- Драйверы VirtIO для виртуальной машины Windows. KVM, CentOS
- Windows 2012 guest best practices
- Contents
- Introduction
- Install
- Prepare
- Launch Windows install
- Install Guest Agent and Services
- Guest Agent
- Drivers and Services
- Check for missing drivers
- Further Information
- RAW vs QCOW2
- VirtIO Drivers
- Windows VirtIO Drivers
- Contents
- Introduction
- Windows OS Support
- Installation
- Using the ISO
- Wizard Installation
- Manual Installation
- Downloading the Wizard in the VM
- Установка драйверов VirtIO в Microsoft Windows
Драйверы VirtIO для виртуальной машины Windows. KVM, CentOS
Что делать, если Windows не видит диск KVM VirtIO? Драйверы VirtIO для KVM дадут возможность создавать более быстрые виртуальные сетевые адаптеры, подключать диски типа virtio к VM. Можно и без них, но зачем делать хуже, если можно лучше? На примере виртуальной машины Windows 7, устанавливаемой на хост KVM (CentOS 7), посмотрим, как подключить такие драйверы при установке гостевой операционной системы.
Была создана виртуальная машина Windows 7:
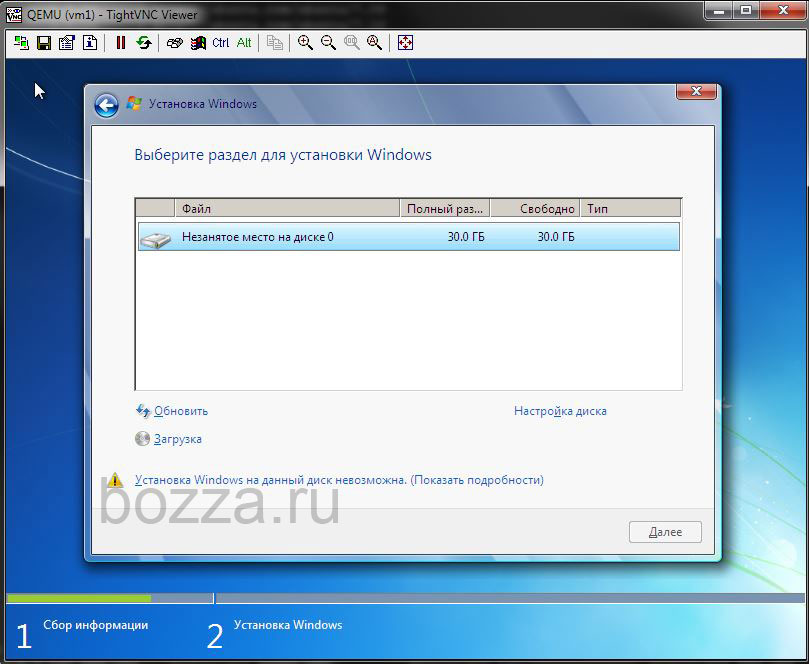
Подключаюсь к консоли TightVNC, начинаю установку — установщик не видит диск. 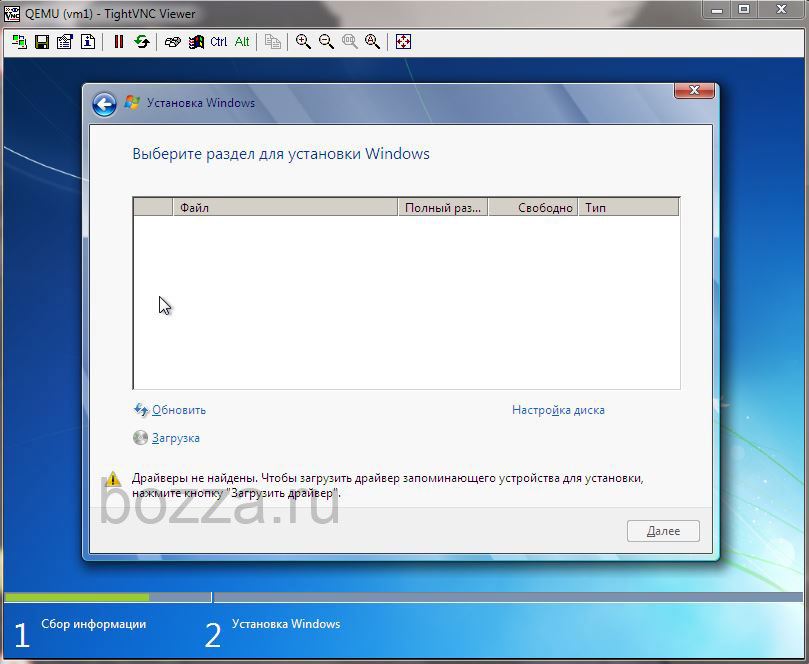
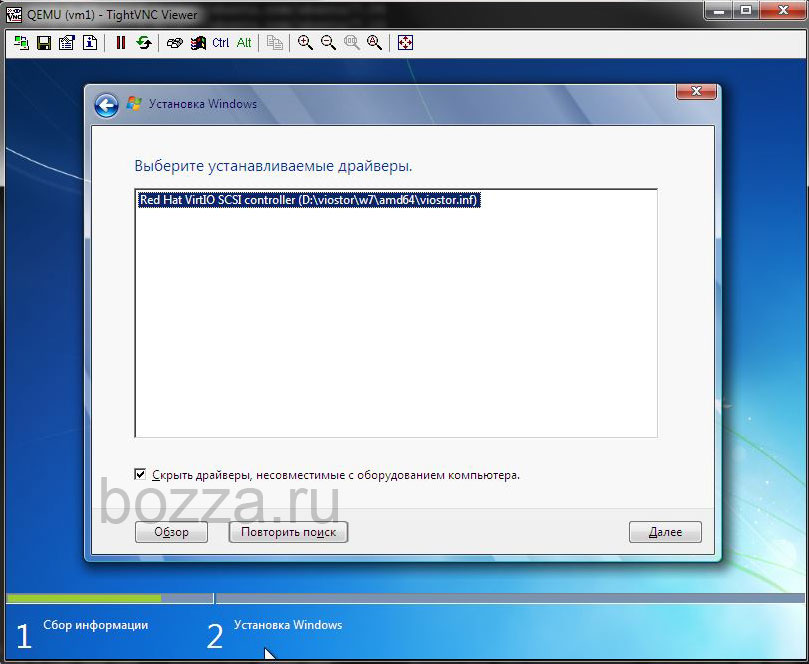
Тип диска был указан virtio. Нужно подсунуть этот драйвер установщику.
# wget https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/virtio-win.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/virtio-win.repo
# yum install virtio-win
Подключаю к VM диск с драйверами:
# virsh attach-disk vm1 /usr/share/virtio-win/virtio-win-0.1.141.iso hda —type cdrom —mode readonly
Disk attached successfully
Теперь выбираем драйвер:
Подключаем снова установочный диск:
# virsh attach-disk vm1 /data/vms-iso/Windows-7-64-prof-from-orig-dvd.iso hda —type cdrom —mode readonly
Disk attached successfully
и продолжаем установку Windows 7.
Аналогичным способом диск с драйверами подключается после установки, для устройств типа сетевых карт и др.
Windows 2012 guest best practices
Contents
Introduction
This is a set of best practices to follow when installing a Windows Server 2012(R2) guest on a Proxmox VE server 6.x.
Install
Prepare
To obtain a good level of performance, we will install the Windows VirtIO Drivers during the Windows installation.
- Create a new VM, select «Microsoft Windows 8.x/2012/2012r2» as Guest OS and enable the «Qemu Agent» in the System tab. Continue and mount your Windows Server 2012 ISO in the CDROM drive
- For your virtual hard disk select «SCSI» as bus with «VirtIO SCSI» as controller. Set «Write back» as cache option for best performance (the «No cache» default is safer, but slower) and tick «Discard» to optimally use disk space (TRIM).
- Configure your memory settings as needed, continue and set «VirtIO (paravirtualized)» as network device, finish your VM creation.
- For the VirtIO drivers, upload the driver ISO (use the stable VirtIO ISO, download it from here) to your storage, create a new CDROM drive (use «Add -> CD/DVD drive» in the hardware tab) with Bus «IDE» and number 3. Load the Virtio Drivers ISO in the new virtual CDROM drive.
- Now your ready to start the VM, just follow the Windows installer.
Launch Windows install
- After starting your VM launch the noVNC console
- Follow the installer steps until you reach the installation type selection where you need to select «Custom (advanced)»
- Now click «Load driver» to install the VirtIO drivers for hard disk and the network.
- Hard disk: Browse to the CD drive where you mounted the VirtIO driver and select folder «vioscsi\2k12\amd64» and confirm. Select the «Red Hat VirtIO SCSI pass-through controller» and click next to install it. Now you should see your drive.
- Network: Repeat the steps from above (click again «Load driver», etc.) and select the folder «NetKVM\2k12\amd64», confirm it and select «Redhat VirtIO Ethernet Adapter» and click next.
- Memory Ballooning: Again, repeat the steps but this time select the «Balloon\2k12\amd64» folder, then the «VirtIO Balloon Driver» and install it by clicking next. With these three drivers you should be good covered to run a fast virtualized Windows 10 system.
- Choose the drive and continue the Windows installer steps.
HINT: There is a video showing the process for a Windows Server 2016 installation which is the same as for Windows Server 2012.
Install Guest Agent and Services
Guest Agent
If you enabled the Qemu Agent option for the VM the mouse pointer will probably be off after the first boot.
To remedy this install the «Qemu Guest Agent». The installer is located on the driver CD under guest-agent\qemu-ga-x86_64.msi.
Drivers and Services
The easiest way to install missing drivers and services is to use the provided MSI installer. It is available on the driver CD since version «virtio-win-0.1.173-2».
Run the «virtio-win-gt-x64.msi» file located directly on the CD. If you do not plan to use SPICE you can deselect the «Qxl» and «Spice» features. Restart the VM after the installer is done.
After all this the RAM usage and IP configuration should be shown correctly in the summary page of the VM.
For more information and configuration about ballooning, see Dynamic Memory Management
Check for missing drivers
Go to the Device Manager to see if there are any drivers missing. For any unknown device:
- Right click an select «Update driver».
- Select «Browse my computer for driver software».
- Select the Driver CD. Make sure that «Include subfolders» is checked.
- Once a driver has been found you might be prompted with a security warning asking if you «Would like to install this device software». Click «Install».
Further Information
RAW vs QCOW2
The RAW file format provides slightly better performance WHILE qcow2 offers advanced features such as copy on write and Live_Snapshots independent of the backing storage. Since Proxmox VE version 2.3, qcow2 is the default format.
VirtIO Drivers
Make it really easy:Build your ISO with drivers already included: Windows guests — build ISOs including VirtIO drivers
Windows VirtIO Drivers
Contents
Introduction
VirtIO Drivers are paravirtualized drivers for kvm/Linux (see http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Virtio). In short, they enable direct (paravirtualized) access to devices and peripherals for virtual machines using them, instead of slower, emulated, ones.
A quite extended explanation about VirtIO drivers can be found here http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/l-virtio.
At the moment these kind of devices are supported:
You can maximize performances by using VirtIO drivers. The availability and status of the VirtIO drivers depends on the guest OS and platform.
Windows OS Support
Windows does not have native support for VirtIO devices included. But, there is excellent external support through opensource drivers, which are available compiled and signed for Windows:
Note that this repository provides not only the most recent, but also many older versions. Those older versions can still be useful when a Windows VM shows instability or incompatibility with a newer driver version.
The binary drivers are digitally signed by Red Hat, and will work on 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows
Installation
Using the ISO
You can download the latest stable or you can download the most recent build of the ISO. Normally the drivers are pretty stable, so one should try out the most recent release first.
You can access the ISO can in a VM by mounting the ISO with a virtual CD-ROM/DVD drive on that VM.
Wizard Installation
You can use an easy wizard to install all, or a selection, of VirtIO drivers.
- Open the Windows Explorer and navigate to the CD-ROM drive.
- Simply execute (double-click on) virtio-win-gt-x64
- Follow its instructions.
- (Optional) use the virtio-win-guest-tools wizard to install the QEMU Guest Agent and the SPICE agent for an improved remote-viewer experience.
- Reboot VM
Manual Installation
- Open the Windows Explorer and navigate to the CD-ROM drive. There you can see that the ISO consists of several directories, each having sub-directories for supported OS version (for example, 2k19, 2k12R2, w7, w8.1, w10, . ).
- Balloon
- guest-agent
- NetKVM
- qxl
- vioscsi
- .
Downloading the Wizard in the VM
You can also just download the most recent virtio-win-gt-x64.msi or virtio-win-gt-x86.msi from inside the VM, if you have already network access.
Then just execute it and follow the installation process.
Установка драйверов VirtIO в Microsoft Windows
В данной статье мы проиллюстрируем пошаговую установку драйверов VirtIO на примере операционной системы Microsoft Windows Server.
Для начала авторизуйтесь в панели управления Cloud2 для присоединения ISO-образа диска с драйверами VirtIO к существующей виртуальной машине:
1. Авторизуемся в панели управления по адресу: https://ru.cloud-2.io/ui/premium/
2. Выбираем нужную виртуальную машину кликая по её названию (1). В открывшейся панели управления переходим во вкладку устройств (2) и нажимаем стилизованную под плюс кнопку подключения ISO-образа (3):
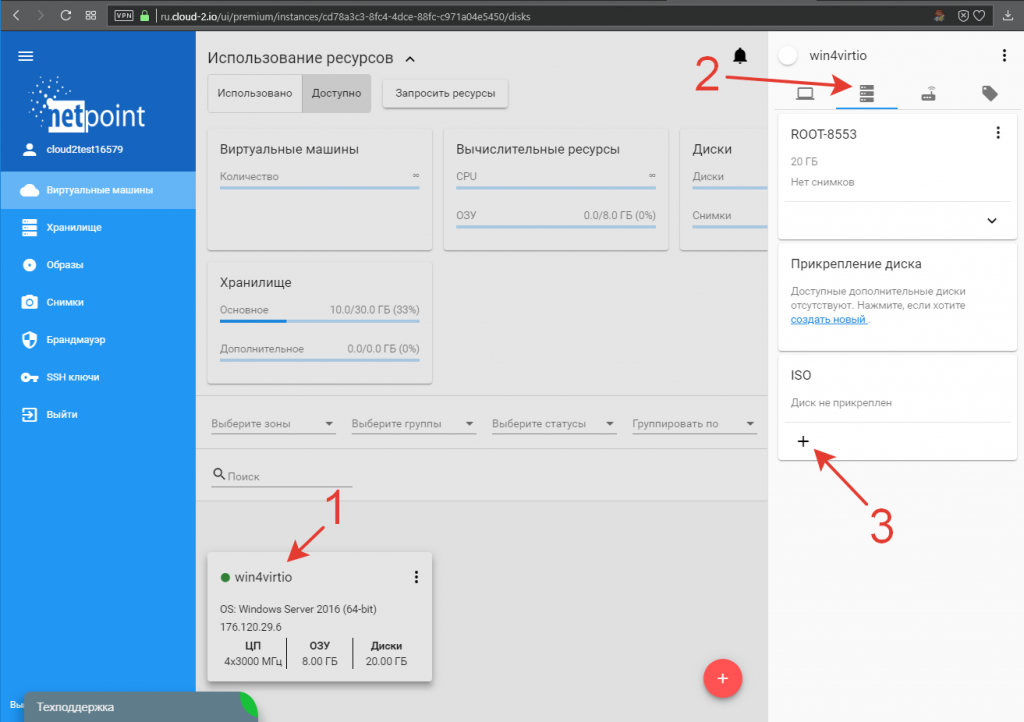
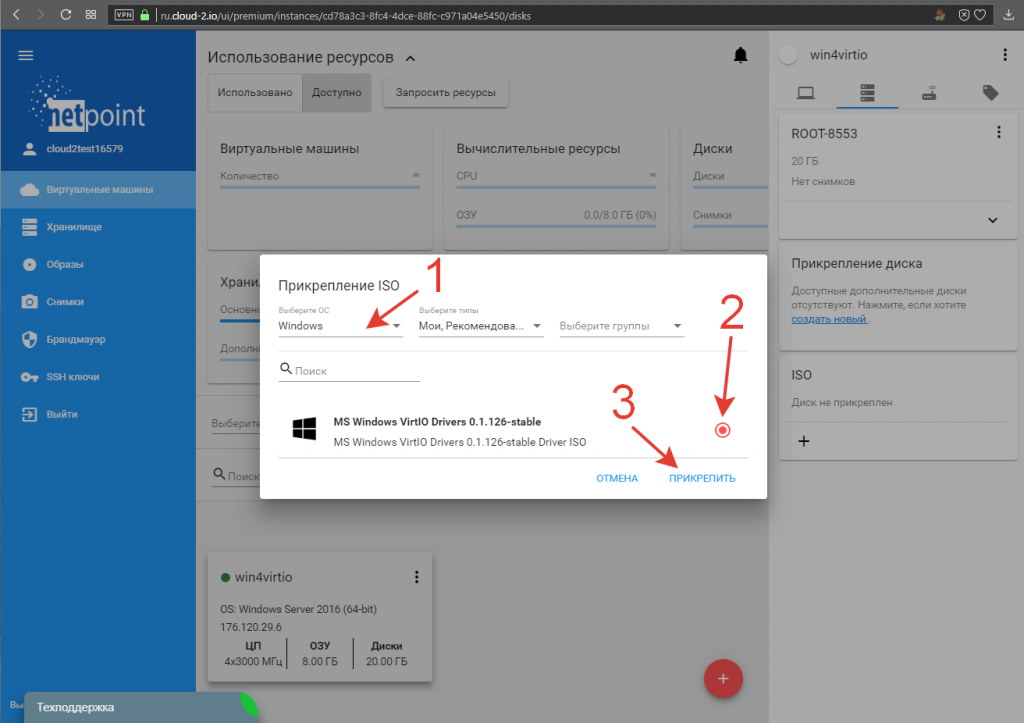
3. В открывшемся окне прикрепления ISO-образа указываем тип операционной системы Windows (1), отмечаем образ диска с драйверами VirtIO (2) и подключаем его к нашей машине (3):
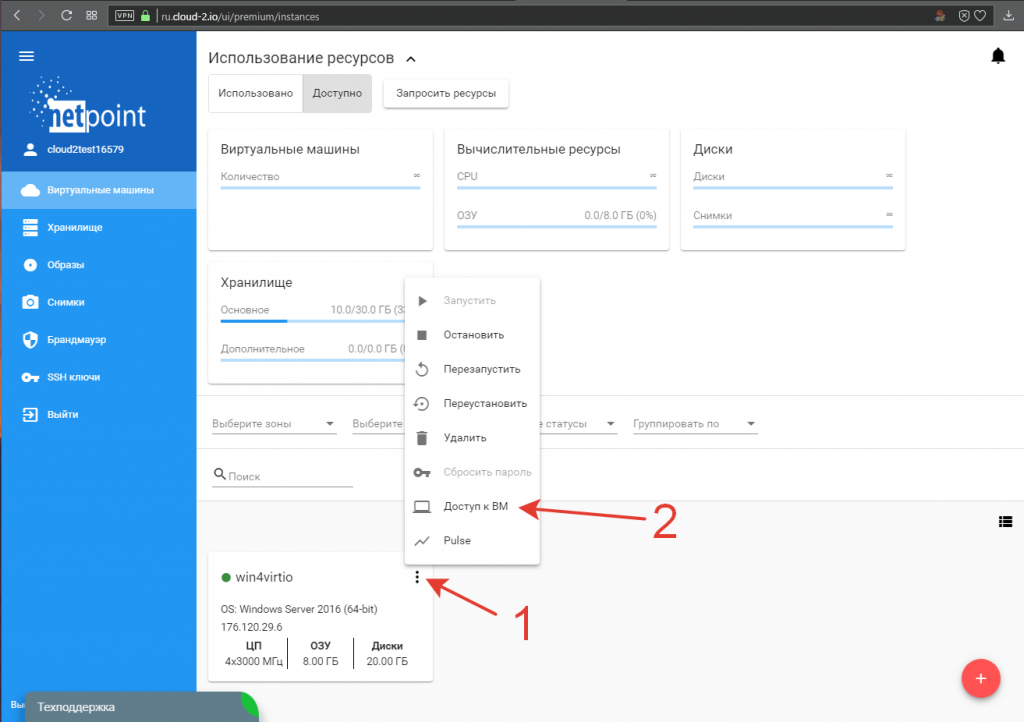
4. Переходим в операционную систему. Для этого подключаемся к машине по RDP или используем встроенную консоль панели управления. Для этого кликаем по стилизованной под три точки кнопке меню виртуальной машины (1) и выбираем пункт «Доступ к ВМ» (2):
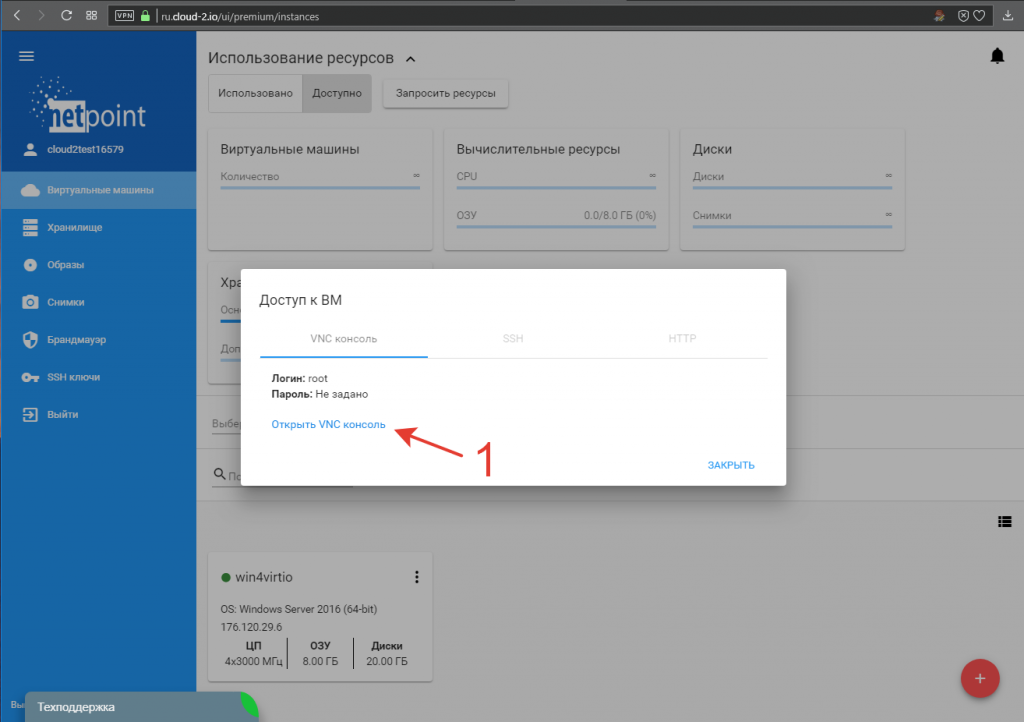
В открывшемся окне нажимаем ссылку «Открыть VNC консоль» (1):
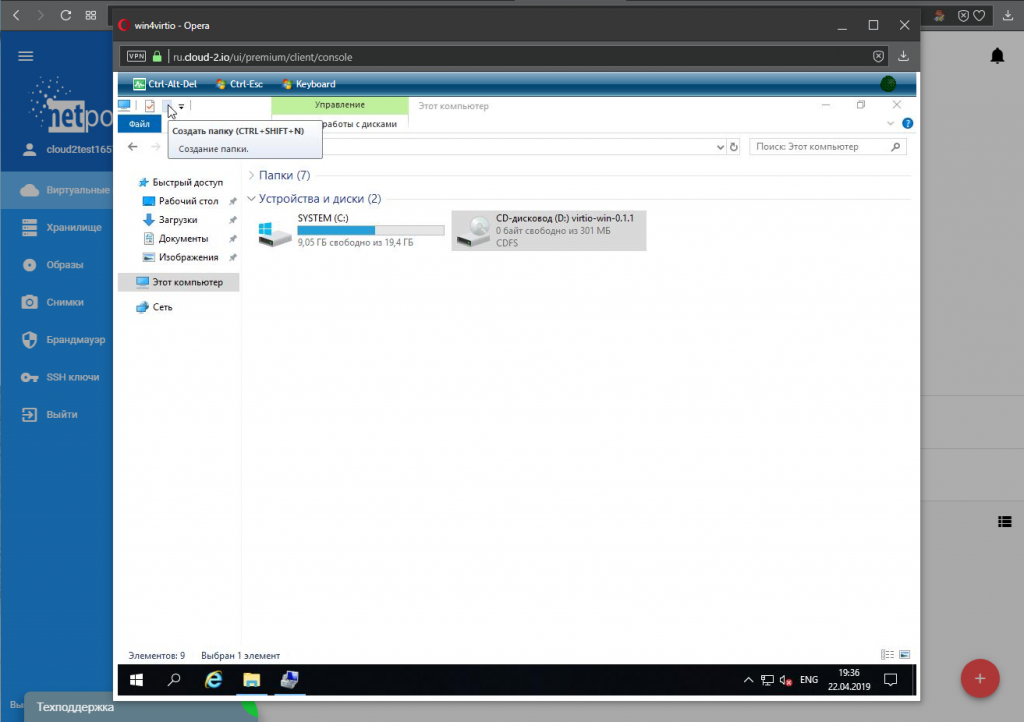
5. В операционной системе с помощью проводника Windows проверяем наличие присоединённого нужного образа с драйверами:
В контекстном меню (правая кнопка мыши) кнопки «Пуск» выбираем пункт «Управление компьютером»:
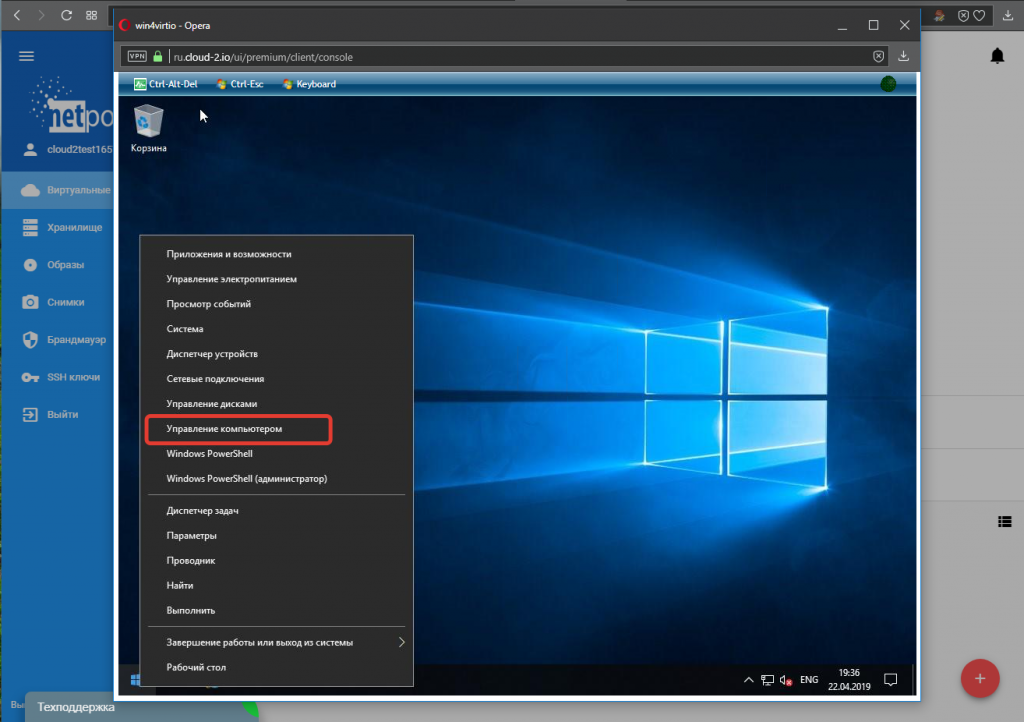
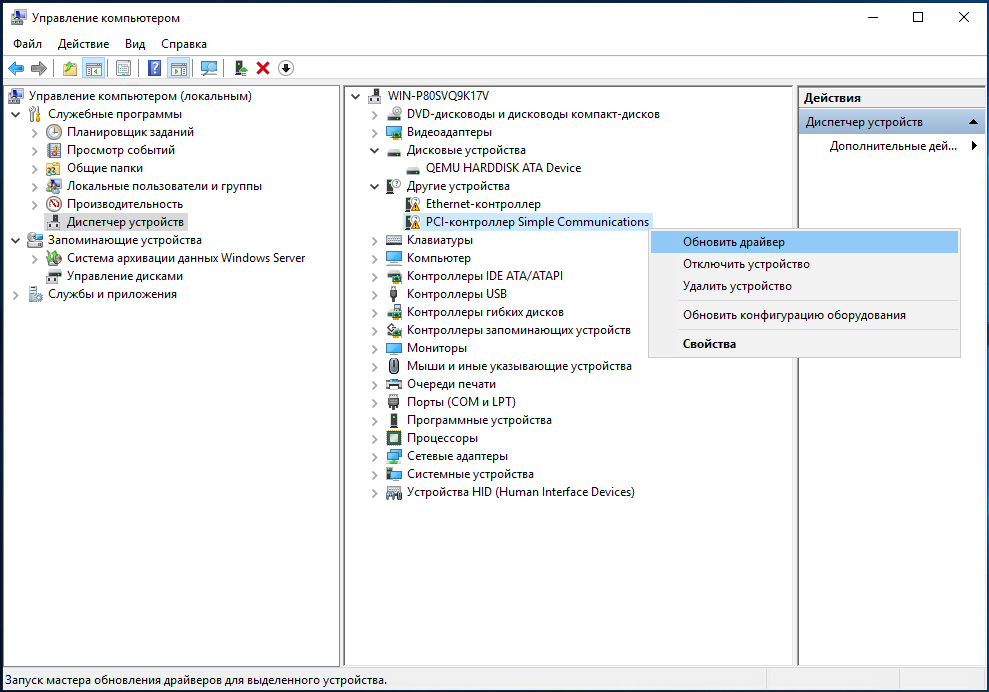
6. В открывшейся панели переходим в Диспетчер устройств (1), где наблюдаем ряд неизвестных нашей системе девайсов (2), которые нам предстоит инициализировать:
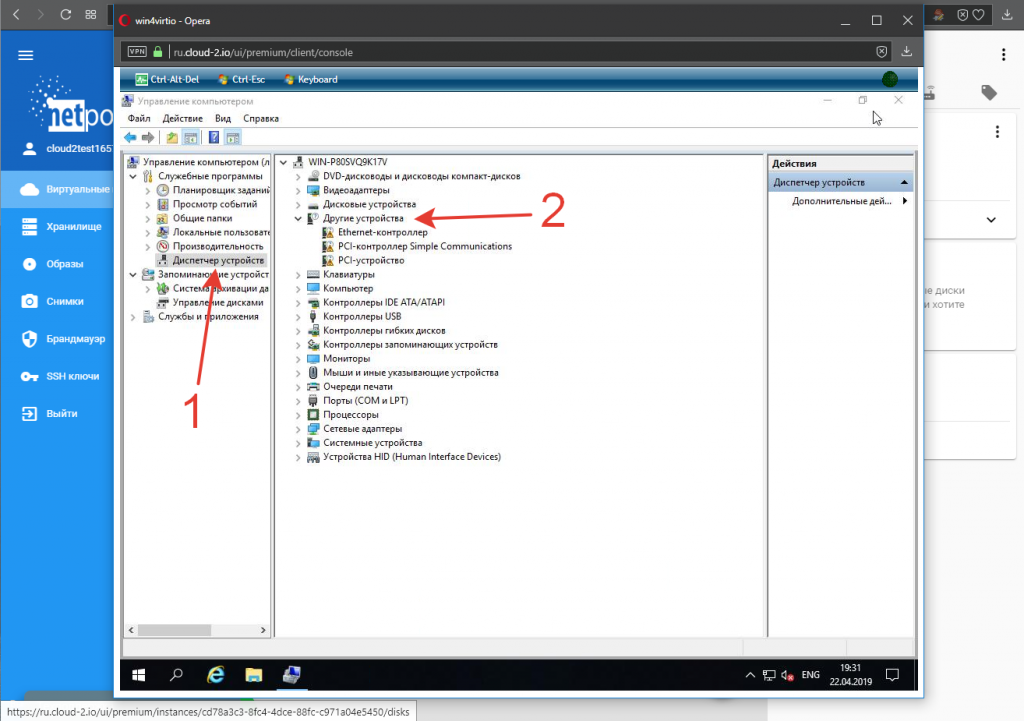
7. Поочерёдно устанавливаем драйвера на каждое устройство с подключенного диска. Устанавливаем драйвер устройства Virtio RNG Device:
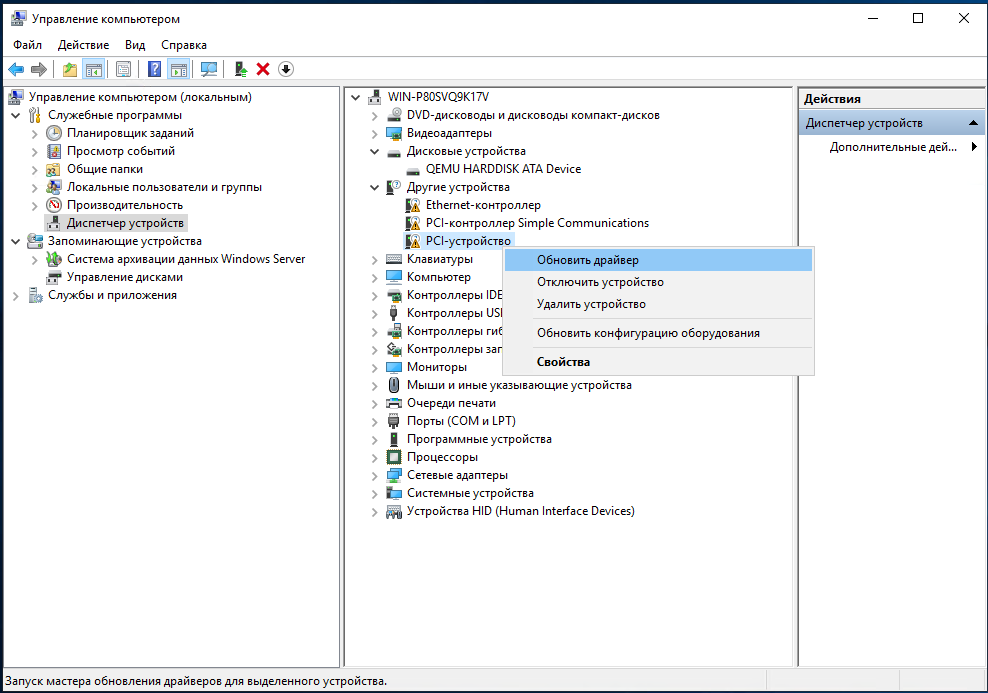
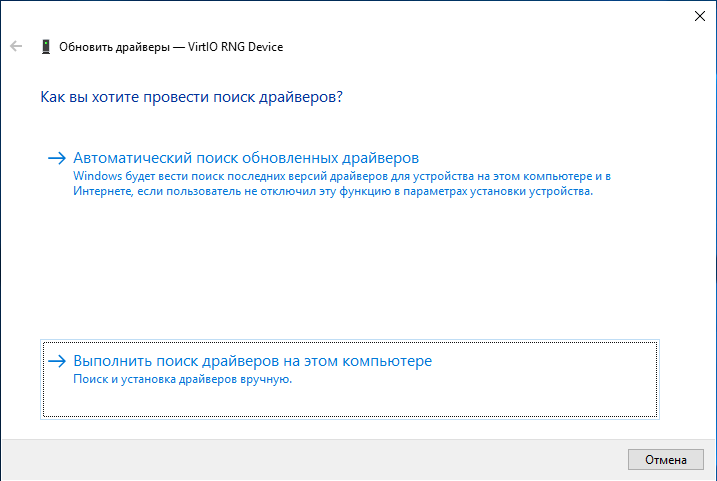
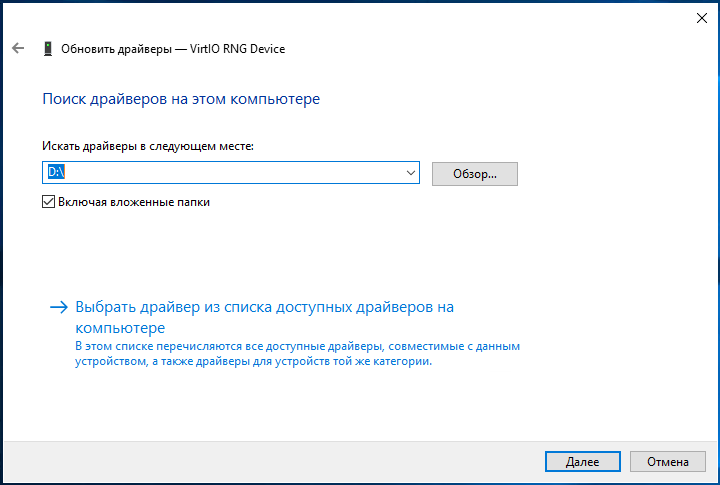
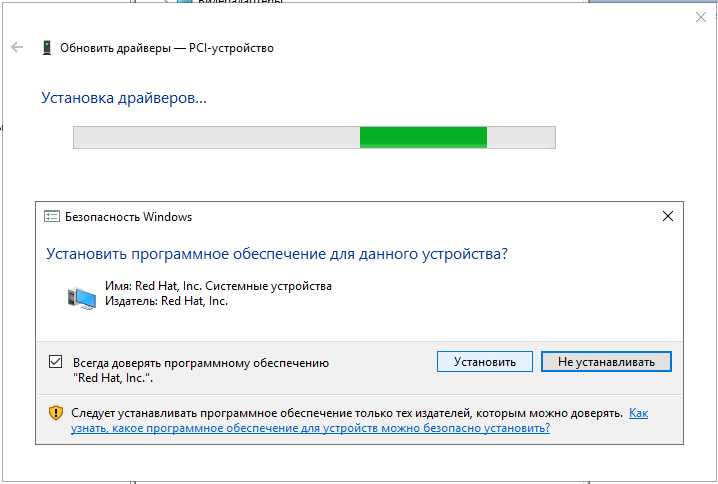
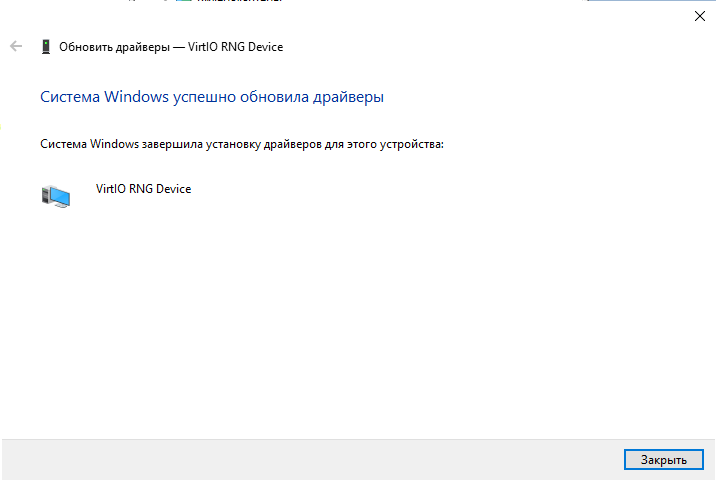
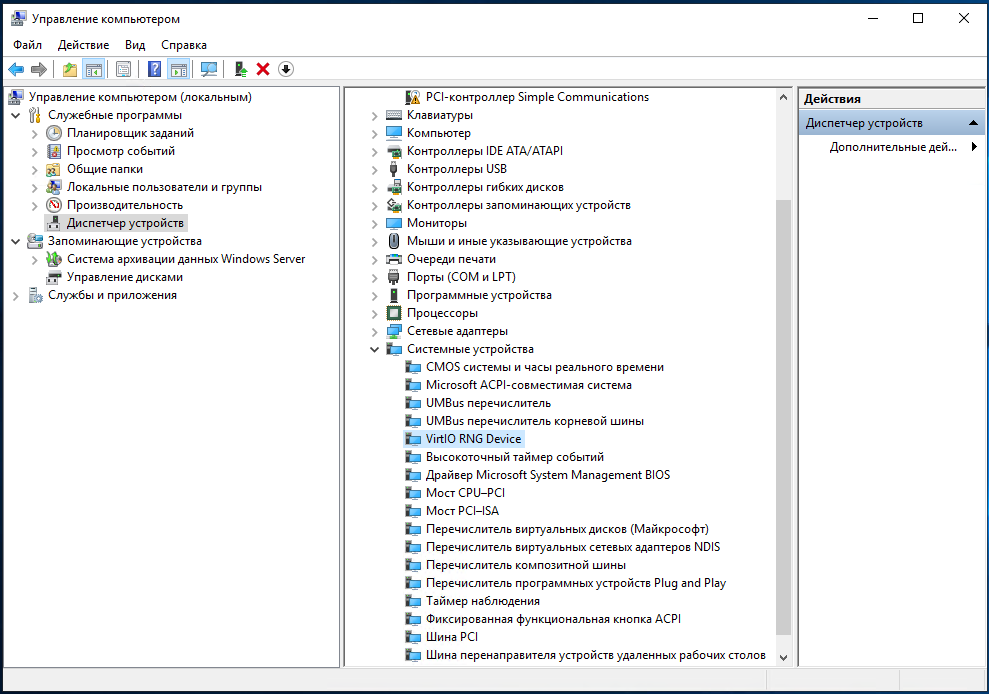
Аналогично устанавливаем последующие драйвера устройств VirtIO Serial Driver и Red Hat VirtIO Ethernet Adapter:
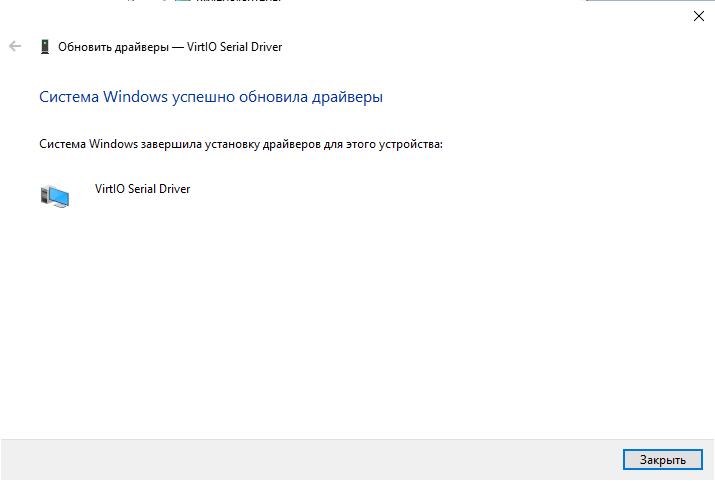
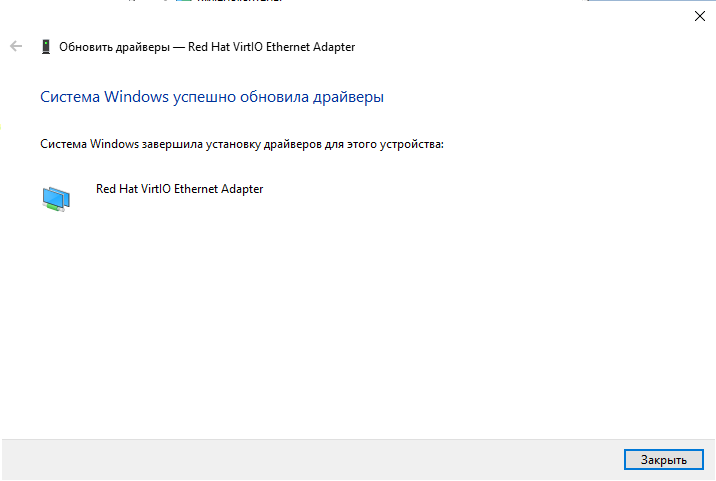
В результате проделанных манипуляций мы получаем полностью установленные VirtIO устройства в нашей системе. Не забудьте отключить ISO в самой системе или в панели управления виртуальной машиной по окончании работ.