- Как установить PHP на Windows
- Скачать PHP:
- Установка PHP:
- Тест PHP:
- Installation on Windows systems
- Table of Contents
- User Contributed Notes 12 notes
- How to Install PHP on Windows
- Learn PHP for free!
- Why PHP?
- Why Install PHP Locally?
- Alternative Installation Options
- Use an All-in-One package
- Use a Linux Virtual Machine
- Use Windows Subsystem for Linux 2
- Use Docker
- Install Apache (optional)
- Install PHP
- Step 1: Download the PHP files
- Step 2: Extract the files
- Step 3: Configure php.ini
- Step 4: Add C:\php to the PATH environment variable
- Step 5: Configure PHP as an Apache module
- Step 6: Test a PHP file
Как установить PHP на Windows
В этой статье вы узнаете как установить php 7.0 и выше на Windows 10, очень просто, надеюсь эта статья будет полезна для вас.
Скачать PHP:
Сначала вам надо скачать PHP 7 для Windows 10 c сайта или для Windows 7, для этого заходим по ссылки, там нажимаем на Zip.
Как можете заметить, я скачиваю тут x64 битную, но не переживаете, там также вы можете скачать x32 битную версию, для этого надо прокрутить чуть ниже и найти, где будет написано x86, если в друг у вас архитектура не x64.
Установка PHP:
После того как скачали сам PHP, пришло время его установить, для архивируем архив который скачали, и создаём папку куда положим все файлы.
Как можете заметить, я поместил все файлы в папку в документах, но это ещё не всё.
Теперь на надо добавить PHP в path, чтобы была возможность запускать PHP скрипты из командной строки, для этого заходим в «Этот компьютер» и там нажимаем правой кнопкой мыши, выбираем «Свойства».
Дальше в открывшемся окне с боку выбираем «Дополнительные параметры системы».
В открывшемся окне нажимаем на кнопку «Переменные среды…».
В открывшемся окне выбираем внизу «Path» и нажимаем кнопку изменить.
Нажимаем «Создать» и вписываем путь, куда вы архивировали ваш PHP, на этом всё и заканчивается, поздравляю вас, вы установили и подключили PHP.
Тест PHP:
Теперь не большой тест, что бы наперника проверить что мы правильно установили PHP, для этого открываем блокнот и делаем не большую PHP программу.
Installation on Windows systems
Table of Contents
Installing PHP on modern Microsoft Windows systems and recommended configuration with common web servers.
If you are looking for information about older systems, such as Windows XP, 2003, 98 or Apache 1.x, see the Legacy Info section.
The Official releases of PHP on Windows are recommended for production use. However, you are welcome to build PHP from Source. You will need a Visual Studio environment. See » Step by Step Build Instructions.
Installing PHP on Azure App Services (aka Microsoft Azure, Windows Azure, or (Windows) Azure Web Apps).
User Contributed Notes 12 notes
If you make changes to your PHP.ini file, consider the following.
(I’m running IIS5 on W2K server. I don’t know about 2K3)
PHP will not «take» the changes until the webserver is restarted, and that doesn’t mean through the MMC. Usually folks just reboot. But you can also use the following commands, for a much faster «turnaround». At a command line prompt, type:
and that will stop the webserver service. Then type:
net start w3svc
and that will start the webserver service again. MUCH faster than a reboot, and you can check your changes faster as a result with the old:
in your page somewhere.
I wish I could remember where I read this tip; it isn’t anything I came up with.
You can have multiple versions of PHP running on the same Apache server. I have seen many different solutions pointing at achieving this, but most of them required installing additional instances of Apache, redirecting ports/hosts, etc., which was not satisfying for me.
Finally, I have come up with the simplest solution I’ve seen so far, limited to reconfiguring Apache’s httpd.conf.
My goal is to have PHP5 as the default scripting language for .php files in my DocumentRoot (which is in my case d:/htdocs), and PHP4 for specified DocumentRoot subdirectories.
Here it is (Apache’s httpd.conf contents):
—————————
# replace with your PHP4 directory
ScriptAlias /php4/ «c:/usr/php4/»
# replace with your PHP5 directory
ScriptAlias /php5/ «c:/usr/php5/»
AddType application/x-httpd-php .php
Action application/x-httpd-php «/php5/php-cgi.exe»
# populate this for every directory with PHP4 code
Action application/x-httpd-php «/php4/php.exe»
# directory where your PHP4 php.ini file is located at
SetEnv PHPRC «c:/usr/php4»
# remember to put this section below the above
# directory where your PHP5 php.ini file is located at
SetEnv PHPRC «c:/usr/php5»
—————————
This solution is not limited to having only two parallel versions of PHP. You can play with httpd.conf contents to have as many PHP versions configured as you want.
You can also use multiple php.ini configuration files for the same PHP version (but for different DocumentRoot subfolders), which might be useful in some cases.
Remember to put your php.ini files in directories specified in lines «SetEnv PHPRC. «, and make sure that there’s no php.ini files in other directories (such as c:\windows in Windows).
And finally, as you can see, I run PHP in CGI mode. This has its advantages and limitations. If you have to run PHP as Apache module, then. sorry — you have to use other solution (the best advice as always is: Google it!).
Hope this helps someone.
If you are installing PHP on Vista just go to David Wang’s blog. http://blogs.msdn.com/david.wang/
archive/2006/06/21/HOWTO-Install-and-Run-PHP-on-IIS7-Part-2.aspx
I made the mistake of setting a ‘wildcard application map’ for PHP on a Windows 2003 / IIS 6.0 / PHP ISAPI installation.
This resulted in «No input file specified» errors whenever I tried to load the default page in my site’s directories. I don’t know why this broke things, but it did.
If anyone has the same problem, this may be the cause.
IIS setup: 403 forbidden error.
We had installed two separate different PHP versions — PHP 5.1.4 followed by 5.2.5.
We configured 5.2.5 php5isapi.dll to be loaded as the .php file type extension.
Despite this, php version 5.1.4 was being loaded. We renamed 5.1.4’s folder and then PHP was not loading at all.
There were no visible references to 5.1.4 in the IIS configuration, but in the file \webConfig.xml, there was a reference to 5.1.4’s isapi under IISFilters.
To fix this problem, we added version 5.2.5’s php5isapi.dll to the ISAPI Filter category for the web site, in the IIS control panel.
I installed by Microsoft Installer, manually, whatever I always received de same error from IIS7.
HTTP Error 404.3 — Not Found
The page you are requesting cannot be served because of the extension configuration. If the page is a script, add a handler. If the file should be downloaded, add a MIME map.
The IIS7 interface is quite diferent and are not all together like IIS6
The 5.3 version have not any of those files: php5stdll, php5isapi.dll. etc.
The installer puts others files in handlers and I decided to use them as substitutes. Nothing done!
After that, I discovered that installer do not install these files within the sites, but in the root default site configuration of IIS7.
So, I copied the root configuration to my site and them it worked (all others procedures were done e.g. copy php.ini to windows folder)
If you get 404 page not found on Windows/IIS5, have a look at C:\SYSTEM32\INETSRV\URLSCAN
There is a .ini file there that prevents some files from being served by IIS, even if they exist, instead IIS will give a 404. The urlscan logfile (same place) should give you some insight into what parameter is preventing a page from loading, if any.
Here’s how to run dual PHP instances with PHP 5.2 and any previous PHP on Windows 2003:
1. Right-click My Computer, go to Advanced tab, and click on Environment Variables.
Add the two installations and their EXT directories to the Path variable. For example, add:
c:\php;c:\php\ext;c:\TMAS\php;c:\tmas\php\ext;
Then, add the newer PHP version’s directory as a variable called PHPRC. For example:
Variable:PHPRC
Value: C:\PHP
Click OK to close the Environment Variables window, and click OK to close System Properties.
2. In registry, under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE>SOFTWARE>PHP, add a REG_SZ key called iniFilePath and give it a value
of the directory where the older PHP is installed. For example:
C:\TMAS\PHP
3. In IIS, go to the Web Service Extensions. Add both versions’ ISAPI module separately to the extensions
list, and allow both.
4. In IIS, go to each website utilizing the PHP versions. Set an ISAPI filter if needed. On the Home Directory
tab, click Configuration, and add .php, .php3, .phtml, and any other extensions needed (perhaps .html?) to
be filtered through PHP, and specify the ISAPI module version needed for each website.
You can now run two versions of PHP. This is because the order of where to look for the .ini file changed
between previous PHP versions and PHP 5.2, as documented at http://us2.php.net/ini:
* SAPI module specific location (PHPIniDir directive in Apache 2, -c command line option in CGI and CLI, php_ini parameter in NSAPI, PHP_INI_PATH environment variable in THTTPD)
* The PHPRC environment variable. Before PHP 5.2.0 this was checked after the registry key mentioned below.
* HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\PHP\IniFilePath (Windows Registry location)
* Current working directory (for CLI)
* The web server’s directory (for SAPI modules), or directory of PHP (otherwise in Windows)
* Windows directory (C:\windows or C:\winnt) (for Windows), or —with-config-file-path compile time option
—————————————————-
PHP 5.2.9.2 Install on XP Pro IIS 5.1 — phpinfo( ) results incorrect
Testing Date: 05.15.09
Background:
For several days now I, as a newbie, have been unsure if I had installed PHP correctly, or not. No matter what I did phpinfo( ) reported «Configuratin File Path» as: “C:\WINDOWS”. I was left to wonder what was wrong.
To help resolve the phpinfo() “issue”, I conducted a series of tests using two scripts:
The first is “test-php-ini-loaded.php”; it is stored in c:\inetpub\wwwroot, and has the following code:
if ( $inipath ) <
echo ‘Loaded php.ini: ‘ . $inipath ;
> else <
echo ‘A php.ini file is not loaded’ ;
>
?>
The second script is simply calls phpinfo( ). It is named test.php, is stored in “c:\inetpub\wwroot”, and has the following code:
( ); ?>
My Dev Environment:
1. Windows XP Pro SP3
2. IIS 5.1 / MMC 3.0
3. PHP 5.2.9.2 – phpMyAdmin not yet installed
4. (plus MySQL 5.1, etc.)
5. Install location is on my local E: drive
How to Install PHP on Windows
Learn PHP for free!
Make the leap into server-side programming with a comprehensive cover of PHP & MySQL.
Normally RRP $39.99 Yours absolutely free
This article explains how to install PHP 8 and Apache 2.4 on Windows 10 (64-bit).
Linux and macOS users often have Apache and PHP pre-installed or available via package managers. Windows 10 requires a little more effort. The steps below may work with other editions of Windows, PHP, and Apache, but check the documentation of each dependency for specific instructions.
Why PHP?
PHP remains the most widespread and popular server-side programming language on the Web. It’s installed by most web hosts, and has a simple learning curve, close ties with the MySQL database, superb documentation, and an excellent collection of libraries to cut your development time. PHP may not be perfect, but it should be considered as an option for your next web application. It’s the language of choice for Facebook, Slack, Wikipedia, MailChimp, Etsy, and WordPress — the Content Management System which powers 40% of the web.
Why Install PHP Locally?
Installing PHP on your development PC allows you to safely create and test websites and applications without affecting the data or systems on your live server.
Alternative Installation Options
Before you jump in, there may be a simpler installation options…
Use an All-in-One package
All-in-one packages are available for Windows which contain Apache, PHP, MySQL, and many other dependencies in a single installation file — such as XAMPP, WampServer and Web.Developer.
These packages are easy to use, but they may not exactly match your live server. Installing Apache and PHP manually will help you learn more about the system and configuration options.
Use a Linux Virtual Machine
Microsoft Hyper-V (provided in Windows 10 Professional) and VirtualBox are free hypervisors which emulate a PC so you can install another operating system.
You can install any version of Linux, then follow its Apache and PHP installation instructions. Alternatively, distros such as Ubuntu Server provide them as standard (although they’re rarely the latest editions).
Use Windows Subsystem for Linux 2
WSL2 is also a virtual machine, but it’s tightly integrated into Windows so activities such as file sharing and localhost resolution is seamless. You can install several Linux distros, so refer to the appropriate Apache and PHP instructions.
Use Docker
Docker creates a wrapper (known as a container) around pre-configured application dependencies such as Apache, PHP, MySQL, MongoDB, and most other web software. Containers look like full Linux Virtual Machines but are considerably more lightweight.
Docker is currently considered the best option for setting up a PHP development environment. Check out SitePoint’s article “Setting Up a Modern PHP Development Environment with Docker” for a complete guide to setting it up.
Install Apache (optional)
If you’re still reading, the following sections describe how to install Apache and PHP directly on Windows.
PHP provides a built-in web server which can be launched by navigating to a folder and running the PHP executable with an -S parameter to set the localhost port. for example:
PHP pages can then be viewed in a browser at http://localhost:8000.
This may be adequate for quick tests, but your live server will use Apache or similar web server software. Emulating that environment as closely as possible will prevent development errors.
To install Apache, download the latest Win64 ZIP file from https://www.apachelounge.com/download/ and extract its Apache24 folder to the root of your C: drive. You’ll also need to install the Visual C++ Redistributable for Visual Studio 2015–2019 ( vc_redist_x64 ); a link is provided on the same page.
Open a cmd command prompt (not PowerShell) and start Apache with:
You may need to accept a firewall exception before the server starts to run. Open http://localhost in a browser and an “It works!” message should appear. Note:
- If you need to change any settings, Apache’s configuration file is located at C:\Apache24\conf\httpd.conf .
- The web server root folder is located at C:\Apache24\htdocs . Initially, it contains a single index.html file with the “It works!” message.
Also not that, if Apache won’t start, it’s likely another application is hogging port 80. (Skype is the prime candidate and the Windows 10 app won’t let you disable it!) If this occurs, edit C:\Apache24\conf\httpd.conf and change the line Listen 80 to Listen 8080 or any other free port. Restart Apache and, from that point onward, you can load web files at http://localhost:8080
The server can be stopped with Ctrl + C . The ReadMe file in the ZIP also provides instructions for installing Apache as a Windows service.
Install PHP
Install PHP by following the steps below. Note that there are several ways to configure Apache and PHP, but this is possibly the quickest method.
Step 1: Download the PHP files
Get the latest PHP 8 x64 Thread Safe ZIP package from https://www.php.net/downloads.php.
Step 2: Extract the files
Create a new php folder in the root of your C:\ drive and extract the contents of the ZIP into it.
PHP can be installed anywhere on your system, but you’ll need to change the paths referenced below if C:\php isn’t used.
Step 3: Configure php.ini
PHP’s configuration file is named php.ini . This doesn’t exist initially, so copy C:\php\php.ini-development to C:\php\php.ini . This default configuration provides a development setup which reports all PHP errors and warnings.
There are several lines you may need to change in a text editor (use search to find the current value). In most cases, you’ll need to remove a leading semicolon ( ; ) to uncomment a setting.
First, enable any required extensions. This will depend on the libraries you want to use, but the following extensions should be suitable for most applications:
If you want to send emails using PHP’s mail() function, enter the details of an SMTP server in the [mail function] section (your ISP’s server should be suitable):
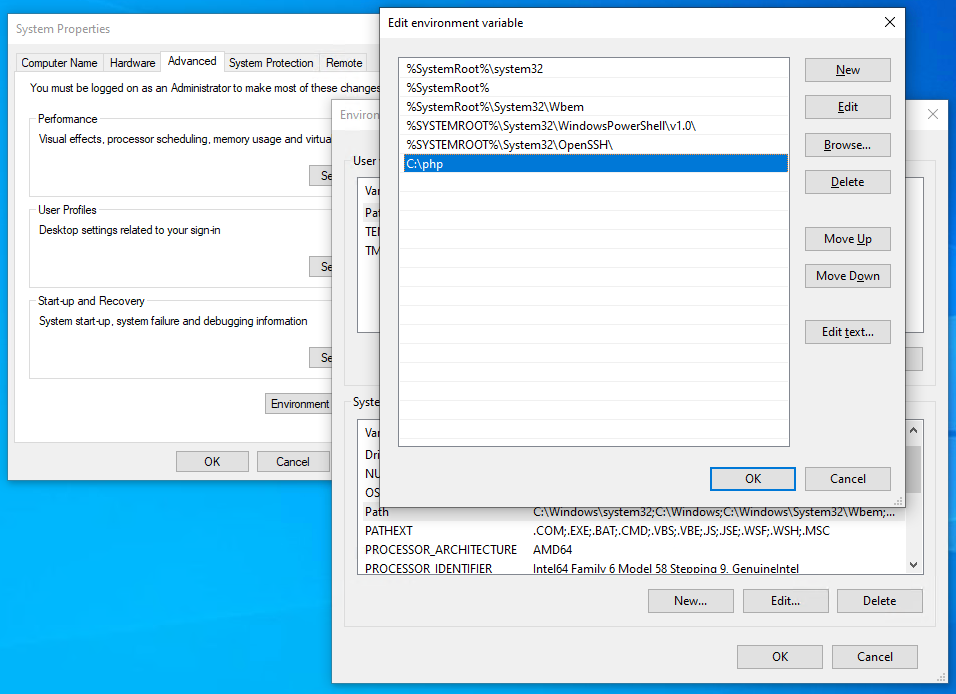
Step 4: Add C:\php to the PATH environment variable
To ensure Windows can find the PHP executable, you need to change the PATH environment variable. Click the Windows Start button and type “environment”, then click Edit the system environment variables. Select the Advanced tab, and click the Environment Variables button.
Scroll down the System variables list and click Path followed by the Edit button. Click New and add C:\php :
Note that older editions of Windows have a single text box where each path is separated by a semi-colon ( ; ).
Now OK your way out. You shouldn’t need to reboot, but you may need to close and restart any cmd terminals you have open.
Step 5: Configure PHP as an Apache module
Ensure Apache isn’t running and open its C:\Apache24\conf\httpd.conf configuration file in a text editor. Add the following lines to the bottom of the file to set PHP as an Apache module (change the file locations if necessary):
Optionally, change the DirectoryIndex setting to load index.php instead of index.html when it can be found. The initial setting is:
Save httpd.conf and test the updates from a cmd command line:
Syntax OK should appear … unless you have errors in your configuration.
If all went well, restart Apache with httpd .
Step 6: Test a PHP file
Create a new file named index.php in Apache’s web page root folder at C:\Apache24\htdocs and add the following PHP code:
Open a web browser and enter your server address: http://localhost/. A “PHP version” page will appear showing the various PHP and Apache configuration settings.
You can now create PHP sites and applications in any sub-folder of C:\Apache24\htdocs . If you need to work on multiple projects, consider defining Apache Virtual Hosts so you can run separate codebases on different localhost domains or ports.