- Как удалить Linux и установить Windows
- Аннотация
- Дополнительная информация
- Примеры таблиц разделов Linux
- Один SCSI-диск
- Несколько SCSI-дисков
- Один IDE-диск
- Несколько IDE-дисков
- How to Remove Linux and Install Windows on Your Computer
- Summary
- More Information
- Examples of Linux Partition Tables
- Single SCSI drive
- Multiple SCSI drives
- Single IDE drive
- Multiple IDE drives
- Remove linux from windows
Как удалить Linux и установить Windows
Версия этой статьи для Microsoft Windows XP: 314458.
Аннотация
В этой статье содержатся инструкции по удалению операционной системы Linux с последующей установкой Windows. При написании статьи предполагалось, что операционная система Linux уже установлена на жесткий диск компьютера, используются разделы native и swap (несовместимые с Windows) и на жестком диске нет свободного места.
Windows и Linux могут совместно использоваться на одном компьютере. Дополнительные сведения об этом см. в документации к операционной системе Linux.
Дополнительная информация
Для установки Windows на компьютер под управлением Linux (с удалением Linux) разделы, которые использует эта операционная система, необходимо удалить вручную. Windows-совместимый раздел будет создан автоматически при установке Windows.
ВНИМАНИЕ! Поскольку выполнение описанных в данной статье действий приведет к полному удалению операционной системы Linux, предварительно убедитесь в наличии загрузочного носителя или компакт-диска Linux. Если впоследствии необходимо будет восстановить операционную систему Linux, создайте резервную копию всех данных, хранящихся на компьютере. Кроме того, необходимо наличие полной версии операционной системы Windows.
В файловых системах Linux в начале каждого дискового раздела находится суперблок для определения размера, формы и состояния файловой системы.
Операционная система Linux обычно устанавливается в раздел типа 83 (Linux native) или 82 (Linux swap). Диспетчер загрузки Linux (LILO) можно настроить на выполнение загрузки из следующих мест:
основная загрузочная запись (Master Boot Record, MBR) жесткого диска;
корневая папка раздела Linux.
Разделы можно удалить с помощью служебной программы Fdisk, которая входит в состав Linux. (Существуют аналогичные служебные программы, например Fdisk в MS-DOS версии 5.0 или выше. Кроме того, разделы можно удалить и при установке.) Чтобы удалить Linux и установить Windows, сделайте следующее.
Удалите используемые Linux разделы native, swap и загрузочный раздел.
Загрузите компьютер с установочной дискеты Linux, введите в командной строке fdisk и нажмите клавишу ВВОД.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ. Чтобы получить справку по использованию программы Fdisk, введите в командной строке m и нажмите клавишу ВВОД.
Чтобы получить информацию о разделах, введите в командной строке p и нажмите клавишу ВВОД. Вначале содержатся сведения о первом разделе первого жесткого диска, а затем — о втором разделе первого жесткого диска.
Введите в командной строке d и нажмите клавишу ВВОД. Появится окно, в котором необходимо указать номер удаляемого раздела. Введите 1 и нажмите клавишу ВВОД, чтобы удалить раздел под номером 1. Повторяйте это действие, пока не удалите все разделы.
Чтобы записать эти данные в таблицу разделов, введите w и нажмите клавишу ВВОД. При записи данных в таблицу разделов могут появиться сообщения об ошибках. В данном случае они не имеют большого значения, поскольку следующим шагом является перезагрузка компьютера и установка новой операционной системы.
Чтобы завершить работу программы Fdisk, введите в командной строке q и нажмите клавишу ВВОД.
Вставьте загрузочную дискету или компакт-диск Windows и для перезагрузки компьютера нажмите сочетание клавиш CTRL+ALT+DELETE.
Установите Windows. Следуйте инструкциям по установке Windows. В процессе установки можно создать на компьютере необходимые разделы.
Примеры таблиц разделов Linux
Один SCSI-диск
Несколько SCSI-дисков
Один IDE-диск
Несколько IDE-дисков
Кроме того, Linux распознает более 40 типов разделов, в том числе следующие:
FAT 16 > 32 M Primary (тип 06)
FAT 16 Extended (тип 05)
FAT 32 без LBA Primary (тип 0b)
FAT 32 с LBA Primary (тип 0c)
FAT 16 с LBA (тип 0e)
FAT 16 с LBA Extended (тип 0f)
Следует помнить, что существуют другие способы удаления операционной системы Linux с последующей установкой Windows XP. В этой статье описан способ, который применяется в том случае, когда операционная система Linux уже функционирует и на жестком диске не осталось свободного места. Существует специальное программное обеспечение для изменения размеров раздела. Корпорация Майкрософт не поддерживает установку Windows в разделы, управляемые подобным образом.
Чтобы удалить одну операционную систему и установить другую, можно, кроме прочего, воспользоваться загрузочным диском MS-DOS версии 5.0 или более поздней, Windows 95 или Windows 98, которые содержат служебную программу Fdisk. Запустите программу Fdisk. Если на компьютере установлено несколько жестких дисков, выберите пятый пункт меню для определения диска, содержащего удаляемый раздел. После этого (или в том случае, если на компьютере имеется только один жесткий диск) выберите пункт 3 (Delete partition or logical DOS drive), а затем — пункт 4 (Delete non-DOS partition). Будет отображен список разделов, отличных от DOS, которые необходимо удалить. Обычно в операционной системе Linux есть два раздела, не являющимися разделами DOS, но их может быть и больше. Поочередно удалите все разделы, которые не являются разделами DOS.
После удаления разделов можно приступать к созданию новых и установке выбранной операционной системы. При помощи служебной программы Fdisk, входящей в состав MS-DOS версии 5.0 и более поздней, Windows 95 или Windows 98, можно создать только один основной и один расширенный разделы из нескольких логических дисков. Максимальный размер основного раздела FAT16 составляет 2 ГБ. Максимальный размер логического диска FAT16 — 2 ГБ. Для получения дополнительных сведений щелкните указанный ниже номер статьи базы знаний Майкрософт:
105074 Вопросы и ответы относительно создания разделов в MS-DOS 6.2
При установке Windows NT 4.0 или Windows 2000 разделы Linux можно удалить, создать новые разделы и отформатировать их, выбрав нужную файловую систему в процессе установки. Windows позволяет создать несколько основных разделов. Максимальный размер раздела, который создается в процессе установки Windows NT 4.0, составляет 4 ГБ. Это ограничение обусловлено особенностями файловой системы FAT16. Для раздела размером 4 ГБ используется кластер 64 КБ. MS-DOS 6.x, Windows 95 и Windows 98 не поддерживают файловые системы с размером кластера 64 КБ, поэтому в процессе установки такие файловые системы обычно преобразуются в NTFS. В отличие от Windows NT 4.0, операционная система Windows 2000 поддерживает файловую систему FAT32. При установке Windows 2000 можно создать диск FAT32 очень большого размера. После завершения установки, в случае необходимости, диск FAT32 можно преобразовать в NTFS.
How to Remove Linux and Install Windows on Your Computer
For a Microsoft Windows XP version of this article, see 314458.
Summary
This article describes how you can remove the Linux operating system from your computer, and install a Windows operating system. This article also assumes that Linux is already installed on the hard disk using Linux native and Linux swap partitions, which are incompatible with the Windows operating system, and that there is no free space left on the drive.
Windows and Linux can coexist on the same computer. For additional information, refer to your Linux documentation.
More Information
To install Windows on a system that has Linux installed when you want to remove Linux, you must manually delete the partitions used by the Linux operating system. The Windows-compatible partition can be created automatically during the installation of the Windows operating system.
IMPORTANT: Before you follow the steps in this article, verify that you have a bootable disk or bootable CD-ROM for the Linux operating system, because this process completely removes the Linux operating system installed on your computer. If you intend to restore the Linux operating system at a later date, verify that you also have a good backup of all the information stored on your computer. Also, you must have a full release version of the Windows operating system you want to install.
Linux file systems use a «superblock» at the beginning of a disk partition to identify the basic size, shape, and condition of the file system.
The Linux operating system is generally installed on partition type 83 (Linux native) or 82 (Linux swap). The Linux boot manager (LILO) can be configured to start from:
The hard disk Master Boot Record (MBR).
The root folder of the Linux partition.
The Fdisk tool included with Linux can be used to delete the partitions. (There are other utilities that work just as well, such as Fdisk from MS-DOS 5.0 and later, or you can delete the partitions during the installation process.) To remove Linux from your computer and install Windows:
Remove native, swap, and boot partitions used by Linux:
Start your computer with the Linux setup floppy disk, type fdisk at the command prompt, and then press ENTER.
NOTE: For help using the Fdisk tool, type m at the command prompt, and then press ENTER.
Type p at the command prompt, and then press ENTER to display partition information. The first item listed is hard disk 1, partition 1 information, and the second item listed is hard disk 1, partition 2 information.
Type d at the command prompt, and then press ENTER. You are then prompted for the partition number you want to delete. Type 1, and then press ENTER to delete partition number 1. Repeat this step until all the partitions have been deleted.
Type w, and then press ENTER to write this information to the partition table. Some error messages may be generated as information is written to the partition table, but they should not be significant at this point because the next step is to restart the computer and then install the new operating system.
Type q at the command prompt, and then press ENTER to quit the Fdisk tool.
Insert either a bootable floppy disk or a bootable CD-ROM for the Windows operating system on your computer, and then press CTRL+ALT+DELETE to restart your computer.
Install Windows. Follow the installation instructions for the Windows operating system you want to install on your computer. The installation process assists you with creating the appropriate partitions on your computer.
Examples of Linux Partition Tables
Single SCSI drive
Multiple SCSI drives
Single IDE drive
Multiple IDE drives
Also, Linux recognizes more than forty different partition types, such as:
FAT 16 > 32 M Primary (Type 06)
FAT 16 Extended (Type 05)
FAT 32 w/o LBA Primary (Type 0b)
FAT 32 w/LBA Primary (Type 0c)
FAT 16 w/LBA (Type 0e)
FAT 16 w/LBA Extended (Type 0f)
Note that there are other ways to remove the Linux operating system and install Windows than the one mentioned above. The preceding method is used in this article because the Linux operating system is already functioning and there is no more room on the hard disk. There are methods of changing partition sizes with software. Microsoft does not support Windows installed on partitions manipulated in this manner.
Another method of removing an operating system from the hard disk and installing a different operating system is to use an MS-DOS version 5.0 or later boot disk, a Windows 95 Startup disk, or a Windows 98 Startup disk that contains the Fdisk utility. Run the Fdisk utility. If you have multiple drives, there are 5 choices; use option 5 to select the hard disk that has the partition to be deleted. After that, or if you have only one hard disk, choose option 3 («Delete partition or logical DOS drive»), and then choose option 4 («Delete non-DOS partition»). You should then see the non-DOS partitions you want to delete. Typically, the Linux operating system has two non-DOS partitions, but there may be more. After you delete one partition, use the same steps to delete any other appropriate non-DOS partitions.
After the partitions are deleted, you can create partitions and install the operating system you want. You can only create one primary partition and an extended partition with multiple logical drives by using Fdisk from MS-DOS version 5.0 and later, Windows 95, and Windows 98. The maximum FAT16 primary partition size is 2 gigabytes (GB). The largest FAT16 logical drive size is 2 GB. For additional information, click the article number below to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
105074 MS-DOS 6.2 Partitioning Questions and Answers
If you are installing Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000, the Linux partitions can be removed and new partitions created and formatted with the appropriate file system type during the installation process. Windows allows you to create more than one primary partition. The largest partition that Windows NT 4.0 allows you to create during installation is 4 GB because of the limitations of the FAT16 file system during installation. Also, the 4-GB partitions use 64-KB cluster sizes. MS-DOS 6.x and Windows 95 or Windows 98 do not recognize 64-KB cluster file systems, so this file system is usually converted to NTFS during installation. Windows 2000, unlike Windows NT 4.0, recognizes the FAT32 file system. During the installation of Windows 2000, you can create a very large FAT32 drive. The FAT32 drive can be converted to NTFS after the installation has completed if appropriate.
Remove linux from windows
We would learn here how to completely uninstall any Linux OS from PC through Windows.
This is a procedure that envolves to steps->
(i) Delete Linux Partition
(ii) Remove Linux OS from EFI System Partition
You must be thinking what is EFI System Partition?
The EFI system partition (ESP) is a partition on a storage device that is used by computers adhering to the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). When a computer is booted, UEFI firmware loads files stored on the ESP to start installed operating systems either windows or Linux(ubuntu/fedora/mint).
Let’s get started with the uninstallation procedure->
(i) Log on to Windows OS in Admin mode.
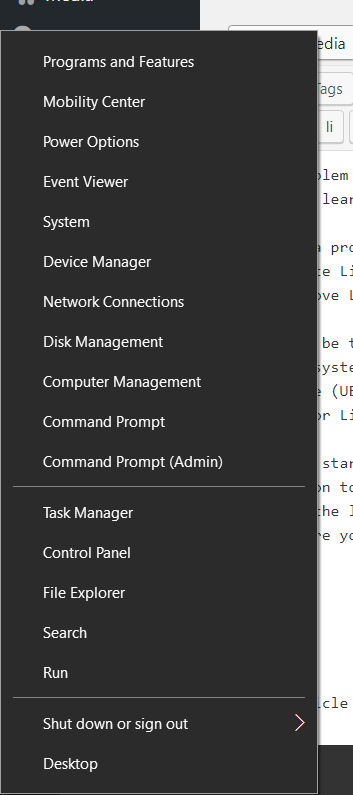
(ii) On the left-corner windows icon right click.
(iii) Here you will see options like
(iv) Open Disk Management
(v) Delete the Partition which does not have a letter (like (C:)) or is not a NTFS partition and is greater than 1GB.
(vi) Now you have successfully completed the first Step.
(vii) Ubuntu/Fedora(Linux OS) is deleted but on restarting your pc you will still see the grub option so we need to uninstall Linux OS from EFI System Partition too.
(viii) Now open the Command Prompt (Admin) ( shown in the options image above ).
(ix) Follow these commands->
Note the line after ‘#’ is just to explain the command
>NOTE:- Restart your PC and the drive X: mounted EFI partition disappears again.
CONGRATULATIONS
Linux OS is now completely uninstalled.
This article is contributed by SHAURYA UPPAL.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important DSA concepts with the DSA Self Paced Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready.