- Как установить Python IDLE в Linux
- Что такое IDLE
- Функции IDLE
- Установка Python IDLE IDE в Linux
- Написание первой программы Python с использованием IDLE
- Python IDLE Отладчик
- Изменение визуальных настроек IDLE Python
- Заключение
- Python
- Contents
- Installation
- Python 3
- Python 2
- Alternative implementations
- Alternative shells
- Old versions
- Package management
- Widget bindings
- Tips and tricks
- Virtual environment
- Tab completion in Python shell
- How to Install Python IDLE in Linux
- IDLE Features
- Install Python IDLE IDE in Linux
- Writing First Python Program Using IDLE
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
Как установить Python IDLE в Linux
Мы все знаем что в Linux Python установлен по умолчанию, но как я не старался я не смог найти IDLE. В этой инструкции я расскажу как установить Python IDLE в Linux. Но для начала давайте разберем что такое IDLE.
Что такое IDLE
IDLE — это интегрированная и обучающая среда, созданная с помощью Python. В которой используется GUI Tkinter toolkit. В основном этим пользуются новички, чтобы познакомиться с Python.
IDLE — это кроссплатформенное приложение, которое работает с Mac OS, Windows и Linux. Но в операционной системе Windows IDLE устанавливается в месте с Python. Для Mac OS и Linux мы должны установить IDLE отдельно.
Функции IDLE
- Удобный текстовый редактор.
- Раскраска кода.
- Советы и рекомендации.
- Автоматическое отступление.
- Отладчик.
- Просмотр локального и глобального пространства имен.
Если вы новичок в программировании на Python. Или и вообще новичок в программировании, то IDLE это лучшее приложение для начала. Но если вы опытный программист, переходящий с другого языка на Python. Тогда мы рекомендуем более продвинутые редакторы, такие как Pycharm, VScode, Sublime Text, VIM и т. д.
Установка Python IDLE IDE в Linux
В большинстве современных дистрибутивов Linux Python устанавливается по умолчанию и поставляется вместе с приложением IDLE. Но бывает такое что он не установлен, как в моем случае. Тогда вы можете установить его с помощью диспетчера пакетов, как показано ниже.
$ sudo apt install idle [на Debian/Ubuntu для Python2]
$ sudo apt-get install idle3 [на Debian/Ubuntu для Python3]
$ sudo yum install python3-tools [на CentOS/RHEL и Fedora]
После завершения установки введите в терминале «idle» . Так же можно перейти в меню Пуск → «idle» → Запустить приложение.
Когда вы открываете IDLE, вы увидите интерактивный терминал. Для выхода из термина можно использовать горячие клавиши ALT + SPACE.
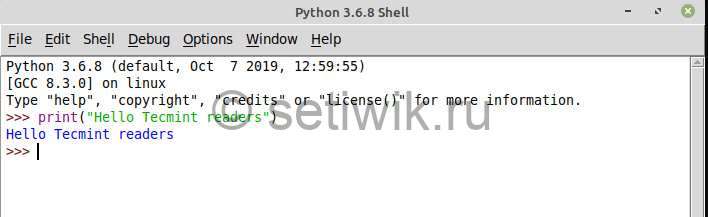
Написание первой программы Python с использованием IDLE
Ну как же можно обойтись без первой программы?
Перейдите в меню Файл → Новый файл → Для того чтоб открыть текстовый редактор. Как только редактор будет открыт, вы сможете писать программу. Чтобы запустить программу из текстового редактора и сохраните файл. Требуется нажать кнопку F5 или Выполнить → Run Module.
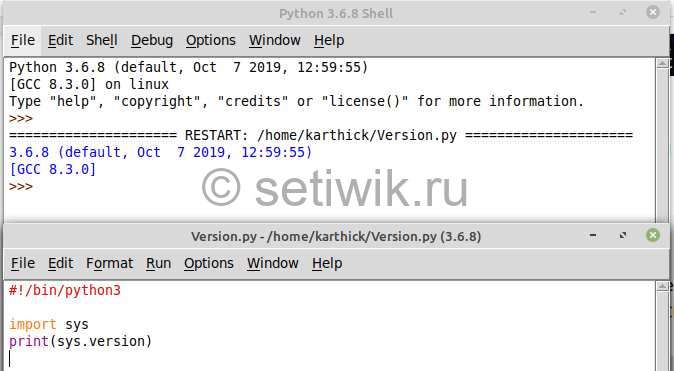
Python IDLE Отладчик
Чтобы получить доступ к отладчику, перейдите в Раздел отладка → Отладчик (Debug → Debugger). Режим отладки будет включен, вы можете отлаживать и шагать через код.

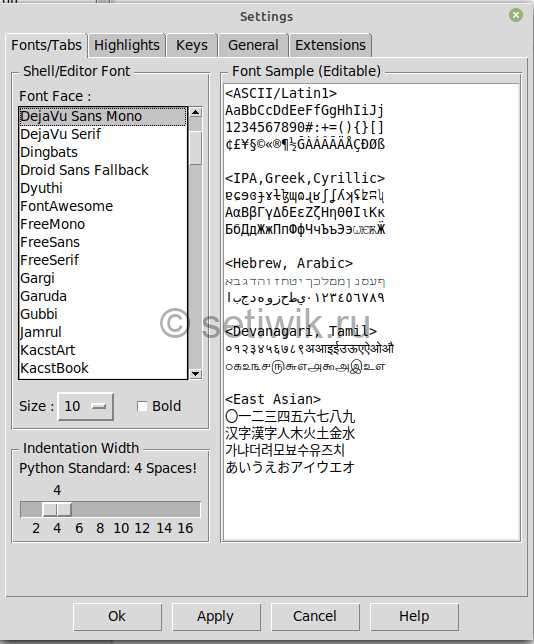
Изменение визуальных настроек IDLE Python
Чтоб поменять цвета, шрифты и другие настройки интерфейса. Перейдите в меню Параметры → Настройка IDLE. Это откроет окно настроек.
Заключение
На сегодня все. Надеюсь вы поняли что такое IDLE и как его установить в Linux. Как написать первую программу python через интерпретатор и текстовый редактор. А так же как получить доступ к отладчику и как изменить настройки IDLE.
Источник
Python
Python is an interpreted, interactive, object-oriented programming language. It incorporates modules, exceptions, dynamic typing, very high level dynamic data types, and classes. It supports multiple programming paradigms beyond object-oriented programming, such as procedural and functional programming. Python combines remarkable power with very clear syntax. It has interfaces to many system calls and libraries, as well as to various window systems, and is extensible in C or C++. It is also usable as an extension language for applications that need a programmable interface. Finally, Python is portable: it runs on many Unix variants including Linux and macOS, and on Windows.
Contents
Installation
Python 3
Python 3 is the latest and actively developed version of the language. See What’s New in Python to see the latest changes in Python 3.
To install the current release of Python 3, install the python package.
If you would like to build the latest RC/betas from source, visit Python Downloads. The Arch User Repository also contains good PKGBUILDs. If you do decide to build the RC, note that the binary (by default) installs to /usr/local/bin/python3.x . As an alternative which does not require superuser capabilities and installs to the home directory, consider using pyenv .
Python 2
Python 2 is an older version of the language. Python 3 and Python 2 are incompatible. For an overview of the differences, see the historical version of the Python2orPython3 document.
Although Python 2 is no longer actively maintained, there are some packages that still depend on it. Python 2 may also be useful for developers maintaining, using or porting legacy Python 2 software.
To get the latest version of Python 2, install the python2 package.
Python 2 will happily run alongside Python 3. You need to specify python2 in order to run this version.
Any program requiring Python 2 needs to use /usr/bin/python2 , instead of /usr/bin/python , which points to Python 3. However, many legacy Python 2 scripts incorrectly specify python in their shebang line. To change this, open the program or script in a text editor and change the first line. The line may show one of the following:
In either case, change python to python2 and the program will then use Python 2 instead of Python 3.
Another way to force the use of python2 without altering the scripts is to call it explicitly with python2 :
Finally, you may not be able to control the script calls, but there is a way to trick the environment. It only works if the scripts use #!/usr/bin/env python . It will not work with #!/usr/bin/python . This trick relies on env searching for the first corresponding entry in the PATH variable.
First create a dummy folder:
Then add a symlink python to python2 and the config scripts in it:
Finally put the new folder at the beginning of your PATH variable:
To check which python interpreter is being used by env , use the following command:
A similar approach in tricking the environment, which also relies on #!/usr/bin/env python to be called by the script in question, is to use a virtual environment.
Alternative implementations
The python package installs CPython, the reference implementation of Python. However, there are also other implementations available. These implementations are usually based on older versions of Python and are not fully compatible with CPython.
Implementations available on Arch Linux include:
- PyPy — A Python implementation written in Python. It has speed and memory usage advantages compared to Cython.
https://www.pypy.org || pypy , pypy3
- Jython — An implementation of the Python language written in Java. It can be used to embed Python scripting into Java programs or use Java libraries in Python programs.
https://www.jython.org/ || jython
- micropython — Python for microcontrollers. It includes a small subset of the Python standard library and is optimized to run on microcontrollers and in constrained environments.
https://micropython.org/ || micropythonAUR
- IronPython — An implementation of the Python programming language which is tightly integrated with .NET. It can use .NET libraries and allows .NET programs to use Python libraries.
https://ironpython.net || ironpython-gitAUR
More implementations exist. Some, such as Stackless, Pyston and Cinder are used internally at large technology companies. Others are historically notable but are no longer maintained due to improvements in the most popular implementations.
Alternative shells
The python package includes an interactive Python shell/REPL which can be launched with the python command. The following shells are also available:
Old versions
Old versions of Python are available via the AUR and may be useful for historical curiosity, old applications that do not run on current versions, or for testing Python programs intended to run on a distribution that comes with an older version:
Extra modules/libraries for old versions of Python may be found on the AUR by searching for python , e.g. searching for python26 for 2.6 modules.
Package management
There are several ways to install Python packages on Arch Linux:
- Official repositories and AUR — A large number of popular packages are available in the Arch repositories. This is the preferred way to install system-wide packages.
- pip(1) — The official package installer for Python. You can use pip to install packages from the Python Package Index and other indexes.
https://pip.pypa.io/ || python-pip
- pipx — Closely related to pip, but creates, for the user running it, an isolated environment for each application and its associated packages, preventing conflicts with system packages. Focused on packages that can be run from the command line directly as applications. You can use pipx to install packages from the Python Package Index and other indexes.
https://pypa.github.io/pipx/ || python-pipx
- Anaconda — An open source package management system and environment management system, originally created for Python programs. You can use Conda to install packages from the Anaconda repositories.
https://docs.conda.io/projects/conda/ || anacondaAUR
- Miniconda — A lightweight alternative to Anaconda which installs the package manager but does not install scientific computing packages by default.
https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html || miniconda3AUR
When installing packages using pip, it is recommended to use a virtual environment to prevent conflicts with system packages in /usr . Alternatively, pip install —user can be used to install packages into the user scheme instead of /usr . pipx and Conda integrate environment management into their workflows.
See the Python Packaging User Guide for the official best practices for package management.
Historically, easy_install (part of python-setuptools ) was used to install packages distributed as Eggs. easy_install and Eggs have been replaced with pip and Wheels. See pip vs easy_install and Wheel vs Egg for more information.
Widget bindings
The following widget toolkit bindings are available:
To use these with Python, you may also need to install the associated widget toolkit packages (e.g. tk must also be installed to use Tkinter).
Tips and tricks
Virtual environment
Python provides tools to create isolated virtual environments into which packages may be installed without conflicting with other virtual environments or the system packages. Virtual environments can also run applications with different versions of Python on the same system.
Tab completion in Python shell
Tab completion is available in the interactive shell by default. Note that the readline completer will only complete names in the global namespace. You can use python-jedi for a richer tab completion experience [1].
Источник
How to Install Python IDLE in Linux
IDLE is an Integrated and learning environment created with Python using the GUI Tkinter toolkit. This is mainly used by beginners to get familiar with Python. IDLE is a cross-platform application that works with Mac OS, Windows, and Linux. In windows, IDLE comes by default with the installation. For Mac OS and Linux, we have to install the IDLE separately.
IDLE Features
- Interactive Interpreter.
- A multi-window text editor.
- Smart intends.
- Code coloring.
- Call tips.
- Auto indentation.
- Debugger with persistent breakpoints.
- Stepping and Viewing of local and global Namespace.
If you are a beginner to Python programming or new to programming, IDLE is the best place to start with. But if you are an experienced programmer switching from another language to Python then you may try more advanced editors like Pycharm, VScode, Sublime Text, VIM, etc.
Install Python IDLE IDE in Linux
In most of today’s modern Linux distributions, Python is installed by default and it comes with the IDLE application. However, If isn’t installed, you can install it using your default package manager as shown.
Once the installation is completed type «idle» from the terminal or go to start menu → type «idle» → Launch application.
When you open the IDLE, the interactive terminal will be displayed first. The interactive terminal provides auto-completion too, you can press (ALT + SPACE) for auto-completion.

Writing First Python Program Using IDLE
Go to File → New File → To open the text editor. Once the editor is opened you can write the program. To run the program from the text editor, save the file and press F5 or Run → Run Module.

To access the debugger go to Debug → Debugger. Debug mode will be on, you can debug and step through the code.

Go to Options → Configure IDLE. This will open settings windows.

That’s all for today. We have seen what IDLE is and how to install it in Linux. How to write the first python program through interpreter and Text editor. How to access the builtin debugger and how to change the settings of IDLE.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник




