- 5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System
- Linux shutdown / reboot command
- 1. «shutdown» command
- 2. «reboot» command
- 3. «halt» command
- 4. «poweroff» command
- 5. REISUB — R E I S U B key strokes
- 10 thoughts on “ 5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System ”
- SSH restart Linux system using reboot command
- How to login using ssh
- SSH restart Linux system
- SSH reboot command example
- sudo: no tty present and no askpass program specified
- A note about rebooting a large number of Linux servers
- Conclusion
- Reboot Linux System Command
- Linux system restart
- Reboot Linux system command
- How do I reboot remote Linux server?
- A note about systemctl command when using systemd
- Conclusion
- ИТ База знаний
- Полезно
- Навигация
- Серверные решения
- Телефония
- Корпоративные сети
- Как перезапустить или перезагрузить Linux сервер из командной строки
- Шаги по перезагрузке Linux с помощью командной строки
- Перезапуск локальной операционной системы Linux
- Альтернативный вариант: перезагрузить Linux с помощью команды reboot
- Перезагрузить удаленный сервер Linux
- Шаг 1. Откройте командную строку
- Шаг 2: используйте команду перезагрузки проблемы подключения SSH ssh сообщает вашей системе, что нужно подключиться к другому компьютеру. Параметр –t заставляет удаленную систему вводить команду в терминале. Замените user@server.com именем пользователя и имя сервера, который вы хотите перезапустить.
5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System
Linux shutdown / reboot command
On Linux, like all tasks, the shutdown and restart operations can also be done from the command line.
The commands are shutdown, halt, poweroff, reboot and REISUB keystrokes.
In this post I am going to show you how to shutdown or restart a linux system using these commands.
The commands are useful specially when you have to reboot a remote linux server, where only shell access is available and no gui.
Servers often need a restart when upgrades are installed or need to shutdown for other maintainance tasks.
The commands are available on any linux system like centos, ubuntu, debian, fedora or suse and do not require the installation of any extra packages.
1. «shutdown» command
The first command is the shutdown command and it can be used to shutdown a system or restart it. It is commonly used to shutdown or reboot both local and remote machines.
To shutdown a machine call the shutdown command like this
The h option is for halt which means to stop. The second parameter is the time parameter. «now» means that shutdown the system right away.
The time parameter can be specified in minutes or hours also. For example
The above command shall flash the message to all other logged in users and give them 5 minutes before the system goes for shutdown.
The shutdown command can be used to restart a system with the r option instead of the h option. Usage is same as before. Just replace the h option with r option.
All other logged in users will see a broadcast message in their terminal like this
At this point a shutdown can be cancelled by calling shutdown with «c» option.
2. «reboot» command
Next command is the reboot command. It can be used to shutdown or reboot linux.
The following command will shutdown linux.
The «p» options stands for poweroff.
To reboot linux just call the reboot command directly without any options.
This will perform a graceful shutdown and restart of the machine. This is what happens when you click restart from your menu.
Reboot linux forcibly
The following command will forcefully reboot the machine. This is similar to pressing the power button of the CPU. No shutdown takes place. The system will reset instantly.
The man page explains it as follows
3. «halt» command
The next command is the halt command. This can shutdown a system
The halt command also has a force option, but you do not want to use it. It is supposed to shutdown the system instantly. But its behaviour may not be consistent. Desktops might hang on running this command.
4. «poweroff» command
There is another command exactly same as the halt command. It does the same things and takes the same options.
5. REISUB — R E I S U B key strokes
The above shown commands can be used when you are in control of your system. What if the system has hanged and is not responding at all. And you do not want to press the power button on the CPU which might lead to data corruption. To save from such a situation, comes the magic sysRQ keys.
A special combination of key presses that will allow you to reboot your linux system, no matter how much it is hanged. Check the wikipedia article. for more information.
Warning : Pressing the following keys would instantly reboot your system. Its similar to pressing the power button of your CPU or executing the reboot -f command.
Now in place of the B key we have to use R E I S U letters first. Each key does a task as mentioned below
1. Hold down the Alt and SysRq (Print Screen) keys.
2. While holding those down, type the following keys in order, several seconds apart: R E I S U B
3. Computer should reboot.
Make sure to have some time gap between each of keys R E I S U B.
The sysrq feature can be controlled by changing the value of /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq. To check if sysrq is enabled on the system or not, echo the value. It should be non zero.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
10 thoughts on “ 5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System ”
It worked on SUSE SLES 11
Now systemctl utility replaces a number of power management commands and even the shutdown command will call systemctl utility to perform the shutdown tasks.
The command reboot does work and immediately rebooted my Bluestar Linux system 4.20.7 (based on Arch Linux).
I am so glad that you could reboot your linux system!
If I’m not mistaken, reboot by itself actually does a shutdown: https://linux.die.net/man/8/reboot . You have to do reboot -f to actually get it to reboot.
Arrrgh so sick of finding the incorrect example of shutdown everywhere. The reboot syntax shown, on Ubuntu and probably in every flavor today, will Immediately reboot your server with no delay or warning. the +5 option is either wrong or in the wrong spot.
Important note – this only applies (AFAIKT) to x86 systems. On arm – no-worky.
what? 20 – 30 mins? O.o Shouldn’t it be 20 – 30 seconds?
I rebooted my linux machine using command reboot -f, it went down. How long does it takes normally to start again?
Its depends upon hardware and file system mounted on Linux box , If it is high end hardware and have been mounted more file system then it will 20-30 mins to come online
Источник
SSH restart Linux system using reboot command
How to login using ssh
The syntax is:
ssh user@server
ssh user@server-ip-address
ssh root@server1.cyberciti.biz
For security reasons root login is always disabled on Linux servers. In that case login as normal user and use the su command or sudo command to gain root shell:
ssh vivek@server1.cyberciti.biz
sudo -i
Verify with id command:
id
SSH restart Linux system
Now, you know how to log in as root user using ssh command:
ssh user@linux-box
We will now reboot the Linux server using ssh. The syntax is as follows (use any one of the following command):
# reboot
# shutdown -r now
# shutdown -r 0
One can use the sudo command as follows:
$ sudo shutdown -r now
All of the above commands would reboot the machine. See “SSH Public Key Based Authentication on a Linux/Unix server” for more information.
SSH reboot command example
There is a shortcut too. You can use ssh to log in and run commands. The syntax is as follows when you log in as non-root user:
ssh -t vivek@server1.cyberciti.biz «sudo reboot»
ssh -t vivek@server1.cyberciti.biz «sudo shutdown -r now»
Of course, if you log in to Linux server as root user, avoid typing sudo:
ssh -t root@server1.cyberciti.biz «reboot»
ssh -t root@server1.cyberciti.biz «shutdown -r now»
Restarting Linux computer using ssh command line option
sudo: no tty present and no askpass program specified
If you skip the -t option to the ssh command, you will see an error that read as follows on screen:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
sudo: no tty present and no askpass program specified
A note about rebooting a large number of Linux servers
You can use bash for loop as follows to reboot 5 servers named www1, www2, db1, db2, and cache1:
And, there is an Ansible tool to reboot Linux machine or server with playbooks too. Say you want to reboot 100 AWS vms or servers. A bash for loop is slow and not very useful. Hence, you use an IT automation tool such as Ansible.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to reboot the Linux machine using ssh. See shutdown(8) man page here for more info.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
Reboot Linux System Command
Linux system restart
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux |
| Est. reading time | 1m |
To reboot Linux using the command line:
- To reboot the Linux system from a terminal session, sign in or “su”/”sudo” to the “root” account.
- Then type “ sudo reboot ” to reboot the box.
- Wait for some time and the Linux server will reboot itself
Reboot Linux system command
You must login as root user to reboot the system. Open the terminal application (or login to remote box using ssh client) and type any one of the following command to reboot the system immediately:
# /sbin/reboot
OR
# /sbin/shutdown -r now
You can also use sudo command under Ubuntu/Debian/Fedora and other Linux based distros:
$ sudo reboot
It is a good idea to provide notification to all logged-in users that the system is going down and, within the last five minutes of TIME, new logins are prevented. Type the following command:
# shutdown -r +5
Sample output:
TIME may have different formats, the most common is simply the word “ now ” which will bring the system down immediately. Other valid formats are +m, where m is the number of minutes to wait until shutting down and hh:mm which specifies the time on the 24hr clock.
How do I reboot remote Linux server?
Simply login as the root user using ssh command:
$ ssh root@remote-server-com /sbin/reboot
OR
$ ssh root@remote-server-com /sbin/shutdown -r now
Sample outputs:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Get notification using the ping command when remote-server-com comes online:
ping -a remote-server-com
It is possible to use sudo command along with normal user over ssh session too. The syntax is:
$ ssh -t vivek@remote-server-com /sbin/reboot
Without the -t you will seen an error “sudo: no tty present and no askpass program specified“, hence you must pass the -t to the ssh command.
A note about systemctl command when using systemd
Are you using systemd as init on your Linux distro? Most modern Linux distro such as Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, Arch, and many uses systemd, and we can use the following command to reboot the system:
sudo systemctl reboot
Conclusion
This page demonstrated how to use reboot command on Linux to reboot the server or desktop for software and kernel updates.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
ИТ База знаний
Курс по Asterisk
Полезно
— Узнать IP — адрес компьютера в интернете
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Калькулятор инсталляции IP — АТС Asterisk
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Как перезапустить или перезагрузить Linux сервер из командной строки
3 минуты чтения
Это клише, но это правда — перезапуск сервера Linux решает множество проблем.
Мини — курс по виртуализации
Знакомство с VMware vSphere 7 и технологией виртуализации в авторском мини — курсе от Михаила Якобсена
Когда система перезагружается, все неисправное программное обеспечение удаляется из активной памяти. Когда система перезагружается, она загружает новую чистую копию программного обеспечения в активную память. Кроме того, некоторые операционные системы требуют перезагрузки для обработки обновлений или изменений конфигурации.

Шаги по перезагрузке Linux с помощью командной строки
Перезапуск локальной операционной системы Linux
Шаг 1: откройте окно терминала
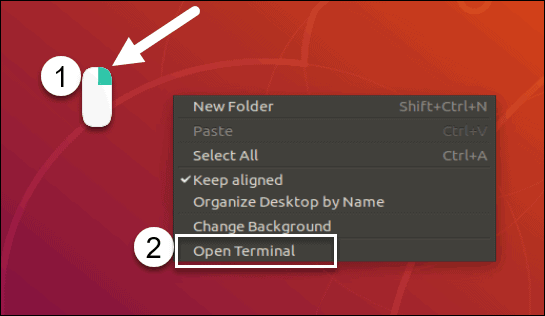
Если в вашей версии Linux используется графический интерфейс, вы можете открыть окно терминала, щелкнув правой кнопкой мыши на рабочем столе и выбрав пункт Open in terminal (Открыть в терминале).
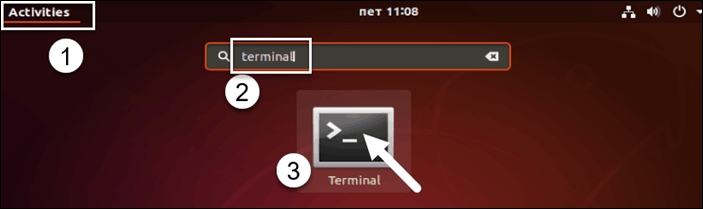
Вы также можете щелкнуть главное меню (обычно находится в нижнем левом или верхнем левом углу) и ввести terminal в строке поиска. Щелкните значок терминала, как показано на рисунке ниже.
Шаг 2. Используйте команду выключения
Поскольку отключение питания — одна из самых основных функций операционной системы, эта команда должна работать для большинства дистрибутивов Linux.
В окне терминала введите следующее:
Команда sudo указывает Linux запустить команду от имени администратора, поэтому вам может потребоваться ввести свой пароль. Ключ –r в конце указывает, что вы хотите перезапустить машину.
Альтернативный вариант: перезагрузить Linux с помощью команды reboot
В терминале введите:
Многие версии Linux не требуют прав администратора для перезагрузки. Если вы получили сообщение о том, что у вас недостаточно прав, введите:
Ваша система должна закрыть все открытые приложения и перезагрузиться.
Перезагрузить удаленный сервер Linux
Шаг 1. Откройте командную строку
Если у вас есть графический интерфейс, откройте терминал щелкнув правой кнопкой мыши на рабочем столе и выбрав пункт Open in terminal (Открыть в терминале), либо можете щелкнуть главное меню (обычно находится в нижнем левом или верхнем левом углу) и ввести terminal в строке поиска.
Если вы предпочитаете использовать сочетание клавиш, нажмите Ctrl + Alt + T ./p>
Шаг 2: используйте команду перезагрузки проблемы подключения SSH ssh сообщает вашей системе, что нужно подключиться к другому компьютеру. Параметр –t заставляет удаленную систему вводить команду в терминале. Замените user@server.com именем пользователя и имя сервера, который вы хотите перезапустить.
Онлайн курс по Linux
Мы собрали концентрат самых востребованных знаний, которые позволят тебе начать карьеру администратора Linux, расширить текущие знания и сделать уверенный шаг к DevOps
Источник