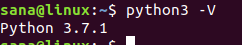- 2. Using Python on Unix platforms¶
- 2.1. Getting and installing the latest version of Python¶
- 2.1.1. On Linux¶
- 2.1.2. On FreeBSD and OpenBSD¶
- 2.1.3. On OpenSolaris¶
- 2.2. Building Python¶
- 2.3. Python-related paths and files¶
- 2.4. Miscellaneous¶
- 2.5. Custom OpenSSL¶
- Как скачать и установить Python 3 на Ubuntu 18.04 (Linux)
- Как проверить текущую версию Python
- Как установить Python 3 на Linux через apt-get
- Как установить Python 3 на Linux из архива
- Ошибки, которые могут возникнуть при установке
- 1. Zipimport.zipimporterror
- 2. No module named ‘_ctypes’
- Как обновить команду python3 до последней версии
- Заключение
- Installing Python 3 on Linux¶
- Working with Python 3¶
- Setuptools & Pip¶
- Pipenv & Virtual Environments¶
- O’Reilly Book
- How to install python modules in a local directory? —user and exporting pythonpath isn’t working
- 3 Answers 3
- For Python 3
- For Python 2
2. Using Python on Unix platforms¶
2.1. Getting and installing the latest version of Python¶
2.1.1. On Linux¶
Python comes preinstalled on most Linux distributions, and is available as a package on all others. However there are certain features you might want to use that are not available on your distro’s package. You can easily compile the latest version of Python from source.
In the event that Python doesn’t come preinstalled and isn’t in the repositories as well, you can easily make packages for your own distro. Have a look at the following links:
for Debian users
for OpenSuse users
for Fedora users
for Slackware users
2.1.2. On FreeBSD and OpenBSD¶
FreeBSD users, to add the package use:
OpenBSD users, to add the package use:
For example i386 users get the 2.5.1 version of Python using:
2.1.3. On OpenSolaris¶
You can get Python from OpenCSW. Various versions of Python are available and can be installed with e.g. pkgutil -i python27 .
2.2. Building Python¶
If you want to compile CPython yourself, first thing you should do is get the source. You can download either the latest release’s source or just grab a fresh clone. (If you want to contribute patches, you will need a clone.)
The build process consists of the usual commands:
Configuration options and caveats for specific Unix platforms are extensively documented in the README.rst file in the root of the Python source tree.
make install can overwrite or masquerade the python3 binary. make altinstall is therefore recommended instead of make install since it only installs exec_prefix /bin/python version .
2.3. Python-related paths and files¶
These are subject to difference depending on local installation conventions; prefix ( $
For example, on most Linux systems, the default for both is /usr .
Recommended location of the interpreter.
prefix /lib/python version , exec_prefix /lib/python version
Recommended locations of the directories containing the standard modules.
prefix /include/python version , exec_prefix /include/python version
Recommended locations of the directories containing the include files needed for developing Python extensions and embedding the interpreter.
2.4. Miscellaneous¶
To easily use Python scripts on Unix, you need to make them executable, e.g. with
and put an appropriate Shebang line at the top of the script. A good choice is usually
which searches for the Python interpreter in the whole PATH . However, some Unices may not have the env command, so you may need to hardcode /usr/bin/python3 as the interpreter path.
To use shell commands in your Python scripts, look at the subprocess module.
2.5. Custom OpenSSL¶
To use your vendor’s OpenSSL configuration and system trust store, locate the directory with openssl.cnf file or symlink in /etc . On most distribution the file is either in /etc/ssl or /etc/pki/tls . The directory should also contain a cert.pem file and/or a certs directory.
Download, build, and install OpenSSL. Make sure you use install_sw and not install . The install_sw target does not override openssl.cnf .
Build Python with custom OpenSSL (see the configure –with-openssl and –with-openssl-rpath options)
Patch releases of OpenSSL have a backwards compatible ABI. You don’t need to recompile Python to update OpenSSL. It’s sufficient to replace the custom OpenSSL installation with a newer version.
Источник
Как скачать и установить Python 3 на Ubuntu 18.04 (Linux)
В этой статье мы скачаем и установим последнюю версию Python 3 на Ubuntu. Затем убедимся, что python установлен корректно, рассмотрим популярные ошибки и их решения.
Все команды выполнялись в Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, но эта статья поможет установить python на Ubuntu 16.04, Debian, Mint и другие Linux-системы.
Мы используем командную строку Ubuntu — Терминал, для работы. Вы можете открыть Терминал через поиск или комбинацию клавиш Ctrl+Alt+T.
Как проверить текущую версию Python
Проверка текущей версии программного обеспечения не только помогает вам получить номер версии этого программного обеспечения, установленного в вашей системе, но и проверяет, действительно ли программное обеспечение установлено в вашей системе.
Мы сделаем то же самое для Python, выполнив следующую команду в нашем терминале:
Версия будет отображаться, как показано в приведенном выше выводе. Число зависит от того, когда вы обновили систему.
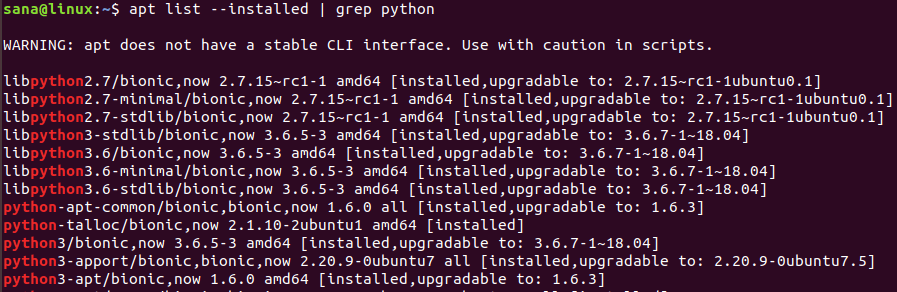
У вас также может быть несколько версий Python, установленных в вашей системе. Следующая команда выведет список всех версий Python, которые есть в вашей системе:
Как установить Python 3 на Linux через apt-get
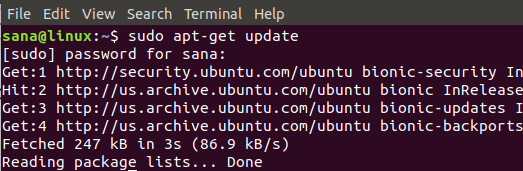
Установка Python 3 на Ubuntu с помощью команды apt-get довольно просто. Во-первых, вам необходимо обновить репозиторий системы, чтобы можно было установить последнюю доступную версию без проблем совместимости. Для этого выполните команду от имени администратора:
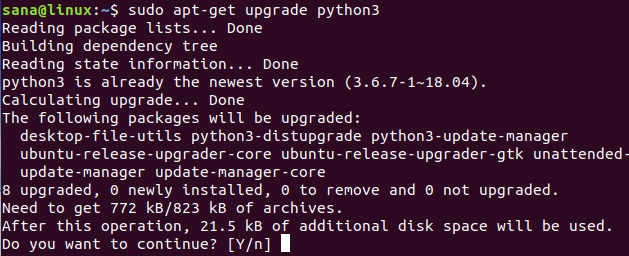
Так как Python уже установлен в нашей системе (это мы проверили в предыдущем разделе), нам нужно обновить его до последней версии следующим образом:
Система может попросить вас ввести пароль для прав sudo , поскольку только авторизованный пользователь может добавлять / удалять и обновлять программное обеспечение в Ubuntu.
Система также запросит подтверждение обновления. Введите Y , а затем нажмите Enter, чтобы продолжить.
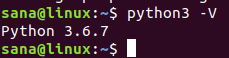
Так вы обновили Python до последней доступной версии. Проверьте:
Если Python не установлен, вы можете установить его с правами sudo используя команду apt-get :
Как установить Python 3 на Linux из архива
Сайт Python.org содержит список всех выпусков Python по этой ссылке:
https://www.python.org/downloads/source/
Поэтому, если вы решите установить Python вручную, можете скачать python любой сборки c официального сайта. На сайте также есть последние версии, которые вы не загрузите с помощью команды apt-get .
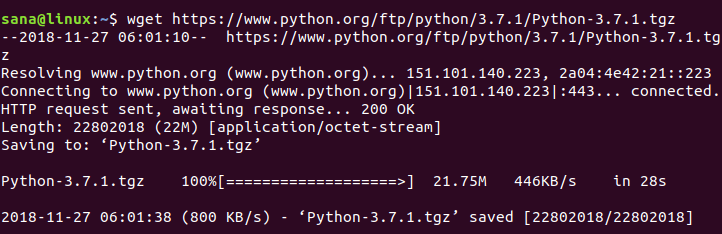
На момент подготовки материала Python-3.7.1 последняя доступная версия, поэтому мы скачаем его файл .tgz с помощью следующей команды:
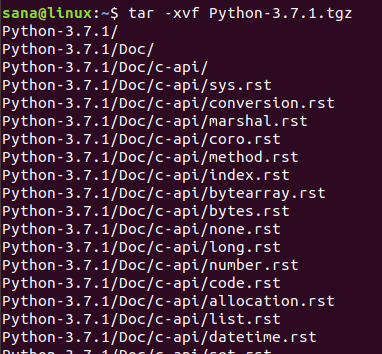
Когда архив с ptyhon будет скачан, выполните следующую команду, чтобы извлечь файлы:
После того, как файлы извлечены, нужно запустить C-программу «configure». Для этого вам необходимо установить компилятор языка программирования C — gcc в вашу Linux-систему. Если он не предустановлен, установите его с помощью следующей команды:
Измените текущую директорию на Python-3.7.1 или на ту версию python, которую вы скачали и извлекли:
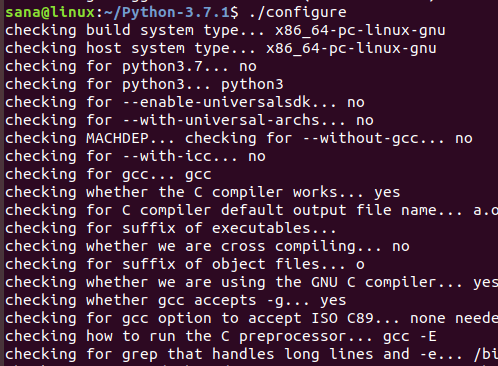
Теперь используйте следующую команду, чтобы запустить скрипт конфигурации:
Теперь пришло время установить Python.
Если вы не можете запустить команду make , установите make с помощью следующей команды:
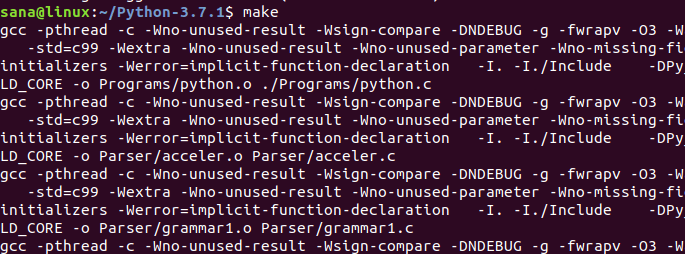
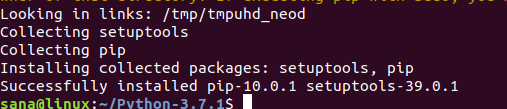
Запустите следующую команду для установки языка программирования Python:
Скачанная версия Python с официального сайта установлена в вашей Linux-системе.
Ошибки, которые могут возникнуть при установке
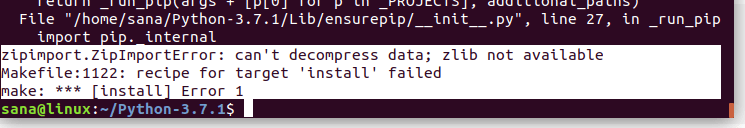
1. Zipimport.zipimporterror
Когда вы запускаете команду sudo make install , можете столкнуться со следующей ошибкой:
Это значит, что нужно установить пакет с именем zlib1g-dev , так как он, возможно, вам не был нужен раньше.
Решение:
Выполните следующую команду с правами sudo, чтобы установить отсутствующий пакет zlib1g-dev :
Затем повторите команду для завершения установки Python:
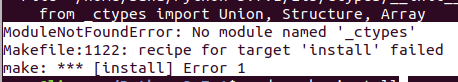
2. No module named ‘_ctypes’
Это ошибка появляется также при запуске команды sudo make install :
Это значит, что нужно установить пакет с именем libffi-dev , так как он, возможно, вам не был нужен раньше.
Решение:
Выполните следующую команду с правами sudo, чтобы установить отсутствующий пакет libffi-dev :
Затем повторите команду для завершения установки Python:
Как обновить команду python3 до последней версии
Перед установкой Python вручную из архива номер версии нашей установки Python был 3.6.7
Когда я проверил номер версии python3.7 , он дает следующий вывод:
Обновите версию python для команды python3 следующей командой:
Теперь команда python3 работает с последней версией Python в моей системе (3.7.1).
Заключение
В большинстве версий Ubuntu уже установлены Python и Pip3, но после прочтения этой статьи вы узнали, как загрузить и обновить их до последних версий.
Источник
Installing Python 3 on Linux¶
This document describes how to install Python 3.6 or 3.8 on Ubuntu Linux machines.
To see which version of Python 3 you have installed, open a command prompt and run
If you are using Ubuntu 16.10 or newer, then you can easily install Python 3.6 with the following commands:
If you’re using another version of Ubuntu (e.g. the latest LTS release) or you want to use a more current Python, we recommend using the deadsnakes PPA to install Python 3.8:
If you are using other Linux distribution, chances are you already have Python 3 pre-installed as well. If not, use your distribution’s package manager. For example on Fedora, you would use dnf :
Note that if the version of the python3 package is not recent enough for you, there may be ways of installing more recent versions as well, depending on you distribution. For example installing the python3.9 package on Fedora 32 to get Python 3.9. If you are a Fedora user, you might want to read about multiple Python versions available in Fedora.
Working with Python 3¶
At this point, you may have system Python 2.7 available as well.
This might launch the Python 2 interpreter.
This will always launch the Python 3 interpreter.
Setuptools & Pip¶
The two most crucial third-party Python packages are setuptools and pip.
Once installed, you can download, install and uninstall any compliant Python software product with a single command. It also enables you to add this network installation capability to your own Python software with very little work.
Python 2.7.9 and later (on the python2 series), and Python 3.4 and later include pip by default.
To see if pip is installed, open a command prompt and run
To install pip, follow the official pip installation guide — this will automatically install the latest version of setuptools.
Note that on some Linux distributions including Ubuntu and Fedora the pip command is meant for Python 2, while the pip3 command is meant for Python 3.
However, when using virtual environments (described below), you don’t need to care about that.
Pipenv & Virtual Environments¶
The next step is to install Pipenv, so you can install dependencies and manage virtual environments.
A Virtual Environment is a tool to keep the dependencies required by different projects in separate places, by creating virtual Python environments for them. It solves the “Project X depends on version 1.x but, Project Y needs 4.x” dilemma, and keeps your global site-packages directory clean and manageable.
For example, you can work on a project which requires Django 1.10 while also maintaining a project which requires Django 1.8.
This page is a remixed version of another guide, which is available under the same license.
This opinionated guide exists to provide both novice and expert Python developers a best practice handbook to the installation, configuration, and usage of Python on a daily basis.
O’Reilly Book
This guide is now available in tangible book form!
All proceeds are being directly donated to the DjangoGirls organization.
Источник
How to install python modules in a local directory? —user and exporting pythonpath isn’t working
I don’t know very much about python but would like to install some python modules in a local directory on a server on which I don’t have sudo access.
I start by going into my desired directory (not root) and create the directory tree needed to store my custom modules
I then export this local path to PYTHONPATH
I then make a new sub-directory to store the python package while extracting
Last, I run the setup.py script with the —user flag to try to get it to install in my specified /local directory
The problem is, nothing is installed in my /root/example/sub-example/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages directory, and instead I find that I now have a new directory at root: /root/.local/lib/python2.7/site-packages
Is there a way to prevent this? I feel like my lack of Python knowledge is causing me to make some silly error that is probably obvious to others. Thanks for the help!
3 Answers 3
create a folder called «lib»
For Python 3
For Python 2
virtualenv is what I would recommend for this case (and pretty much any other case). I use it for pretty much everything I do in Python.
It allows you to essentially create a sandbox containing a Python environment that is bootstrapped from a Python install on your machine, and to install any modules you want into it.
It should not, in general, require the use of sudo, since you’re not touching the system install. You can generally pip install a module right into the virtualenv, and then you run your scripts out of that virtualenv. You would basically just need a location you can read/write/execute from, say a directory you create in your user’s home directory.
You can keep track of what’s installed by doing a pip freeze > requirements and checking that into an SCM, and then a new virtualenv can be recreated using that file, ready to run your scripts.
The link I provided above has more details about how to use virtualenv.
Edit in response to comment from OP:
You can still use pip install outside of virtualenv, and I would recommend that. However, that can only operate on various Python installs that may be on the box (invoke pip from the bin directory of the install you want to use).
However, that won’t work for installation into arbitrary directories. For that, you could try to unzip the egg file (they are supposed to be zip files) into the directory you want, and then make sure that directory is on the PYTHONPATH . Some egg files are available for direct download off of PyPI, although some are source only.
I think is approach is much more complex and prone to problems than virtualenv would be, though.
Источник