- SSH-туннели — пробрасываем порт
- Easy Port Forwarding using SSH
- The Serveo Method
- Using Localhost.run Method
- Port Forwarding Without Router [New 2020 Method]
- Hacking Articles
- Port Forwarding & Tunnelling Cheatsheet
- Table of Content
- Apache Virtual Host
- Lab Configuration
- Port Forwarding
- Tunnelling
- Lab Requirements
- Sshuttle
- Chisel
- Rpivot using Socks4 proxy
- Dynamic SSH Tunneling
- Local SSH Tunneling
- Local SSH Tunnelling using Plink.exe
- Dynamic SSH Tunneling using Plink.exe
- Tunnelling using Revsocks
- Tunnelling with Metasploit (SOCKS 5 and 4a)
- SOCKS 4a
- Tunnelling with DNScat2
- ICMP Tunneling
- Conclusion
SSH-туннели — пробрасываем порт
Не всегда есть возможность, да и не всегда надо, строить полноценный туннель с интерфейсной парой адресов. Иногда нам нужно лишь «прокинуть» вполне определённые порты.
Тут важно понимать, что туннель можно организовать как изнутри сети, к ресурсам которой вы хотите получить доступ, на внешний ssh-сервер. Также можно организовать туннель с хоста в Интернете на пограничный ssh-сервер сети, чтобы получить доступ к внутренним ресурсам.
Итак. По-порядку.
Строим туннель из сети в мир.
теперь введя на хосте 99.88.77.66:
мы попадём на хост 10.11.12.13.
Таким-же образом можно получить доступ к любому другому ресурсу, например:
Введя на хосте 99.88.77.66:
получим дамп web-ресурса на 10.11.12.14.
Строим туннель из мира в сеть.
Аналогично, вводим на своём хосте:
и получаем доступ к web-ресурсу узла 192.168.0.10, который находится за хостом 88.77.66.55.
Поддерживаем туннели в поднятом состоянии
Ни для кого не секрет, что связь иногда обрывается, туннели при этом будут отваливаться по таймауту.
Чтобы не утруждать себя дополнительным монотонным вбиванием команды на поднятие туннеля и мониторингом этого процесса, автоматизируем его. Смело вводим:
и создаём расписание примерно следующего вида:
Сохраняемся. Проверяем по
что расписание принято.
Это лишь ещё один момент особой админской магии… Надеюсь, что лишних вопросов не должно водникнуть. С дополнительными опциями ssh можно ознакомиться в
По практическому опыту — cron-задания на перезапуск абсолютно недостаточно.
Разве что соединение абсолютно стабильно. В реальной жизни встречается в 0% случаев.
Даже соединённые напрямую кабелем две сетевые карты легко могут потерять n-ное количество пакетов и tcp-соединение «упадёт».
Клиент и сервер будут пребывать в святой уверенности, что всё в порядке, просто вторая сторона ничего не передаёт.
Нужен keepalive.
Примерно так:
Интервал и счётчик — по вкусу.
Добавлять их надо либо в /etc/ssh_config, либо в
/.ssh/config, либо прямо в команде через опцию -o.
В принципе, судя по man ssh_config, первую из опций можно и опустить. но, на всякий случай, пусть будет.
Источник
Easy Port Forwarding using SSH
Sometime we need to run our localhost website or server over internet. To do this we need to forward our port that other device can access our website from anywhere in the world by internet. Usually we can forward our port by configuring settings in router, but if we don’t have router or don’t wanna use our router or not have static ip, then we have a very easy option. We can remotely forward port using SSH.
 |
| Image Copyright: SRU Computer Science |
To do this we use a free service called serveo.net and localhost.run. This requires no installation and no sign-up. Serveo is a SSH server. Whenever a user connects to this service they got a public URL that URL can be use to connect to their localhost server.
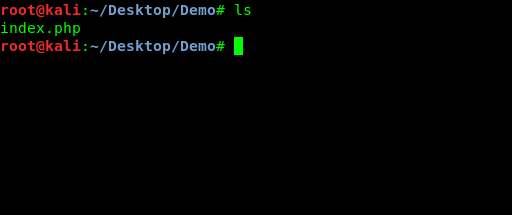
We are in our Kali Linux system. Here we have a website in php. We can use a html file also.
Now we set this in our localhost. For this we check our local ip by using following command:
The screenshot of our local ip is following :
Here we start a basic web server using php by using following command:
Here the 192.168.10.100 is our local ip and we run this server in port 80. The screenshot of the command is following:
Here we need to remember that we must run this server in the directory where we saved the php/html file. We have successfully started our website or web server in our local network. Let we check this by typing our local ip and port in browser. The screenshot is following :
We can see in the screenshot that URL is our local ip. That means it is hosted in localhost. Now we want to access our website outside of our network that means from anywhere via internet.
We minimize the terminal window (Don’t close this terminal, because it’s running our server) and open another new terminal window to run SSH.
The Serveo Method
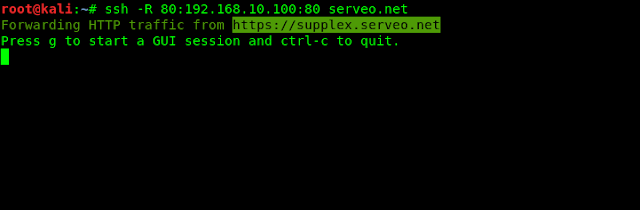
For this we apply following command:
Here 80 is our port and we are using ssh using serveo.net service.
Then we can see that our localhost is forwarding in a unique URL, as following screenshot.
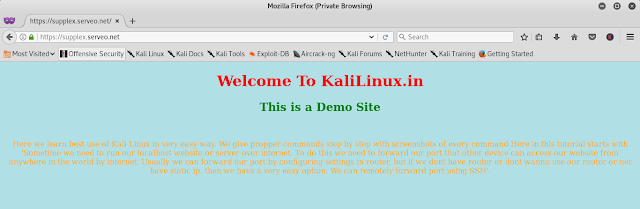
Now we can access our localhost by using this URL. Copy this URL and paste it in the address bar of browser in any devices and see the magic.
It’s done. But wait serveo have some other features.
We can request serveo to get back our old URL. If it is free then serveo will assign it for us again.
We have a old serveo connection with lente.servo.net. We try to get it again. So we request for that subdomain by using following command:
Here we got that subdomain. Now we can access our localhost with this older URL.
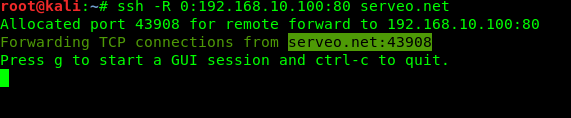
If we want to forward random port then our first port fiels in command will be 0. like following command:
The screenshot of this command is following :
We can open our website with serveo.net:our_assigned_port from anywhere.
In the following screenshot we have opened this link in our mobile device.
Using Localhost.run Method
Well it is almost similar to serveo.net then why we adding this? Because these free services sometimes goes down during overload on the server. If one service is not working then we can try another. So we can use it by applying following command:
If it prompt for RSA fingerprint we type yes and press enter.
We got the shareable link in the last line, we can use this link to connect ssh.
That’s it. Using this method we can forward port without VPN or router. This is so easy to configure it and the connection is stable unlike ngrok, ngrok is not much stable in free version.
Liked our works ? Show support by sharing and encourage us by commenting in the comment section. Follow our blog for more tutorials like this and for quick updates follow us on Twitter and Medium.
Источник
Port Forwarding Without Router [New 2020 Method]
Port Forwarding is always a headache for those who don’t have a router. There are some methods to forward our port without router. Today we are going to share the most easiest method to forward our ports, so we can use our PC’s home server and locally hosted website from anywhere.
To do this we are going to use Portmap.io services. We can use HTTP/HTTPS, TCP, UDP protocols and unlimited bandwidth in any OS (Windows, Mac, Linux, Android, IOS). There are limited features in the free plan, but those are enough for us. Let see how we can set up this on our Kali Linux machine.
First we open portmap.io website in our browser. Using Portmap services we can easily forward our port without router.
| https://portmap.io/ |
Here we move to sign in option.
We fill our details (login, mail, password, captcha etc) and click on «Register».
Here our account is created but to active it we need to verify our email id. So we open our mail id and verify it by clicking on activation link.
Then our account is activated.
Lets navigate to configuration.
We create a new configuration here.
Now we provide the name of our configuration, we can give any name here. Then we select the type and protocol.
We can choose as per our requirement. For an example we choose type OpenVPN and protocol tcp. Then we click on generate.
Then configuration file will generate, and we download it on our system.
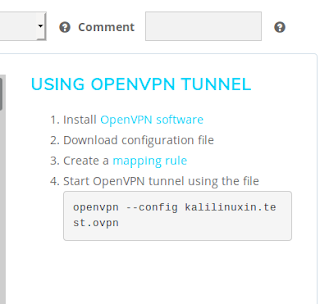
Now we can use this ovpn file with OpenVPN to make a OpenVPN tunnel. OpenVPN is available foe all major operating systems like Windows, Linux, Mac, Android, ios etc.
In our Kali Linux system OpenVPN comes pre-installed. So we can use the OpenVPN command for us showing in the website. We copy it in our clipboard.
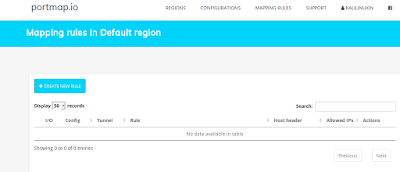
Before use this command we create the mapping rule to select which port we want to forward.
Here we create a new rule. In the free term we can’t more then one rule.
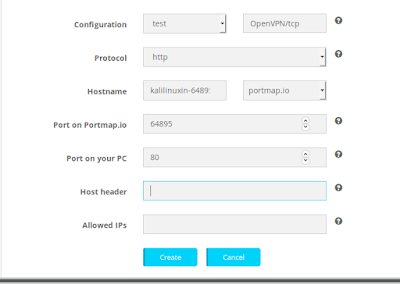
Here the configuration section will be default as our configuration file.
In protocol we choose http for an example. hostname can’t be changed in free plan, but we can choose the domain, we select the portmap.io domain. Here we leave the port on portmap as it is.
We have choose http protocol so we choose port 80 on our PC port. Here we have configured like following screenshot.
Then we click on create. Then our rule will be created as following:-
We can use this on any device with the OpenVPN configuration file to open our localhost.
This is how we can use port forwarding without router in our Kali Linux system. This method can be very useful in hosting any kind of services in our localhost.
We are curious to know which kind to service you want to forward first from your localhost ? Phishing page? Spyware server? or something else tell us in the comment section.
For more Tutorial follow our blog and for updates and small tutorials follow us in Twitter and Medium.
Источник
Hacking Articles
Raj Chandel’s Blog
Port Forwarding & Tunnelling Cheatsheet
In this article, we are going to learn about the concepts and techniques of Port forwarding and Tunnelling. This article stands as an absolute cheatsheet on the two concepts.
Port forwarding transmits a communication request from one address and the port number while sending the packets in a network. Tunnelling has proven to be highly beneficial as it lets an organisation create their Virtual Private Network with the help of the public network and provide huge cost benefits for users on both the end.
Table of Content
- Apache Virtual Host
- Lab Configuration
- Port Forwarding
- Port Forwarding using Metasploit
- SSH Local Port Forwarding (SSH Tunneling)
- Port Forwarding using Socat
- Tunnelling
- Tunnelling using Sshuttle
- Tunnelling using Chisel
- Chisel using Socks5 Proxy
- Rpivot using Socks4 Proxy
- Dynamic SSH Tunnelling
- Local SSH Tunneling
- Local SSH tunnelling using plink.exe
- Dynamic SSH tunnelling using plink.exe
- Tunnelling using Revsocks
- Metasploit (socks5 and socks4a)
- Tunnelling with DNScat2
- ICMP tunnelling
- Conclusion
Apache Virtual Host
Virtual Web hosting is a concept which you may have come across in various Capture-the-Flags challenges and lately it is also being used by the professionals in the corporate environment to host their common services under a lesser number of IP address.
Virtual web hosting can be defined as a method of running several web servers on a single host. By using this method, one computer can host thousands of websites. The Apache web servers have become one of the most popular web-serving methods as they are extremely prevailing and supple.
The Apache has the potential to customise itself into a virtual host which allows hosting an individual website. This essentially lets the network administrators make use of a single server to host various websites or domains. This functions extremely smooth till one’s server can bear the load of the multiple servers being hosted.
Lab Configuration
The lab requirements comprise of:
- VMware Workstation
- Ubuntu
- Kali Linux
Let us start with configuring Apache2 services. To do this you will need to have Apache installed in your Linux systems. You can install it using
Then we need to create a directory for the websites we have to host.
Then go to the /etc/apache2 directory and edit the file ports.conf and add ‘Listen 127.0.0.1:8080‘ before ‘Listen 80’ as in the image below.
Now let us create the test.conf file and add the following code in /etc/apache2/sites-available/
Now let us make use the tool a2ensite to enable our website and the let us restart our apache2.
Therefore, here we finish the setup of our lab by creating a virtual host.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is establishing a secure connection between a remote user and local machines. In organisations on can give their source and destination port numbers to make use of tunnelling with the help of Linux. Along with this, they should also mention the destination which can be the IP address or name of the host.
Let’s switch on the Kali Linux machine and check if the webpage is being hosted. But here it shows that it is unavailable. So, to let us see how the local address and port can be forwarded to the remote host. This can be achieved using various methods, so let’s see them one-by-one.
Port Forwarding using Metasploit
Now we take SSH session using Metasploit. Here we get the meterpreter session and then on using netstat command, we observe that port 8080 is running on the local host.
Here we make use of portfwd to forward all the traffic to the Kali machine, where you mention the local and the remote port and the local address.
When we load this page on the web browser using 127.0.0.1:8081 in the Kali machine, we see that the contents of the web page are displayed.
SSH Local Port Forwarding
It is the method used in SSH to forward the ports of application from a client machine to the server machine. By making use of this, the SSH client listens for connections on a port which has been configured, and tunnels to an SSH server when a connection is received. This is how the server connects to a destination port which is configured and is present on a machine other than the SSH server.
This opens a connection to the machine with IP 192.168.1.108 and forwards any connection of port 8080 on the local machine to port 8081. To know more about SSH tunnelling, visit here.
Here we can see that the contents of the web page are displayed when we load this page on the web browser using 127.0.0.1:8081 in the Kali machine.
Port Forwarding using Socat
Socat is generally a command-line utility in the Linux which is used to transfer data between two hosts. Here we use it for port forwarding where all the TCP connections to 127.0.0.1:8080 will be redirected to port 1234.
When we load this page on the web browser using 192.168.1.108:1234 in the Kali machine, we see that the contents of the web page are displayed.
Tunnelling
Tunnelling is the process of accessing resources remotely using the public network. The tunnels which are established are point-to-point and remote users can be linked at the other end of the tunnels. The job of the tunnelling protocols is to encapsulate the traffic from a user situated remotely and it is sent to the other end of the public network which is then decapsulated and sent to its destined user. The tunnel by default is not encrypted and its level of security is determined with the help of TCP/IP protocol that has selected.
Let us look at how we can perform Tunnelling using various methods and tools.
Lab Requirements
- Kali Linux with IP address 192.168.1.2
- Ubuntu with 2 NIC, consisting of two IP addresses – 192.68.1.108, 192.168.226.128
- Metasploitable 2 with IP address 192.168.226.129
Sshuttle
Sshuttle facilitates to generate a VPN connection from a local machine to a remote Kali Linux with the help of SSH. For the proper functioning, one must have root access on the local machine but the remote Kali Linux can have any type of account. Sshuttle can run more than once concurrently on a particular client machine.
Let’s see how we can use Sshuttle to get the access of a Metasploitable 2 machine which has a different subnet using Ubuntu machine which has two internet addresses with different subnets but also has the subnet in which the Kali Linux is present.
Now let’s check the IP addresses of the Kali Linux machine
On checking the IP address of the Ubuntu machine we see that it has two IP addresses with different subnets.
Let’s install the tool Sshuttle in the Kali Linux machine.
A connection is created remotely with the Ubuntu ([email protected]) and then the address of Metasploitable 2(192.168.226.129) using Sshuttle. Mention the password of Ubuntu and hence you are connected.
Subsequently, when you put the Metasploitable 2 IP address in your Kali Linux’s browser, you will able to access the Metasploitable 2 on port 80.
Hence, here we saw that using Sshuttle, we first connected the Kali Linux with Ubuntu. Once the connection with Ubuntu was made, using that, a connection between Kali Linux and Metasploitable 2 was created.
Chisel
It is a TCP/UDP tunnel, which helps in transporting over and is secured using SSH. It includes both, the client and the Kali Linux. It is generally used in passing through firewalls but can also be used to provide a secure connection to one’s network. Let us see how this works.
First, let us install Chisel and golang in our Kali Linux machines.
Note: Golang is the programming language in which Chisel has been written, so for proper functioning we also install golang.
Now as we now have a copy of the chisel source, we can now proceed to build our binaries for Linux land hence compile the packages of the chisel using go build to begin.
To listen on port 8000 on the Kali Linux and allow clients to specify reverse port forwarding. Here the reverse tunnelling has been activated.
Install Chisel on Ubuntu
Now let us install chisel and golang on Ubuntu, and compile all the packages.
After this done, let’s run chisel on Ubuntu to connect Kali Linux and Metasploitable 2.
Open the web browser in the Kali Linux machine to check the connection between the Kali Linux and Metasploitable 2 which is created on the local address and port 5000.

Chisel using Socks5 proxy
We can follow the initial set-up steps in Ubuntu and Kali Linux as seen in the chisel above proceed ahead.
To listen on port 8000 on the Kali Linux and allow clients to specify reverse port forwarding. Here the reverse tunnelling has been activated.
In ubuntu machine, the next step is to connect to our client using the new reverse socks option.
Now we connect the Ubuntu to Metasploitable 2.
Here we point our Socks5 client which is Metasploitable 2 to the Kali Linux using Ubuntu.
Now let’s open the web browser in the Kali Linux and go to configure the proxy settings. Here we are manually configuring the proxy, therefore, mention the SOCKS host address as the local address i.e., 127.0.0.1 and choose socks5 proxy on port 1080. Also, mention the local address in the ‘no proxy for’ box.
When you open the web browser in the Kali Linux machine and add the Metasploitable 2 IP, you see that the Kali Linux is connected to the Metasploitable 2.
Rpivot using Socks4 proxy
RPIVOT generally provides tunnel traffic into the internal network using socks 4 proxy. Its working is like SSH dynamic port forwarding but is in the opposite direction. It also has a client-server architecture. When a run client on the machine it will tunnel the traffic through and for that the Kali Linux should be enabled so that it can listen to the connections from the client.
Let’s install Rpivot in the Kali Linux machine. Then go to its directory and start the listener on port 9999, which creates socks version 4 proxy on 127.0.0.1 on a port while connecting with the client
Now install rpivot in the Ubuntu machine and connect it with the Kali Linux
Now go to the web browser in your Kali Linux machine, and manually configure the proxy. Set the Socks host address as local address and port as 1080. Select the Socks version 4 and mention the local address for ’no proxy for’.
Now when you open the web browser in your Kali Linux machine, but the IP address of the Metasploitable 2 and hence you will be able to see the connection.
Dynamic SSH Tunneling
Dynamic SSH Tunneling provides a connection with the range of ports by making SSH work like a SOCKS proxy Kali Linux. A SOCKS proxy is an SSH tunnel where applications send their traffic using a tunnel where the proxy sends it traffic like how it is sent to the internet. In SOCKS proxy, it is mandatory to configure the individual client. Dynamic Tunneling can receive connections from numerous ports.
In Kali Linux machine let’s run the command to connect with the Ubuntu using Dynamic SSH tunnelling.
Once the connection between the Kali Linux and Ubuntu is made, let’s open the browser in the Kali Linux machine and configure the proxy in the settings. Choose to manually configure the proxy and mention the local address as the socks host and the port number as 7000. Now select the socks version 5 and mention the local address in ‘no proxy for’ section.
Hence when you put the IP of the Metasploitable 2 in the browser of the Kali Linux, you will have an accessible connection Metasploitable 2 using dynamic Tunnelling.
Local SSH Tunneling
Here, all the connections which are trying to connect with the Metasploitable 2 using Ubuntu with the local destination and port. The -L indicates the local port.
In the Kali Linux machine, add the localhost and then the Metasploitable 2 username and password to create local SSH tunnelling
You can open the Kali Linux’s browser and mention the local address along with the port 7000 on which the traffic was transferred.
Local SSH Tunnelling using Plink.exe
Here we are making use of command-line in windows machine for tunnelling, where a command-line tool for Putty is being used called plink.exe. Here all the connections which are trying to connect with the Metasploitable 2 using Ubuntu with the local destination and port.
Now open the web browser in the window’s machine and put the local address and the port 7000 on which the traffic of Metasploitable 2 was forwarded. You see that there was local SSH Tunnelling between Metasploitable 2 and the Kali Linux using plink.exe
Dynamic SSH Tunneling using Plink.exe
Plink.exe is the windows command line for putty in the windows machine which we will use for Dynamic Tunneling can receive connections from numerous ports.
In Kali Linux machine let’s run the command to connect with the Ubuntu using Dynamic SSH tunnelling.
Once the connection between the Kali Linux and Ubuntu is established, let us open the browser in the Kali Linux machine and configure the proxy in the settings. Choose to manually configure the proxy and mention the local address as the socks host and the port number as 8000. Now select the socks version 5 and mention the local address in ‘no proxy for’ section.

Hence when you put the IP of the Metasploitable 2 in the browser of the Kali Linux, you will have an accessible connection Metasploitable 2 using dynamic SSH tunnelling with the help of plink.exe.

Tunnelling using Revsocks
Revsocks stands for Reverse socks5 tunneler. You can download it from here in the windows operating system. Here in the windows system, we are trying to connect with Ubuntu using socks5.
Now let’s open Ubuntu and download revsocks for Linux. Here we connect Ubuntu with Metasploitable 2 and then we move to proxy settings.
Now in the Windows machine, open the browser and open proxy settings. Here, choose to manually configure the manual proxy configuration and mention the local address in the socks host and mention the port number as 1080. Choose the socks version 5 and then mention the local address in the ’no proxy for’ space.
When you open the web browser in the Windows machine and mention the IP address of the Metasploitable 2, you will be connected with the Metasploitable 2 using revsocks.
Tunnelling with Metasploit (SOCKS 5 and 4a)
Here we start Metasploit in the Kali machine. Then a connection is established with Ubuntu using the auxiliary module with the help of SSH. Once the connection is established, a meterpreter session was created. Then we make use of post module with autoroute. The autoroute post module will help create an additional route through the meterpreter which will allow us to dive deeper in the network. Here we will connect with Metasploitable 2. Next, we will use the auxiliary module for socks5. This is now a deprecated module. Set the localhost address and exploit. The auxiliary module will then start running.
Now go to the web browser in the Kali Linux machine, open the browser and open proxy settings. Here, choose to manually configure the manual proxy configuration and mention the local address in the socks host and mention the port number as 1080. Choose the socks version 5 and then mention the local address in the ’no proxy for’ space.
When you open the web browser in the Kali Linux and mention the IP address of the Metasploitable 2, you will be connected with the Metasploitable 2 using Metasploit.
SOCKS 4a
Now let’s start Metasploit in the Kali machine where the connection is established with Ubuntu with the help of auxiliary module using SSH. Then a meterpreter session was created. Then we will use the post-module where we will use autoroute. The autoroute post module will help to create additional routes through the meterpreter which will allow us to dive deeper in the network. Here we will connect with Metasploitable 2. Next, we will use the auxiliary module for socks4a. This is now a deprecated module. Instead, we can use the new module Set the localhost address and exploit. The auxiliary module will then start running.
Hence, open the web browser in the Kali Linux machine, and open proxy settings. Now, choose to manually configure the manual proxy configuration and mention the local address in the socks host and mention the port number as 1080. Choose the socks version 4a and then mention the local address in the ’no proxy for’ space.
When you open the web browser in the Kali Linux and mention the IP address of the Metasploitable 2, you will be connected with the Metasploitable 2 using Metasploit.

Tunnelling with DNScat2
DNScat2 is a tool which can be used to create a tunnel with the help of DNS protocol. A connection to port 53 should be established to access any data. DNScat2 mainly consists of a client and a Kali Linux. In our scenario, we need to establish a connection between Metasploitable 2 and Kali Linux using Ubuntu as the medium.
Let’s begin with installing DNScat2 in the Kali Linux machine using apt install which will automatically build dependencies.
DNScat2 Tunneling on Port 22
Once this is done, the dnscat2 server will start running.
In the Ubuntu machine, we will install dnscat2 using git clone. Here we will have to install the dependencies manually to get the tool started.
Now let’s establish a connection between the Kali Linux and Ubuntu.
Once the connection is successfully established, a session will be created on the Kali Linux’s end. Now let us check the sessions that are available and interact with them and then send in a request to create a shell. Once the request is accepted a new window will open and the session 2.
Using the second session, you now have access to the Ubuntu machine. So now let’s check the IP address of the client one machine. Here we see that Ubuntu has two NIC cards installed within it.
Now we will connect the Metasploitable 2 port 22 to the port 8888 to create a DNS tunnel between them using the shell.
Open a new tab in the Kali Linux machine and login to the Metasploitable 2 machine with its credentials and now you will be able to communicate with Metasploitable 2 using the Kali Linux.
DNScat2 Tunnelling on port 80
We can perform the same using port 80.
When you open the web browser in the Kali Linux machine and mention the URL of the Metasploitable 2 machines, you will see that the connection was successfully established between the Kali Linux and the Metasploitable 2 using Ubuntu.
The same can be done in the windows system Follow this link here to download a suitable dnscat2 client for your system of windows. To get a detailed explanation on DNScat2 you can read here .
ICMP Tunneling
The main aim of the ICMP tunnel is to send TCP connection where an SSH session will be used in an encapsulated form of ICMP packets. Let’s first configure the ICMP tunnel on the Ubuntu machine. You can read a detailed article from here.
We will first download and install icmptunnel on the server-side and compile the file by unpacking its components.
Then we will disable ICMP echo reply on both the Ubuntu and the Kali Linux. This halts the kernel from responding to any of its packets.
Now let’s start the ICMP tunnel on Ubuntu on server mode and assign it a new IP address for tunnelling.
Now let’s install and set up ICMP tunnel on the client-side i.e Kali Linux as we did in Ubuntu.

Once the other IP address for tunnelling is created in the Kali machine, let’s connect over SSH with the credentials of the server-side with IP address 10.0.0.1.
When you open Wireshark and capture the packets, you only see that all the packets of SSH which is a TCP protocol is being transported on the ICMP protocol.
Conclusion
Therefore in this article, we have seen the effectiveness of various port forwarding and Tunnelling methods to provide a secure and encrypted connection.
Author: Jeenali Kothari is a Digital Forensics enthusiast and enjoys technical content writing. You can reach her on Here
Источник