- Get Started
- Download
- Как установить Python на Linux
- О языке программирования Python
- Подготовка к установке Python под Ubuntu 20 (Debian 10)
- Установка новой версии Python из deadsnakes PPA
- Сборка Python 3.9.2 в Linux из исходников
- Особенности установки Python на CentOS
- Как создать и настроить виртуальную среду
- Работа с пакетом virtualenv
- Работа с виртуальной средой с помощью virtualenvwrapper и pip
- Заключение
- Download the latest source release
- Download the latest version of Python
- Active Python Releases
- Looking for a specific release?
- Sponsors
- Licenses
- Sources
- Alternative Implementations
- History
- Release Schedules
- Information about specific ports, and developer info
- OpenPGP Public Keys
- Other Useful Items
- Want to contribute?
The core of extensible programming is defining functions. Python allows mandatory and optional arguments, keyword arguments, and even arbitrary argument lists. More about defining functions in Python 3
Lists (known as arrays in other languages) are one of the compound data types that Python understands. Lists can be indexed, sliced and manipulated with other built-in functions. More about lists in Python 3
Calculations are simple with Python, and expression syntax is straightforward: the operators + , — , * and / work as expected; parentheses () can be used for grouping. More about simple math functions in Python 3.
Experienced programmers in any other language can pick up Python very quickly, and beginners find the clean syntax and indentation structure easy to learn. Whet your appetite with our Python 3 overview.
Python knows the usual control flow statements that other languages speak — if , for , while and range — with some of its own twists, of course. More control flow tools in Python 3
Python is a programming language that lets you work quickly and integrate systems more effectively. Learn More
Get Started
Whether you’re new to programming or an experienced developer, it’s easy to learn and use Python.
Download
Python source code and installers are available for download for all versions!
Documentation for Python’s standard library, along with tutorials and guides, are available online.
Looking for work or have a Python related position that you’re trying to hire for? Our relaunched community-run job board is the place to go.
Источник
Как установить Python на Linux
Оглавление
О языке программирования Python
В последнее время, среди нового поколения разработчиков программного обеспечения большую популярность набирает язык программирования Python (Питон). На примере Python, мы видим высокоуровневый язык, который не нуждается в компиляторе и применяется для написания самого разного вида софта (мобильные приложения, веб-разработка, СПО под Линукс, системы искусственного интеллекта и machine learning, Data Science и др.). Надо отметить, что профессия программиста на Python сейчас достаточно популярна и востребована среди молодежи, ей обучают на многочисленных курсах, да и предложения по зарплате очень даже неплохие.
Так как программы, разработанные на Python, не компилируются, то роль интерпретатора байт-кода играет CPython. Исходный код программ, написанных на питоне, хранится в файлах с расширением .py.
В ОС Linux язык Python играет важную роль, он используется для системного администрирования, и именно на нем написаны такие известные программы, как GIMP, Blender и др. В Линукс интерпретатор питон уже установлен «по умолчанию», но как правило, разработчику необходима или наиболее свежая версия или же несколько версий Python сразу. На сегодня, последняя стабильная версия языка Python — это 3.9.2, скачать ее можно на официальном сайте проекта.
В этой статье мы расскажем все тонкости установки Python для Linux, на примере Ubuntu 20, Debian 10, а также CentOS 7/8.
Подготовка к установке Python под Ubuntu 20 (Debian 10)
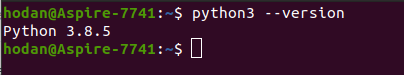
Как мы уже писали ранее, Python должен быть установлен «по умолчанию» в стандартном пакете сборки Ubuntu 20.04. Перед выполнением инсталляционных работ, наша задача — проверить какая версия питон у нас уже установлена в системе. Сделать это можно с помощью следующей команды:
В нашей ОС Ubuntu 20 уже есть версия Python 3.8.5. Существует еще одна полезная команда, с помощью которой можно узнать, какие вообще версии Python установлены в нашей ОС Линукс, см. ниже на скриншоте:
Сейчас мы покажем, как установить Python на Ubuntu двумя популярными способами:
- с помощью apt (используя deadsnakes PPA);
- из исходников, скачанных с официального сайта.
Все команды следует выполнять или под пользователем root, или используя sudo.
Установка новой версии Python из deadsnakes PPA
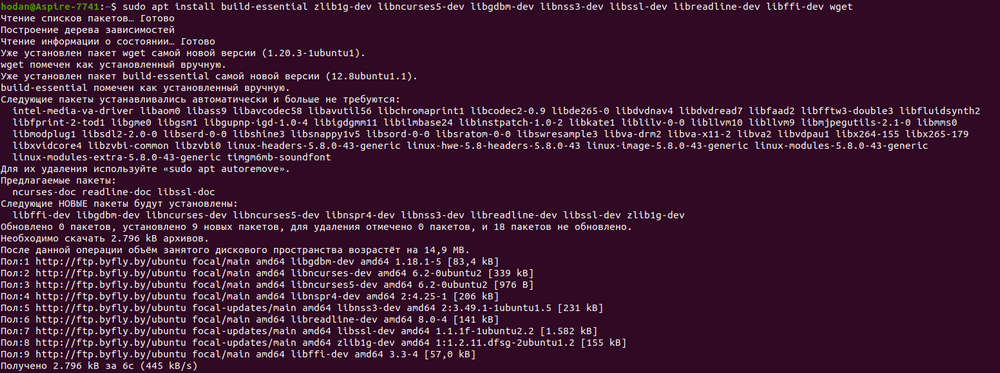
Первоначально, введем команды для обновления списка пакетов и установки необходимых нам для дальнейшей работы библиотек:
Затем необходимо включить deadsnakes PPA (Personal Package Archive), для этого выполним следующую команду:
После этого действия, еще раз выполним команду:
Сейчас установим версию Python 3.9:
На следующем этапе, мы опять проверим список установленных в системе версий Python и видим, что добавилась версия 3.9:
Сборка Python 3.9.2 в Linux из исходников
Этот способ может показаться немного сложнее предыдущего, но зато с помощью него можно установить самую свежую версию Python, которая доступна на официальном сайте. Процесс установки опробован на ОС Ubuntu 20, также его можно применять и на Debian 10.
Зайдем на FTP сервер официального сайта проекта Python (https://www.python.org/ftp/python) и выберем там архив с последней стабильной версией питон:
Перед началом процесса работ по установке выполним команды для обновления системы:
На следующем шаге, необходимо инсталлировать необходимые нам для работы пакеты:
Затем перейдем в папку /tmp и скачаем в нее архив с официального сайта Python*:
*Примечание: можно использовать как команду wget, так и команду curl.
Cейчас распакуем этот архив во временную папку и затем его сразу же и удалим:
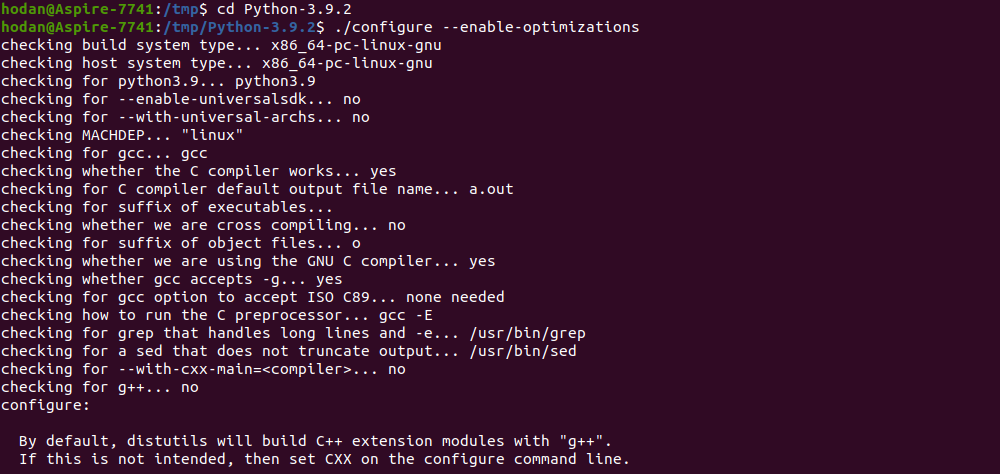
На следующем этапе, запустим команду, которая выполнит подготовку к установке (enable-optimization — служит для оптимизации двоичного файла Python). Исполнение данной команды займет некоторое время:
Для того, чтобы начать процесс сборки, выполним команду*:
*Примечание: цифра 2 указывает на количество ядер процессора. Узнать эти данные можно с помощью команды nproc.
Если в процессе сборки будут замечены проблемы, то необходимо запустить сборку в однопоточном режиме, следующим образом (без параметров -j 2), просто выполнив команду make.
Теперь установим Python 3.9.2 с помощью команды altinstall, последняя версия Python инсталлируется наряду со старыми версиями, т.е. у вас в ОС будет несколько версий языка Python. Если же вы используете команду install, то новая версия питон будет установлена поверх старых (а все старые версии будут удалены).
*Процесс инсталляции Python путем сборки пакета из исходников может занять длительное время.
В результате, в нашей ОС Ubuntu 20 (Debian 10) будет установлено сразу несколько версий языка Python, у нас конкретно — это версии 3.9.2 и 3.8.5, проверить можно с помощью команд:
Особенности установки Python на CentOS
Для инсталляции Python на CentOS версии 7 необходимо использовать репозиторий epel (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) или же DNF (Dandified YUM, т.е. yum нового поколения) для CentOS 8.
Для способа с использованием DNF выполним следующие команды:
- Проверим обновления нашего диспетчера пакетов:
- Установим стабильную версию Python 3 из репозитория:
- Проверим, какая точно версия Python у нас инсталлировалась:
- Чтобы установить инструментарий для разработчиков, выполним следующую команду:
Если же вы будете использовать репозиторий epel, то следуйте простым инструкциям:
- Подключите репозиторий epel для начала работы:
- Затем установите Python (например, версии 3.6):
- Для проверки номера версии введите команду:
- Для отображения последней установленной в вашей ОС версии используйте команду:
Как создать и настроить виртуальную среду
Для чего нужна виртуальная среда? С помощью виртуальной среды мы можем для каждого своего проекта на языке Python выделить отдельную область (со своими зависимостями, с установленными модулями питон, разными версиями языка и т.д.).
Работа с пакетом virtualenv
Например, у нас есть Project A и Project B, для каждого из них мы можем создать свою виртуальную среду, сделать это можно с помощью venv, выполнив несложные команды:
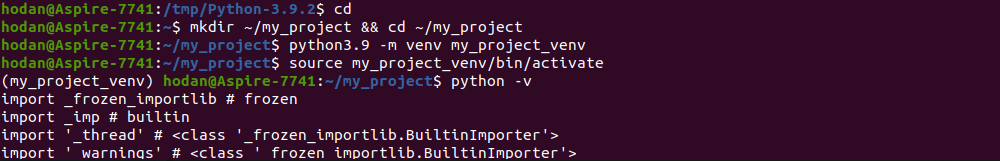
- Создаем каталог для нового проекта my_project и переходим в него:
- Выполним команду, чтобы создать виртуальную среду:
- На данном этапе необходимо ее активировать:
На скриншоте ниже показано, что далее работа с проектом ведется уже внутри виртуальной среды:
Работа с виртуальной средой с помощью virtualenvwrapper и pip
Все действия исполняем для пользователя root, чтобы перейти в root, выполним команду:
- Для начала устанавливаем менеджер пакетов pip:
Осуществим установку virtualenv и virtualenvwrapper:
Затем необходимо отредактировать файл .bashrc (в директории пользователя root, если работаете под root или же в директории другого пользователя):
Добавим в конец файла следующие строки:
Сохраним изменения и закроем файл.
А) Для создания новой виртуальной среды (например, ansible) используется команда:
Б) Для удаления виртуальной среды:
В) Чтобы активировать нужную вам виртуальную среду:
Г) Для выхода из среды:
Д) Показать список установленных пакетов:
Е) Для инсталляции конкретных пакетов:
Заключение
В этой статье мы рассказали нашим читателям об использовании языка программирования Python и подробно изложили два способа установки последней версии Python для ОС Linux (на Ubuntu 20, Debian 10, CentOS 7 и 8). Также дали основные понятия о работе с виртуальной средой.
Источник
Download the latest source release
Download the latest version of Python
Looking for Python with a different OS? Python for Windows, Linux/UNIX, macOS, Other
Want to help test development versions of Python? Prereleases, Docker images
Looking for Python 2.7? See below for specific releases
Active Python Releases
- 3.10 bugfix 2021-10-04 2026-10 PEP 619
- 3.9 bugfix 2020-10-05 2025-10 PEP 596
- 3.8 security 2019-10-14 2024-10 PEP 569
- 3.7 security 2018-06-27 2023-06-27 PEP 537
- 3.6 security 2016-12-23 2021-12-23 PEP 494
- 2.7 end-of-life 2010-07-03 2020-01-01 PEP 373
Looking for a specific release?
Python releases by version number:
- Python 3.10.0 Oct. 4, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.12 Sept. 4, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.15 Sept. 4, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.7 Aug. 30, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.12 Aug. 30, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.6 June 28, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.11 June 28, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.11 June 28, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.14 June 28, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.5 May 3, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.10 May 3, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.4 April 4, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.9 April 2, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.2 Feb. 19, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.8 Feb. 19, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.13 Feb. 15, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.10 Feb. 15, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.7 Dec. 21, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.1 Dec. 7, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.0 Oct. 5, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.6 Sept. 24, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.10 Sept. 5, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.9 Aug. 17, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.12 Aug. 17, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.5 July 20, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.4 July 13, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.8 June 27, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.11 June 27, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.3 May 13, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.18 April 20, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.7 March 10, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.2 Feb. 24, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.1 Dec. 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.6 Dec. 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.10 Dec. 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.9 Nov. 2, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.8 Oct. 29, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.17 Oct. 19, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.5 Oct. 15, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.0 Oct. 14, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.4 July 8, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.9 July 2, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.3 March 25, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.10 March 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.7 March 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.16 March 4, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.2 Dec. 24, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.8 Dec. 24, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.1 Oct. 20, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.7 Oct. 20, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.6 Aug. 2, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.9 Aug. 2, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.0 June 27, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.6 June 27, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.15 May 1, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.5 March 28, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.8 Feb. 5, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.5 Feb. 5, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.4 Dec. 19, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.3 Oct. 3, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.7 Sept. 19, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.14 Sept. 16, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.7 Aug. 9, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.4 Aug. 8, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.2 July 17, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.1 March 21, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.6 Jan. 17, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.3 Jan. 17, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.0 Dec. 23, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.13 Dec. 17, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.5 June 27, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.2 June 27, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.12 June 25, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.4 Dec. 21, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.1 Dec. 7, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.11 Dec. 5, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.0 Sept. 13, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.10 May 23, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.3 Feb. 25, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.9 Dec. 10, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.2 Oct. 13, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.6 Oct. 12, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.6 Oct. 12, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.8 July 2, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.7 June 1, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.1 May 19, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.0 March 17, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.5 March 9, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.4 Feb. 9, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.3 Nov. 17, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.6 Nov. 10, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.9 Oct. 29, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.5 May 15, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.2 May 15, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.5 May 12, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.4 April 6, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.1 April 6, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.4 April 6, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.0 Sept. 29, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.3 April 10, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.8 April 10, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.5 April 9, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.3 April 9, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.2 Sept. 3, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.1 July 9, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.2 June 11, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.4 June 11, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.7 June 3, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.6 May 26, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.0 Feb. 20, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.3 Nov. 27, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.1 Nov. 27, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.6 Aug. 24, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.0 July 3, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.2 March 20, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.5 March 18, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.5 Jan. 31, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.4 Oct. 26, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.3 Oct. 2, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.1 Aug. 17, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.0 June 26, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.2 April 14, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.0.1 Feb. 13, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.4 Dec. 23, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.3 Dec. 19, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.6 Dec. 19, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.1 Dec. 4, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.0.0 Dec. 3, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.0 Oct. 2, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.7 March 11, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.5 March 11, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.2 Feb. 21, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.1 April 19, 2007 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.6 Nov. 1, 2006 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.4 Oct. 18, 2006 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.0 Sept. 19, 2006 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.3 April 15, 2006 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.2 Sept. 27, 2005 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.1 March 30, 2005 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.5 Feb. 8, 2005 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.0 Nov. 30, 2004 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.4 May 27, 2004 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.3 Dec. 19, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.2 Oct. 3, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.1 Sept. 23, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.0 July 29, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.2.3 May 30, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.2.2 Oct. 14, 2002 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.2.1 April 10, 2002 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.1.3 April 9, 2002 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.2.0 Dec. 21, 2001 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.0.1 June 22, 2001 DownloadRelease Notes
Sponsors
Visionary sponsors like Google help to host Python downloads.
Licenses
All Python releases are Open Source. Historically, most, but not all, Python releases have also been GPL-compatible. The Licenses page details GPL-compatibility and Terms and Conditions.
Sources
For most Unix systems, you must download and compile the source code. The same source code archive can also be used to build the Windows and Mac versions, and is the starting point for ports to all other platforms.
Download the latest Python 3 and Python 2 source.
Alternative Implementations
This site hosts the «traditional» implementation of Python (nicknamed CPython). A number of alternative implementations are available as well.
History
Python was created in the early 1990s by Guido van Rossum at Stichting Mathematisch Centrum in the Netherlands as a successor of a language called ABC. Guido remains Python’s principal author, although it includes many contributions from others.
Release Schedules
Information about specific ports, and developer info
OpenPGP Public Keys
Source and binary executables are signed by the release manager or binary builder using their OpenPGP key. Release files for currently supported releases are signed by the following:
Release files for older releases which have now reached end-of-life may have been signed by one of the following:
- Anthony Baxter (key id: 0EDD C5F2 6A45 C816)
- Georg Brandl (key id: 0A5B 1018 3658 0288)
- Martin v. Löwis (key id: 6AF0 53F0 7D9D C8D2)
- Ronald Oussoren (key id: C9BE 28DE E6DF 025C)
- Barry Warsaw (key ids: 126E B563 A74B 06BF, D986 6941 EA5B BD71, and ED9D77D5)
You can import a person’s public keys from a public keyserver network server you trust by running a command like:
or, in many cases, public keys can also be found at keybase.io. On the version-specific download pages, you should see a link to both the downloadable file and a detached signature file. To verify the authenticity of the download, grab both files and then run this command:
Note that you must use the name of the signature file, and you should use the one that’s appropriate to the download you’re verifying.
- (These instructions are geared to GnuPG and Unix command-line users.)
Other Useful Items
- Looking for 3rd party Python modules? The Package Index has many of them.
- You can view the standard documentation online, or you can download it in HTML, PostScript, PDF and other formats. See the main Documentation page.
- Information on tools for unpacking archive files provided on python.org is available.
- Tip: even if you download a ready-made binary for your platform, it makes sense to also download the source. This lets you browse the standard library (the subdirectory Lib) and the standard collections of demos (Demo) and tools (Tools) that come with it. There’s a lot you can learn from the source!
- There is also a collection of Emacs packages that the Emacsing Pythoneer might find useful. This includes major modes for editing Python, C, C++, Java, etc., Python debugger interfaces and more. Most packages are compatible with Emacs and XEmacs.
Want to contribute?
Want to contribute? See the Python Developer’s Guide to learn about how Python development is managed.
Источник