- Tasks
- Components of a Task
- Task APIs
- Task Scheduler 1.0 Tasks
- команды SchTasks schtasks commands
- Необходимые разрешения Required permissions
- Use the at command to schedule tasks
- Summary
- Overview of the at command
- Create a scheduled task
- Examples
- Cancel a scheduled task
- Examples to cancel scheduled tasks
- View scheduled tasks
- Examples to view scheduled tasks
- Troubleshooting
- References
Tasks
A task is the scheduled work that the Task Scheduler service performs. A task is composed of different components, but a task must contain a trigger that the Task Scheduler uses to start the task and an action that describes what work the Task Scheduler will perform.
When a task is created, it is stored in a task folder. Task folders can be accessed through the ITaskFolder interface (TaskFolder for scripting), and tasks can be accessed through the IRegisteredTask interface (RegisteredTask for scripting) when they are created. You can change access control lists (ACLs) for tasks and task folders in order to grant or deny certain users and groups access to a task or task folder. This can be done by using the IRegisteredTask::SetSecurityDescriptor method, the ITaskFolder::SetSecurityDescriptor method, or by specifying a security descriptor when a task is registered by using the RegisterTaskDefinition or RegisterTask method.
If the Local System account is denied access to a task file or task folder, then the Task Scheduler service can produce unexpected results.
Components of a Task
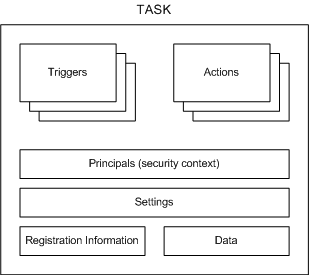
The following illustration shows the task components.
The following list contains a brief description of each task component:
Triggers: Task Scheduler uses event or time-based triggers to know when to start a task. Every task can specify one or more triggers to start the task.
For more information about triggers, see Task Triggers.
Actions: These are the actions, the actual work, that is performed by the task. Every task can specify one or more actions to complete its work.
For more information about actions, see Task Actions.
Principals: Principals define the security context in which the task is run. For example, a principal might define a specific user or user group that can run the task.
For more information about principals, see Security Contexts for Tasks.
Settings: These are the settings that the Task Scheduler uses to run the task with respect to conditions that are external to the task itself. For example, these settings can specify the priority of the task with respect to other tasks, whether multiple instances of the task can be run, how the task is handled when the computer is in an idle condition, and other conditions.
For more information about task settings, see ITaskSettings (TaskSettings for scripting).
By default, a task will be stopped 72 hours after it starts to run. You can change this by changing the ExecutionTimeLimit setting.
Registration Information: This is administrative information that is gathered when the task is registered. For example, this information describes the author of the task, the date when the task was registered, an XML description of the task, and other information.
For more information about task registration information, see Task Registration Information.
Data: This is additional documentation about the task that is supplied by the author of the task. For example, this data may contain XML Help that can be used by users when they run the task.
Task APIs
Task Scheduler 2.0 provides two sets of APIs: a set of scripting objects and interfaces for Task Scheduler 2.0. For more information, see Task Scheduler Reference.
Task compatibility, which is set through the Compatibility property, should only be set to TASK_COMPATIBILITY_V1 if a task must be accessed or modified from a WindowsВ XP, Windows ServerВ 2003, or WindowsВ 2000 computer. Otherwise, it is recommended that you use Task Scheduler 2.0 compatibility because it has more features.
Starting with Task Scheduler 2.0, the ITaskService interface (TaskService for scripting) is used as a starting point to create tasks in specified folders. The ITaskDefinition interface (TaskDefinition for scripting) is used to hold all the components of a task, such as the settings, actions, and triggers. The ITaskTrigger, IAction, and ITaskSettings APIs provide properties that are then used to define the other components of the task. Task Scheduler 1.0 provides the ITask interface, which is supported only for backward compatibility.
For scripting, the Task Scheduler interfaces map to scripting objects that have the similar names, properties, and methods. For example, the TaskService scripting object has the same properties and methods as the ITaskService interface.
For more information and examples about how to use the Task Scheduler interfaces, scripting objects, and XML, see Using the Task Scheduler.
Task Scheduler 1.0 Tasks
A Task Scheduler 1.0 task is any application or file type that the Task Scheduler can execute. These may include any of the following (as supported by the operating system on which the task will execute): Win32 applications, Win16 applications, OS/2 applications, MS-DOS applications, batch files (*.bat), command files (*.cmd), or any properly registered file type.
Data that describes a task is kept in a task file that is stored in the Scheduled Tasks folder. For more information, see Scheduled Tasks folder. The name of these task files include the name of the task, followed by a .job file name extension.
For more information about adding Task Scheduler 1.0 tasks, see Adding Work Items.
For more information about enumerating through Task Scheduler 1.0 tasks, see Enumerating Tasks.
For a Windows ServerВ 2003, WindowsВ XP, or WindowsВ 2000 computer to create, monitor, or control tasks on a WindowsВ Vista computer, the following operations should be completed on the WindowsВ Vista computer, and the user who is calling the ITaskScheduler::SetTargetComputer method must be a member of the Administrators group on the remote WindowsВ Vista computer.
To enable the «Share File and Printers» exception in Windows Firewall
- Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Classic View and then double-click the Windows Firewall icon.
- In the Windows Firewall window, click the Exceptions tab and select File and Printer Sharing exception check box.
To enable the «Remote Registry» service
- Open a Command Prompt window and enter the following command: net start «Remote Registry».
команды SchTasks schtasks commands
Планирует выполнение команд и программ периодически или в определенное время, добавляет и удаляет задачи из расписания, запускает и останавливает задачи по требованию, а также отображает и изменяет запланированные задачи. Schedules commands and programs to run periodically or at a specific time, adds and removes tasks from the schedule, starts and stops tasks on demand, and displays and changes scheduled tasks.
Средство schtasks.exe выполняет те же операции, что и запланированные задачи на панели управления. The schtasks.exe tool performs the same operations as Scheduled Tasks in Control Panel. Эти инструменты можно использовать совместно и взаимозаменяемы. You can use these tools together and interchangeably.
Необходимые разрешения Required permissions
Чтобы запланировать, просмотреть и изменить все задачи на локальном компьютере, необходимо быть членом группы «Администраторы». To schedule, view, and change all tasks on the local computer, you must be a member of the Administrators group.
Чтобы запланировать, просмотреть и изменить все задачи на удаленном компьютере, необходимо быть членом группы «Администраторы» на удаленном компьютере или использовать параметр /u для предоставления учетных данных администратора удаленного компьютера. To schedule, view, and change all tasks on the remote computer, you must be a member of the Administrators group on the remote computer, or you must use the /u parameter to provide the credentials of an Administrator of the remote computer.
Параметр /u в операции /CREATE или /Change можно использовать, если локальный и удаленный компьютеры находятся в одном домене или если локальный компьютер находится в домене, которому доверяет домен удаленного компьютера. You can use the /u parameter in a /create or /change operation if the local and remote computers are in the same domain, or if the local computer is in a domain that the remote computer domain trusts. В противном случае удаленный компьютер не может проверить подлинность указанной учетной записи пользователя и не сможет проверить, является ли эта учетная запись членом группы «Администраторы». Otherwise, the remote computer can’t authenticate the user account specified, and it can’t verify that the account is a member of the Administrators group.
Задача, которую планируется запустить, должна иметь соответствующее разрешение; Эти разрешения зависят от задачи. The task you plan to run must have the appropriate permission; these permissions vary by task. По умолчанию задачи выполняются с разрешениями текущего пользователя локального компьютера или с разрешениями пользователя, заданного параметром /u , если он включен. By default, tasks run with the permissions of the current user of the local computer, or with the permissions of the user specified by the /u parameter, if one is included. o запустите задачу с разрешениями другой учетной записи пользователя или с системными разрешениями, используя параметр /ru . o run a task with permissions of a different user account or with system permissions, use the /ru parameter.
Use the at command to schedule tasks
This article describes how to use the at command to create and to cancel scheduled tasks.
Original product version: В Windows 2000
Original KB number: В 313565
This article applies to Windows 2000. Support for Windows 2000 ends on July 13, 2010. For more information, see the Microsoft Support Lifecycle Policy.
Summary
In Windows 2000, you can use the Task Scheduler tool in Control Panel to schedule tasks. You can also use the at command to schedule tasks manually.
Overview of the at command
You can use the at command to schedule a command, a script, or a program to run at a specified date and time. You can also use this command to view existing scheduled tasks.
To use the at command, the Task Scheduler service must be running, and you must be logged on as a member of the local Administrators group. When you use the at command to create tasks, you must configure the tasks so that they run in the same user account.
The at command uses the following syntax:
at \\computername time/interactive | /every: date, . /next: date, . command
at \\computername id/delete | /delete /yes
The following list describes the parameters that you can use with the at command:
\computername: Use this parameter to specify a remote computer. If you omit this parameter, tasks are scheduled to run on the local computer.
time: Use this parameter to specify the time when the task is to run. Time is specified as hours: minutes based on the 24-hour clock. For example, 0:00 represents midnight and 20:30 represents 8:30 P.M.
/interactive: Use this parameter to allow the task to interact with the desktop of the user who is logged on at the time the task runs.
/every: date. : Use this parameter to schedule the task to run on the specified day or days of the week or month, for example, every Friday or the eighth day of every month. Specify date as one or more days of the week (use the following abbreviations: M,T,W,Th,F,S,Su) or one or more days of the month (use the numbers 1 through 31). Make sure that you use commas to separate multiple date entries. If you omit this parameter, the task is scheduled to run on the current day.
/next: date, . Use this parameter to schedule the task to run on the next occurrence of the day (for example, next Monday). Specify date as one or more days of the week (use the following abbreviations: M,T,W,Th,F,S,Su) or one or more days of the month (use the numbers 1 through 31). Make sure that you use commas to separate multiple date entries. If you omit this parameter, the task is scheduled to run on the current day.
command: Use this parameter to specify the Windows 2000 command, the program (.exe or .com file), or the batch program (.bat or .cmd file) that you want to run. If the command requires a path as an argument, use the absolute path name (the entire path beginning with the drive letter). If the command is on a remote computer, use the Uniform Naming Convention (UNC) path name (\ServerName\ ShareName). If the command is not an executable (.exe) file, you must precede the command with cmd /c , for example, cmd /c copy C:\*.* C:\temp .
id: Use this parameter to specify the identification number that is assigned to a scheduled task.
/delete: Use this parameter to cancel a scheduled task. If you omit the id parameter, all scheduled tasks on the computer are canceled.
/yes: Use this parameter to force a yes answer to all queries from the system when you cancel scheduled tasks. If you omit this parameter, you are prompted to confirm the cancellation of a task.
When you use the at command, the scheduled task is run by using the credentials of the system account.
Create a scheduled task
Click Start, point to Programs, point to Accessories, and then click Command Prompt.
At the command prompt, type the net start command, and then press ENTER to display a list of currently running services:
If Task Scheduler is not displayed in the list, type the following line, and then press ENTER:
At the command prompt, type the following line (use the parameters that are appropriate to your situation), and then press ENTER:
Examples
To copy all files from the Documents folder to the MyDocs folder at midnight, type the following line, and then press ENTER:
To back up the Products server at 11:00 P.M. each weekday, create a batch file that contains the backup commands (for example, Backup.bat), type the following line, and then press ENTER to schedule the backup:
To schedule a net share command to run on the Sales server at 6:00 A.M. and to redirect the listing to the Sales.txt file in the shared Reports folder on the Corp server, type the following line, and then press ENTER:
Cancel a scheduled task
Click Start, point to Programs, point to Accessories, and then click Command Prompt.
At the command prompt, type the net start command, and then press ENTER to display a list of currently running services.
If Task Scheduler is not displayed in the list, type the following line, and then press ENTER:
At the command prompt, type the following line (use the parameters that are appropriate to your situation), and then press ENTER:
Examples to cancel scheduled tasks
- To cancel all tasks that are scheduled on the local computer, type at /delete , and then press ENTER.
- To cancel the task ID 8 on a computer that is named MyServer, type at \\MyServer 8 /delete , and then press ENTER.
View scheduled tasks
To view the tasks that you created by using the at command, follow these steps:
Click Start, point to Programs, point to Accessories, and then click Command Prompt.
At the command prompt, type the net start command, and then press ENTER to display a list of currently running services.
If Task Scheduler is not displayed in the list, type the following line, and then press ENTER:
At the command prompt, do one of the following steps:
- To view a list of tasks that you scheduled by using the at command, type the at \\computername line, and then press ENTER.
- To view a specific scheduled task, type the at \\computername id command, and then press ENTER.
Examples to view scheduled tasks
- To view all scheduled tasks on the local computer, type at , and then press ENTER.
- To view all scheduled tasks on a computer named Support, type at \\support , and then press ENTER.
- To view the task ID 18 on the local computer, type at 18 , and then press ENTER.
Troubleshooting
When you type at \\computername to view a list of scheduled tasks, some (or all) of the scheduled tasks that you created by using the at command are not listed.
This behavior can occur if you modified the tasks in the Scheduled Tasks folder after you used the at command to create the task. When you use the at command to schedule a task, the task is displayed in the Scheduled Tasks folder in Control Panel. You can view or modify the task. However, if you modify the task, when you use the at command, you cannot view the task.
When you use the at command to schedule a task, the task does not run at the specified time or date.
This behavior can occur if one of the following conditions is true:
The command syntax is incorrect.
After you schedule a task, type at \\computername to confirm that the syntax is correct. If the information that is displayed under Command Line is incorrect, cancel the task, and then recreate it.
You schedule a task to run a command that is not a .exe file.
The at command does not automatically load cmd (the command interpreter) before it runs commands. Unless you are running a .exe file, you must load Cmd.exe at the beginning of the command, for example, at cmd /c dir > c:\test.txt .
References
For more information about how to use the at command in Windows 2000, see Windows 2000 Help. To do so, click Start, click Help, click the Index tab, and then type at command.