- Установить QEMU c GUI без использования интернета
- Links
- Contents
- Development
- Developers
- Unofficial QEMU binaries
- Alternate QEMU repositories / Forks
- GUIs and management tools/systems
- Legacy GUI front ends
- How to install Qemu/KVM and Virt-Manager GUI on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
- Install KVM and Virt Virtual Machine Manager GUI on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
- 1. Open a command terminal
- 2. Install QEMU/KVM on Ubuntu 20.04 Server
- 3. Install Virt-Manager GUI for KVM on Linux
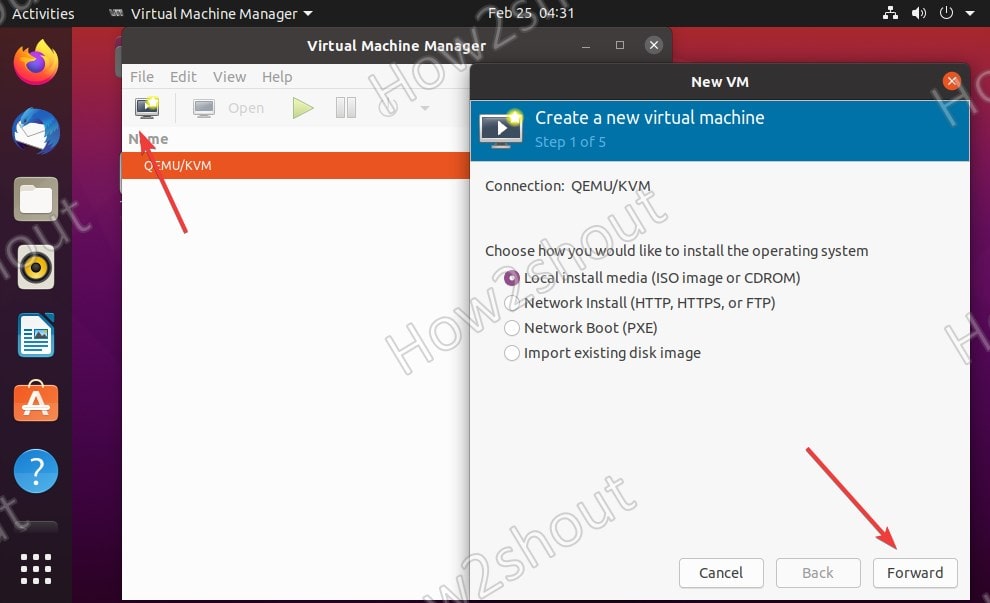
- 4. Create a New Virtual Machine
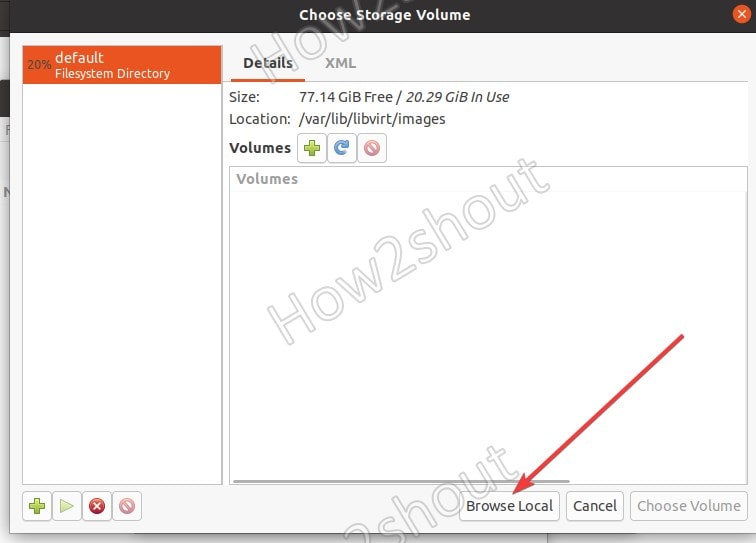
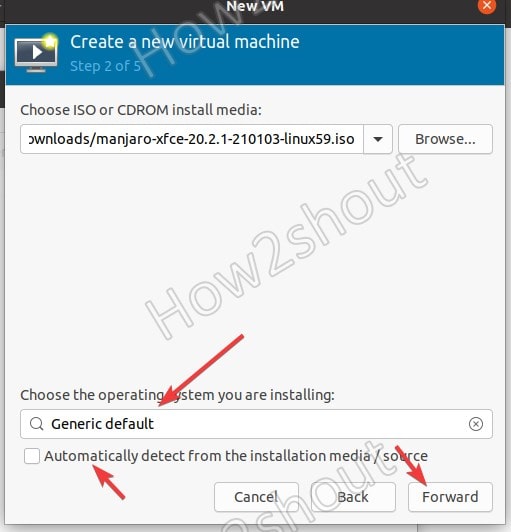
- 5. Browse the ISO file
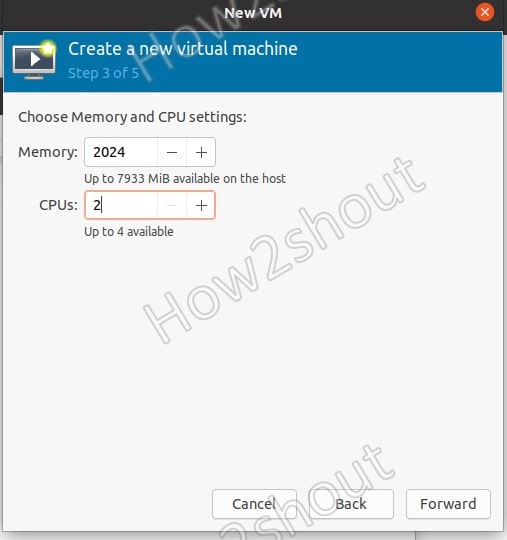
- 6. Choose Memory and CPU settings
- 7. Create a disk image for the KVM virtual machine
- 8. Select Network
- 9. Virtual Machine Interface on QEMU/KVM
- How To Install QEMU KVM (qemu-kvm) with GUI (virt-manager) in Ubuntu
- System Summary
- Install KVM
- Add User to Group libvirtd
- Install A GUI for KVM
- Common Problem
Установить QEMU c GUI без использования интернета
Здравствуйте. Подскажите, как установить QEMU c GUI локально на пк, без использования интернета? Если можно последовательность действий и какие зависимости нужны и откуда их качать?
Так же интересуют, какие зависимости нужны для Virtual Box?
Что это? Раскрой мысль.
Качай qemu, качай virt-manager, читай зависимости, собирай, компилируй.
Только учти, что поддержка kvm/vfio/virtio и прочего должна быть включена в ядре.
Если дистр дебиан, то берешь последнюю минорную версию стейбла, качаешь с помощью jigdo _все_ исошники. дальше нарезаешь исошники на болванки и подсовываешь при установке пакетов эти болванки в привод.
минус в том, что обновления (имхо) будут доступны только при обновлении минорной версии, там два диска или сколько можно подоткнуть для например с 8.6 на 8.7 чтобы обновить.
VirtualBox есть своя в дебиане, единственно, если надо, можно будет скачать плагин вручную и поставить, остальное, в т.ч. Guest Additions есть (правда не той версии, что сам VirtualBox, а ниже. но гости работают ОК).
Качать и ставить также как и при подключенным к интернету машине. все команды для работы с репозиторием на двд работатют, просто надо поизучать, потратить время на привыкание. искать, ставить и т п.
Домашнее задание: найти GUI для QEMU
Пробуйте :-). Единственно, если сторонний софт надо будет ставить, есть опция использования скачивания из репы без установки (нужна инструментальная машина, желательно с таким же дистром, подключенная к интернету).
Скачать необходимые пакеты из репозитория на машине с интернетом? Например для centos:
Подскажите, как установить QEMU c GUI локально на пк, без использования интернета?
Установить на какую систему? Откуда вы собрались брать пакеты без интернета?
Источник
Links
Contents
Development
- Savannah project page
- QEMU patches from the mailing list
- IRC channel: #qemu on irc.oftc.net
Developers
A few blogs from developers are syndicated at Virt Tools Planet. For enrolling a blog into the planet, please submit a patch to this file to Dan Berrange.
Unofficial QEMU binaries
- Precompiled Windows versions, provided by Prashant Satish
- Precompiled Windows versions (32 and 64 bit), provided by Stefan Weil
- Precompiled Windows versions (currently only up to 2.6.0), provided by Eric Lassauge
- Slackware packages
Alternate QEMU repositories / Forks
- Openmoko (Neo1973) target
- Malc’s GIT repository including audio improvements, an x86 interpreter (useful for MSDOS demos heavily using self modifying code), full A/V capture
- Android emulation — see also http://gsoc11-qemu-android.blogspot.de/
- AR7 routers, TCG interpreter (maintained by Stefan Weil)
- Motorola 680×0 (not coldfire — maintained by Laurent Vivier)
- PA-RISC target — early stages (needs linux-user rework for stack growing up)
- kqemu archive includes patches for the former acceleration module
- qemu-linaro — obsolete (but includes OMAP3 support)
- Blackfin target (maintained by Mike Frysinger)
- 6502 CPU target
- AT91SAM9263 emulation
- Android Goldfish
- Android Ranchu
- Imagination META
- Macintosh 128k
- QEMU with Windbg stub
GUIs and management tools/systems
- libvirt provides an API for managing QEMU/KVM (and other hypervisors) exposed in C, Perl, Python, OCaml, Ruby, and Java, with bridges to AMQP/QMF and DMTF CIM.
- virt-install, virt-clone, virt-convert a set of command line tools for provisioning new VMs from install media, existing VMs and appliances, respectively. See also ‘virsh’ command line shell with libvirt.
- virt-manager, Virtual Machine Manager. A graphical desktop management app using libvirt. Can manage a single local host, or securely multiple remote hosts. Support QEMU, KVM, Xen and more
- AQEMU GUI for QEMU and KVM (Linux), docs (German)
- Ganeti, a cluster virtual server management software tool built on top of existing virtualization technologies such as Xen or KVM and other Open Source software.
- qemu-java, a full Java API to QEmu’s QApi, commandline image manipulation. This is a good foundation API for building integration testing systems, richer QEmu-based applications, and so forth.
- QtEmu, a graphical user interface for QEMU written in Qt5 for GNU/Linux, FreeBSD, Windows and MacOS
Legacy GUI front ends
These projects seem to be abandoned, thus these GUIs likely do not work with the latest version of QEMU anymore and the links are only provided here for historical reasons:
- qemudo, QEMU Web Interface
- JavaQemu, a GUI for QEMU written in Java
Источник
How to install Qemu/KVM and Virt-Manager GUI on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
When it comes to running virtual machines on home Linux systems or for personal use most of us either go for VirtualBox or Vmware workstation player, however, there is more best option i.e KVM/Qemu. Qemu and KVM both are open source platforms for performing virtualization on Linux platforms. KVM stands for Kernel Virtual Machine, where QEMU is an emulator that can also be used as a virtualizer with the help of KVM to provide a native speed by accessing Intel VT-x or AMD V technology of modern processors.
KVM is a virtualization module that can easily be installed in any Linux kernel to allow it to function as a type 1 hypervisor.
Thus, the installation of KVM becomes a lot easier, we only need a Linux-based system such as Ubuntu and a processor with intel-v / VT-x or AMD-v support. All new processors have this instruction set extension. Only the small processors, such as the Atom from Intel, or very old processors may lack this feature.
However, by default to manage KVM virtual machines we need to use the command line, unlike VirtualBox or VMware it will not have a graphical user interface out of the box. Still, we can use various Graphical user interface Virtual Machine Manager applications such as Virt-Manager (Virtual Machine Manager), Gnome Boxes, and more… Here is the list of all such open-source platforms: 8 Best Open-source Virtual machine manager for Linux
Here we will see the installation of the popular Virt-Manager that makes KVM machines easy to operate just like VirtualBox. The special feature of VMM is that it forms a kind of intermediate layer, so that the management of the virtual machines is uniform, regardless of which virtualization solution is used, which reduces the administrative effort. The configuration is stored in XML files so that it can be corrected manually if necessary. We can also use VVM to manage the Virtual machines running on remote servers’ KVM using an encrypted connection.
Install KVM and Virt Virtual Machine Manager GUI on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
The given steps are also applicable for Ubuntu 18.04, Debian, Linux Mint, MX Linux, Elementary OS, Kali Linux, and other similar Linux distros.
1. Open a command terminal
If you are installing KVM on some Ubuntu server then you already on the command line, whereas GUI desktop users can access the terminal from the All applications area or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl +ALT +T.
The first thing we perform is the running of the system update command:
2. Install QEMU/KVM on Ubuntu 20.04 Server
Well, you can install KVM on both Desktop and Server editions of Ubuntu, it is your choice. However, the command for doing it will be the same for both. Nevertheless, for a small office or running multiple virtual machines, it is recommended to use a command-line server that will consume fewer system resources so that your VMs will have more power to work. So, here is the command to setup KVM along with other tools for its proper management and functioning.
3. Install Virt-Manager GUI for KVM on Linux
Our KVM is already installed, now it’s time to install a Graphical user interface to create, start, stop or delete virtual machines using Virt-Manager.
Once the installation is completed go to Applications and search for Virtual Machine Manager, as its icon appears click to run it.
Note: If your KVM is installed on some CLI server, then install Virt-Manager on some other Linux PC or laptop with GUI. You can also use Virt-Viewer to remotely view VMs on Windows platforms, however, that would not allow you to create a new VM.
4. Create a New Virtual Machine
To create a new VM, click on the PC icon and then select the source of the operating system you want to install. However, most of the time, it will be the ISO image, thus select the default “Local install media ISO image or CDROM”.
5. Browse the ISO file
Now, click on the Browse Local button and select the ISO of the Linux or Windows operating system you want to set up for VM.
After the ISO selection, uncheck “Automatically detect from the installation media /source” because in some cases it won’t identify what type of OS we are about to install. Thus, uncheck it and search to select that manually.
6. Choose Memory and CPU settings
Here in this step, we select the amount of RAM and number of CPU cores we want to assign for our virtual machine on KVM.
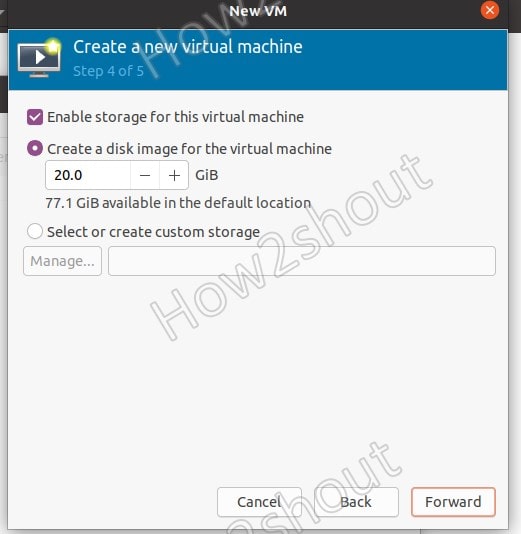
7. Create a disk image for the KVM virtual machine
To store data of VM, create a disk image or virtual hard disk. By default, it would be 20 GB, but we can increase it as per the requirement of the operating system we are about to install.
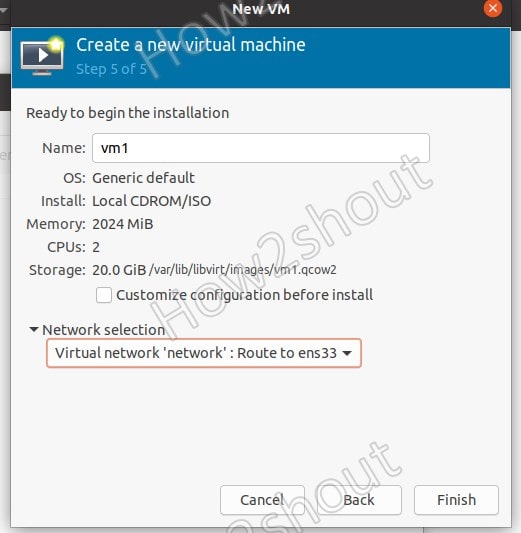
8. Select Network
The default virtual network for KVM’s VM will be in bridge mode. Thus, leave it as it is unless you want something particular in terms of routing network data.
9. Virtual Machine Interface on QEMU/KVM
Once all the above steps are done, the VM will start and you have the access to its interface for further installation of OS.
Источник
How To Install QEMU KVM (qemu-kvm) with GUI (virt-manager) in Ubuntu
A GNU/Linux user actually can do machine virtualization without using Oracle VirtualBox, by just taking advantage of already included feature of Linux kernel, KVM. KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a kernel module of Linux which enables a GNU/Linux operating system to run virtual machine of another operating system (just like VirtualBox). But because KVM is a part of the kernel (kernel module), it is very lightweight and fast (compared to VirtualBox and VMWare as external things). While KVM works in kernel-space, we use QEMU as the machine emulator for user-space. This QEMU KVM combination gives the users lightweight virtualization and good performance (but with no GUI). We can make it perfect with Red Hat Virtual Machine Manager as the GUI for QEMU KVM virtualization. QEMU, KVM, and Virtual Machine Manager are all free software. We introduce here how to install them in Ubuntu.
System Summary
We are using a 32 bit laptop with Ubuntu 16.04 as the host operating system while writing this article.
Install KVM
Explanation: this command needs about 15 MB data to download in Ubuntu 16.04 32 bit. Package qemu-kvm contains the basic QEMU KVM programs, package libvirt-bin contains programs for the libvirt library (the library which takes advantage from Linux kernel’s virtualization feature), package ubuntu-vm-builder contains Ubuntu VM Builder scripts (to help creating ready to use virtual machine in Ubuntu), and package bridge-utils contains programs to connect your host network to the virtual machine.
Add User to Group libvirtd
For all Ubuntu version: you must do relogin after installing or adding your username to libvirtd group in your sistem. For Ubuntu 14.04 and later: you don’t need to add your username to libvirtd group because that configuration happens automatically while you are installing KVM. For Ubuntu prior to 14.04 until 9.10: add your username manually to libvirtd group by this command:
or suppose your username is myname so the exact command would be:
Remember to always do relogin after installing or adding user regarding to installation of KVM so this group configuration activated effectively.
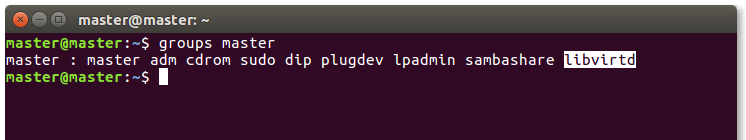
If you want to make sure your username is already a member of libvirtd group, try this command:
or suppose your username is myname so the exact command would be:
and you should see libvirtd listed as the result like this picture.
Install A GUI for KVM
Perform below command:
Explanation: this command needs about 12 MB data to download in Ubuntu 16.04 32 bit. Package virt-manager contains the program virt-manager, a desktop GUI tool for virtual machine from Red Hat. This program is the GUI for our QEMU KVM in this context. Think about installation of VirtualBox, but imagine VirtualBox installation splitted by installing the core component and then the GUI component. That is a close analogue for this QEMU KVM installation tutorial. Note: VirtualBox is a different product by different developer with different technology compared to QEMU KVM with virt-manager. The picture is shown below.
Common Problem
Without relogin, or without adding username into libvirtd group, you may see Virtual Machine Manager error like picture below. If you have followed the rest of article, you just need to relogin.
Источник