partitions
- What’s new in WindowsВ 10
- Drive types
- Solid-state drives
- Advanced format drives
- Factory-encrypted hard drives
- Multiple hard drives
- Partitions
- System and utility partitions
- Microsoft reserved partition (MSR)
- Recovery partitions
- Data partitions
- BIOS/MBR-based hard drive partitions
- Partition Requirements
- System partition
- Windows partition
- Recovery tools partition
- Data partitions
- Partition layout
- System and utility partitions
- Sample files: configuring disk layout by using WindowsВ PE and DiskPart scripts
- Next steps
Create and format a hard disk partition
To create a partition or volume (the two terms are often used interchangeably) on a hard disk, you must be logged in as an administrator, and there must be either unallocated disk space or free space within an extended partition on the hard disk.
If there is no unallocated disk space, you can create some by shrinking an existing partition, deleting a partition, or by using a third-party partitioning program.
Open Computer Management by selecting the Start button. The select Control Panel > System and Security > Administrative Tools, and then double-click Computer Management.
In the left pane, under Storage, select Disk Management.
Right-click an unallocated region on your hard disk, and then select New Simple Volume.
In the New Simple Volume Wizard, select Next.
Enter the size of the volume you want to create in megabytes (MB) or accept the maximum default size, and then select Next.
Accept the default drive letter or choose a different drive letter to identify the partition, and then select Next.
In the Format Partition dialog box, do one of the following:
If you don’t want to format the volume right now, select Do not format this volume, and then select Next.
To format the volume with the default settings, select Next.
Review your choices, and then select Finish.
Note: When you create new partitions on a basic disk, the first three will be formatted as primary partitions. Beginning with the fourth, each one will be configured as a logical drive within an extended partition.
Hard drives and partitions
Learn methods of deploying WindowsВ to different drives, including hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), or virtual hard drives (VHDs), and with different partition layouts, including with data and utility partitions.
What’s new in WindowsВ 10
Use Compact OS and single-sourcing to save more space on the hard drive: Compact OS, single-sourcing, and image optimization.
Use the FFU image format to apply images faster to your devices: Deploy Windows using Full Flash Update (FFU)
In WindowsВ 10 for desktop editions (Home, Pro, Enterprise, and Education), we’ve changed the partition layout. While we still use a separate recovery tools image, Windows no longer needs a separate full-system recovery image to use push-button reset features. This can save several GB of drive space.
We now recommend that you place the Windows recovery tools partition immediately after the Windows partition. This allows Windows to modify and recreate the partition later if future updates require a larger recovery image.
If you use scripts to deploy Windows, check out the sample scripts we’ve created for different device firmware types (the newer UEFI-based BIOS, or the legacy BIOS). To learn more, see UEFI/GPT-based hard drive partitions and BIOS/MBR-based hard drive partitions.
It’s no longer necessary to run the Windows System Assessment Tests (WinSAT) on SSD drives. Windows detects SSD drives and tunes itself accordingly.
On UEFI/GPT-based drives, we’ve reduced the recommended size of the MSR partition from 128MB to 16MB.
Drive types
You can install Windows to a hard drive, such as a hard disk drive or a solid-state drive. For additional security, you can use hard drives that the factory has pre-encrypted. A single computer may contain multiple drives.
Solid-state drives
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a hard drive that uses solid-state memory to store persistent data. An SSD must have a minimum of 16В gigabytes (GB) of space to install Windows. For more information about drive space and RAM considerations, see Compact OS, single-sourcing, and image optimization.
NoteВ В It’s no longer necessary to run the Windows System Assessment Tests (WinSAT) on SSD drives. Windows now detects SSD drives and will tune itself accordingly.
Advanced format drives
You can use some Advanced Format Drives to provide additional drive space.
Advanced Format 512 emulation (512e) drives are supported on either BIOS-based or UEFI-based computers.
Advanced Format 4K Native (4Kn) drives are supported on UEFI-based computers only.
WarningВ В For Advanced Format 4K Native drives (4-KB-per-sector) drives, the minimum partition size is 260 MB, due to a limitation of the FAT32 file format. The minimum partition size of FAT32 drives is calculated as sector size (4KB) x 65527 = 256 MB. For more information, see Configure UEFI/GPT-Based hard drive partitions.
Factory-encrypted hard drives
To help protect your deployment environment, you can use a factory pre-encrypted hard drive to prevent unauthorized access before you install Windows or any other software. For more information, see Factory Encrypted Drives.
Multiple hard drives
If you install Windows on a device that has multiple hard drives, you can use the disk location path to make sure that your images are applied to the intended drives.
To do this, use the diskpart SELECT DISK= command to select each drive. For example:
NoteВ В The system drive might not appear as disk 0 in the DiskPart tool. The system might assign different numbers to drives when you reboot. Different computers that have the same drive configuration can have different disk numbers.
Partitions
You can divide your hard drive into multiple partitions. You can create separate system, recovery, Windows, or data partitions.
To enhance the security of the Windows partition or a data partition, you can use BitLocker to encrypt the partition. For more information, see BitLocker Drive Encryption.
The partition types must match the firmware of the computer. You can install Windows on hard drives that are based on any of the following types of firmware:
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS). Uses the Master Boot Record (MBR) partition structure.
Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) (Class 1): Uses the GUID Partition Table (GPT) partition structure.
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) Class 2: Uses the GPT partition structure. Also includes a compatibility support module (CSM) that enables you to use BIOS functions, including the MBR partition structure. This module can be enabled or disabled in the firmware.
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) Class 3: Uses the GPT partition structure.
To determine your system type, consult your hardware manufacturer.
System and utility partitions
A system partition is a partition that contains the hardware-specific files that are needed to load Windows.
By default, during Windows Setup, Windows stores these hardware-specific files in a separate partition. This enables the computer to use the following:
Security tools. Some security tools, such as BitLocker, require a separate system partition.
Recovery tools. Some recovery tools, such as Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE), require a separate system partition.
Multiple operating systems. If a computer has multiple operating systems, such as WindowsВ 10 for desktop editions and WindowsВ 7, the computer displays a list of operating systems. The user can then select which operating system to boot. When the system boot files are on a separate partition, it is easier to remove a Windows partition or replace the partition with a new copy of Windows.
We recommend adding system utility partitions before the Windows partition, because in the event that a full-system recovery is needed, this partition order helps to prevent the recovery tools from overwriting the system and utility partitions.
For information about how to configure system partitions while you apply images, see Capture and Apply Windows, System, and Recovery Partitions.
Microsoft reserved partition (MSR)
The MSR is used on UEFI/GPT systems, to support software components that formerly used hidden sectors.
For more information about configuring MSR partitions, see Configure UEFI/GPT-Based Hard Drive Partitions.
For more information about MSR partitions, see Windows and GPT FAQ
Recovery partitions
Add a separate partition for the Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE) at the end of the hard drive, just after the Windows partition. With this partition order, if future updates require adding to or replacing the Windows RE tools partition, Windows will be able to manage the partition size automatically.
For BIOS/MBR-based systems, it’s still possible to combine the Windows RE tools partition with the system partition. To save drive space, consider creating logical partitions to get around the four-partition limit. For more info, see Configure more than four partitions on a BIOS/MBR-based hard disk.
For WindowsВ 10 for desktop editions, it’s no longer necessary to create and maintain a separate full-system recovery image. Windows can perform a push-button reset using built-in tools.
Data partitions
You can include a separate data partition to enable easier maintenance for situations where either the primary operating system is likely to be replaced, or when multiple operating systems exist on the same device, such as WindowsВ 10 and WindowsВ 7. When a device has multiple hard drives, a data partition may be stored on another drive.
WarningВ В For typical single-drive configurations, we do not recommend that you use a separate data partition. There are two main reasons:
- The partition may not automatically protect data that is stored outside the user profile folders. For example, a guest user might have access to files in an unprotected data partition.
- If you change the default location of the user profile folders to any volume other than the system volume, you cannot service your image. The computer may not apply updates, fixes, or service packs to the installation. For a list of known issues related to changing the default folder locations, see Description of known issues with the FolderLocation settings.
BIOS/MBR-based hard drive partitions
Create custom partition layouts for your hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and other drives when deploying Windows to BIOS–based devices.
NoteВ В If you use a custom partition layout on WindowsВ 10 for desktop editions (Home, Pro, Enterprise, and Education), update the push-button recovery script so the recovery tools can recreate the custom partition layout when needed.
Partition Requirements
When you deploy Windows to a BIOS-based device, you must format hard drives by using an MBR file system. Windows does not support the GUID partition table (GPT) file system on BIOS-based computers.
An MBR drive can have up to four standard partitions. Typically, these standard partitions are designated as primary partitions. For information about how to create additional partitions beyond this limit, see Configure More than Four Partitions on a BIOS/MBR-Based Hard Disk.
System partition
Each bootable drive must contain a system partition. The system partition must be configured as the active partition.
The minimum size of this partition is 100 MB.
Windows partition
- This partition must have at least 20 gigabytes (GB) of drive space for 64-bit versions, or 16 GB for 32-bit versions.
- The Windows partition must be formatted using the NTFS file format.
- The Windows partition must have 16 GB of free space after the user has completed the Out Of Box Experience (OOBE) and Automatic Maintenance has completed.
- This partition can have a maximum of 2 terabytes (TB) of space. Software tools to extend the visible partition space beyond 2 TB are not supported on BIOS because they can interfere with software solutions for application compatibility and recovery.
Recovery tools partition
Create a separate recovery partition to support automatic failover and to support booting WindowsВ BitLocker Drive Encryption-encrypted partitions.
We recommend that you place this partition in a separate partition, immediately after the Windows partition. This allows Windows to modify and recreate the partition later if future updates require a larger recovery image.
The Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE) tools require additional free space:
- A minimum of 52 MB is required but 250 MB is recommended, to accomodate future updates, especially with custom partition layouts.
When calculating free space, note:
- The recovery image, winre.wim, is typically between 250-300MB, depending on what drivers, languages, and customizations you add.
- The file system itself can take up additional space. For example, NTFS may reserve 5-15MB or more on a 750MB partition.
Data partitions
The recommended partition layout for WindowsВ 10 does not include utility or data partitions.
However, if utility or data partitions are required, they should be placed either before the Windows partition or after the Windows RE partition. By keeping the Windows and recovery partitions together, then when future updates of Windows RE area available, Windows will be able to grow the Windows RE partition by shrinking the Windows partition.
This layout makes it more difficult for end users to remove the data partition and merge the space with the Windows partition. For example, the Windows RE partition may need to be moved to the end of the unused space reclaimed from the data partition, so that the Windows partition can be extended. WindowsВ 10 does not include functionality or utility to facilitate this process. However, manufacturers can develop and provide such a utility if PCs are shipped with data partitions.
Each partition can have a maximum of 2 terabytes (TB) of space.
If you’re going to be adding more than four total partitions to the disk, see Configure More than Four Partitions on a BIOS/MBR-Based Hard Disk for more info.
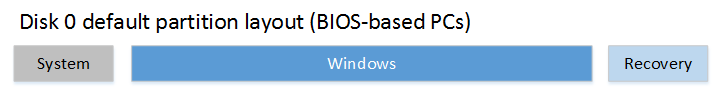
Partition layout
If you install Windows using a bootable USB key made by Windows Imaging and Configuration Designer (ICD), it creates the following layout by default: a system partition, a Windows partition, and a recovery tools partition.
System and utility partitions
By default, system partitions do not appear in File Explorer. This helps protect end users from accidentally modifying a partition.
To keep system and utility partitions from being reset, use type 0x27. Do not use any of the following types: 0x7, 0x0c, 0x0b, 0x0e, 0x06, and 0x42.
To set partitions as utility partitions
- When you are deploying Windows by using Windows ICD, the partition type will be set automatically.
- When you are deploying Windows by using the DiskPart tool, use the set command after you create the partition.
To verify that system and utility partitions exist
- Click Start, right-click This PC, and then click Manage. The Computer Management window opens.
- Click Disk Management. The list of available drives and partitions appears.
- In the list of drives and partitions, confirm that the system and utility partitions are present and are not assigned a drive letter.
Sample files: configuring disk layout by using WindowsВ PE and DiskPart scripts
For image-based deployment, boot the PC to Windows PE, and then use the DiskPart tool to create the partition structures on your destination PCs.
NoteВ В In these DiskPart examples, the partitions are assigned the letters: System=S, Windows=W, and Recovery=R.
Change the Windows drive letter to a letter that’s near the end of the alphabet, such as W, to avoid drive letter conflicts. Do not use X, because this drive letter is reserved for Windows PE. After the device reboots, the Windows partition is assigned the letter C, and the other partitions don’t receive drive letters.
If you reboot, WindowsВ PE reassigns disk letters alphabetically, starting with the letter C, without regard to the configuration in Windows Setup. This configuration can change based on the presence of different drives, such as USB flash drives.
The following steps describe how to partition your hard drives and prepare to apply images. You can use the code in the sections that follow to complete these steps.
To partition hard drives and prepare to apply images
Save the following code as a text file (CreatePartitions-BIOS.txt) on a USB flash drive.
Use WindowsВ PE to boot the destination computer.
Clean and partition the drive. In this example, F is the letter of the USB flash drive.
If you use a custom partition layout on WindowsВ 10 for desktop editions, update the push-button recovery script so the recovery tools can recreate the custom partition layout when needed.
Important To avoid bare metal recovery boot issues due to partition size, it is recommended that manufacturers allow the bare metal recovery feature’s auto generation script to create the partition used for the recovery WIM. If manufacturer’s wish to use a custom DISKPART script for partition creation, the recommended minimum partition size is 990MB and a minimum of 250MB of free space.
Next steps
Use a deployment script to apply the Windows images on the newly created partitions. For more information, see Capture and Apply Windows, System, and Recovery Partitions.