- Python — Environment Setup
- Local Environment Setup
- Getting Python
- Installing Python
- Unix and Linux Installation
- Windows Installation
- Macintosh Installation
- Setting up PATH
- Setting path at Unix/Linux
- Setting path at Windows
- Python Environment Variables
- Running Python
- Interactive Interpreter
- Script from the Command-line
- Integrated Development Environment
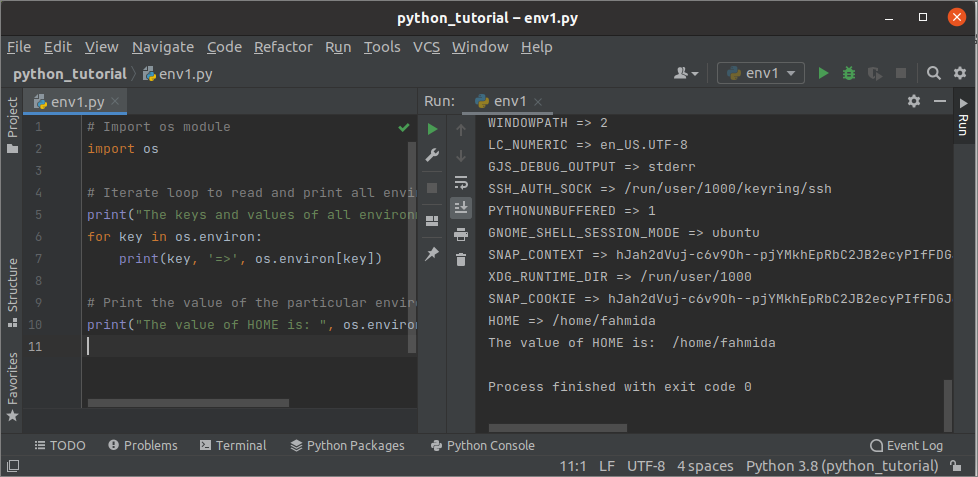
- Чтение и запись переменных окружения в Python
- Чтение переменных окружения на Python
- Считываем одну или все переменные окружения
- Результат:
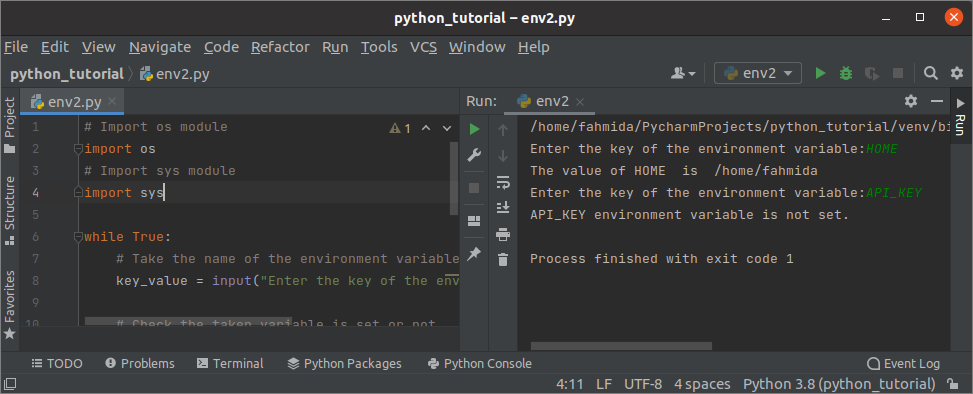
- Проверяем, присвоено ли значение переменной окружения
- Результат:
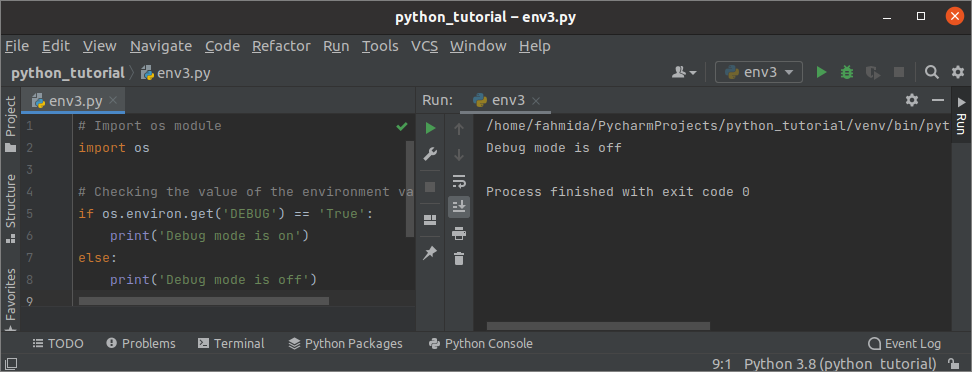
- Проверяем переменную на истинность
- Результат:
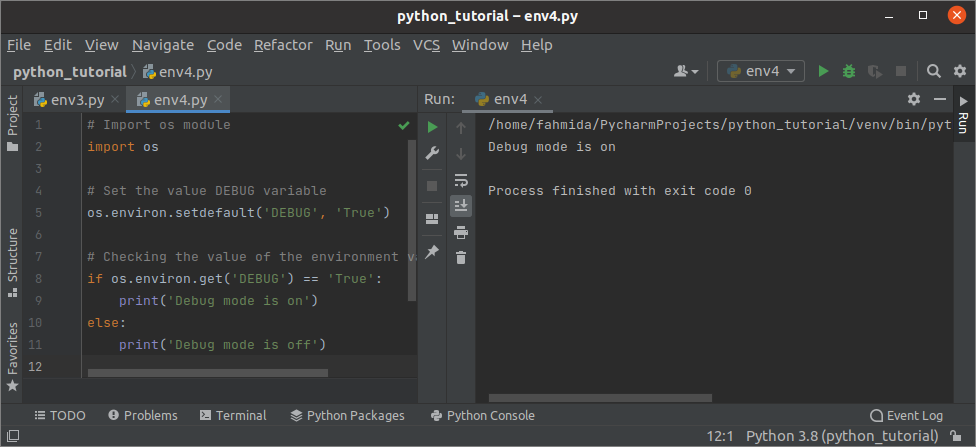
- Присваиваем значение переменной окружения
- Результат:
- Заключение
- Переменные окружения для Python проектов
- Переменные окружения для Python проектов
- Конфигурационные файлы
- Переменные окружения
- Библиотека python-dotenv
- Утилита direnv
Python — Environment Setup
Python is available on a wide variety of platforms including Linux and Mac OS X. Let’s understand how to set up our Python environment.
Local Environment Setup
Open a terminal window and type «python» to find out if it is already installed and which version is installed.
- Unix (Solaris, Linux, FreeBSD, AIX, HP/UX, SunOS, IRIX, etc.)
- Win 9x/NT/2000
- Macintosh (Intel, PPC, 68K)
- OS/2
- DOS (multiple versions)
- PalmOS
- Nokia mobile phones
- Windows CE
- Acorn/RISC OS
- BeOS
- Amiga
- VMS/OpenVMS
- QNX
- VxWorks
- Psion
- Python has also been ported to the Java and .NET virtual machines
Getting Python
The most up-to-date and current source code, binaries, documentation, news, etc., is available on the official website of Python https://www.python.org/
You can download Python documentation from https://www.python.org/doc/. The documentation is available in HTML, PDF, and PostScript formats.
Installing Python
Python distribution is available for a wide variety of platforms. You need to download only the binary code applicable for your platform and install Python.
If the binary code for your platform is not available, you need a C compiler to compile the source code manually. Compiling the source code offers more flexibility in terms of choice of features that you require in your installation.
Here is a quick overview of installing Python on various platforms −
Unix and Linux Installation
Here are the simple steps to install Python on Unix/Linux machine.
Follow the link to download zipped source code available for Unix/Linux.
Download and extract files.
Editing the Modules/Setup file if you want to customize some options.
run ./configure script
This installs Python at standard location /usr/local/bin and its libraries at /usr/local/lib/pythonXX where XX is the version of Python.
Windows Installation
Here are the steps to install Python on Windows machine.
Follow the link for the Windows installer python-XYZ.msi file where XYZ is the version you need to install.
To use this installer python-XYZ.msi, the Windows system must support Microsoft Installer 2.0. Save the installer file to your local machine and then run it to find out if your machine supports MSI.
Run the downloaded file. This brings up the Python install wizard, which is really easy to use. Just accept the default settings, wait until the install is finished, and you are done.
Macintosh Installation
Recent Macs come with Python installed, but it may be several years out of date. See http://www.python.org/download/mac/ for instructions on getting the current version along with extra tools to support development on the Mac. For older Mac OS’s before Mac OS X 10.3 (released in 2003), MacPython is available.
Jack Jansen maintains it and you can have full access to the entire documentation at his website − http://www.cwi.nl/
jack/macpython.html. You can find complete installation details for Mac OS installation.
Setting up PATH
Programs and other executable files can be in many directories, so operating systems provide a search path that lists the directories that the OS searches for executables.
The path is stored in an environment variable, which is a named string maintained by the operating system. This variable contains information available to the command shell and other programs.
The path variable is named as PATH in Unix or Path in Windows (Unix is case sensitive; Windows is not).
In Mac OS, the installer handles the path details. To invoke the Python interpreter from any particular directory, you must add the Python directory to your path.
Setting path at Unix/Linux
To add the Python directory to the path for a particular session in Unix −
In the csh shell − type setenv PATH «$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python» and press Enter.
In the bash shell (Linux) − type export PATH=»$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python» and press Enter.
In the sh or ksh shell − type PATH=»$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python» and press Enter.
Note − /usr/local/bin/python is the path of the Python directory
Setting path at Windows
To add the Python directory to the path for a particular session in Windows −
At the command prompt − type path %path%;C:\Python and press Enter.
Note − C:\Python is the path of the Python directory
Python Environment Variables
Here are important environment variables, which can be recognized by Python −
| Sr.No. | Variable & Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| Sr.No. | Option & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |