- How to set the path and environment variables in Windows
- Setting the path and variables in Windows 10
- Setting the path and variables in Windows 8
- Setting the path and variables in Windows Vista and Windows 7
- Setting the path and variables in Windows 2000 and Windows XP
- What is the default Windows %PATH%?
- Setting path in the MS-DOS and Windows command line
- Системная переменная окружения PATH в Windows
- Для чего используется
- Пример
- Добавить директорию в PATH
- Изучить содержимое PATH
- Ошибки
- -bash: syntax error near unexpected token `(‘
- Postgesql
- How to Add to Windows PATH Environment Variable
- Add Directories to PATH Variable
How to set the path and environment variables in Windows
Setting the path and environment variables differs depending on the version of the Windows operating system you have on your computer. Choose a link below for your version of Windows.
Administrator privileges are usually required to modify the path and environment variables.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 10
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to access the Power User Task Menu.
- In the Power User Task Menu, select the System option.
- In the Settings window, scroll down to the Related settings section and click the System info link.
- In the System window, click the Advanced system settings link in the left navigation pane.
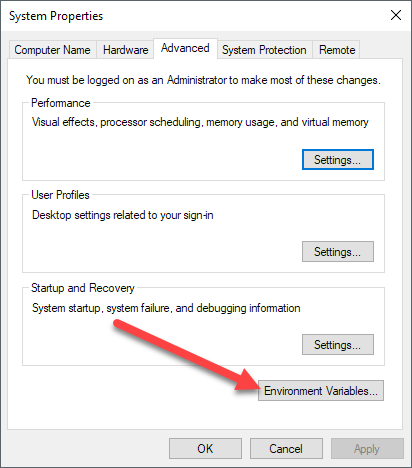
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variablesbutton near the bottom of that tab.
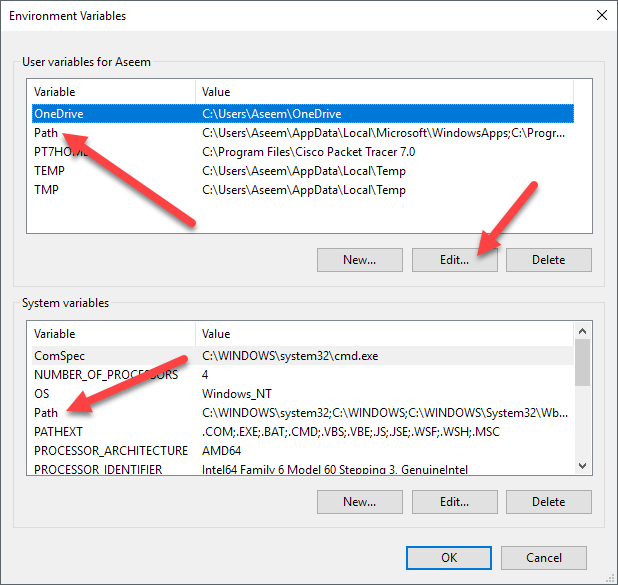
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the variable name and variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 8
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to access the Power User Task Menu.
- In the Power User Task Menu, select the System option.
- Click the Advanced System Settings link in the left column.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variablesbutton near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the variable name and variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows Vista and Windows 7
- On the desktop, right-click the Computer icon and select Properties. If you don’t have a Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties.
- Click the Advanced System Settings link in the left column.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variablesbutton near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the Variable name and Variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 2000 and Windows XP
The path is now managed by Windows 2000 and Windows XP and not the autoexec.bat or autoexec.nt files, as was done with earlier versions of Windows. To change the system environment variables, follow the steps below.
- From the desktop, right-click My Computer and click Properties. If you don’t have a My Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the My Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties.
- In the System Propertieswindow, click the Advancedtab.
- In the Advanced section, click the Environment Variablesbutton.
- In the Environment Variables window (as shown below), highlight the Path variable in the System Variable section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the Variable name and Variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
What is the default Windows %PATH%?
The path is based on programs installed on the computer, so there is no «default path.» However, the Windows minimum path is often the path below.
Keep in mind that as you install programs, the path is updated with the paths for the newly installed programs. So, if you have erased your path after installing other programs, those programs may be affected.
Setting path in the MS-DOS and Windows command line
To view and set the path in MS-DOS and in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Источник
Системная переменная окружения PATH в Windows
Если Вам нужно настроить PATH в Linux — перейдите сюда
| Для чего используется | |
| Пример | |
| Добавить директорию в PATH | |
| Изучить содержимое PATH | |
| Ошибки | |
| Postgesql |
Для чего используется
Когда Вы выполняете какую-либо команду в консоли, система ищет соответствие между названием этой команды и программой, которую можно выполнить.
Искать по всему жёсткому диску было бы слишком долго, поэтому поиск осуществляется только по некоторым директориям.
Список этих особых директорий хранится в системной переменной PATH.
Пример
Предположим, что возникла необходимость запускать какую-то программу, например Firefox , непосредственно из командной строки.
Без предварительной подготовки ввод Firefox в консоль выдаст ошибку.
‘firefox’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
Чтобы решить эту проблему нужно добавить директорию с испоняемым файлом firefox в PATH
Добавить директорию в PATH
Быстрый способ перейти к редактированию PATH — нажать клавишу Win и ввести в поиск env
Правый клик на Этот Компьютер (This PC) → Свойства (Properties)
Дополнительные параметры системы (Advanced system settings)
Дополнительно (Advanced) → Переменные среды (Environment Variables)
Если хотите менять для всей системы, то в окошке «Переменные среды» (System Variables) найдите строку PATH в блоке «Системные переменные» (System variables) выделите кликом и нажмите кнопку «Изменить. » (Edit. )
Если хотите менять только для своего пользователя, то делайте это в блоке «Переменные среды пользователя %USERNAME%» (User variables for %USERNAME%)
Создайте новый путь (New)
Введите адрес директории в которой лежит нужная программа. В нашем случае это
C:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox
Перезапустите консоль или открываем новую и пишем там firefox.
Браузер должен запуститься.
Изучить содержимое PATH
В PowerShell достаточно выполнить
Name Value —- —— Path C:\Windows\system32;C:\Windows;C:\Windows\System32\Wbem;C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPo.
В cmd.exe посмотреть список переменных окружения можно выполнив команду set без параметров.
Выдача содержит системные переменные и переменные пользователя а также дополнительную информацию. Содержимое PATH выделено зелёным.
Ошибки
-bash: syntax error near unexpected token `(‘
Скорее всего Вы пытаетесь добавить в unix PATH адрес из Windows, c пробелами, скобками и так далее.
andrey@olegovich-10:/usr/share$ export PATH=/mnt/c/Program Files (x86)/Common Files/Oracle/Java/javapath_target_1128437:$PATH
-bash: syntax error near unexpected token `(‘
Для решения этой проблемы Вам нужно экранировать пробелы и скобки. Если импортируется много путей и ввод очень длинный — немного проще записать PATH=$PATH:/путь , если Вам подходит запись в конец.
Также нужно помнить, что все лишние пробелы сломают импорт — для проверки можно сделать весь скрипт в одну строку в текстовом редакторе.
Также стоит помнить, что если Вы работаете в bash под Windows , то переменные окружения нужно задавать через Windows.
andrey@olegovich-10:/usr/share$ export PATH=$PATH:/mnt/c/Program\ Files\ \(x86\)/Common\ Files/Oracle/Java/javapath_target_1128437
Postgesql
Приведу пример для использования psql из bash под Windows — это может пригодиться если Вы хотите временно добавить путь к psql в PATH чтобы запустить Postrgres скрипт.
Источник
How to Add to Windows PATH Environment Variable
Works for Windows 10 or 7
If you’re a coder or programmer, you probably spend a decent amount of time using the command prompt to execute programs or compile code. In order to complete those tasks, you most likely have to use a command from a library or software package installed (like Python) on your system.
By default, most of these programs will add their own custom shortcuts to the Windows environment variables. The most used environment variable in Windows is probably the PATH variable. It basically allows you to run any executables that are located inside the paths specified in the variable at the command prompt without having to give the full path to the executable.
In this article, I’ll show you how you can add more paths to the Windows PATH variable in case you want to run executables from your own custom directories. It’s worth noting that the procedure below is for Windows 10, but it’s almost exactly the same for Windows 7 also.
Add Directories to PATH Variable
To get started, right-click on the Computer or This PC icon on the desktop and select Properties. If you don’t have that icon on your desktop already, you can add any missing desktop icons easily.
On the System dialog page, you’ll see an Advanced system settings link on the left-hand side.
This will bring up the System Properties dialog, which should already be open to the Advanced tab. Go ahead and click on the Environment Variables button at the very bottom.
On the Environment Variables dialog, you’ll see two sets of variables: one for user variables and the other for system variables. Both lists have the PATH variable, so you have to decide which one to edit.
If you only need the commands for your own user account, then edit the user variable. If you need it to work across the computer system regardless of which user is logged in, then edit the system variable. Click on Path and then click on Edit.
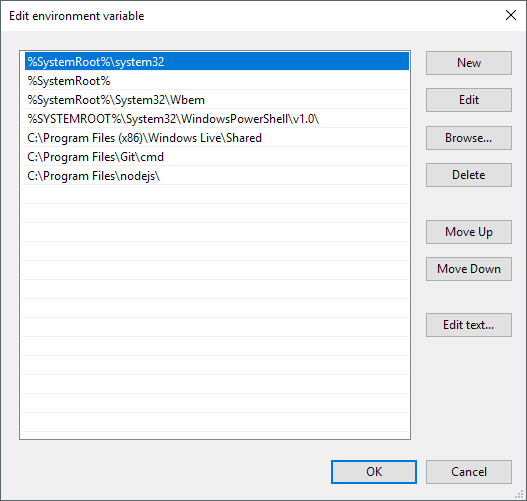
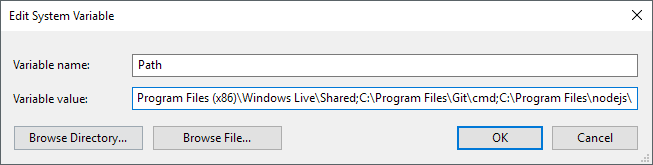
On the Edit environment variable dialog, you’ll see a list of all the paths that are currently in the PATH variable. As you can see, Node.js and Git already added their paths so that I can run Git commands and Node.js commands from anywhere while in the command prompt.
To add a new path, simply click on New and it’ll add a new line to the bottom of the list. If you know the path, simply type it in or copy and paste it. If you prefer, you can also click Browse and then navigate to the desired path.
To edit any path, simply select it and then click on the Edit button. You can also delete paths using the Delete button. Note that you can also move items up and down on the list. When you type a command at the command prompt, Windows has to search through each directory stored in the PATH variable to see if that executable exists or not. If you want your executable to be found faster, just move that path up to the top of the list.
This can also come in handy if you have multiple versions of the same command in different paths and need to have one run instead of the other. The one that shows up higher in the list will be run when you type in the command.
Lastly, if you click on Edit text, it will load a dialog where you can edit the Path variable using the old interface where all the paths are listed in one text box.
That’s all there is to it! If you want to learn more about environment variables, make sure to check out my post on how to create your own custom environment variables. Enjoy!
Founder of Help Desk Geek and managing editor. He began blogging in 2007 and quit his job in 2010 to blog full-time. He has over 15 years of industry experience in IT and holds several technical certifications. Read Aseem’s Full Bio
Источник