- Ping with mtu windows
- Как сменить MTU через реестр
- Как узнать значение MTU
- Windows
- Linux
- ip address
- ifconfig
- FreeBSD
- Провайдера
- Ping MTU – Find a Path’s MTU using PING Command
- How Does Path MTU Discovery Work?
- How do routers discover MTU in a path?
- Simulating the Path MTU Discovery Process
- How to Find the Path’s MTU with Ping?
Ping with mtu windows
Всем привет! Сегодня хочу рассказать как изменить MTU в Windows. Напомню MTU — Maximum transmission unit (MTU) — это максимальный объём данных, который может быть передан протоколом за одну итерацию. К примеру, Ethernet MTU равняется 1500, что означает, что максимальный объём данных, переносимый Ethernet фреймом не может превышать 1500 байт. Очень часто рядовым пользователям приходится его менять, когда необходимо раздать свой интернет
У каждого провайдера или сетевого устройства, данное значение может быть свое. например 1492 очень часто встречается на роутерах Dlink, и если устройству на устройство будет например приходить пакет 1500 байт, а у него мту настроено 1492, то часть пакетов будут приходить битые, глюки могут выражаться, например у вас не полностью будут отображаться интерфейс сайта, что то загрузилось, а что то нет, первый признак, проверить Maximum transmission unit.
Итак посмотрим какое значение mtu у гугла, откроем командную строку и вводим следующую команду.
Как изменить значение MTU в Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7-01
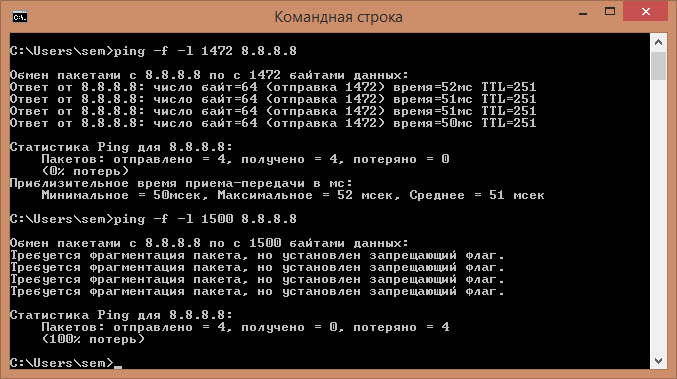
И смотрим ответ, если ответ получен без потери пакетов, то увеличиваем значение, если выдаст «Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен запрещающий флаг.», значит уменьшаем и так, пока не получим крайнее верхнее значение пакета, которое проходит до нашего сервера. У меня получилось 1500 (1472+28). Значит дальше я и буду его устанавливать в качестве значения MTU
Далее, вводим команду:
Она покажет MTU для всех сетевых подключений. Нам необходимо узнать как называется интерфейс основного сетевого подключения. Посмотреть названия можно командой
Как изменить значение MTU в Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7-04
либо в центре управления сетями.
Как изменить значение MTU в Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7-04
У меня это Ethernet, у вас же смотрите по обстановке. Но в большинстве случаев он будет называться так же.
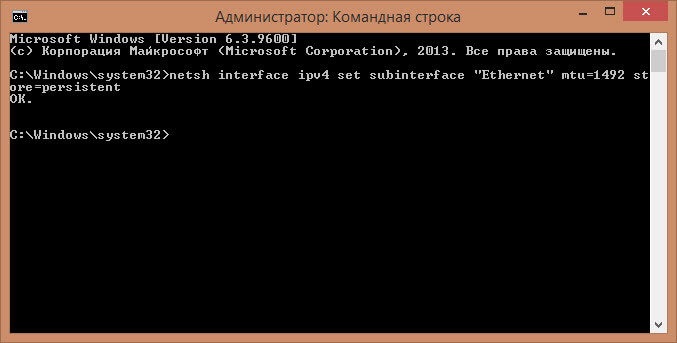
Далее, вводим следующую команду (для ее выполнения требуется чтобы командная строка была запущена от имени администратора)
Где вместо Ethernet пишем название своего интерфейса, а в значение MTU пишем полученное на первом шаге инструкции
Как изменить значение MTU в Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7-06
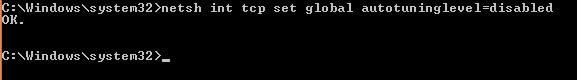
как отключить автоматическую настройку значения MTU для сетевых подключений:
Чтобы включить автоматическую настройку обратно, нужно заменить disabled на normal
Как изменить значение MTU в Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7-07
После этого значение mtu будет такое как вам нужно. Вот мы с вами и разобрали как изменить mtu в Windows. Так что значение mtu теперь для вас не секрет.
Как сменить MTU через реестр
Для тех, кто не любит командную строку, есть PowerShell и реестр. В реестре Windows есть ветка:
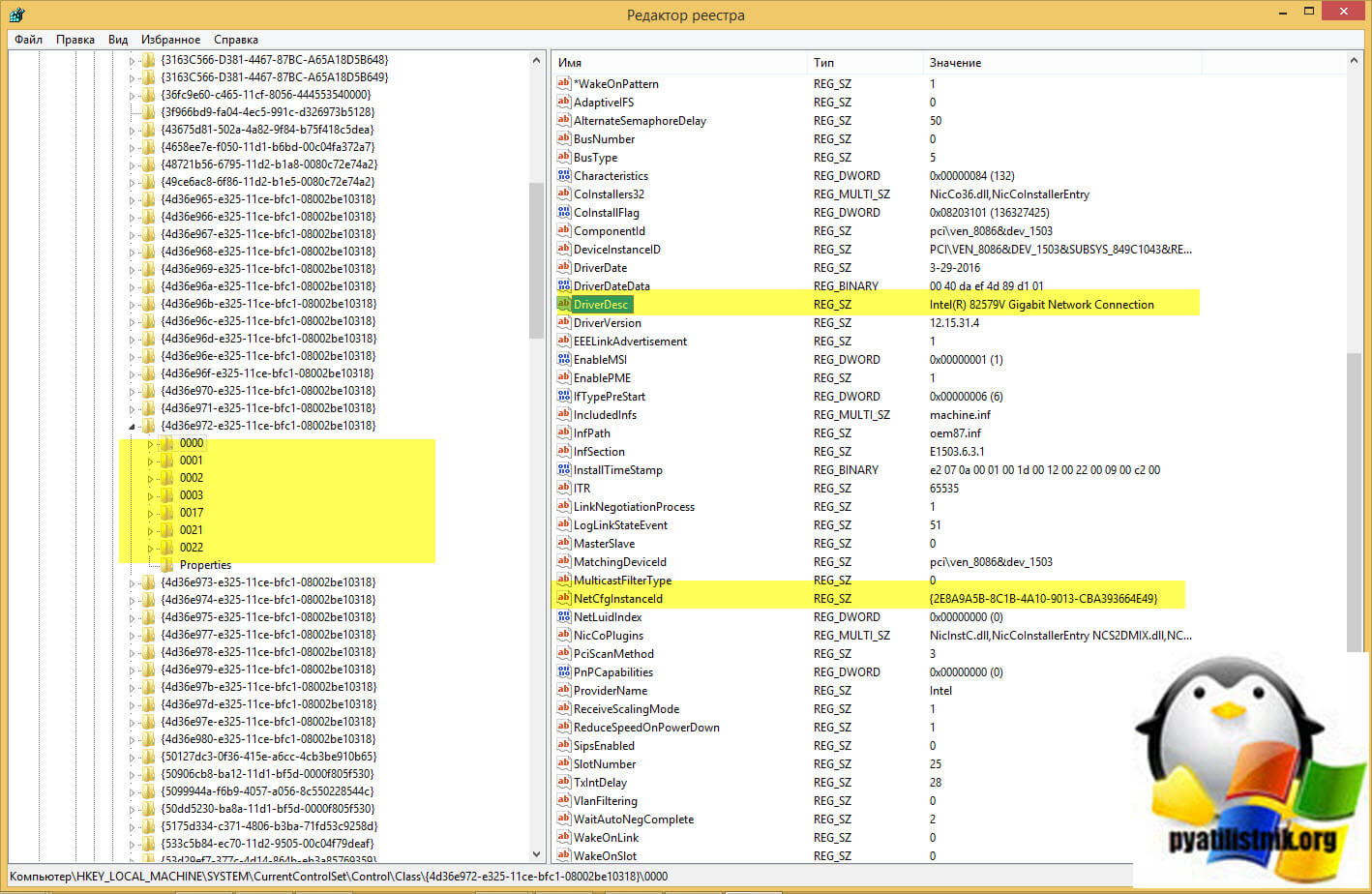
Класс содержит информацию, о всех ваших сетевых картах, а именно драйверах, их версиях и GUID самой карты. GUID потребуется для определения сетевой карты в другой ветке реестра, но не переживайте я покажу более быстрый метод определения и сопоставления GUID и сетевой карты через PowerShell. На что в данном разделе нужно обратить внимание:
- Папки 0000, 0001 и так далее — это папки перечисляющие ваши сетевые интерфейсы в Windows, тут вам нужно будет найти нужный по параметрам указанными ниже
- DriverDesc — Описание драйвера, по сути вы увидите тут производителя вашей сетевой карты, оно поможет вам определить правильный адаптер
- NetCfgInstanceId — это GUID карточки
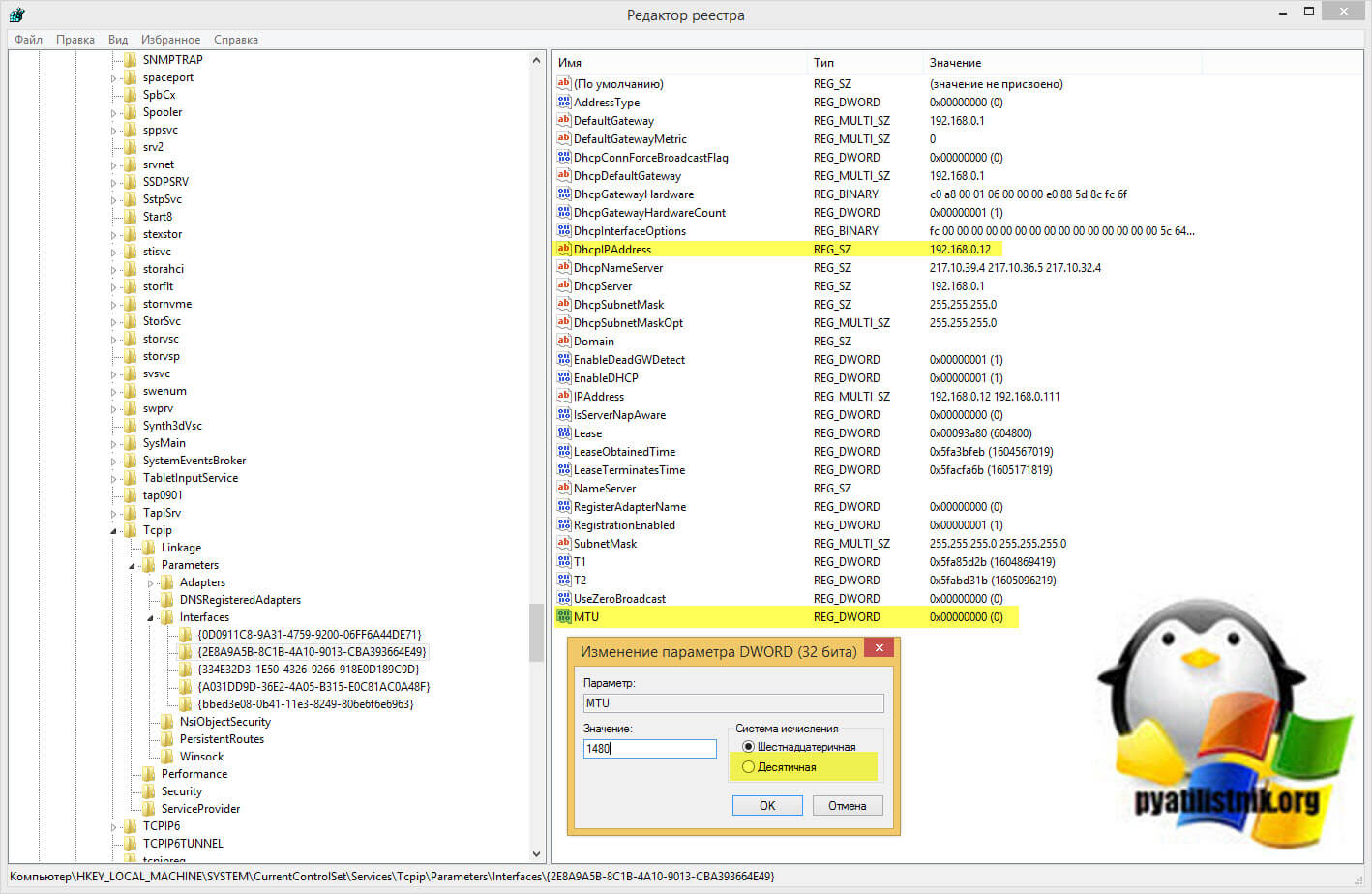
Теперь зная GUID идем по пути:
Среди интерфейсов находим нужный, можно удостовериться, что у него правильный IP-адрес. Найдите ключ MTU, если его нет, то нужно создать REG_DWORD с нужным значением.
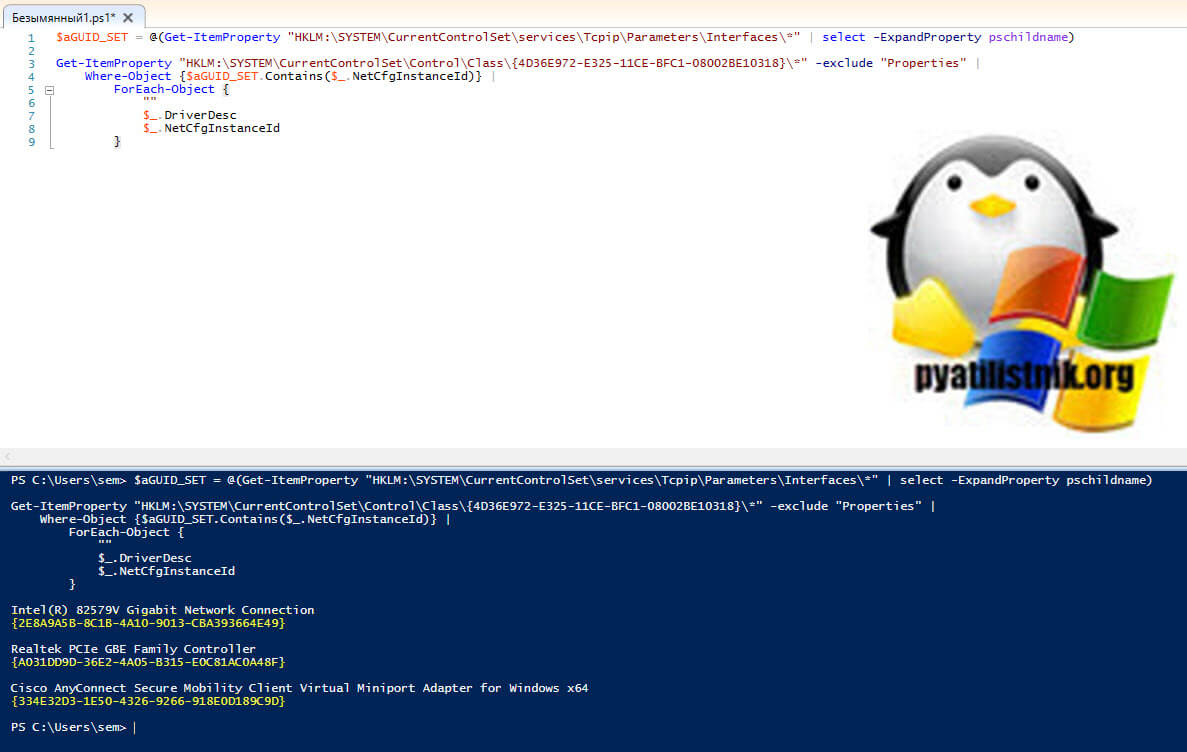
Теперь как не заморачиваться с поиском GUID сетевой карты. Откройте PowerShell ISE и запустите мой скрипт:
$aGUID_SET = @(Get-ItemProperty «HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\*» | select -ExpandProperty pschildname)
Get-ItemProperty «HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class\<4d36e972-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318>\*» -exclude «Properties» |
Where-Object <$aGUID_SET.Contains($_.NetCfgInstanceId)>|
ForEach-Object <
«»
$_.DriverDesc
$_.NetCfgInstanceId
>
Или просто если нужно вывести все GUID из нужной ветки:
Как узнать значение MTU
Windows
Нажмите комбинащию клавишь Win + R
В появившемся окне введите cmd и нажмите OK
В открывшемся черном окне введите команду:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
В первой колонке ответа мы увидим значение MTU:
* в данном примере, значение MTU равно 1500 для сетевого адаптера Ethernet.
Linux
ip address
В более современных системах используется утилита для работы с сетевыми интерфейсами — ip address. Вводим команду:
В полученном результате находим нужный сетевой интерфейс и строчку на подобие:
eth0:
mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
* то, что мы ищем — mtu 1500.
ifconfig
В более ранних системах или с установленным ifconfig вводим:
* где eth0 — сетевой адаптер, для которого хотим узнать MTU.
В полученном результате находим что-то на вроде:
eth0: flags=4163 mtu 1500
* где mtu 1500 — наше значение.
FreeBSD
В данной системе работаем с уже описанным выше ifconfig:
em0: flags=8843 metric 0 mtu 1500
Провайдера
Чтобы определить оптимальное значение MTU для нашего сетевого адаптера, подключенного к сети Интернет, необходимо узнать значение, используемое на оборудовании поставщика.
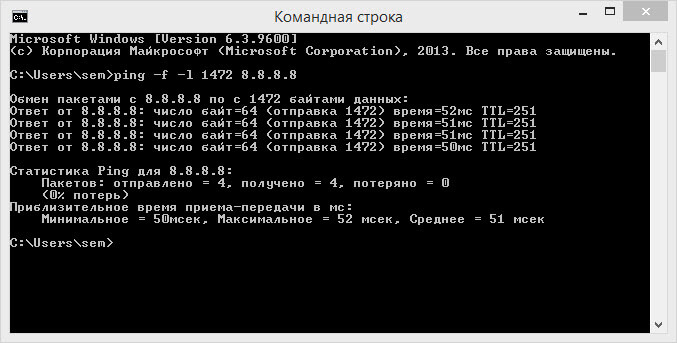
Для этого выполняем ping с запретом фрагментации сетевых пакетов (-f) и выставлением определенного размера пакета (-l):
ping dmosk.ru -f -l 1472
* 1472 будет соответствовать MTU — 1500, так как к пакету мы должны еще прибавить 28 (заголовок).
Наша задача — подобрать значение пакета, при котором будет идти пинг:
Ответ от 90.156.242.197: число байт=1472 время=13мс TTL=56
Ответ от 90.156.242.197: число байт=1472 время=12мс TTL=56
Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен запрещающий флаг.
Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен запрещающий флаг.
Значит значение -l нужно уменьшить, пока сигнал не начнет проходить.
Находим значение, которое стоит на границе с ошибкой и прибавляем к нему заголовок пакета — 28. Так мы получаем наше оптимальное MTU.
На данный момент большинство Интернет провайдеров предоставляет услуги связи с фрагментом в 1500. Старые подключения от Ростелеком или подключения на основе PPPoE могут работать на меньших значениях.
Ping MTU – Find a Path’s MTU using PING Command
In some cases, higher-layer protocols may create large-size packets that not all network paths can support, such as the case of the jumbo frames.
These large packets (or frames) exceed the conventional Ethernet 1500 bytes of MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit).
So, the routers along the path with a default Ethernet MTU in their interfaces will fragment any of these large size packets that threaten to hurt their performance.
An improperly configured MTU can lead to failed transfers and intermittent connectivity.
But what is more daunting is that troubleshooting these kinds of problems can be really challenging.
Fortunately, we can do advanced troubleshooting and find the path MTU with the precious simple networking tool — The Ping Command.
How Does Path MTU Discovery Work?
The default Ethernet II MTU size is 1500 bytes, which is the largest size allowed in most of the Internet.
Although this value is known to be suitable for most environments, it is sometimes adjusted to a higher or lower value.
Adjusting MTU values can help match and improve the capacity of the network.
Larger MTU values can lead to lower network overhead, while a smaller MTU can help decrease the network delay.
How do routers discover MTU in a path?
Modern routers and endpoints use a process known as Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD) to find the path MTU, which is smaller than its interface MTU.
The goal of this process is to find the MTU size of a path while avoiding IP fragmentation.
The PMTUD works by setting the “Don’t Fragment (DF)” flag bit ON, within the IP packet header.
Routers along the path will receive these incoming packets and compare them with their MTU.
If the router interface’s MTU is smaller than the packet’s, and the packet contains the “Don’t Fragment” flag bit on, then the router will be forced to drop the packet and send back an ICMP Fragmentation Needed error message.
Knowing that the path MTU is too large, the source can adjust its packet’s MTU accordingly.
The process is repeated until the MTU has the right size to go through the entire path without fragmentation.
Simulating the Path MTU Discovery Process
You can simulate the Path MTU Discovery process using the ICMP Ping command with additional flags.
Perform a Ping to the target destination address. It can be the local gateway, a server, or a remote IP address.
To do this, we will be using the following additional Ping Flags:
- -f: Set Don’t Fragment flag in packet (IPv4-only).
- -l size: Send buffer size.
Start by adjusting the TCP send buffer (size) with the “-l” flag. In the following Windows OS screenshot, you can see that we are sending an ICMP packet of 2000 bytes in size to the public IP 1.1.1.1
The Ethernet packet with a size of 2000 bytes is generally larger than most MTU in typical networks.
The packet is successfully going through the path and reaching its destination because it is being fragmented by the routers along the path.
Now, let’s see what happens when we set the “Don’t Fragment” flag, with the following command:
ping (destination IP) (-f) (-l (packet size))
When a packet is too large for a path MTU, a router would usually fragment it into pieces for a safer delivery.
But, as you can see from the screenshot above, now the destination returns a “Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set”.
Since we are choosing not to fragment packets, all the routers along the path will see no choice than to drop the packet.
For other Operating Systems:
Linux Ping Command:
ping (-M do) (-s (packet size)) (destination)
macOS Ping Command:
ping (-D) (-s (packet size)) (destination)
How to Find the Path’s MTU with Ping?
Now, to find the path MTU with a Ping command, you would need to repeat the process shown before and adjust the packet size every time.
You will ultimately find the path MTU by trial and error.
In the previous ping test, we used the 2000 bytes as the packet size.
You would probably want to start with a number around 1800-2000 bytes and move down every couple of 100 bytes until you get a successful ping reply.
As you can see in the following screenshot, we started with 1800, tested with 1500, until 1400 finally gave a successful reply.
That means the path MTU between our source and destination is somewhere between 1400 and 1500 bytes.
The next step would be to move the size up between 10-50 bytes until you get another successful reply.
We tested with 1450 bytes and got a reply, which means our value is above that.
Repeating this process led us to find the value, which is 1452 bytes.
The routers along the path were still fragmenting 1453 bytes (but not 1452). They considered 1453 to be too large to traverse the path.
But 1452 was the first proper packet size that returned a successful ICMP reply. My MTU value 1452 is common in Ethernet II.
But one more thing…
We have to take into account the size of the TCP/IP header, which can range between 20-60 bytes. The header size varies according to the transmission media.
According to a chart from Wikipedia.
My Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) header takes up 8 bytes in size, while the IPv6 header accounts for 40 bytes in size. So, the size of my TCP/IP header is 48 bytes (40+8).
Let’s take the packet size that gave us the ping reply (1452 bytes) and add it to the header size (48 bytes).
That leads us to the real MTU size, which is 1500 bytes, the common Ethernet MTU.
1452 is the data payload size or Maximum Segment Size (MSS), that results from the 1500 MTU.