- PSWindowsUpdate: Managing Windows Updates from PowerShell
- PSWindowsUpdate: Install Windows Update PowerShell Module
- Overview of PSWindowsUpdate Cmdlets
- PowerShell: List All Windows Updates Available for a Computer
- Install-WindowsUpdate: Installing Windows Updates with PowerShell
- Install Windows Update on Remote Computers with PowerShell
- Get-WUHistory: Viewing Windows Update History using PowerShell
- Remove-WindowsUpdate: Uninstalling Windows Updates
- Hide-WindowsUpdate: How to Hide Windows Updates with PowerShell?
- Модуль PSWindowsUpdate: управление обновлениями Windows из PowerShell
- Установка модуля управления обновлениями PSWindowsUpdate
- Обзор команд модуля PSWindowsUpdate
- Управление обновлениями Windows на удаленных компьютерах через PowerShell
- Получаем список доступных обновлений Windows из PowerShell
- Install-WindowsUpdate: установка обновлений с помощью PSWindowsUpdate
- Get-WUHistory: просмотр истории установленных обновлений Windows
- Remove-WindowsUpdate: Удаление обновлений
- Hide-WindowsUpdate: как скрыть ненужные обновления с помощью PowerShell
PSWindowsUpdate: Managing Windows Updates from PowerShell
It is very convenient to use the special PSWindowsUpdate module for PowerShell to manage Windows updates from the command line interface. The PSWindowsUpdate is not integrated into Windows and is a third-party module available in Technet Script Gallery. PSWindowsUpdate allows administrators to remotely check, install, remove and hide updates on Windows servers and workstations. The PSWindowsUpdate module is especially valuable to manage updates on Windows Server Core, Hyper-V editions having no graphic interface, as well as when configuring a Windows image in the audit mode.
PSWindowsUpdate: Install Windows Update PowerShell Module
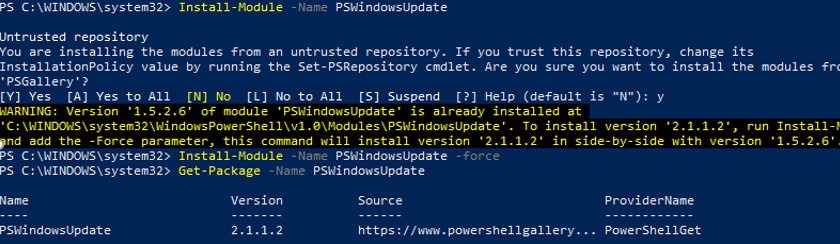
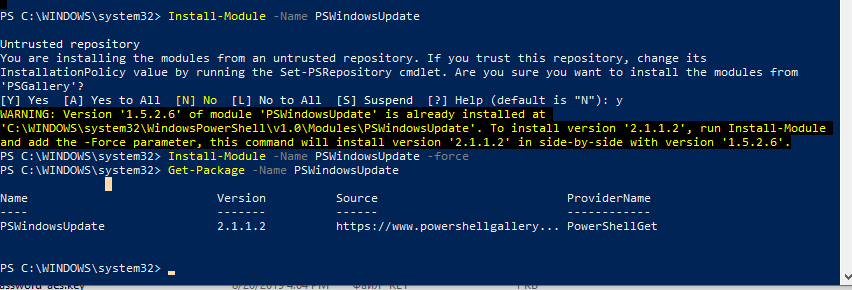
You can install the PSWindowsUpdate module on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016 from the online repository (PSGallery) using the PackageManagement with a single command:
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate
In my case, a warning appeared that PSWindowsUpdate 1.5.2.6 was already installed appeared. To install a newer module version, you need to run the command:
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate –Force
After the installation is complete, you need to check the package:
Get-Package -Name PSWindowsUpdate
If you have an older Windows version (Windows 7/8.1/Windows Server 2008 R2/2012 R2) or you don’t have direct Internet access, you can install PSWindowsUpdate manually.
This module can be installed on any supported Windows versions starting from Vista / Windows Server 2008 with PowerShell 2.0 installed (though, PoSh 3.0 or newer is recommended).
After installing the PSWindowsUpdate module on your computer, you can remotely install it on other computers or servers using the Update-WUModule cmdlet. For example, to copy the PSWindowsUpdate module from your computer to two remote servers, run the commands (you need to access the remote servers via SMB protocol, TCP port 445):
$Targets = «lon-fs02», «lon-db01»
Update-WUModule -ComputerName $Targets –Local
To save (export) the PoSh module to a shared network folder for further importing of the module on other computers, run:
Save-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate –Path \\lon-fs02\psmodules\
Overview of PSWindowsUpdate Cmdlets
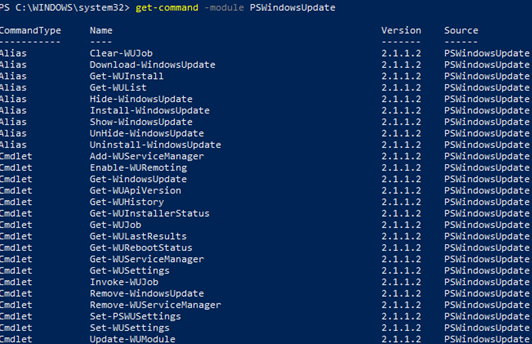
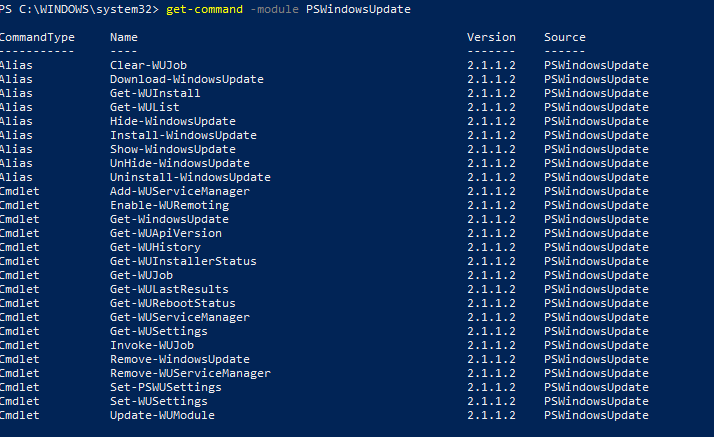
You can display the list of available cmdlets in the PSWindowsUpdate module as follows:
get-command -module PSWindowsUpdate
Let’s describe the usage of the module commands in brief:
- Clear-WUJob – use the Get-WUJob to call the WUJob in Task Scheduler;
- Download-WindowsUpdate (alias for Get-WindowsUpdate –Download ) — get a list of updates and download them;
- Get-WUInstall, Install-WindowsUpdate (alias for Get-WindowsUpdate –Install ) – install updates;
- Hide-WindowsUpdate (alias for Get-WindowsUpdate -Hide:$false ) – hide update;
- Uninstall-WindowsUpdate – remove update using Remove-WindowsUpdate;
- Add-WUServiceManager – register the update server (Windows Update Service Manager) on the computer;
- Enable-WURemoting — enable Windows firewall rules to allow remote use of the PSWindowsUpdate cmdlets;
- Get-WindowsUpdate (Get-WUList) — displays a list of updates that match the specified criteria, allows you to find and install the updates. This is the main cmdlet of the PSWindowsUpdate module. Allows to download and install updates from a WSUS server or Microsoft Update. Allows you to select update categories, specific updates and set the rules of a computer restart when installing the updates;
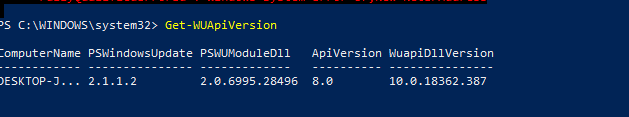
- Get-WUApiVersion – get the Windows Update Agent version on the computer;
- Get-WUHistory – display a list of installed updates (update history);
- Get-WUInstallerStatus — check the Windows Installer service status;
- Get-WUJob – run WUJob update tasks in the Task Scheduler;
- Get-WULastResults — dates of the last search and installation of updates (LastSearchSuccessDate and LastInstallationSuccessDate);
- Get-WURebootStatus — allows you to check whether a reboot is needed to apply a specific update;
- Get-WUServiceManager – list update sources;
- Get-WUSettings – get Windows Update client settings;
- Invoke-WUJob – remotely call WUJobs jobs in the Task Scheduler to immediately execute PSWindowsUpdate commands;
- Remove-WindowsUpdate – allows to uninstall an update by KB ID;
- Remove-WUServiceManager – disable Windows Update Service Manager;
- Set-PSWUSettings – save PSWindowsUpdate module settings to the XML file;
- Set-WUSettings – configure Windows Update client settings;
- Update-WUModule – update the PSWindowsUpdate module version (you can update the module on a remote computer by copying it from the current one, or updating from PSGallery).
PowerShell: List All Windows Updates Available for a Computer
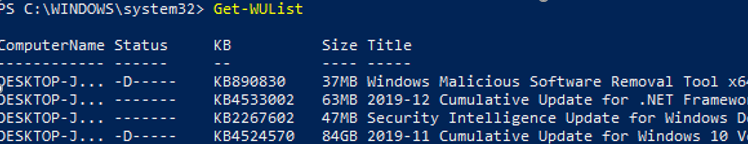
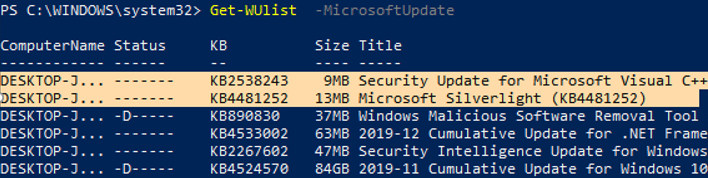
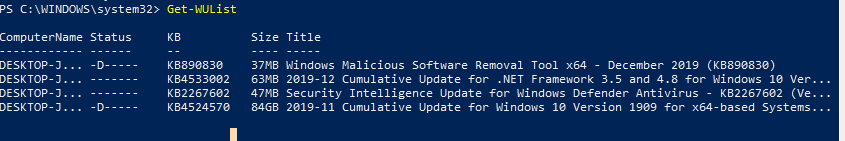
You can list the updates available for this computer on the update server using the Get-WindowsUpdate or Get-WUList commands.
To check the list of available updates on a remote computer, run this command:
Get-WUList –ComputerName server2
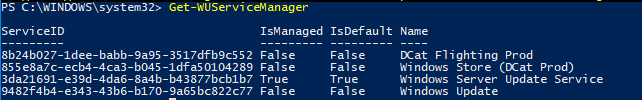
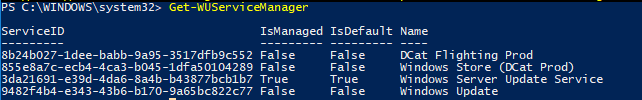
You can check where your Windows should get updates from. Run the following command:
As you can see, the computer is configured to receive updates from the local WSUS server (Windows Server Update Service = True). In this case, you should see a list of updates approved for your computer.
If you want to scan your computer on Microsoft Update servers in the Internet (in addition to Windows updates, these servers contain Office and other Microsoft product updates), run this command:
You will get this warning:
To allow scanning on Microsoft Update, run this command:
Add-WUServiceManager -ServiceID «7971f918-a847-4430-9279-4a52d1efe18d» -AddServiceFlag 7
You can now scan to Microsoft Update. As you can see, in this case, additional updates were found for Microsoft Visual C ++ 2008 and Microsoft Silverlight.
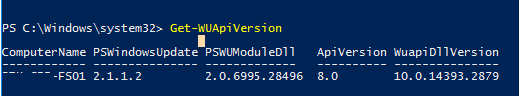
To check the version of the Windows Update Agent on the computer, run the command:
To remove certain products or packages from the list of updates received by your computer, you can exclude them by:
- Category (-NotCategory);
- Title (-NotCategory);
- Update number (-NotKBArticleID).
For example, let’s exclude OneDrive, drivers and the specific KB from the list of updates:
Get-WUlist -NotCategory «Drivers» -NotTitle «OneDrive» -NotKBArticleID KB4489873
Install-WindowsUpdate: Installing Windows Updates with PowerShell
To automatically download and install all available updates for your computer, run the command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -MicrosoftUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
The AcceptAll key accepts installation of all update packages, and AutoReboot allows Windows to automatically restart after the updates are installed.
You can save the update installation history to the log file (you can use it instead of WindowsUpdate.log file).
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -Install -AutoReboot | Out-File «c:\logs\$(get-date -f yyyy-MM-dd)-WindowsUpdate.log» -force
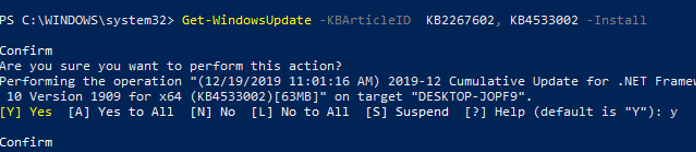
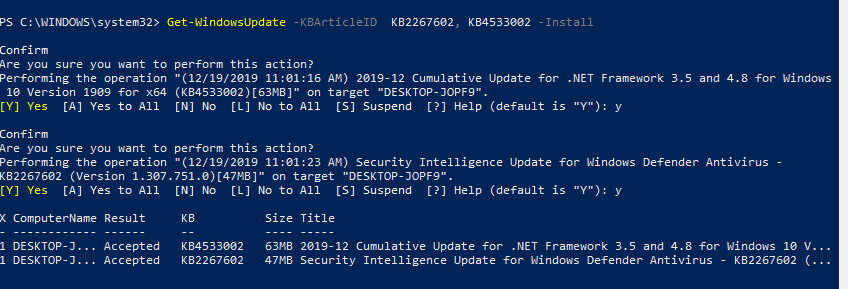
You can install only the specific update packages by KB number:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602, KB4533002 -Install
In this case, you need to confirm the installation of each update manually.
If you want to exclude some updates from the installation list, run this command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -NotCategory «Drivers» -NotTitle OneDrive -NotKBArticleID KB4011670 -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot
Install Windows Update on Remote Computers with PowerShell
The PSWindowsUpdate module allows you to install updates remotely on multiple workstations or servers at once (the PSWindowsUpdate must be installed/imported on these computers). It is very convenient since an administrator doesn’t have to log on manually to all servers when update installation is scheduled.
Almost all PSWindowsUpdate module cmdlets allow you to manage and install updates on remote computers. To do this, use the attribute: -Computername server1, server2, server3
In order to manage updates on remote computers, you need to add host names to your winrm trusted host list:
Install the PSWindowsUpdate module on remote computers and allow to access the process dllhost.exe via dynamic RPC ports in the Windows Defender Firewall.
The following command will install all available updates on three remote servers:
In newer versions of the PSWindowsUpdate module, use the following command to remotely install updates on multiple computers:
You can install updates on a remote computer and send an email report to the administrator:
Install-WindowsUpdate -ComputerName nysrv1 -MicrosoftUpdate -AcceptAll — IgnoreReboot -SendReport –PSWUSettings @
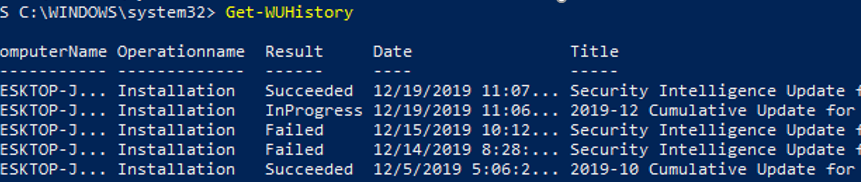
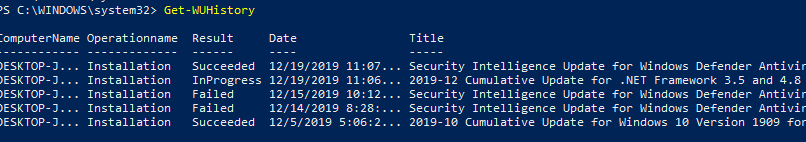
Get-WUHistory: Viewing Windows Update History using PowerShell
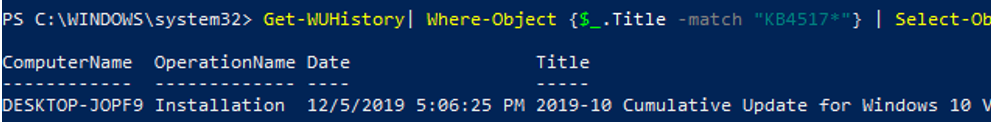
Using the Get-WUHistory cmdlet, you can get the list of updates installed on a computer earlier automatically or manually.
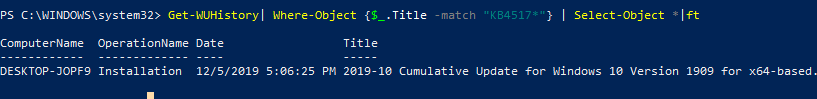
You can get the information about the date of installation of a specific update:
Get-WUHistory| Where-Object <$_.Title -match "KB4517389">| Select-Object *|ft
To find out if the update has been installed on multiple remote computers, you can use this PowerShell code:
«server1″,»server2» | Get-WUHistory| Where-Object <$_.Title -match "KB4011634">| Select-Object *|ft
Remove-WindowsUpdate: Uninstalling Windows Updates
To correctly uninstall the updates from PowerShell, you can use the Remove-WindowsUpdate cmdlet. Just specify the KB number as an argument of the KBArticleID parameter. To delay automatic computer restart, add the –NoRestart key:
Remove-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB4489873 -NoRestart
Hide-WindowsUpdate: How to Hide Windows Updates with PowerShell?
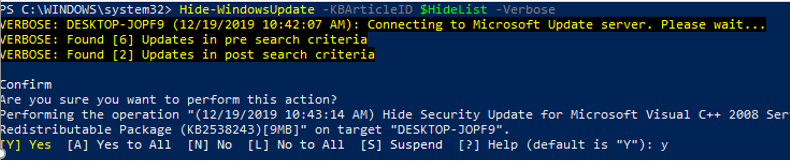
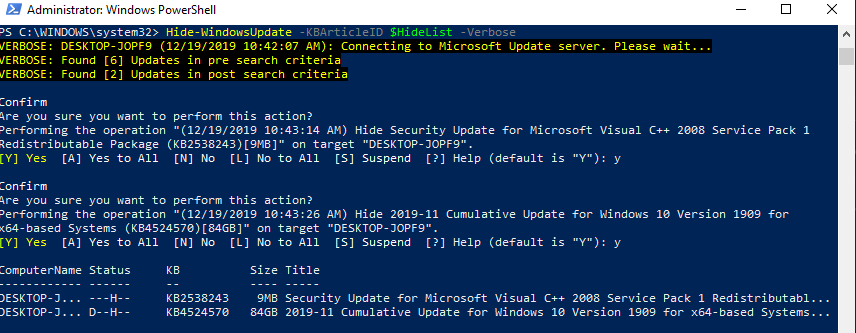
You can hide the specific updates so they will be never installed by Windows Update service on your computer (most often you need to hide the driver updates). For example, to hide the KB4489873 and KB4489243 updates, run these commands:
$HideList = «KB4489873», «KB4489243»
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList –Hide
Now the next time you scan for updates using the Get-WUInstall command, the hidden updates won’t be displayed in the list of updates available for installation.
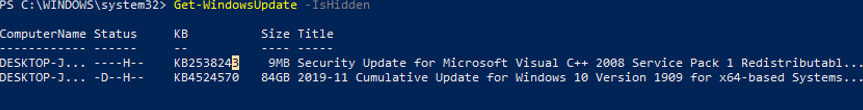
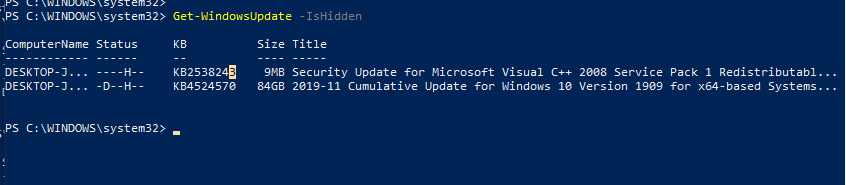
This is how you can display the list of updates hidden on this computer:
Notice that the H (Hidden) attribute has appeared in the Status column of hidden updates.
To remove an update from hidden ones, run this command:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -WithHidden -Hide:$false
Show-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList
For those who feel uncomfortable in the PowerShell console, I would recommend a graphic Windows Update MiniTool to manage Windows 10 updates.
Модуль PSWindowsUpdate: управление обновлениями Windows из PowerShell
Для управления обновлениями Windows из командной строки очень удобно использовать специальный PowerShell модуль – PSWindowsUpdate. Модуль PSWindowsUpdate не встроен в Windows и является сторонним модулем, доступным в галерее скриптов Technet. PSWindowsUpdate позволяет администраторам удаленно проверять, устанавливать, удалять и скрывать определенные обновления на компьютерах и рабочих станциях. Модуль PSWindowsUpdate особо ценен при использовании для управления обновлениями в Core редакциях Windows Server, в которых отсутствуют графический интерфейс, а также при настройке образа Windows в режиме аудита.
Установка модуля управления обновлениями PSWindowsUpdate
Если вы используете Windows 10, вы можете установить модуль PSWindowsUpdate из онлайн репозитория через менеджер пакетов PackageManagement всего одной командой:
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate
В моем случае появилось предупреждение, что версия PSWindowsUpdate 1.5.2.6 уже установлена. Чтобы установить более новую версию, нужно запустить команду:
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate –Force
После окончания установки нужно проверить наличие пакета:
Get-Package -Name PSWindowsUpdate
Если у вас установлена более старая версия Windows (Windows 7/8.1/ Windows Server 2008 R2/ 2012 R2) или отсутствует прямой доступ в Интернет, вы можете установить модуль PSWindowsUpdate вручную.
Модуль PSWindowsUpdate можно установить на любые поддерживаемые версии Windows, начиная с Vista / Windows Server 2008 с установленным PowerShell 2.0 (но рекомендуется PowerShell версии 3.0 и выше).
После установки модуля PSWindowsUpdate на своем компьютере вы можете удаленно установить его на другие компьютеры или сервера с помощью командлета Update-WUModule . Например, чтобы скопировать PSWindowsUpdate модуль с вашего компьютера на два удаленных сервера, выполните команды (нужен доступ к удаленным серверам по протоколу SMB, порт TCP 445):
$Targets = «Server1», «Server2»
Update-WUModule -ComputerName $Targets –Local
Чтобы сохранить модуль в сетевой каталог для дальнейшего импорта модуля на других компьютерах, выполните:
Save-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate –Path \\fs01\ps\
Обзор команд модуля PSWindowsUpdate
Список доступных командлетов модуля можно вывести так:
get-command -module PSWindowsUpdate
Вкратце опишем назначение команд модуля:
- Clear-WUJob – использовать Get-WUJob для вызова задания WUJob в планировщике;
- Download-WindowsUpdate (алиас для Get-WindowsUpdate –Download) — получить список обновлений и скачать их;
- Get-WUInstall, Install-WindowsUpdate (алиас для Get-WindowsUpdate –Install) – установить обвновления;
- Hide-WindowsUpdate (алиас для Get-WindowsUpdate -Hide:$false) – скрыть обновление;
- Uninstall-WindowsUpdate -удалить обновление с помощью Use Remove-WindowsUpdate;
- Add-WUServiceManager – регистрация сервера обновления (Windows Update Service Manager) на компьютере;
- Enable-WURemoting — включить правила файервола, разрешающие удаленное использование командлета PSWindowsUpdate;
- Get-WindowsUpdate (Get-WUList) — выводит список обновлений, соответствующим указанным критериям, позволяет найти и установить нужное обновление. Это основной командлет модуля PSWindowsUpdate. Позволяет скачать и установить обновления с сервера WSUS или Microsoft Update. Позволяет выбрать категории обновлений, конкретные обновления и указать правила перезагрузки компьютера при установке обновлений;
- Get-WUApiVersion – получить версию агента Windows Update Agent на компьютере;
- Get-WUHistory – вывести список установленных обновлений (история обновлений);
- Get-WUInstallerStatus — проверка состояния службы Windows Installer;
- Get-WUJob – запуска заданий обновления WUJob в Task Scheduler;
- Get-WULastResults — даты последнего поиска и установки обновлений (LastSearchSuccessDate и LastInstallationSuccessDate);
- Get-WURebootStatus — позволяет проверить, нужна ли перезагрузка для применения конкретного обновления;
- Get-WUServiceManager – вывод источников обновлений;
- Get-WUSettings – получить настройки клиента Windows Update;
- Invoke-WUJob – удаленное вызов заданий WUJobs в Task Schduler для немедленного выполнения заданий PSWindowsUpdate.
- Remove-WindowsUpdate – удалить обновление;
- Remove-WUServiceManager – отключить Windows Update Service Manager;
- Set-PSWUSettings – сохранить настройки модуля PSWindowsUpdate в XML файл;
- Set-WUSettings – настройка параметров клиента Windows Update;
- Update-WUModule – обновить модуль PSWindowsUpdate (можно обновить модуль на удаленном компьютере, скопировав его с текущего, или обновить из PSGallery).
Управление обновлениями Windows на удаленных компьютерах через PowerShell
Практически все командлеты модуля PSWindowsUpdate позволяют управлять установкой обновлений на удаленных компьютерах. Для этого используется атрибут -Computername Host1, Host2, Host3.
Чтобы управлять обновлениями на удаленных компьютерах, нужно добавить их имена в список доверенных хостов winrm:
Установите модуль PSWindowsUpdate на удаленных компьютерах и разрешите в файерволе доступ по динамическим RPC портам к процессу dllhost.exe.
Получаем список доступных обновлений Windows из PowerShell
Вывести список обновлений, доступных для данного компьютера на сервере обновлений можно с помощью команд Get-WindowsUpdate или Get-WUList.
Чтобы проверить список доступных обновлений на удаленном компьютере, выполните:
Get-WUList –ComputerName server2
Вы можете проверить, откуда должна получать обновления ваша ОС Windows. Выполните команду:
Как вы видите, компьютер настроен на получение обновлений с локального сервера WSUS (Windows Server Update Service = True). В этом случае вы должны увидесть список обновлений, одобренных для вашего компьютера на WSUS.
Если вы хотите просканировать ваш компьютер на серверах Microsoft Update (кроме обновлений Windows на этих серверах содержатся обновления Office и других продуктов) в Интернете, выполните команду:
Вы получаете предупреждение:
Чтобы разрешить сканирование на Microsoft Update, выполните команду:
Add-WUServiceManager -ServiceID «7971f918-a847-4430-9279-4a52d1efe18d» -AddServiceFlag 7
Теперь можете выполнить сканирование на Microsoft Update. Как вы видите, в данном случае были найдены дополнительные обновления для Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 и Microsoft Silverlight.
Чтобы проверить версию агента Windows Update на компьютере, выполните команду:
Чтобы убрать определенные продукты или конкретные пакеты из списка обновлений, которые получает ваш компьютер, вы их можете исключить по:
- Категории (-NotCategory);
- Названию (-NotTitle);
- Номеру обновления (-NotKBArticleID).
Например, исключим из списка обновления драйверов, OneDrive и одну конкретную KB:
Get-WUlist -NotCategory «Drivers» -NotTitle OneDrive -NotKBArticleID KB4533002
Install-WindowsUpdate: установка обновлений с помощью PSWindowsUpdate
Чтобы автоматически загрузить и установить все доступные обновления для вашей Windows, выполните:
Install-WindowsUpdate -MicrosoftUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
Ключ AcceptAll включает одобрение установки для всех пакетов, а AutoReboot разрешает автоматическую перезагрузку Windows после установки обновлений.
Можете сохранить историю установи обновлений в лог файл (можно использовать вместо WindowsUpdate.log).
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -Install -AutoReboot | Out-File «c:\$(get-date -f yyyy-MM-dd)-WindowsUpdate.log» -force
Можно установить только конкретные обновления по номерам KB:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602, KB4533002 -Install
В данном случае нужно подтверждать установку каждого обновления вручную.
Если вы хотите исключить некоторые обновления из списка на установку, выполните:
Install-WindowsUpdate -NotCategory «Drivers» -NotTitle OneDrive -NotKBArticleID KB4011670 -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot
Модуль позволяет удаленно запустить установку обновлений сразу на нескольких компьютерах или серверах (на компьютерах должен присутствовать модуль PSWindowsUpdate). Это особенно удобно, так как позволяет администратору не заходить вручную на все сервера во время плановой установки обновлений. Следующая команда установит все доступные обновление на трех удаленных серверах:
В модуле PSWindowsUpdate 2.1 вместо командлета Invoke-WUInstall нужно использовать Invoke-WUJob. Этот командлет создает на удаленном компьютере задание планировщика, запускаемое от SYSTEM.
Поэтому в новых версиях модуля для удаленной установки обновлений используйте такую команду:
Можно установить обновления на удаленном компьютере и отправить email отчет администратору:
Install-WindowsUpdate -ComputerName server1 -MicrosoftUpdate -AcceptAll — IgnoreReboot -SendReport –PSWUSettings @
Get-WUHistory: просмотр истории установленных обновлений Windows
С помощью команды Get-WUHistory вы можете получить список обновлений, установленных на компьютере ранее автоматически или вручную.
Можно получить информацию о дате установки конкретного обновления:
Get-WUHistory| Where-Object <$_.Title -match "KB4517389">| Select-Object *|ft
Чтобы получить информацию об наличии установленного обновления на нескольких удаленных компьютерах, можно воспользоваться таким кодом:
«server1″,»server2» | Get-WUHistory| Where-Object <$_.Title -match "KB4011634">| Select-Object *|ft
Remove-WindowsUpdate: Удаление обновлений
Для корректного удаления обновлений используется командлет Remove-WindowsUpdate. Вам достаточно указать номер KB в качестве аргумента параметра KBArticleID. Чтобы отложить автоматическую перезагрузку компьютера можно добавить ключ –NoRestart :
Remove-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB4011634 -NoRestart
Hide-WindowsUpdate: как скрыть ненужные обновления с помощью PowerShell
Вы можете скрыть определенные обновления, чтобы они никогда не устанавливались службой обновлений Windows Update на вашем компьютер (чаще всего скрывают обновления драйверов). Например, чтобы скрыть обновления KB2538243 и KB4524570, выполните такие команды:
$HideList = «KB2538243», «KB4524570»
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -Hide
или используйте alias:
Hide-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -Verbose
Теперь при следующем сканировании обновлений с помощью команды Get-WUlist скрытые обновления не будут отображаться в списке доступных для установки патчей.
Вывести список обновлений, которые скрыты на данном компьютере можно так:
Обратите внимание, что в колонке Status у скрытых обновлений появился атрибут H (Hidden).
Отменить скрытие некоторых обновлений можно так:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -WithHidden -Hide:$false
Show-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList
Для тех, кто себя некомфортно чувствует в консоли PowerShell, для управления обновлениями Windows 10 могу порекомендовать графическую утилиту Windows Update MiniTool.