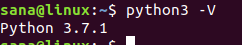- Как скачать и установить Python 3 на Ubuntu 18.04 (Linux)
- Как проверить текущую версию Python
- Как установить Python 3 на Linux через apt-get
- Как установить Python 3 на Linux из архива
- Ошибки, которые могут возникнуть при установке
- 1. Zipimport.zipimporterror
- 2. No module named ‘_ctypes’
- Как обновить команду python3 до последней версии
- Заключение
- Запуск python скрипта в Linux
- Запуск python скрипта в Linux
- Download the latest source release
- Download the latest version of Python
- Active Python Releases
- Looking for a specific release?
- Sponsors
- Licenses
- Sources
- Alternative Implementations
- History
- Release Schedules
- Information about specific ports, and developer info
- OpenPGP Public Keys
- Other Useful Items
- Want to contribute?
Как скачать и установить Python 3 на Ubuntu 18.04 (Linux)
В этой статье мы скачаем и установим последнюю версию Python 3 на Ubuntu. Затем убедимся, что python установлен корректно, рассмотрим популярные ошибки и их решения.
Все команды выполнялись в Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, но эта статья поможет установить python на Ubuntu 16.04, Debian, Mint и другие Linux-системы.
Мы используем командную строку Ubuntu — Терминал, для работы. Вы можете открыть Терминал через поиск или комбинацию клавиш Ctrl+Alt+T.
Как проверить текущую версию Python
Проверка текущей версии программного обеспечения не только помогает вам получить номер версии этого программного обеспечения, установленного в вашей системе, но и проверяет, действительно ли программное обеспечение установлено в вашей системе.
Мы сделаем то же самое для Python, выполнив следующую команду в нашем терминале:
Версия будет отображаться, как показано в приведенном выше выводе. Число зависит от того, когда вы обновили систему.
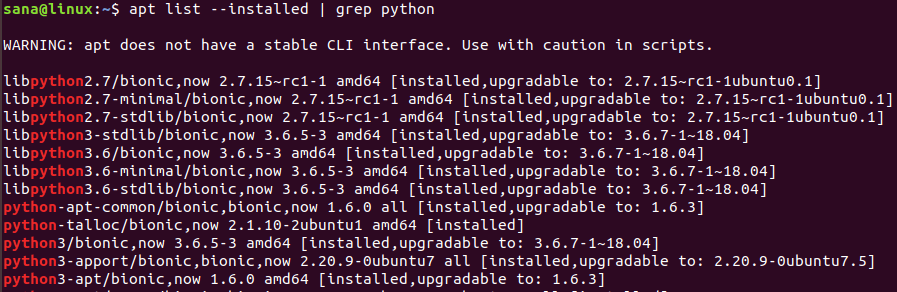
У вас также может быть несколько версий Python, установленных в вашей системе. Следующая команда выведет список всех версий Python, которые есть в вашей системе:
Как установить Python 3 на Linux через apt-get
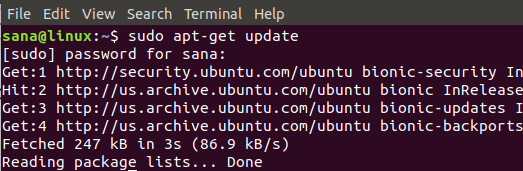
Установка Python 3 на Ubuntu с помощью команды apt-get довольно просто. Во-первых, вам необходимо обновить репозиторий системы, чтобы можно было установить последнюю доступную версию без проблем совместимости. Для этого выполните команду от имени администратора:
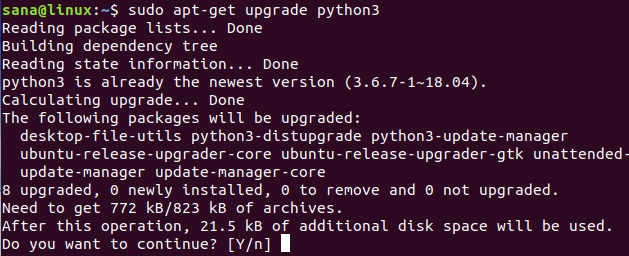
Так как Python уже установлен в нашей системе (это мы проверили в предыдущем разделе), нам нужно обновить его до последней версии следующим образом:
Система может попросить вас ввести пароль для прав sudo , поскольку только авторизованный пользователь может добавлять / удалять и обновлять программное обеспечение в Ubuntu.
Система также запросит подтверждение обновления. Введите Y , а затем нажмите Enter, чтобы продолжить.
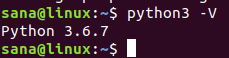
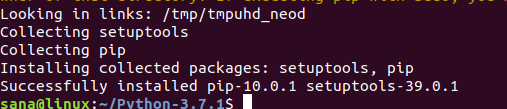
Так вы обновили Python до последней доступной версии. Проверьте:
Если Python не установлен, вы можете установить его с правами sudo используя команду apt-get :
Как установить Python 3 на Linux из архива
Сайт Python.org содержит список всех выпусков Python по этой ссылке:
https://www.python.org/downloads/source/
Поэтому, если вы решите установить Python вручную, можете скачать python любой сборки c официального сайта. На сайте также есть последние версии, которые вы не загрузите с помощью команды apt-get .
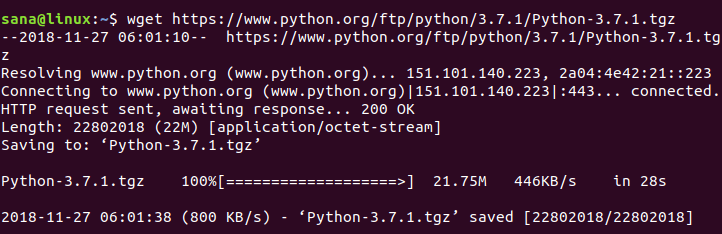
На момент подготовки материала Python-3.7.1 последняя доступная версия, поэтому мы скачаем его файл .tgz с помощью следующей команды:
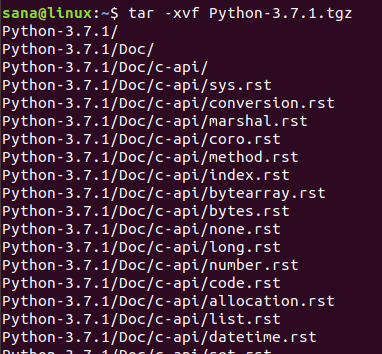
Когда архив с ptyhon будет скачан, выполните следующую команду, чтобы извлечь файлы:
После того, как файлы извлечены, нужно запустить C-программу «configure». Для этого вам необходимо установить компилятор языка программирования C — gcc в вашу Linux-систему. Если он не предустановлен, установите его с помощью следующей команды:
Измените текущую директорию на Python-3.7.1 или на ту версию python, которую вы скачали и извлекли:
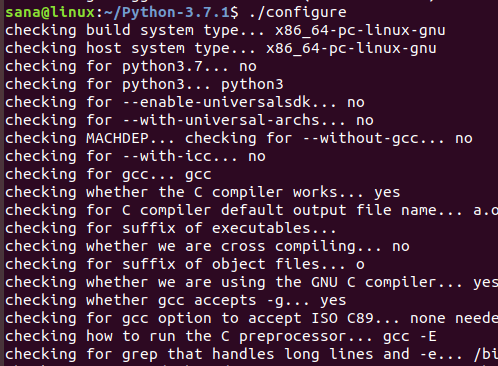
Теперь используйте следующую команду, чтобы запустить скрипт конфигурации:
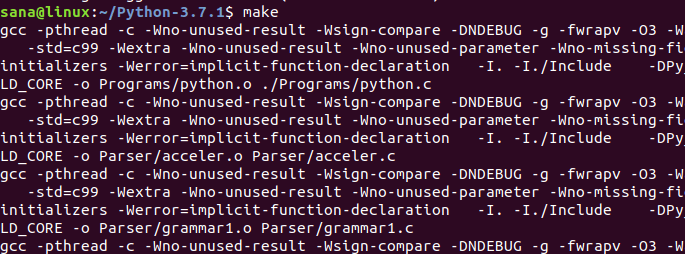
Теперь пришло время установить Python.
Если вы не можете запустить команду make , установите make с помощью следующей команды:
Запустите следующую команду для установки языка программирования Python:
Скачанная версия Python с официального сайта установлена в вашей Linux-системе.
Ошибки, которые могут возникнуть при установке
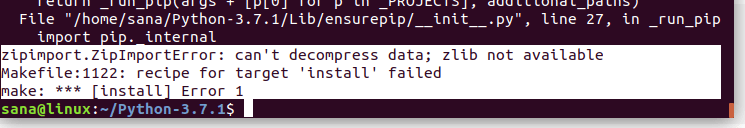
1. Zipimport.zipimporterror
Когда вы запускаете команду sudo make install , можете столкнуться со следующей ошибкой:
Это значит, что нужно установить пакет с именем zlib1g-dev , так как он, возможно, вам не был нужен раньше.
Решение:
Выполните следующую команду с правами sudo, чтобы установить отсутствующий пакет zlib1g-dev :
Затем повторите команду для завершения установки Python:
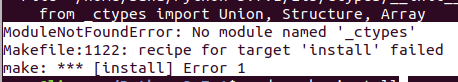
2. No module named ‘_ctypes’
Это ошибка появляется также при запуске команды sudo make install :
Это значит, что нужно установить пакет с именем libffi-dev , так как он, возможно, вам не был нужен раньше.
Решение:
Выполните следующую команду с правами sudo, чтобы установить отсутствующий пакет libffi-dev :
Затем повторите команду для завершения установки Python:
Как обновить команду python3 до последней версии
Перед установкой Python вручную из архива номер версии нашей установки Python был 3.6.7
Когда я проверил номер версии python3.7 , он дает следующий вывод:
Обновите версию python для команды python3 следующей командой:
Теперь команда python3 работает с последней версией Python в моей системе (3.7.1).
Заключение
В большинстве версий Ubuntu уже установлены Python и Pip3, но после прочтения этой статьи вы узнали, как загрузить и обновить их до последних версий.
Источник
Запуск python скрипта в Linux
Python — очень популярный язык программирования для написания различных системных скриптов в Linux. В Windows, там где не хватает возможностей командной оболочки используется PowerShell. В Linux же, когда возможностей Bash не хватает используется язык Python.
На этом языке написано огромное количество системных программ, среди них пакетный менеджер apt, видеоредактор OpenShot, а также множество скриптов, которые вы можете установить с помощью утилиты pip. В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим как запустить Python скрипт в Linux с помощью терминала различными способами.
Запуск python скрипта в Linux
Для примера нам понадобится Python скрипт. Чтобы не брать какой-либо из существующих скриптов, давайте напишем свой:
print(«Hello from losst!»)
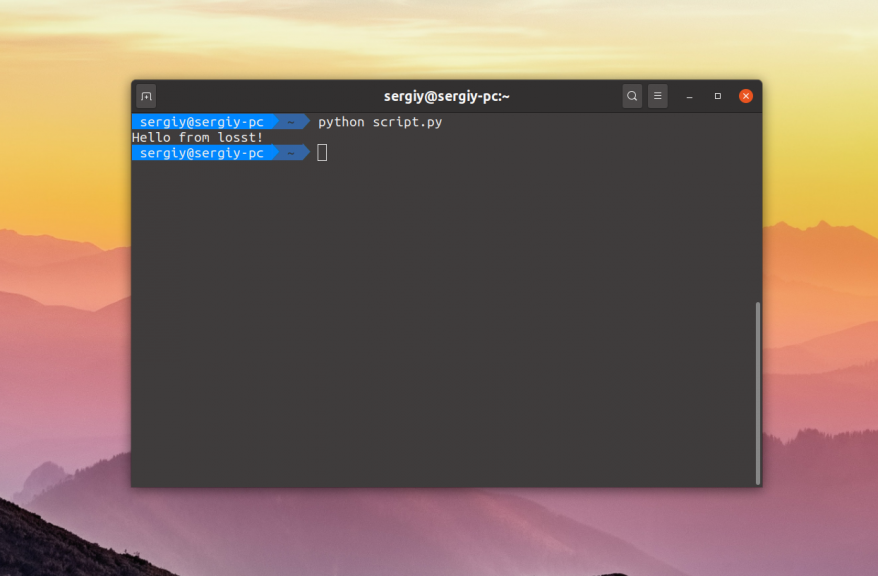
Для того чтобы запустить скрипт необходимо передать его интерпретатору Python. Для этого просто откройте терминал с помощью сочетания клавиш Ctrl + Alt + T, перейдите в папку со скриптом и выполните:
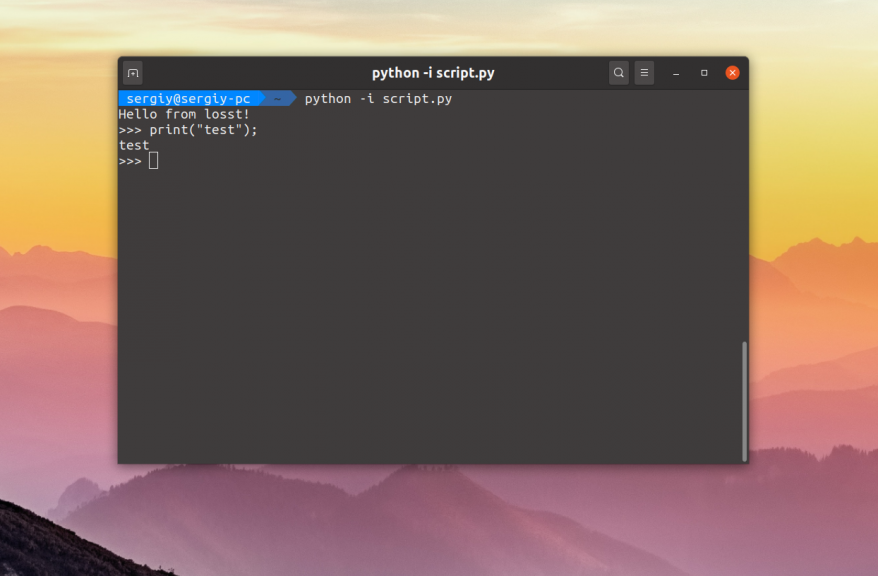
Если вы хотите, чтобы после выполнения скрипта открылась консоль, в которой можно интерактивно выполнять команды языка Python используйте опцию -i:
python -i script.py
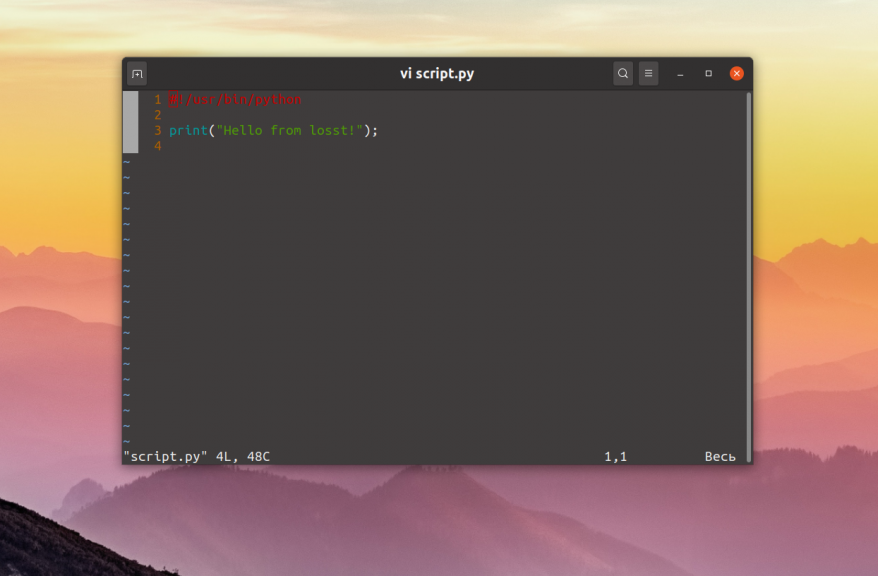
Но как вы могли заметить, при запуске apt или openshot не надо писать слово python. Это намного удобнее. Давайте разберемся как это реализовать. Если вы не хотите указывать интерпретатор в командной строке, его надо указать в самом скрипте. Для этого следует в начало скрипта добавить такую строчку:
Сохраните изменения, а затем сделайте файл скрипта исполняемым с помощью такой команды:
chmod ugo+x script.py
После этого можно запустить скрипт Python просто обращаясь к его файлу:
Если убрать расширение .py и переместить скрипт в каталог, находящийся в переменной PATH, например /usr/bin/, то его можно будет выполнять вот так:
Как видите, запуск команды python Linux выполняется довольно просто и для этого даже есть несколько способов. А каким способом пользуетесь вы? Напишите в комментариях!
Источник
Download the latest source release
Download the latest version of Python
Looking for Python with a different OS? Python for Windows, Linux/UNIX, macOS, Other
Want to help test development versions of Python? Prereleases, Docker images
Looking for Python 2.7? See below for specific releases
Active Python Releases
- 3.10 bugfix 2021-10-04 2026-10 PEP 619
- 3.9 bugfix 2020-10-05 2025-10 PEP 596
- 3.8 security 2019-10-14 2024-10 PEP 569
- 3.7 security 2018-06-27 2023-06-27 PEP 537
- 3.6 security 2016-12-23 2021-12-23 PEP 494
- 2.7 end-of-life 2010-07-03 2020-01-01 PEP 373
Looking for a specific release?
Python releases by version number:
- Python 3.10.0 Oct. 4, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.12 Sept. 4, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.15 Sept. 4, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.7 Aug. 30, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.12 Aug. 30, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.6 June 28, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.11 June 28, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.11 June 28, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.14 June 28, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.5 May 3, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.10 May 3, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.4 April 4, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.9 April 2, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.2 Feb. 19, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.8 Feb. 19, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.13 Feb. 15, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.10 Feb. 15, 2021 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.7 Dec. 21, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.1 Dec. 7, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.9.0 Oct. 5, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.6 Sept. 24, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.10 Sept. 5, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.9 Aug. 17, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.12 Aug. 17, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.5 July 20, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.4 July 13, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.8 June 27, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.11 June 27, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.3 May 13, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.18 April 20, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.7 March 10, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.2 Feb. 24, 2020 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.1 Dec. 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.6 Dec. 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.10 Dec. 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.9 Nov. 2, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.8 Oct. 29, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.17 Oct. 19, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.5 Oct. 15, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.8.0 Oct. 14, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.4 July 8, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.9 July 2, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.3 March 25, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.10 March 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.7 March 18, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.16 March 4, 2019 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.2 Dec. 24, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.8 Dec. 24, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.1 Oct. 20, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.7 Oct. 20, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.6 Aug. 2, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.9 Aug. 2, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.7.0 June 27, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.6 June 27, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.15 May 1, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.5 March 28, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.8 Feb. 5, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.5 Feb. 5, 2018 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.4 Dec. 19, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.3 Oct. 3, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.7 Sept. 19, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.14 Sept. 16, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.7 Aug. 9, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.4 Aug. 8, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.2 July 17, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.1 March 21, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.6 Jan. 17, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.3 Jan. 17, 2017 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.6.0 Dec. 23, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.13 Dec. 17, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.5 June 27, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.2 June 27, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.12 June 25, 2016 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.4 Dec. 21, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.1 Dec. 7, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.11 Dec. 5, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.5.0 Sept. 13, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.10 May 23, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.3 Feb. 25, 2015 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.9 Dec. 10, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.2 Oct. 13, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.6 Oct. 12, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.6 Oct. 12, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.8 July 2, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.7 June 1, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.1 May 19, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.4.0 March 17, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.5 March 9, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.4 Feb. 9, 2014 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.3 Nov. 17, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.6 Nov. 10, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.9 Oct. 29, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.5 May 15, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.2 May 15, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.5 May 12, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.4 April 6, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.1 April 6, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.4 April 6, 2013 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.3.0 Sept. 29, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.3 April 10, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.8 April 10, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.5 April 9, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.3 April 9, 2012 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.2 Sept. 3, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.1 July 9, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.2 June 11, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.4 June 11, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.7 June 3, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.6 May 26, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.2.0 Feb. 20, 2011 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.3 Nov. 27, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.1 Nov. 27, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.6 Aug. 24, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.7.0 July 3, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.2 March 20, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.5 March 18, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.5 Jan. 31, 2010 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.4 Oct. 26, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.3 Oct. 2, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.1 Aug. 17, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.1.0 June 26, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.2 April 14, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.0.1 Feb. 13, 2009 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.4 Dec. 23, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.3 Dec. 19, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.6 Dec. 19, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.1 Dec. 4, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 3.0.0 Dec. 3, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.6.0 Oct. 2, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.7 March 11, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.5 March 11, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.2 Feb. 21, 2008 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.1 April 19, 2007 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.6 Nov. 1, 2006 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.4 Oct. 18, 2006 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.5.0 Sept. 19, 2006 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.3 April 15, 2006 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.2 Sept. 27, 2005 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.1 March 30, 2005 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.5 Feb. 8, 2005 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.4.0 Nov. 30, 2004 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.4 May 27, 2004 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.3 Dec. 19, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.2 Oct. 3, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.1 Sept. 23, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.3.0 July 29, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.2.3 May 30, 2003 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.2.2 Oct. 14, 2002 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.2.1 April 10, 2002 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.1.3 April 9, 2002 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.2.0 Dec. 21, 2001 DownloadRelease Notes
- Python 2.0.1 June 22, 2001 DownloadRelease Notes
Sponsors
Visionary sponsors like Google help to host Python downloads.
Licenses
All Python releases are Open Source. Historically, most, but not all, Python releases have also been GPL-compatible. The Licenses page details GPL-compatibility and Terms and Conditions.
Sources
For most Unix systems, you must download and compile the source code. The same source code archive can also be used to build the Windows and Mac versions, and is the starting point for ports to all other platforms.
Download the latest Python 3 and Python 2 source.
Alternative Implementations
This site hosts the «traditional» implementation of Python (nicknamed CPython). A number of alternative implementations are available as well.
History
Python was created in the early 1990s by Guido van Rossum at Stichting Mathematisch Centrum in the Netherlands as a successor of a language called ABC. Guido remains Python’s principal author, although it includes many contributions from others.
Release Schedules
Information about specific ports, and developer info
OpenPGP Public Keys
Source and binary executables are signed by the release manager or binary builder using their OpenPGP key. Release files for currently supported releases are signed by the following:
Release files for older releases which have now reached end-of-life may have been signed by one of the following:
- Anthony Baxter (key id: 0EDD C5F2 6A45 C816)
- Georg Brandl (key id: 0A5B 1018 3658 0288)
- Martin v. Löwis (key id: 6AF0 53F0 7D9D C8D2)
- Ronald Oussoren (key id: C9BE 28DE E6DF 025C)
- Barry Warsaw (key ids: 126E B563 A74B 06BF, D986 6941 EA5B BD71, and ED9D77D5)
You can import a person’s public keys from a public keyserver network server you trust by running a command like:
or, in many cases, public keys can also be found at keybase.io. On the version-specific download pages, you should see a link to both the downloadable file and a detached signature file. To verify the authenticity of the download, grab both files and then run this command:
Note that you must use the name of the signature file, and you should use the one that’s appropriate to the download you’re verifying.
- (These instructions are geared to GnuPG and Unix command-line users.)
Other Useful Items
- Looking for 3rd party Python modules? The Package Index has many of them.
- You can view the standard documentation online, or you can download it in HTML, PostScript, PDF and other formats. See the main Documentation page.
- Information on tools for unpacking archive files provided on python.org is available.
- Tip: even if you download a ready-made binary for your platform, it makes sense to also download the source. This lets you browse the standard library (the subdirectory Lib) and the standard collections of demos (Demo) and tools (Tools) that come with it. There’s a lot you can learn from the source!
- There is also a collection of Emacs packages that the Emacsing Pythoneer might find useful. This includes major modes for editing Python, C, C++, Java, etc., Python debugger interfaces and more. Most packages are compatible with Emacs and XEmacs.
Want to contribute?
Want to contribute? See the Python Developer’s Guide to learn about how Python development is managed.
Источник