- Process Hacker Forums
- Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
- Process Hacker
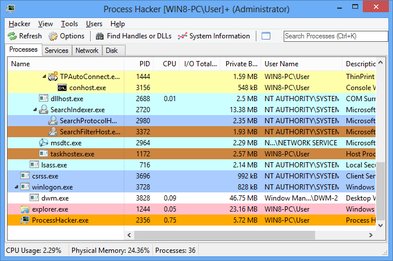
- Graphs and statistics allow you quickly to track down resource hogs and runaway processes.
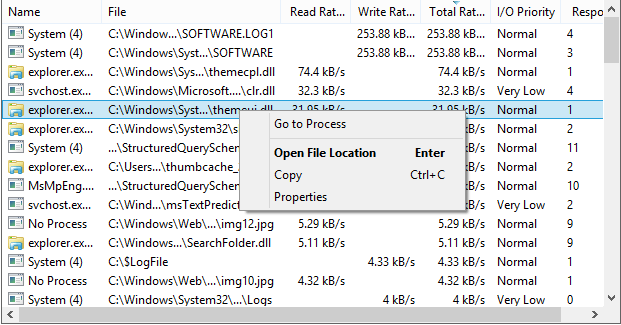
- Can’t edit or delete a file? Discover which processes are using that file.
- See what programs have active network connections, and close them if necessary.
- See a hightly detailed overview of system activity with highlighting.
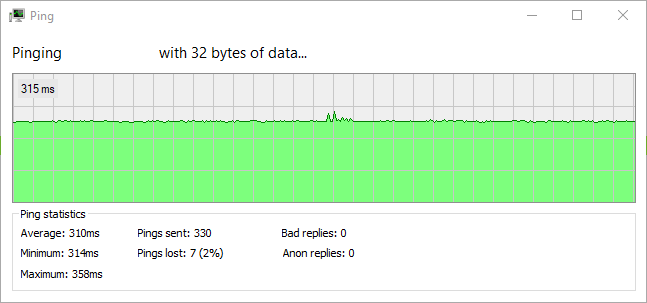
- See a hightly detailed overview of connection stability.
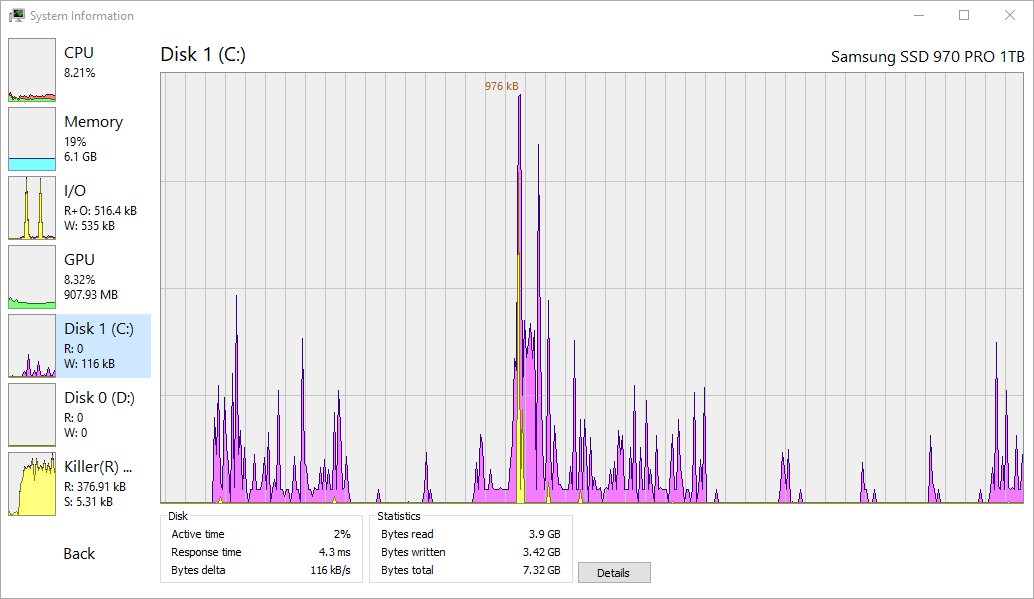
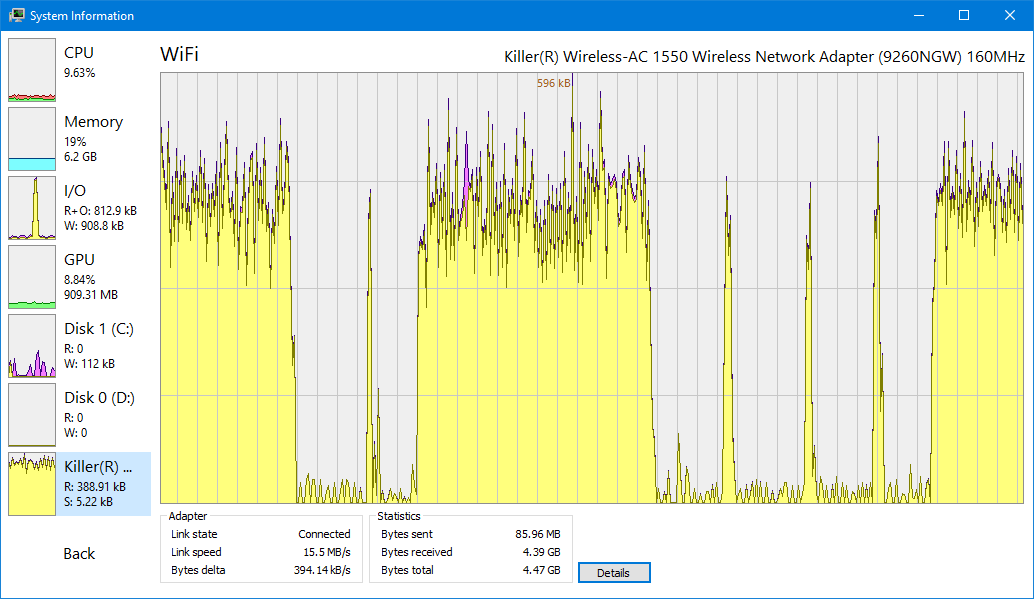
- Get real-time information on disk access.
- Get real-time information on disk usage.
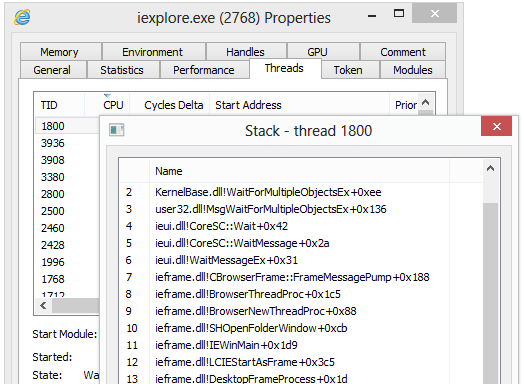
- View detailed stack traces with kernel-mode, WOW64 and .NET support.
- Get real-time information on network usage.
- Go beyond services.msc: create, edit and control services.
- Get real-time information on gpu usage.
- Process hacker 2 linux
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.md
- Process hacker 2 linux
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.md
- About
Process Hacker Forums
Process Hacker Discussion Forum
Porting Process Hacker to Linux
Porting Process Hacker to Linux
30 Apr 2015 20:06
I know it’s a very small suggestion.
No just kidding.
The issue is that I don’t know any task/process manager on Linux which is as nearly nice as Process Hacker is. I’m especially missing the coloured processes, process tree view, all the many, many columns where you can choose from (especially the commando line column) and all the other special features of PH.
I don’t know how difficult it is to port this to another OS, but if there would be a Linux version available it would be fantastic.
Or, alternatively, maybe you can recommend me an Linux task manager with similar features.
BTW I know that PH can be executed with Wine (more or less without crashes). However this is of course not what I want, because I want to see the Linux processes.
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
01 May 2015 05:52
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
01 May 2015 11:49
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
01 May 2015 12:27
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
07 Jun 2015 02:24
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
17 Dec 2015 16:08
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
29 Jan 2016 23:07
There’s systemd, it can be made possible if the required stuff is there and the special needs of something like PH are managed in a really secure way.
But it wouldn’t be PH, and but System Hacker. systemd is able to control every part of the system if used properly,including package management and configuring even your network.
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
30 Jan 2016 00:38
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
30 Jan 2016 13:18
@viksoftru We are not here to discuss systemd.
BTW my «problem» is to have a nice task manager on Linux. And I think with a task manager (similar to PH) for Linux this can be solved.
@timofonic
This sounds good. Obviously we do not need the full functionality of PH and so call it «System hacker» if you like.
I just like the colour support, the folding and the very tidied view of PH, which I cannot have on Linux as there is just not such a nice task manager.
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
30 Jan 2016 13:39
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
30 Jan 2016 13:49
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
30 Jan 2016 13:52
Re: Porting Process Hacker to Linux
30 Jan 2016 15:47
When you try to start Process Hacker under Wine you are working within the emulated her a subset of Windows, but to control the processes and objectives of the host system from it, you can never since this task manager has to work at the level of OS kernel as it is functional subsystem at best case you can manage some running in the same session, the WINE Windows-task itself if management application is fully compatible with the emulator.
And you if I understand you correctly would like to find a functional analogue of Process Hacker, but designed for the OS of Linux? Porting programs Class Process Hacker Wednesday another architecture OS requires the development from scratch because you have to redo the whole logic of their algorithms so as to take into account the often fundamental differences in the pattern of resource management computer installation and architecture of the source and target operating system and the only thing that we can take this general design ideas and some methods of work to show their friendliness to humans. Everything else in the programs of this class very deeply linked with the architecture of the operating system for which they are created and can not be transferred to other system platforms without a radical processing.
You better put a GUI-shell-like KDE, GNome, XFce — they have a similar built-in tools, and enhancing their need is even possible to ask for their development, but yes, as an example of what you would like them to see the possible cause Process Hacker.
Источник
Process Hacker
A free, powerful, multi-purpose tool that helps you monitor system resources, debug software and detect malware.
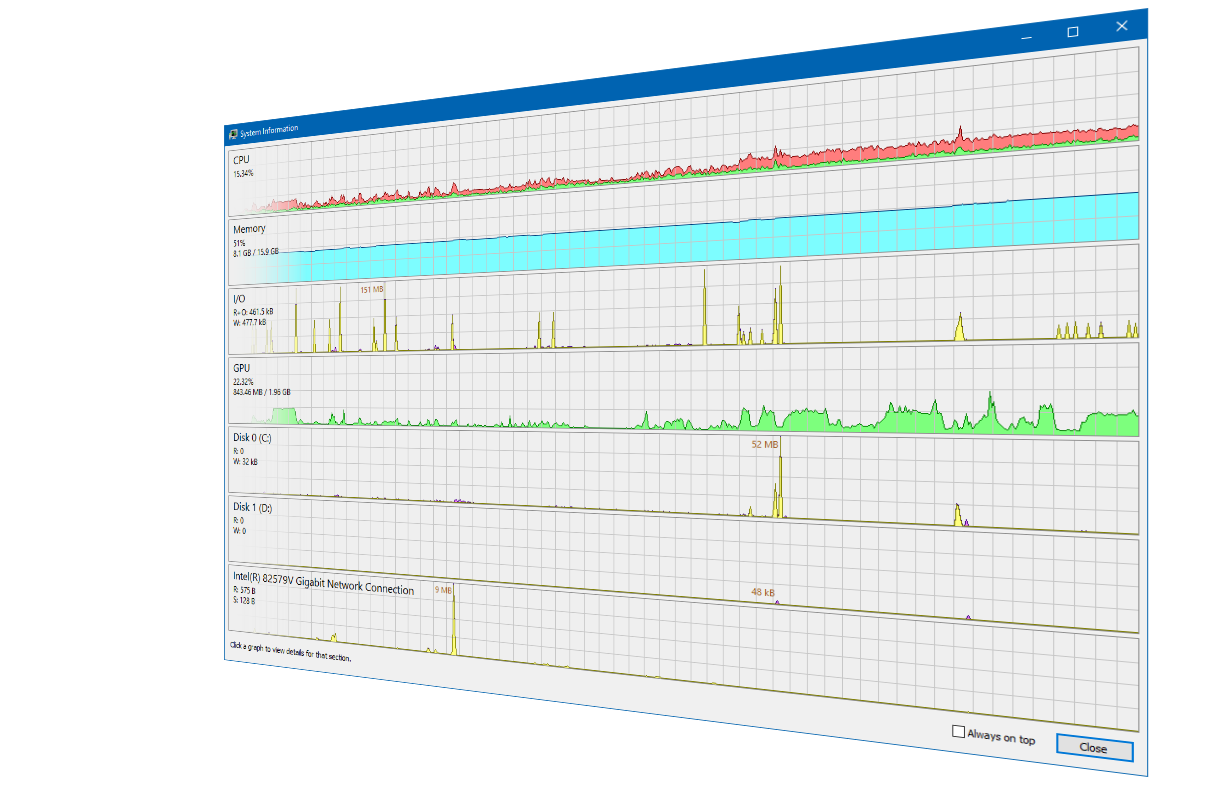
Graphs and statistics allow you quickly to track down resource hogs and runaway processes.
Use Ctrl+I to view system performance information. Move your cursor over a graph to get a tooltip with information about the data point under your cursor. You can double-click the graph to see information about the process at that data point, even if the process is no longer running.
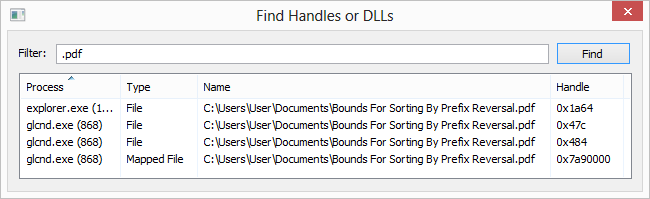
Can’t edit or delete a file? Discover which processes are using that file.
Use Ctrl+F to search for a handle or DLL. If all else fails, you can right-click an entry and close the handle associated with the file. However, this should only be used as a last resort and can lead to data loss and corruption.
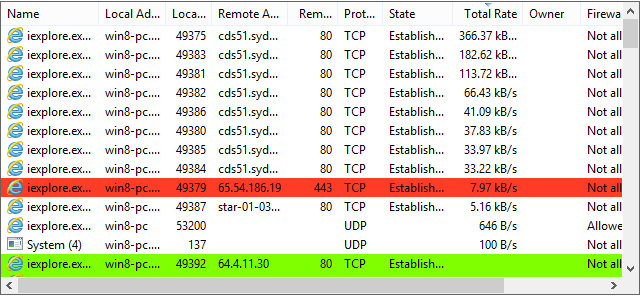
See what programs have active network connections, and close them if necessary.
Use Ctrl+I to view system performance information. Move your cursor over a graph to get a tooltip with information about the data point under your cursor. You can double-click the graph to see information about the process at that data point, even if the process is no longer running.
See a hightly detailed overview of system activity with highlighting.
Add extra columns to show even more system activity and information!
See a hightly detailed overview of connection stability.
Use the ping tool from the network tab to check the connection quality and stability.
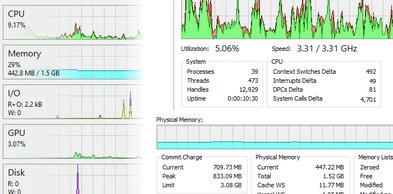
Get real-time information on disk access.
This may look very similar to the Disk Activity feature in Resource Monitor, but Process Hacker has a few more features!
Get real-time information on disk usage.
Enable disk statistics for detailed disk usage information.
View detailed stack traces with kernel-mode, WOW64 and .NET support.
Hover your cursor over the first column (with the numbers) to view parameter and line number information when available.
Get real-time information on network usage.
Enable network adapter statistics for detailed information network usage information.
Go beyond services.msc: create, edit and control services.
By default, Process Hacker shows entries for drivers in addition to normal user-mode services. You can turn this off by checking View > Hide Driver Services.
Get real-time information on gpu usage.
By default, Process Hacker shows gpu usage for all processes. Hover your cursor over the graph for detailed information when available.
Источник
Process hacker 2 linux
A free, powerful, multi-purpose tool that helps you monitor system resources, debug software and detect malware—mirror of https://github.com/processhacker2/processhacker.git
This branch is not ahead of the upstream master.
No new commits yet. Enjoy your day!
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md




A free, powerful, multi-purpose tool that helps you monitor system resources, debug software and detect malware.
Windows 7 or higher, 32-bit or 64-bit.
- A detailed overview of system activity with highlighting.
- Graphs and statistics allow you quickly to track down resource hogs and runaway processes.
- Can’t edit or delete a file? Discover which processes are using that file.
- See what programs have active network connections, and close them if necessary.
- Get real-time information on disk access.
- View detailed stack traces with kernel-mode, WOW64 and .NET support.
- Go beyond services.msc: create, edit and control services.
- Small, portable and no installation required.
- 100% Free Software (GPL v3)
Building the project
Requires Visual Studio (2019 or later).
Execute build_release.cmd located in the build directory to compile the project or load the ProcessHacker.sln and Plugins.sln solutions if you prefer building the project using Visual Studio.
You can download the free Visual Studio Community Edition to build the Process Hacker source code.
Please use the GitHub issue tracker for reporting problems or suggesting new features.
If you are running Process Hacker from a USB drive, you may want to save Process Hacker’s settings there as well. To do this, create a blank file named «ProcessHacker.exe.settings.xml» in the same directory as ProcessHacker.exe. You can do this using Windows Explorer:
- Make sure «Hide extensions for known file types» is unticked in Tools > Folder options > View.
- Right-click in the folder and choose New > Text Document.
- Rename the file to ProcessHacker.exe.settings.xml (delete the «.txt» extension).
Plugins can be configured from Hacker > Plugins.
If you experience any crashes involving plugins, make sure they are up to date.
Disk and Network information provided by the ExtendedTools plugin is only available when running Process Hacker with administrative rights.
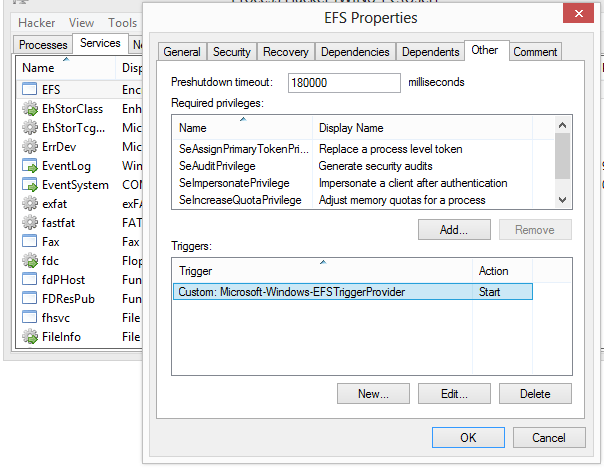
Process Hacker uses a kernel-mode driver, KProcessHacker, to assist with certain functionality. This includes:
- Capturing kernel-mode stack traces
- More efficiently enumerating process handles
- Retrieving names for file handles
- Retrieving names for EtwRegistration objects
- Setting handle attributes
Note that by default, KProcessHacker only allows connections from processes with administrative privileges (SeDebugPrivilege). To allow Process Hacker to show details for all processes when it is not running as administrator:
- In Registry Editor, navigate to: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\KProcessHacker3
- Under this key, create a key named Parameters if it does not exist.
- Create a DWORD value named SecurityLevel and set it to 2. If you are not using an official build, you may need to set it to 0 instead.
- Restart the KProcessHacker3 service (sc stop KProcessHacker3, sc start KProcessHacker3).
Источник
Process hacker 2 linux
A free, powerful, multi-purpose tool that helps you monitor system resources, debug software and detect malware.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md




A free, powerful, multi-purpose tool that helps you monitor system resources, debug software and detect malware.
Windows 7 or higher, 32-bit or 64-bit.
- A detailed overview of system activity with highlighting.
- Graphs and statistics allow you quickly to track down resource hogs and runaway processes.
- Can’t edit or delete a file? Discover which processes are using that file.
- See what programs have active network connections, and close them if necessary.
- Get real-time information on disk access.
- View detailed stack traces with kernel-mode, WOW64 and .NET support.
- Go beyond services.msc: create, edit and control services.
- Small, portable and no installation required.
- 100% Free Software (GPL v3)
Building the project
Requires Visual Studio (2019 or later).
Execute build_release.cmd located in the build directory to compile the project or load the ProcessHacker.sln and Plugins.sln solutions if you prefer building the project using Visual Studio.
You can download the free Visual Studio Community Edition to build the Process Hacker source code.
Please use the GitHub issue tracker for reporting problems or suggesting new features.
If you are running Process Hacker from a USB drive, you may want to save Process Hacker’s settings there as well. To do this, create a blank file named «ProcessHacker.exe.settings.xml» in the same directory as ProcessHacker.exe. You can do this using Windows Explorer:
- Make sure «Hide extensions for known file types» is unticked in Tools > Folder options > View.
- Right-click in the folder and choose New > Text Document.
- Rename the file to ProcessHacker.exe.settings.xml (delete the «.txt» extension).
Plugins can be configured from Hacker > Plugins.
If you experience any crashes involving plugins, make sure they are up to date.
Disk and Network information provided by the ExtendedTools plugin is only available when running Process Hacker with administrative rights.
Process Hacker uses a kernel-mode driver, KProcessHacker, to assist with certain functionality. This includes:
- Capturing kernel-mode stack traces
- More efficiently enumerating process handles
- Retrieving names for file handles
- Retrieving names for EtwRegistration objects
- Setting handle attributes
Note that by default, KProcessHacker only allows connections from processes with administrative privileges (SeDebugPrivilege). To allow Process Hacker to show details for all processes when it is not running as administrator:
- In Registry Editor, navigate to: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\KProcessHacker3
- Under this key, create a key named Parameters if it does not exist.
- Create a DWORD value named SecurityLevel and set it to 2. If you are not using an official build, you may need to set it to 0 instead.
- Restart the KProcessHacker3 service (sc stop KProcessHacker3, sc start KProcessHacker3).
About
A free, powerful, multi-purpose tool that helps you monitor system resources, debug software and detect malware.
Источник