Process Explorer v16.32
By Mark Russinovich
Published: April 28, 2020

Run now from Sysinternals Live.
Introduction
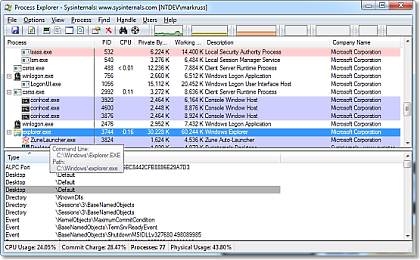
Ever wondered which program has a particular file or directory open? Now you can find out. Process Explorer shows you information about which handles and DLLs processes have opened or loaded.
The Process Explorer display consists of two sub-windows. The top window always shows a list of the currently active processes, including the names of their owning accounts, whereas the information displayed in the bottom window depends on the mode that Process Explorer is in: if it is in handle mode you’ll see the handles that the process selected in the top window has opened; if Process Explorer is in DLL mode you’ll see the DLLs and memory-mapped files that the process has loaded. Process Explorer also has a powerful search capability that will quickly show you which processes have particular handles opened or DLLs loaded.
The unique capabilities of Process Explorer make it useful for tracking down DLL-version problems or handle leaks, and provide insight into the way Windows and applications work.
Related Links
- Windows Internals Book The official updates and errata page for the definitive book on Windows internals, by Mark Russinovich and David Solomon.
- Windows Sysinternals Administrator’s Reference The official guide to the Sysinternals utilities by Mark Russinovich and Aaron Margosis, including descriptions of all the tools, their features, how to use them for troubleshooting, and example real-world cases of their use.
Download

Run now from Sysinternals Live.
Runs on:
- Client: Windows Vista and higher (Including IA64).
- Server: Windows Server 2008 and higher (Including IA64).
Installation
Simply run Process Explorer (procexp.exe).
The help file describes Process Explorer operation and usage. If you have problems or questions please visit the Process Explorer forum on Technet.
Note on use of symbols
When you configure the path to DBGHELP.DLL and the symbol path uses the symbol server, the location of DBGHELP.DLL also has to contain the SYMSRV.DLL supporting the server paths used. See SymSrv documentation or more information on how to use symbol servers.
Learn More
Here are some other handle and DLL viewing tools and information available at Sysinternals:
- The case of the Unexplained. In this video, Mark describes how he has solved seemingly unsolvable system and application problems on Windows.
- Handle — a command-line handle viewer
- ListDLLs — a command-line DLL viewer
- PsList — local/remote command-line process lister
- PsKill — local/remote command-line process killer
- Defrag Tools: #2 — Process Explorer In this episode of Defrag Tools, Andrew Richards and Larry Larsen show how to use Process Explorer to view the details of processes, both at a point in time and historically.
- Windows Sysinternals Primer: Process Explorer, Process Monitor and More Process Explorer gets a lot of attention in the first Sysinternals Primer delivered by Aaron Margosis and Tim Reckmeyer at TechEd 2010.
—>
Windows Processor Requirements
This specification details the processors that can be used with Customer Systems that include Windows Products (including Custom Images). Updates to this specification may be released in the future as requirements change.
For each listed edition, Company must use only the processors listed, as specified in the tables below. The requirements below apply whenever the edition below is pre-installed or provided on external media, including as downgrade or down edition software.
For clarity, Company must also meet all processor and other requirements specified in Minimum Hardware Requirements for Windows 10, located at https://msdn.microsoft.com/library/windows/hardware/dn915086(v=vs.85).aspx (or updated URL).
If after the inclusion of a processor series in this specification (“Listed Processor”), a processor becomes commercially available that uses the same naming convention or identifier as a Listed Processor but has additional or different features or functionality (“New Processor”), Company must not use New Processor for Customer Systems without Microsoft’s prior written permission. If Company believes a processor has been omitted from this list, please contact Company’s Microsoft OEM or ODM Account Manager.
The processors listed in the tables below, represent the latest processor generations and models which are supported for the listed Windows Edition. Previous generations of processors and models (indicated by «Up through»), remain supported in addition to the listed processors and models.
Some product editions or edition/processor configurations listed below may have no or limited support. Information on support is available at Microsoft Support Policy (https://support.microsoft.com/lifecycle) and Microsoft Lifecycle FAQ (https://support.microsoft.com/help/18581). For specific hardware support, please refer to your Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) provider.
Windows Client Edition Processors
| Windows Edition | Intel Processors | AMD Processors | Qualcomm Processors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 and earlier editions | Up through the following 6th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7-6xxx, Core m3/m5/m7-6xxx, and Xeon E3-xxxx v5), and through series equivalent Intel Atom, Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 6th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-8xxx & E-Series Ex-8xxx & FX-870K) | N/A |
| Windows 8.1 | Up through the following 6th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7-6xxx, Core m3/m5/m7-6xxx, and Xeon E3-xxxx v5), and through series equivalent Intel Atom, Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 6th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-8xxx & E-Series Ex-8xxx & FX-870K) | N/A |
| Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB 1507 | Up through the following 6th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7-6xxx, Core m3/m5/m7-6xxx, and Xeon E3-xxxx v5), and through series equivalent Intel Atom, Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 6th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-8xxx & E-Series Ex-8xxx & FX-870K) | N/A |
| Windows 10 1511 | Up through the following 7th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7-7xxx, Core m3-7xxx, and Xeon E3-xxxx v6), and Intel Atom, Celeron, and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx) | N/A |
| Windows 10 1607 | Up through the following 7th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7/i9-7xxx, Core m3-7xxx, and Xeon E3-xxxx v6), Intel Atom, Celeron, and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx) | N/A |
| Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB 1607 | Up through the following 7th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7/i9-7xxx, Core m3-7xxx, and Xeon E3-xxxx v6), Intel Atom, Celeron, and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx) | N/A |
| Windows 10 1703 | Up through the following 7th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7/i9-7xxx, Core m3-7xxx, and Xeon E3-xxxx v6) and 8th Generation Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7-8xxxU), Intel Atom (J4xxx/J5xxx and N4xxx/N5xxx), Celeron, and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx), AMD Athlon 2xx, and AMD Ryzen 3/5/7 2xxx | N/A |
| Windows 10 1709 | Up through the following 8th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7/i9-8xxxK/U/H/G, and Intel Xeon E-21xx [1] ), Intel Atom (J4xxx/J5xxx and N4xxx/N5xxx), Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx); AMD Athlon 2xx, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7/Threadripper 2xxx, AMD Opteron [2] and AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] Processors | Qualcomm Snapdragon 835 |
| Windows 10 1803 | Up through the following 9th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7/i9-9xxx), and Intel Xeon E-21xx [1] ), Intel Atom (J4xxx/J5xxx and N4xxx/N5xxx), Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx); AMD Athlon 2xx, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7/Threadripper 2xxx, AMD Opteron [2] and AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] Processors | Qualcomm Snapdragon 835 and 850 |
| Windows 10 1809 | Up through the following 10th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7/i9-10xxx), and Intel Xeon W-12xx/W-108xx [1] , Intel Xeon SP 32xx, 42xx, 52xx, 62xx, and 82xx [1] , Intel Atom (J4xxx/J5xxx and N4xxx/N5xxx), Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx); AMD Athlon 2xx processors, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7/Threadripper 2xxx, AMD Opteron [2] and AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] | Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 |
| Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 1809 | Up through the following 10th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7/i9-10xxx), and Intel Xeon W-12xx/W-108xx [1] , Intel Xeon SP 32xx, 42xx, 52xx, 62xx, and 82xx [1] , Intel Atom (J4xxx/J5xxx and N4xxx/N5xxx), Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx); AMD Athlon 2xx processors, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7 4xxx, AMD Opteron [2] and AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] | N/A |
| Windows 10 1903 | Up through the following 11th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7-11xxx), and Intel Xeon W-12xx/W-108xx [1] , Intel Xeon SP 32xx, 42xx, 52xx, 62xx, and 82xx [1] , Intel Atom (J4xxx/J5xxx and N4xxx/N5xxx), Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx); AMD Athlon 2xx processors, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7/9/Threadripper 3xxx, AMD Opteron [2] and AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] | Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 and 8cx |
| Windows 10 1909 | Up through the following 11th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7-11xxx), and Intel Xeon W-12xx/W-108xx [1] , Intel Xeon SP 32xx, 42xx, 52xx, 62xx, and 82xx [1] , Intel Atom (J4xxx/J5xxx and N4xxx/N5xxx), Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx); AMD Athlon 2xx processors, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7/9/Threadripper 3xxx, AMD Opteron [2] and AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] | Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 and 8cx |
| Windows 10 2004 | Up through the following 11th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7-11xxx), and Intel Xeon W-12xx/W-108xx [1] , Intel Xeon SP 32xx, 42xx, 52xx, 62xx, and 82xx [1] , Intel Atom (J4xxx/J5xxx and N4xxx/N5xxx), Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx); AMD Athlon 2xx processors, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7/9 4xxx, AMD Opteron [2] and AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] | Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 and 8cx |
| Windows 10 20H2 | Up through the following 11th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3/i5/i7-11xxx), and Intel Xeon W-12xx/W-108xx [1] , Intel Xeon SP 32xx, 42xx, 52xx, 62xx, and 82xx [1] , Intel Atom (J4xxx/J5xxx and N4xxx/N5xxx), Celeron and Pentium Processors | Up through the following AMD 7th Generation Processors (A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx); AMD Athlon 2xx processors, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7/9 4xxx, AMD Opteron [2] and AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] | Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 and 8cx |
[1] Intel Xeon processors are supported on Windows 10 Pro for Workstations and Windows 10 Enterprise only
[2] AMD Opteron and AMD EPYC processors are supported on Windows 10 Pro for Workstations and Windows 10 Enterprise only
Windows IoT Core Processors
| Windows Edition | Intel Processors | Qualcomm Processor | Broadcom | NXP Processors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 1703 | Up through currently enabled Intel Joule, Atom, Celeron and Pentium Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Qualcomm Snapdragon Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Broadcom Processors [3] | N/A |
| Windows 10 1709 | Up through currently enabled Intel Joule, Atom, Celeron and Pentium Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Qualcomm Snapdragon Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Broadcom Processors [3] | N/A |
| Windows 10 1803 | Up through currently enabled Intel Joule, Atom, Celeron and Pentium Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Qualcomm Snapdragon Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Broadcom Processors [3] | N/A |
| Windows 10 IoT Core 1809 (SAC) | Up through currently enabled Intel Atom, Celeron and Pentium Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Qualcomm Snapdragon Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Broadcom Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled NXP i.MXProcessors [3] |
| Windows 10 IoT Core 1809 (LTSC) | Up through currently enabled Intel Atom, Celeron and Pentium Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Qualcomm Snapdragon Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled Broadcom Processors [3] | Up through currently enabled NXP i.MXProcessors [3] |
[3] Information on which processors are currently enabled is available atВ /windows/iot-core/learn-about-hardware/socsandcustomboards
Windows 10 IoT Enterprise
Review the Windows Client Edition Processors support matrix above for Windows 10 IoT Enterprise.
NOTE: The processor support matrix only reflects the core OS support for the processor. There may be other dependencies like hardware-specific drivers which are not reflected in this matrix. Please contact your OEM or processor manufacturer for hardware-specific support.
Windows Server Processors
| Windows Edition | Intel Processors | AMD Processors | Hygon Processors [6] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2012 R2 [4] | Up through the following 7th Generation Intel Processors (Intel Core i3-7xxx/Celeron/Pentium; Xeon E3 v6); Xeon SP 32xx, 42xx, 52xx, 62xx, and 82xx; Xeon D 15xx; and Atom C33xx | Up through the following AMD 7th generation processors (AMD A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx), AMD Ryzen Family, AMD EPYC 7xx1, AMD EPYC 7xx2, and AMD EPYC 7xx3 | N/A |
| Windows Server 2016 [5] | Up through the following 9th Generation Intel Processors (Core i3-9xxx, Pentium G5xxx, Celeron G49xx); Xeon E22xx; Xeon SP 32xx, 42xx, 52xx, 62xx, and 82xx; Xeon D 21xx; and Atom C33xx | Up through the following AMD 7th generation processors (AMD A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx), AMD Ryzen Family, AMD EPYC 7xx1, AMD EPYC 7xx2, and AMD EPYC 7xx3 | N/A |
| Windows Server 2019 | Up through the following 9th Generation Intel Processors (Core i3-9xxx, Pentium G5xxx, Celeron G49xx); Xeon E22xx; Xeon SP 32xx, 42xx, 52xx, 62xx, and 82xx; Xeon D 21xx; and Atom C33xx | Up through the following AMD 7th generation processors (AMD A-Series Ax-9xxx & E-Series Ex-9xxx & FX-9xxx), AMD Ryzen Family, AMD EPYC 7xx1, AMD EPYC 7xx2, and AMD EPYC 7xx3 | Hygon C86 7xxx |
[4] Company may submit for certification (in the Windows Hardware Compatibility Program) Customer Systems running Windows Server 2012R2 and the identified processors until December 31, 2018; after such date, no new Customer Systems will be certified running Windows Server 2012R2.
[5] Microsoft continues to evaluate the processor list and potential end dates for certification (in the Windows Hardware Compatibility Program) for Customer Systems running Windows Server 2016.
[6] China Market Only
NOTE: The list of supported processors above does not in itself determine Microsoft support for Windows Server. The listing is a prerequisite for system certification. Only systems based on the above approved processors can be certified for Windows Server.