- Ping – setting don’t fragment bit in Linux/FreeBSD/Solaris/Cisco/Juniper
- Команда ping в Linux
- Как работает ping?
- Команда Ping
- Как пользоваться Ping?
- Выводы
- 15 Linux ping command examples for network diagnostics
- What is the use of the ping command?
- How does ping command work?
- Can I ping with a proxy?
- Ping IPv6 protocol
- Ping a specific port
- Ping with time
- Ping all the hosts on a given subnet
- How to end a ping?
- End after a specific count
Ping – setting don’t fragment bit in Linux/FreeBSD/Solaris/Cisco/Juniper
Ping.
Many times while debugging network problems of various kinds you need to send some packets of desirable size and don’t fragment bit being set. I list below how to do it for the different equipment/OSes. Let’s start with the most popular operating system among network folks – Linux:
Linux
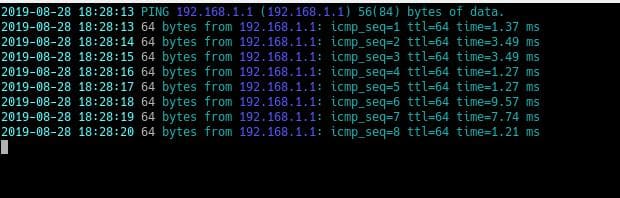
By default ping in any Linux-based system (It also means any distribution – Slackware, Ubuntu, CentOS etc) is sent with Don’t fragment (df) bit set . You don’t need to add any command line switches for that. Here is what you get by default ping in Linux:
Defaults:
Don’t fragment bitВ (in echo request)В — set
Ip packet size – 84 bytes
Sending intervalВ — 1 second
Some examples.
-В sending station:
-В В receiving station:
[root@darkstar
]#tcpdump -s 1500 -n -vv icmp
To change sent packet size: -sВ , bytes (8 bytes of ICMP header will be added automatically).
Sending host:
[root@darkstar
]#ping 10.99.99.158 -s 1300
Receiving host:
freeBSD#tcpdump -n -v -s 1500 icmp
To change sending interval (mostly used together with large packet size) :
-iВ
Sending host:
[root@darkstar
]#ping -s 1300 -i 0.2 10.99.99.158
Receiving host:
freeBSD#tcpdump -n -v -s 1500 icmp
To force Linux to send pings with DF bit cleared (i.e. not set):
ping –M don’t
]#ping -s 1300 -M dontВ 10.99.99.158
freeBSD#tcpdump -n -v -s 1500 icmp
SideNote: FreeBSD ping has a nice add-on (see below) – sweeping size of the packets, while Linux doesn’t have such extra feature, Below is script to emulate it on Linux:
Here:
size – size of data in ICMP packet (bytes);
-I 0.5 – interval of 5 seconds (optional);
-c 3 — number of pings in each size session (NOT optional – or you will enter an endless loop which even Ctrl-C won’t be able to stop )
See it in action:
[root@darkstar
]#awk ‘ BEGINВ
Don’t fragment bit — not setВ ;В use df-bit to set
Running with defaults:
Receiving host:
[root@darkstar
]# tcpdump -n -vВ -s 1500 icmp
Set df bit and size of the packet (Note – when you set size of the ping you set IP packet size and not ICMP data size as in Nix systems).
Repeat count is set to 3 .
Tokyo#ping 191.91.21.41 size 1300 df-bit rep 3
Receiving host:
[root@darkstar
]# tcpdump -n -vВ -s 1500 icmp
Sweeping ping size.
This feature is available from extended ping menu:
Juniper routers (JunOS):
Defaults:
Ip packet size : 84 bytes
Don’t fragment bit – not set; use do-not-fragment to set
IntervalВ — 1 sec;В use interval to change
Sending pings with df bit set and size 1470 bytes
root@Juniper> ping 192.168.37.29 do-not-fragment size 1470
If packet size is too large and df is set you get this:
root@Juniper> ping 192.168.37.29 do-not-fragment size 13000
Источник
Команда ping в Linux
Всем знакомы ситуации, когда интернет на компьютере неожиданно разрывается, такое поведение можно наблюдать при использовании ADSL модемов, Wifi на большом расстоянии, GSM и других подобных ненадежных технологий. Быстро выяснить есть ли на компьютере интернет можно с помощью утилиты ping.
Но область ее применения намного шире, ее используют сетевые администраторы для проверки доступности удаленного узла в сети, она применяется в различных скриптах и многих других местах. В этой статье будет рассмотрена команда ping в Linux, мы поговорим о том, как пользоваться утилитой, как она работает, рассмотрим ее опции и возможности.
Как работает ping?
Утилита ping — это очень простой инструмент для диагностики сети. Она позволяет проверить доступен удаленный хост или нет и все. Для этого утилита проверяет, может ли хост отвечать на сетевые запросы с помощью протокола ICMP.
Надеюсь, не нужно говорить, что все данные по сети передаются в виде небольших пакетов. Программа передает небольшой пакет с данными ICMP и ожидает получить обратно пакет ответа, если получает, то считается что удаленный узел доступен. ICMP или Internet Control Message Protocol — это надстройка над протоколом IP, которая используется для передачи служебных сообщений и сообщений и ошибках.
Протокол ICMP может передавать только два типа пакетов — это сообщения с отчетами про ошибки и сообщения запросов. В свою очередь, сообщения запросов делятся на:
- Сообщение эхо-запрос;
- Сообщение эхо-ответ.
Попытаемся разобраться что делает команда ping. Итак, когда вы отправляете запрос ping удаленному узлу, утилита устанавливает для каждого пакета уникальный идентификатор, а также TTL и время отправки пакета. Если хост доступен, он отправляет ответ, на основе времени отправки утилита может вычислить время прохождения пакета туда и обратно. Затем отправляется следующий пакет. В конце рассчитывается общее количество отправленных и принятых пакетов, процент потерь и другие данные.
Команда Ping
Теперь нам осталось немного попрактиковаться. Но перед тем, как мы перейдем к практике давайте рассмотрим синтаксис команды и ее опции. Синтаксис довольно прост:
$ ping опции адрес_узла
Формат команды ping очень прост. В качестве адреса узла можно передавать как ip адрес, так и доменное имя. Опции настраивают поведение утилиты. Рассмотрим основные из них:
- -4 — использовать только ipv4 (по умолчанию);
- -6 — использовать только ipv6;
- -A — адаптивный режим, время между отправками пакета адаптируется к времени передачи и приема пакета, но не меньше чем 200мс;
- -b — разрешить ping широковещательного адреса;
- -с — количество пакетов, которые нужно отправить;
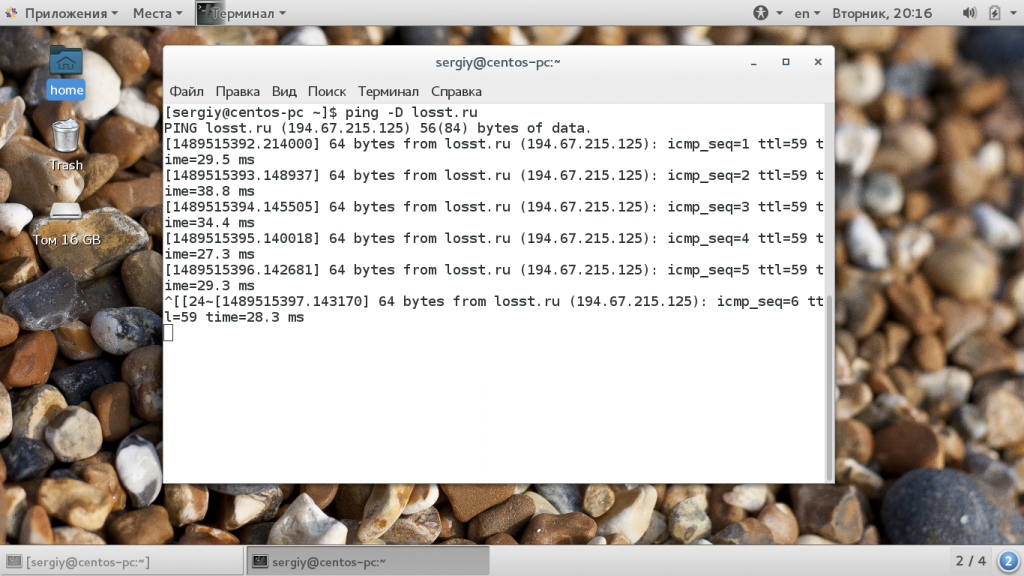
- -D — выводить время в виде UNIX timestamp;
- -f — режим флуда, в этом режиме пакеты передаются без задержек, может использоваться для совершения DoS атак на отдельные узлы. Количество точек, которые выводит утилита обозначает количество потерянных пакетов;
- -i — интервал в секундах между отправкой пакетов;
- -I — использовать этот сетевой интерфейс для отправки пакетов;
- -l — режим перегрузки, отправляется очень много пакетов и система не следит за ответными пакетами;
- -n — не получать домены для ip адресов;
- -r — игнорировать таблицы маршрутизации и отправить пакет на указанный интерфейс;
- -s — размер одного пакета;
- -t — установить TTL вручную;
- -v — более подробный вывод.
Теперь, когда мы рассмотрели основные параметры команды ping и ее синтаксис, пришло время практики, дальше поговорим о том, как сделать ping определенного узла в Linux.
Как пользоваться Ping?
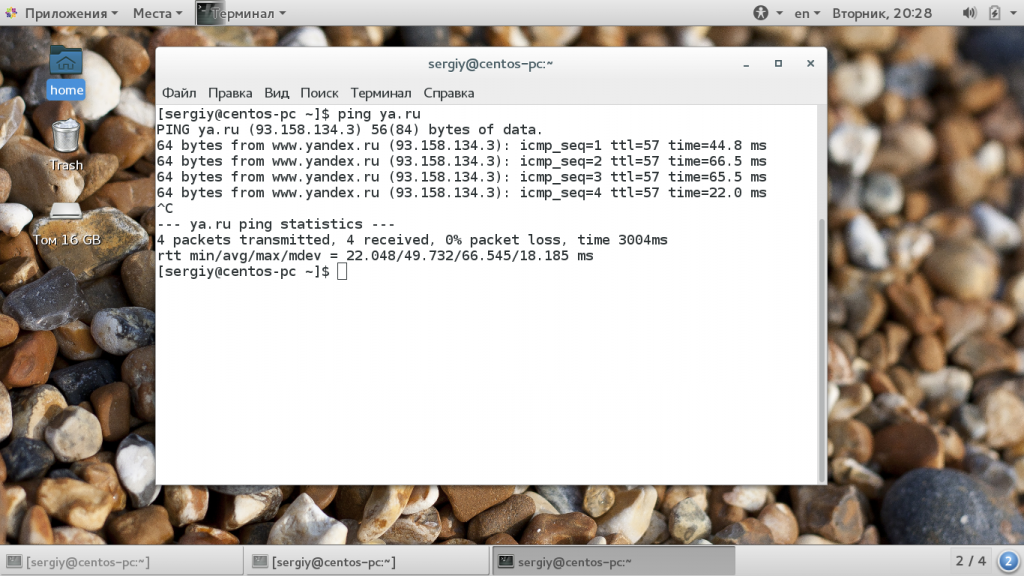
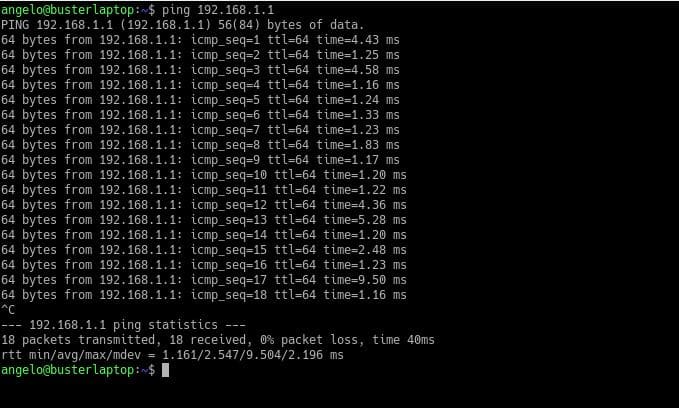
Для проверки работоспособности сети часто используется программа ping любого сайта, который всегда доступен, например, google.com или еще проще и короче ya.ru. Вам будет достаточно передать утилите в параметрах этот адрес, она сама найдет ip и сделает все нужное:
Как я и писал выше, для каждого пакета выводится уникальный идентификатор icmp_seq, количество узлов до целевого узла ttl и время, потраченное на доставку пакета time. Чтобы остановить ping нажмите сочетание клавиш Ctrl+C. В конце утилита вывела общую статистику:
- packets transmitted — отправлено пакетов;
- received — получено пакетов;
- packet loss — процент потерянных пакетов;
- time — обще время работы;
rtt min/avg/max/mdev — минимальное время/среднее время/максимальное время/квадратичное отклонение.
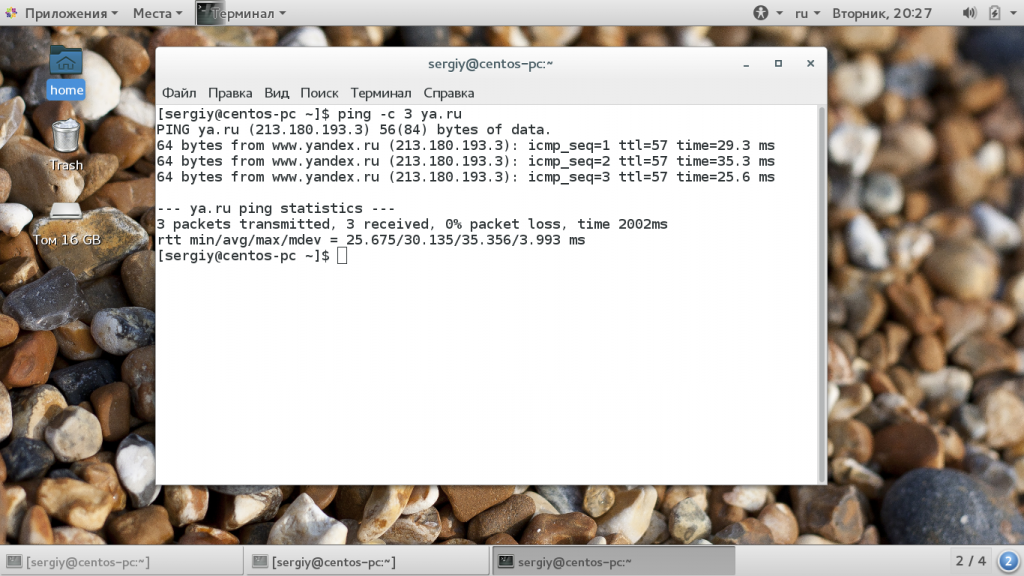
Если выполнение команды ping не остановить, то пакеты могут отправляться очень долгое время, это создает дополнительную нагрузку на сервер и поэтому не желательно. Вы можете сразу в вызове команды ограничить количество отправляемых пакетов с помощью опции -c:
Точно так же как мы выполняем ping для домена, можно указать ip адрес напрямую. Это позволяет проверить есть ли сеть когда неверно настроены серверы DNS. Например:
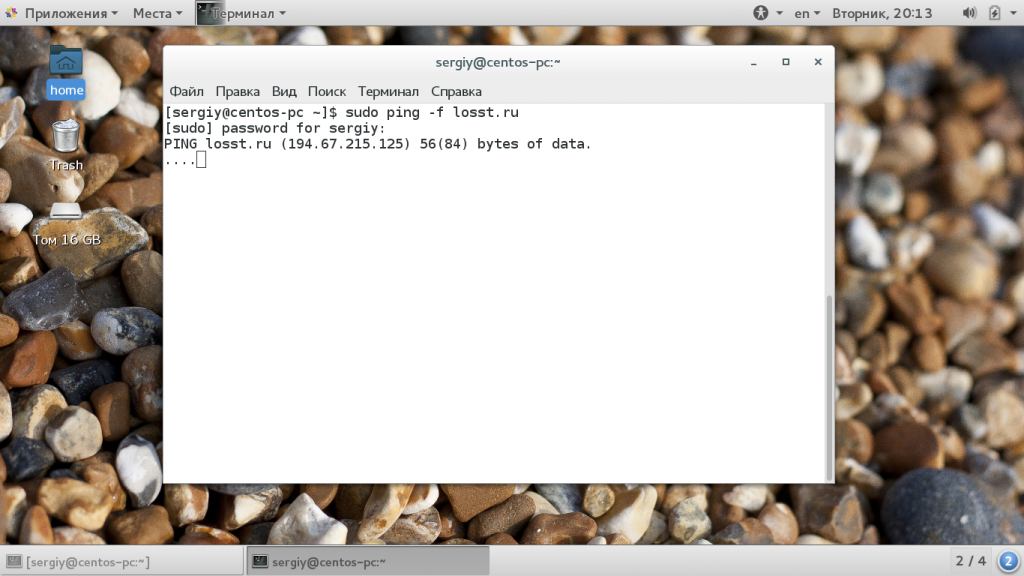
Следующий вид отправки ping сообщений, это ping флуд. С помощью таких пакетов можно выполнить нагрузочное тестирование канала или даже заглушить интернет соединение на одной из машин. Но эти функции можно использовать только с правами суперпользователя. Для организации ping флуда укажите опцию -f:
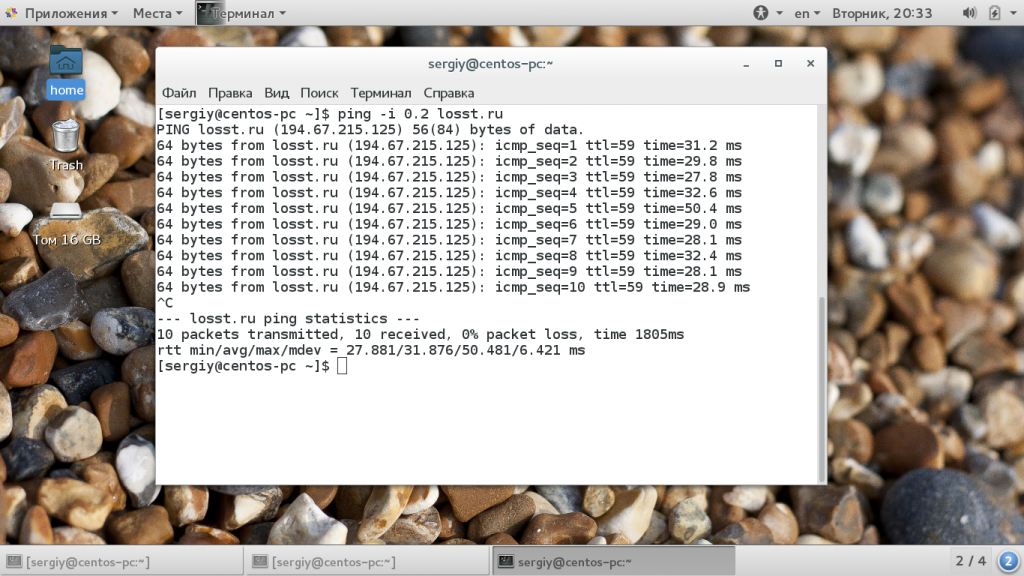
По умолчанию, в обычном режиме, каждый следующий пакет отправляется, когда получен ответ на предыдущий. Но вы можете сами установить интервал между отправкой пакетов -i:
ping -i 0.2 losst.ru
Здесь программа ping выполняет так званный, настраиваемый флуд, вы указываете с какой интенсивностью нужно отправлять пакеты. С помощью опции -D вы можете увидеть Unix Timestamp для каждого сообщения:
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели что такое команда ping в linux, как ее использовать основные параметры и методы применения. Этот очень простой инструмент можно применять для тестирования неполадок сети и их исправления. В этом плане утилита может стать незаменимой.
Источник
15 Linux ping command examples for network diagnostics
Thanks to Linux, we have access to many tools that facilitate networking administration & diagnostics. In this sense, the Linux ping command is one of the most useful tools for sysadmins and network administrators.
Its basic function is to determine if one host of the network is reachable or not. However, in this post, we will address other more advanced capabilities of the Linux Ping command.
Table of Contents
What is the use of the ping command?
The ping command is one of the most basic tools for working with networks. Its purpose is to diagnose network connection errors.
In this way, it is possible to know if a network node has lost connectivity. On the other hand, it is also useful to perform other diagnostic tasks such as the following:
- Measure the time taken by two network nodes to communicate.
- We will also be able to identify the IP address of a specific host. We can use this feature on both the Internet and in a private network.
- The ping command can be used in a bash script to perform automatic checks with network nodes.
- It allows knowing if there is a connection with specific equipment.
As you can see, it is a necessary command for the administration of networks and servers.
How does ping command work?
In Linux, the functioning of the ping command is quite simple to explain. The command sends a series of small packets to a specific node.
You can test this node using either the IP address or the hostname. Then, after you send the packet, the command verifies and measures the time it takes to receive a response from the destination node.
As you may expect, the response time may be affected due to conditions such as the geographical location between the connection points or any piece of the hardware used between the two nodes.
For example, in wired private networks, the command will get better times than with a network with multiple routers or bridges.
However, the information that the command will generate will judge whether the network is in good or bad condition.
The syntax of the command is as follows:
Some of the most useful and used options of the ping command are the following:
- -c: With this option, you can specify how many packets to send.
- -s: This option allows you to change the default size of the packets.
- -v: verbose mode.
- -w: Specifies a time in seconds that the execution of the command will end. No matter how many packets the command has sent or received.
- -i: With this option, you can specify the network interface to use.
The destination node can be specified by an IP address or a hostname.
Can I ping with a proxy?
A proxy is a server or application that acts as an intermediary for the connection between two points on a network. It is the man in the middle who makes the request directly to another node.
The problem is that the Ping command requires a direct network connection between the nodes.
Therefore, the Ping command generally cannot function properly if there is a proxy behind it.
A possible solution is that many websites offer the Ping command service. On the other hand, for some tasks of the ping command, it is possible to use the curl command. Also, you can use a VPN so that it will hide your IP.
However, in some Linux distributions, this command is not installed by default. First, verify it and then install it if it is not installed.
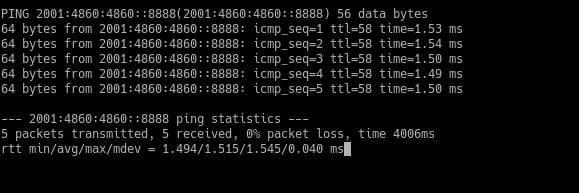
Ping IPv6 protocol
Normally, when using the Ping command, we use IP addresses with the IPv4 protocol. However, with the advent of the IPv6 protocol, it is increasingly common to notice addresses in this format.
The Linux kernel supports the IPv6 protocol since version 2.2, so all Linux distributions currently support it.
The basic syntax is as follows:
On old versions, there was ping6 command. On recent versions of Linux, ping6 doesn’t exist anymore, and its functionality has been merged into ping, and it works the same way as you saw.
The basic syntax is as follows:
With the option -c, we can specify the number of packets to send and with -i for the network interface you will use. For example:
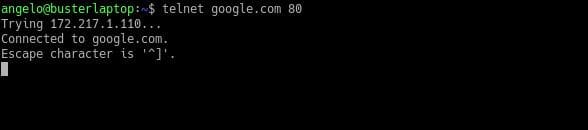
Ping a specific port
Sometimes we want to know if a specific port on a node is active. However, the ping command does not provide this functionality, but it is possible to do it with the telnet command that is installed by default on Linux.
To do this, just use the following syntax:
In this way, it is possible to ping a specific port of a network node in a primitive way.
Ping with time
Although the ping command displays useful information, it may be a little simple. However, it is possible to modify the operation of the command a little, to make it show the date the packet is sent.
This can make the information pleasing to the eye and might be useful for scripts and logs.
This syntax is sufficient to do it. However, you need to install the ccze package.
As you can see, it shows the time for every packet sent.
Ping all the hosts on a given subnet
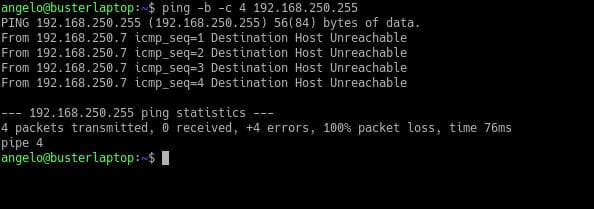
You can send a ping signal to all hosts on a network or subnet. For this, it is enough to add the option -b and ping the broadcast IP address of any network which ends with 255.
So if the destination is unreachable, maybe they block ICMP packets sent by the ping command, or maybe there is a network problem or a problem on the routing table.
How to end a ping?
By default, the ping command on Linux continuously sends test packets to hosts. However, once the information is available, it becomes necessary to terminate the execution of the ping command.
To do so, simply press the following keys:
This way, the command will immediately stop working.
End after a specific count
You can limit the count of packets to 10 or whatever. When it finishes sending the ten packets, it will stop.
Источник