- Powertop
- Contents
- Installation
- Usage
- Apply settings
- Troubleshooting
- Error: Cannot load from file
- Calibration to prevent inaccurate measurement
- Экономия заряда батареи ноутбука с помощью утилиты powertop
- Экономия заряда батареи ноутбука с помощью утилиты powertop
- PowerTop – Monitors Total Power Usage and Improve Linux Laptop Battery Life
- What is PowerTOP?
- Requirements
- How to Install Powertop in Linux
- How Do I use PowerTop in Linux?
- Understanding PowerTop Options and Usage
- PowerTop Usage with Examples
- Summary
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
Powertop
Powertop is a tool provided by Intel to enable various powersaving modes in userspace, kernel and hardware. It is possible to monitor processes and show which of them are utilizing the CPU and wake it from its Idle-States, allowing to identify applications with particular high power demands.
Contents
Installation
Usage
Powertop suggests a few methods to reduce the power consumption further. However, in interactive mode, powertop does not display the parameters. To find out which ones are suggested, proceed as follows:
- If you have changed parameters (e.g. in powertop), reboot so that the system has default state of the parameters.
- Use powertop to produce a report on parameters: powertop —html=powerreport.html (as the root user)
- Open the report in your favorite web browser. The «Tuning» tab of the report now shows the actual parameters suggested by the tool to apply to save power. You may extract the commands with awk -F ‘ ‘ ‘/tune/ < print $4 >‘ powerreport.html .
Apply settings
There are two ways to automatically apply the suggested settings:
- Recommended: You can apply these settings at boot by using module parameters, udev rules and sysctl. For details, see the power management page.
- You can use the —auto-tune feature from powertop which sets all tunable options to their GOOD setting. This can be combined with systemd service to have the tunables set on boot. Remember to enable/start the service.
Troubleshooting
Error: Cannot load from file
If you receive an error like the following when starting powertop, it is likely that powertop has not collected enough measurement data yet. To fix this, keep powertop running for a certain time connected to battery power only.
Calibration to prevent inaccurate measurement
If you experience inaccurate measurement, then it is likely that you need to calibrate powertop first. This can be done by running powertop with the —calibrate parameter.
Источник
Экономия заряда батареи ноутбука с помощью утилиты powertop
Оригинал: Saving laptop power with powertop
Автор: Paul W. Frields
Дата публикации: 11 июня 2015 г.
Перевод: А.Панин
Дата перевода: 5 августа 2015 г.
Экономия заряда батареи ноутбука с помощью утилиты powertop
Если вы судите о ноутбуках по одному параметру, скорее всего данным параметром является время автономной работы от батареи. Вам наверняка хотелось бы более продуктивно использовать каждый ампер-час для увеличения времени, которое можно потратить на работу, чтение или просто на развлечения. Поэтому неплохо узнать, на что расходуется заряд батареи ноутбука.
Вы можете использовать утилиту powertop для ознакомления со списком потребителей заряда батареи в процессе автономной работы системы. Данная утилита исполняется в терминале, поэтому вам придется самостоятельно запустить эмулятор терминала. После этого следует выполнить в нем следующую команду:
Утилите powertop необходим доступ к аппаратному обеспечению для осуществления замеров расхода энергии батареи. Исходя из этого, вам придется запускать данную утилиту также с повышенными привилегиями:
Вывод утилиты powertop должен быть аналогичен выводу, представленному на рисунке ниже. Потребление энергии в рамках вашей системы с высокой вероятностью будет отличаться:
Утилита выводит данные в рамках нескольких экранов. Вы можете переключаться между ними с помощью клавиши Tab и сочетания клавиш Shift+Tab . Для завершения работы утилиты следует использовать клавишу Esc . Список горячих клавиш также приведен в нижней части экрана для удобства пользователей.
Утилита выводит информацию об использовании заряда батареи различными аппаратными устройствами и драйверами. При этом она также выводит значения любопытных параметров, таких, как количество обрабатываемых в течение секунды прерываний. (Современные центральные процессоры являются настолько быстрыми, что обычно бездействуют в течение большей части секундного интервала.)
Если вы желаете максимизировать заряд батареи, вам следует минимизировать количество операций по переводу центрального процессора из режима энергосбережения в стандартный режим работы. Одним из способов соответствующей минимизации является использование страницы параметров настройки системы «Tunables» утилиты powertop . Метка «Bad» используется для указания на значение параметра, которое не способствует экономии заряда батареи, хотя и может способствовать повышению быстродействия системы. Метка «Good» используется для указания на значение параметра, соответствующее режиму энергосбережения. Вы можете использовать клавишу Enter для изменения каждого изменяемого значения параметра.
Пакет программного обеспечения powertop также содержит службу, которая автоматически устанавливает отмеченные с помощью меток «Good» оптимальные значения параметров настройки системы с целью перевода системы в оптимальный режим энергосбережения. Для ее запуска следует выполнить следующую команду:
Если вы желаете, чтобы данная служба запускалась автоматически после загрузки системы, выполните следующую команду:
Предостережение относительно использования данной службы для установки значений параметров настройки системы: Некоторые значения параметров настройки системы могут привести к повреждению пользовательских данных или (при использовании некоторого специфического оборудования) к некорректной работе системы. К примеру, установка значения параметра «VM writeback timeout» влияет на длительность периода ожидания перед записью измененных данных на устройство хранения данных. Следовательно, значение данного параметра является компромиссом между энергоэффективностью системы и безопасностью хранения данных. В том случае, если энергоснабжение системы будет по какой-либо причине полностью нарушено, вы потеряете изменения данных за последние 15 секунд, а не за 5 секунд, как при использовании стандартных параметров системы. Однако, для большинства пользователей ноутбуков данная особенность работы системы не является проблемой, так как система в любом случае выведет предупреждение о критическом снижении заряда батареи.
Источник
PowerTop – Monitors Total Power Usage and Improve Linux Laptop Battery Life
One of the most important characteristics of a good Linux machine especially with laptops is power management in terms of prolonging battery life. Linux has utilities that can help you to monitor and keep track of your battery performance, though many of us still face problems in getting the right power settings to manage power consumption and improve battery life.

In this article we are going to look at a Linux utility called PowerTOP that helps you to get the appropriate system settings to manage power on your Linux machine.
What is PowerTOP?
PowerTOP is a terminal-based diagnosis tool developed by Intel that helps you to monitor power usage by programs running on a Linux system when it is not plugged on to a power source.
An important feature of PowerTOP is that it provides an interactive mode which allows a user to experiment with different power management settings.
Requirements
PowerTOP requires the following components:
- Development Tools such as C++, g++, libstdc++, autoconf, automake, and libtool.
- In addition to the above, it also requires pciutils-devel, ncurses-devel and libnl-devel components
- kernel version => 2.6.38
How to Install Powertop in Linux
PowerTOP can be easily available to install from system default repositories by using your respective package manager.
Important: Please note that installing powertop from the default system repositories, will get you a older version.
If you’re looking to install most recent version (i.e. v2.7 released on 24 Nov, 2014) of powertop, you have to build it and install it from source, for this you must have following dependencies install on the system.
After installing all the above required packages, now it’s time to download most latest version of PowerTop and install it as suggested:
How Do I use PowerTop in Linux?
To use this tool, one needs root privileges because all the information required by powertop to measure power usage by applications is gathered directly from the system hardware.
Try to use it with laptop battery power to see the effects on the system. It shows the total power usage by the system and by the individual components of the system listed in different categories: devices, processes, system timer, kernel works and interrupts.
Understanding PowerTop Options and Usage
To set all the tunabale options to the best settings without the interactive mode, use the —auto-tune option.
To run it in calibration mode, use the —calibrate option. If you run powertop on laptop battery, it tracks power consumption as well as processes running on the system and after getting enough power measurements, it reports power estimates.
You can then use this option to get more appropriate estimates when using this option, to implement a calibration cycle through different display levels and workloads.
To run it in debug mode, use the —debug option.
You can also generate a report for data analysis by using the —csv=filename . The report generated is called a CSV report and when you do not spell out a file name, a default name powertop.csv is used.
To generate a html report file, use the —html=filename option. You can specify for how long in seconds a report can be generated by using the —time=seconds .
You can specify a workload file to execute as part of the calibration before generating a report by using the —workload=workload_filename .
To show help messages use the —help option or view the manpage.
To specify the number of times a test should be run by using the —iteration option.
PowerTop Usage with Examples
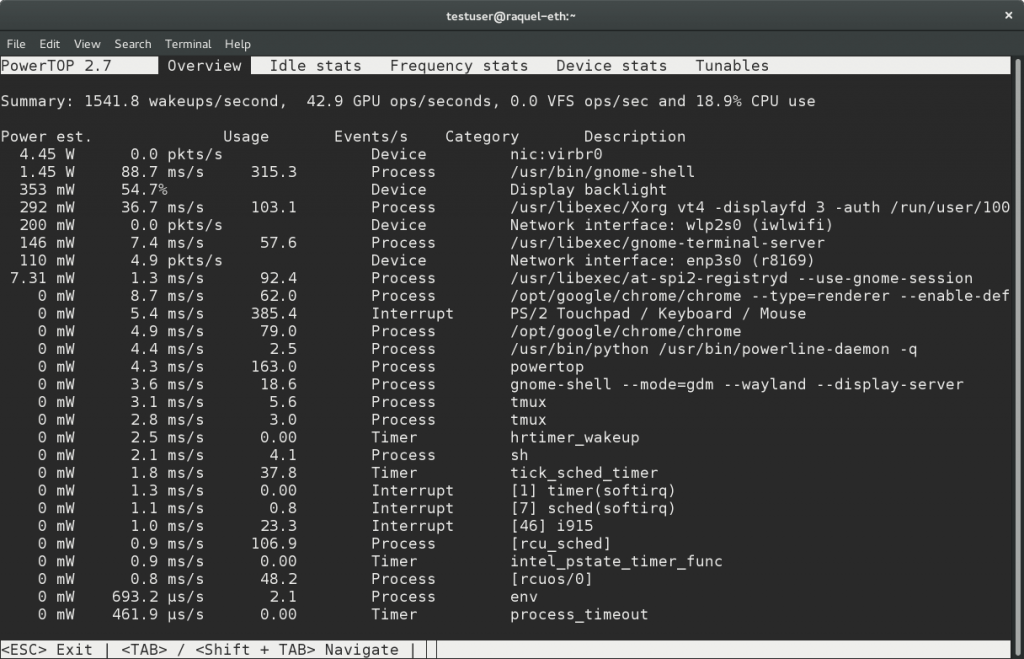
If you run powertop without any of the above options, it starts in an interactive mode as shown in the output below.
The overview screen
This display screen allows you to view a list of the system components that are either sending wake-ups to the CPU most frequently or are using the most power on the system.

The Idle stats screen
It displays various information about processor C-states.

The Frequency stats screen
This screen displays the frequency of wake-ups to the CPU.

The Device stats screen
It provides information similar to the Overview display screen but only for devices.

The Tunables screen
It provides suggestions for optimizing your system for good power consumption.

As you can see from the output above, there are different display screens available and to switch between them, you can use Tab and Shift+Tab keys. Exit powertop by pressing the Esc key as listed at the bottom of the screen.
It displays the number times your system wakes up each second, when you view the device stats display screen, it shows statistics of power usage by different hardware components and drivers.
To maximize battery power, you have to minimize system wake-ups. And to do this, you can use the Tunables display screen.
“Bad” identifies a setting that is not saving power, but may be good for the performance of your system.
Then “Good” identifies a setting that is saving power. Hit [Enter] key on any tunable to switch it to the other setting.
The example below shows output when using the —calibrate option.
After the calibration cycles, powertop will show the overview screen with a summary of operations as below.
Generating PowerTop CSV Report
The next example shows generating a CSV report for twenty seconds.

Now let’s view the CSV report using cat command.

Generate PowerTop HTML Report
You can generate a html report as follows, the html file extension is added automatically to the filename.

The sample html report file as viewed from a browser.

This tool also has a daemon service that helps to automatically set all tunables to “Good” for optimal power saving, and you can use it as follows:
To make the daemon service start at boot time, run the following command:
Summary
You need to take caution when using daemon service because certain tunables pose a risk of data loss or weird system hardware behavior. This is evident with the “VM writeback timeout” settings that affects the time your system waits before writing any changes of data to the actual disk.
When the system loses all it power, then you risk losing all changes made on data for the last few seconds. Therefore you have to choose between saving power and securing your data.
Try to use this tool for some period of time and observe the performance of your battery. You can post a comment to tell us about many other similar tools or add information on usage of powertop, about error you encountered. Remember to always stay connected to Tecmint to get more of such guides.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник