- 3 Genius Ways to Delete a File in Use in Windows
- Force Deleting a File in Use in Windows
- More Related Articles:
- From Command Prompt
- Using a Third-Party Tool – Unlocker
- How to Restore a File If It Has Been Deleted Accidentally
- Your Safe & Reliable Data Recovery Software
- Video Tutorial on How to Recover Deleted Files on Windows 10/8/7 Easily?
- How to Delete Temporary Files in Windows
- Safely delete temp files in Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista and XP
- How to Delete Temporary Files in Windows
- Other Types of Temporary Files in Windows
- Check Your Browser Cache
- Handy Tools for Easy Removal
- “File in use” error on Windows 10 [Fix]
- How do I fix the file in use error?
- 1. File in use error
- Revo Uninstaller Pro
- Bitraser File Eraser
- 2. How do I fix the File in use error in Excel?
3 Genius Ways to Delete a File in Use in Windows
Amy Dennis
Dec 21, 2020 • Filed to: Recover & Repair Files • Proven solutions
When working on Microsoft Windows, how many times have you seen a message telling that the particular file you are attempting to delete is already in use and that the program using the file must be stopped before Windows allows you to remove the file from the PC?
Annoying!! Isn’t it?
Well, not anymore.
Here are the three genius ways that you can use to force delete a file that is in use and Windows doesn’t allow you to remove it normally.
Force Deleting a File in Use in Windows
This method works most of the time. All you need to do is to force terminate the program that is using the file. Assuming that you already know which program is using the file that you want to remove, this is how you delete the file:
Note:В Windows 7 is used here as a reference PC.
Force terminating a process shuts down the entire program and you may lose any unsaved data that any other file that relies on the program may have. It is advisable to save all your work progress before proceeding.
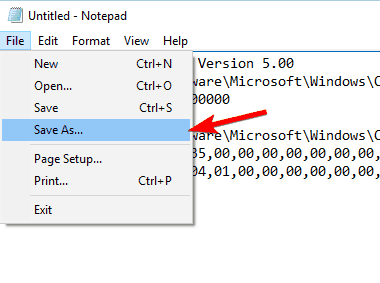
1. On your desktop screen, right-click the taskbar.
2. From the context menu that appears, clickВ Start Task Manager.
3. In the Task Manager box, if not already there, go to theВ ProcessesВ tab.
4. From the displayed list of running processes, right-click the one that you know is using the file that you want to delete.
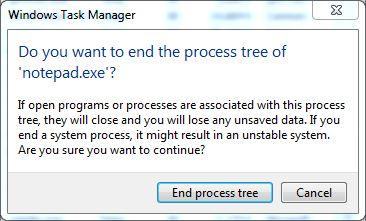
5. From the context menu, clickВ End ProcessВ orВ End Process Tree. (End process treeВ is clicked here.)
6. On the confirmation box that pops up, click theВ End process treeВ button from the bottom.
7. Once the process has been forcefully terminated, you can easily remove the file as it is no longer used until the process starts running again.
Note:В In some cases, you need to be quick in deleting the file after force terminating the process. This is because some processes are stubborn and even if you terminate them forcefully, they restart automatically after a few seconds.
More Related Articles:
From Command Prompt
This method requires you to open Command Prompt on your Windows PC. For the files used by some local processes (the processes that can be started and closed by a standard – non-administrator user account), opening Command Prompt on a standard user account would suffice. However, if the file is used by any system process, the elevated Command Prompt must be initialized. An elevated Command Prompt is the command window that has all the administrator rights and all the administrative tasks can be performed via commands in its interface.
This is what you need to do:
Note:В A Windows 7 PC is used in this example.
1. On your Windows PC, locate the folder that contains the file in use that you want to delete. (Do not enter into the folder.)
2.В Shift + right-clickВ the folder.
3. From the advanced context menu that appears, clickВ the Open command window hereВ or press theВ WВ key on the keyboard.
Note:В This method does not allow you to open an elevated command window.
Note: To start elevated Command Prompt, click the Start button, type CMD in the search box at the bottom of the Start menu, right-click CMD from the suggested programs’ list, click Run as administrator from the context menu, and on the User Account Control confirmation box, type the password for the admin account (or click Yes if Windows doesn’t ask you for the password) to provide your consent to continue. After the elevated command window opens up, you must use the DOS commands like CD and DIR to locate the directory where the file you want to delete is placed and to check the presence of the file respectively.
4. In the command window, type theВ DEL /F file nameВ command and pressВ EnterВ to force delete the file that is in use.
Note:В In the above command,В the file nameВ must be replaced by the name of the file along with its extension that you want to delete. For exampleВ del /f TestFile.txt.
WARNING!! – A file deleted using the DEL command does not move it to the Recycle Bin but deletes it permanently. Use the DEL command with caution.
5. Once the file is deleted, you can close Command Prompt by clicking theВ CloseВ button from the top-right corner of the window or by typingВ EXITВ in the command window and pressingВ Enter.
Using a Third-Party Tool – Unlocker
Even though you can use any of the two methods described above to remove a file that is in use, a third-party tool such as Unlocker makes your task extremely simple. The best part is that Unlocker is a freeware and is free to download and use. This is how Unlocker works:
Note:В A Windows 7 computer is used for reference.
1. Log on to your Windows PC.
2. Ensure that it is connected to the Internet.
3. Open any web browser of your choice and open your preferred search engine. (Google, Yahoo!, Bing, etc.)
4. Using the search engine, search for Unlocker.
5. Once found, download Unlocker’s installable file and install the program using the normal installation method, or get its portable version.
Note:В Unlocker is installed on this referenceВ PC.
6. After this, locate the file that you want to delete but is in use.
7. Right-click the file.
8. From the context menu that is displayed, clickВ Unlocker.
9. On theВ User Account ControlВ confirmation box, clickВ YesВ to provide your consent to continue launching the program.
10. On the displayed interface, from the available list of files in use, click to select the one that you want to unlock.
11. From the bottom of the interface, clickВ UnlockВ to unlock the file while leaving the corresponding application open. Alternatively, you can also click theВ Kill ProcessВ button to force terminate the running process that is responsible for engaging the file.
12. Once the file is unlocked, you can right-click the file and clickВ DeleteВ from the context menu.
13. ClickВ YesВ on theВ Delete FileВ confirmation box when/if displayed.
How to Restore a File If It Has Been Deleted Accidentally
Even if the file has been forcefully unlocked using any of the methods, it is moved to the Recycle Bin when deleted (except for when deleted using the command line). That being said, restoring the file from the Recycle Bin is simple. This is what you need to do.
1. On your Windows desktop screen, double-click the Recycle Bin’s icon.
2. Once inside theВ Recycle Bin, right-click the file that you want to restore.
3. From the context menu, clickВ Restore.
Note:В If a file has been deleted permanently (e.g. when removed with the DEL command), you need an efficient file recovery software such as RecoveritВ Data RecoveryВ to recover the file back.
Your Safe & Reliable Data Recovery Software
- Recover lost or deleted files, photos, audio, music, emails from any storage device effectively, safely and completely.
- Supports data recovery from recycle bin, hard drive, memory card, flash drive, digital camera, and camcorders.
- Supports to recover data for sudden deletion, formatting, hard drive corruption, virus attack, system crash under different situations.
Although the above-mentioned tricks work almost every time, you must take the utmost care while deleting any file that is in use. Deleting a wrong file may cause consequences like permanent or temporary system failure or data loss. To avoid this, before force deleting your files, make sure you have thoroughly verified the following:
- The file in use does not contain any important data.
- Force terminating the process to unlock the file doesn’t cause any permanent damage to its corresponding program.
- You have backed up the file before deleting it.
- You have tried (and failed) other ways to do what you want to do, and that force deleting the file is the only option left.
Video Tutorial on How to Recover Deleted Files on Windows 10/8/7 Easily?
Recent Videos from Recoverit
How to Delete Temporary Files in Windows
Safely delete temp files in Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista and XP
One really easy way to free up some disk space in Windows is to delete temporary files, sometimes referred to as temp files. Temp files are exactly what they probably sound like: files that your operating system only needed to exist temporarily while in use, but are now just wasting space.
Most temporary files are stored in what’s called the Windows Temp folder, the location of which differs from computer to computer, and even user to user. The steps for that are below.
Manually cleaning out the Temp folder in Windows usually takes less than a minute but it could take longer depending on how large the collection of temporary files is.
You can delete temp files in the way outlined below in any version of Windows, including Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
How to Delete Temporary Files in Windows
Follow these simple steps to delete your temporary Windows files:
Windows 10: Select the Cortana search box just to the right of the Start button on the taskbar.
Windows 8.1: Right-click or tap-and-hold the Start button and then choose Run.
Windows 8.0: The easiest way to access Run is from the Apps screen.
In earlier versions of Windows, choose Start to bring up the search box or find Run.
Another way to open the Run dialog box is to enter the WIN+R keyboard shortcut.
In the Run window or search box, enter the following command exactly:
The q parameter suppresses confirmation prompts to delete the files and folders, and s is for deleting all the subfolders and files in the temp folder.
If the %temp% environment variable is for some reason not working, feel free to substitute in the actual folder location mentioned in Step 2 above, but make sure you type the correct folder path, and to be safe, surround the path in quotes like this:
Other Types of Temporary Files in Windows
The Windows Temp folder isn’t the only place that temporary files, and other no-longer-needed groups of files, are stored on Windows computers.
The Temp folder that you found in Step 2 above is where you’ll find some of the operating-system-created temporary files in Windows, but the C:\Windows\Temp\ folder contains a number of additional files that you no longer need to keep.
Feel free to open that Temp folder and delete anything you find in there.
Check Your Browser Cache
Your browser also keeps temporary files, usually in an attempt to speed up your browsing by loading cached versions of web pages when you revisit them. Review How to Clear Your Browser’s Cache for help deleting these types of temporary files.
Other, harder-to-find locations contain temporary files, too. Disk Cleanup, a utility included in all versions of Windows, can help remove the contents of some of those other temp folders for you automatically. You can open that in a Run dialog box (WIN+R) via the cleanmgr command.
Handy Tools for Easy Removal
Dedicated «system cleaners» like the free CCleaner program can make this, and similar jobs, really easy. Many free computer cleaner programs exist to choose from, too, including Wise Disk Cleaner and Baidu PC Faster.
Check how much free space your hard drive has, both before and after you delete temporary files, to see how much space you recovered.
“File in use” error on Windows 10 [Fix]
- Sometimes you cannot delete or modify a file because you get the File in use error.
- The article below acts as a troubleshooting guide for when you encounter this issue on your PC.
- It is one of many similar articles included in our dedicated Uninstall Hub.
- For more interesting guides and tutorials, take a look at our expanded How-To page.
The File in use error message usually appears when you try to delete a certain file while it’s being used by a different application or a user. This can be an annoying error, so today we’re going to show you how to fix it on Windows 10.
How do I fix the file in use error?
1. File in use error
1.1. Uninstall the problematic applications
Third-party applications can sometimes cause the File in use error to appear. Users reported that this problem occurred while working with ISO files. According to them, the cause of the problem was an application called Virtual Clone Drive.
After removing the Virtual Clone Drive, the error was resolved completely.
One way to instantly get rid of any kind of software from your PC is to go for a professional uninstaller, and no better can fit the job at hand than Revo Uninstaller Pro.
This software solution is lightweight, can run on even the most dated of PCs, and it has one goal, to uninstall any software on your PC, without leaving a single trace that it was ever there.
You get to choose between two scanning modes when you uninstall a program:
- A fast but superficial scanning mode that will simply uninstall your programs
- A slower, more in-depth scanning mode that will uninstall your programs, and delete any associated files and folders that may have been installed along with them.
Revo Uninstaller Pro
1.2. Use third-party applications to remove the file
According to users, you might be able to fix File in use error simply by using a third-party tool. If you have problems removing files, you might want to try Bitraser File Eraser.
This product is the perfect choice for when you are dealing with stubborn files that can’t get erased the old-fashioned way. In the case at hand, it will also help you with deleting the files that may be causing the File in use error message as well.
As an added bonus, you can use this tool as an overall deleter, as it can also easily handle Erase files, folders, web browsing history, saved passwords, etc.
The best part about all this is that the product can be tested for free for 30 days, so you have plenty of time to try before you buy.
Bitraser File Eraser
1.3. Close all running applications
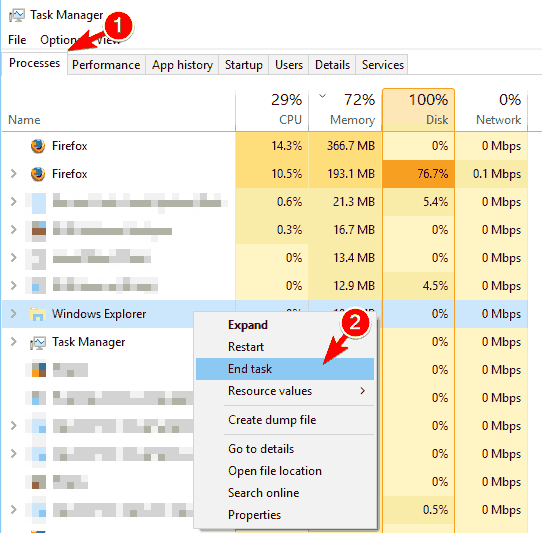
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- When Task Manager opens, navigate to Processes tab.
- Locate Windows Explorer on the list, right click it and choose End Task.
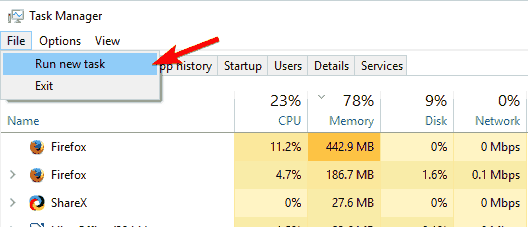
- Once Windows Explorer closes, select File > Run a new task.
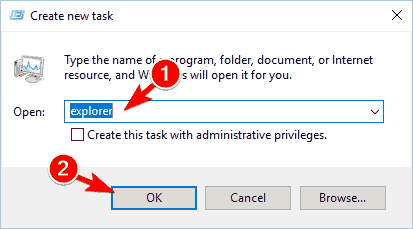
- The Create new task window will now appear. Enter explorer and click OK to start Windows Explorer again.
If you’re getting the File in use error, it’s most likely that the file is being used by a different application. Sometimes, certain apps can use files in the background and cause this error to appear.
To fix the issue, be sure to close all running applications and try to delete the file. In addition, restart your PC and try to delete the file again.
If that doesn’t work, you might want to try moving all other files to a different folder. After doing that, try to delete the folder that has the problematic file in it. Lastly, you can try restarting File Explorer.
Once Windows Explorer starts, try to delete the file again. If that doesn’t work, you can try to terminate the process that’s related to the problematic file. For example, if you can’t delete a PDF file, try terminating your PDF application from Task Manager.
1.4. Try to delete the file from Safe Mode
- Click the Start button.
- Now click on Power button. Hold the Shift key on your keyboard and choose the Restart option from the menu.
- Once your PC restarts, you’ll see a list of options. Select Troubleshoot from the menu.
- Select Advanced options > Startup Settings and click the Restart button.
- A list of options will appear. Choose any version of Safe Mode by pressing the appropriate key.
If you can’t delete a file due to the File in use error, you might want to try removing it from Safe Mode. Once the Safe Mode starts, try to delete the file again.
1.5. Use Command Prompt
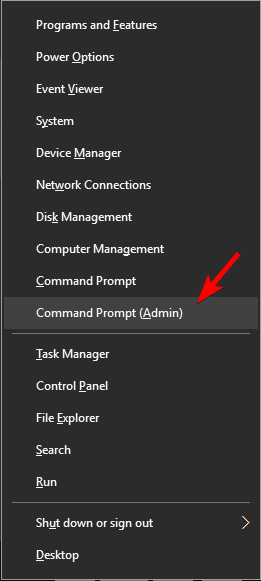
- Open Command Prompt as administrator. To do that, press Windows Key + X to open Win + X menu and choose Command Prompt (Admin).
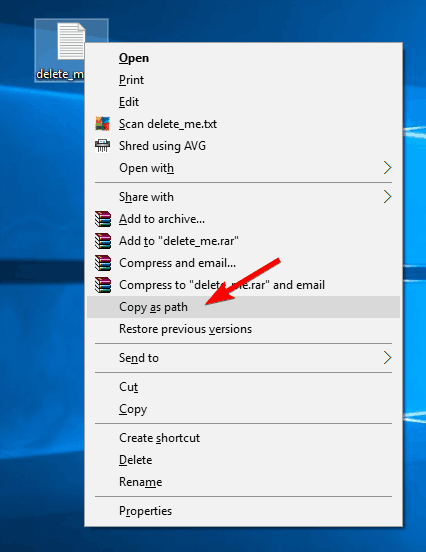
- Once the Command Prompt opens, find the problematic file, hold the Shift key, and right-click it. Now choose Copy as path from the menu.
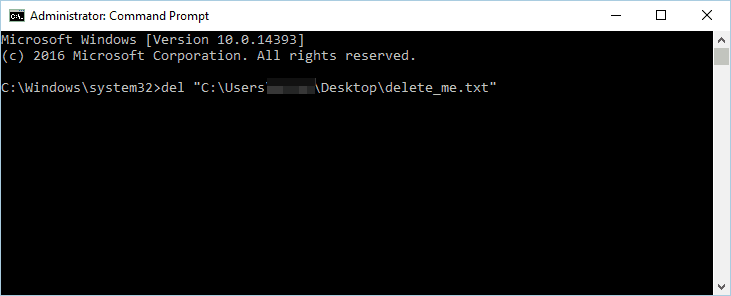
- In Command Prompt, enter del and press Ctrl + V to paste the file path. Don’t run the command yet.
- Use Task Manager to close Windows Explorer. We explained how to do that in Solution 1, so be sure to check it out. In order to successfully remove the file, it’s important not to restart Windows Explorer.
- Switch back to Command Prompt and press Enter to run the command that you entered in Step 2.
- After the command is executed, you can close Command Prompt and restart Windows Explorer
If you don’t want to rely on third-party solutions to fix this problem, you can use Command Prompt instead.
1.6. Change the file extension of the problematic file
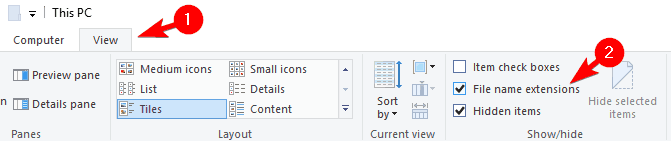
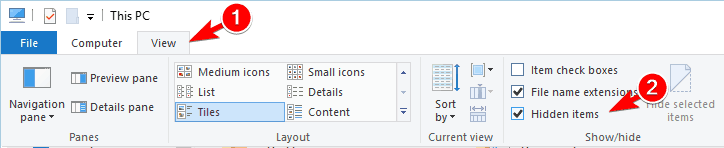
According to users, you might be able to fix this problem simply by changing the file extension of the problematic file. In order to do that, first you need to turn on the option to show file extensions. To do that, follow these steps:
- Open File Explorer.
- Click the View tab and check File name extensions option.
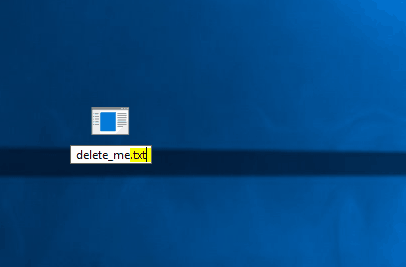
- After doing that, you need to find the problematic file, select it and press F2 on your keyboard.
- Change the file extension to .txt or any other extension.
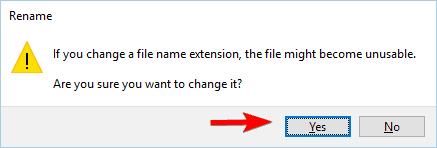
- A warning message will appear. Click Yes.
After you change the file extension, try to delete the file again.
1.7. Switch to Details view
- Open File Explorer and locate the problematic file.
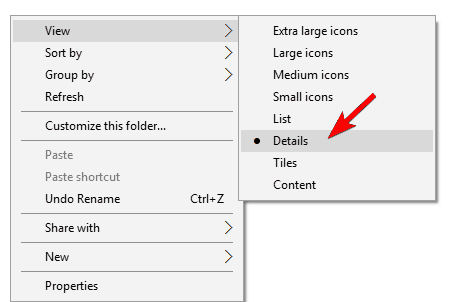
- Right-click the empty space and choose View > Details.
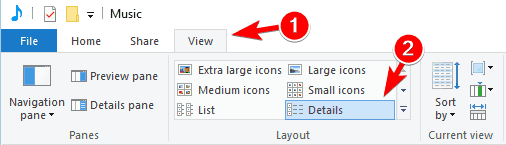
- Optional: You can do the same thing by navigating to the View tab and clicking on Details.
According to users, the File in use error can appear due to your thumbnails. Sometimes, Windows has issues unloading thumbnails, preventing you from deleting your files.
To fix the problem, you just have to switch to Details view in File Explorer and you should be able to delete the file.
After switching to Details view, all thumbnails will be disabled and you should be able to delete the file. Users suggest moving the file to Desktop and closing the File Explorer window.
By doing so, the preview pane won’t be available and you should be able to delete the problematic file with ease.
1.8. Disable thumbnail generation
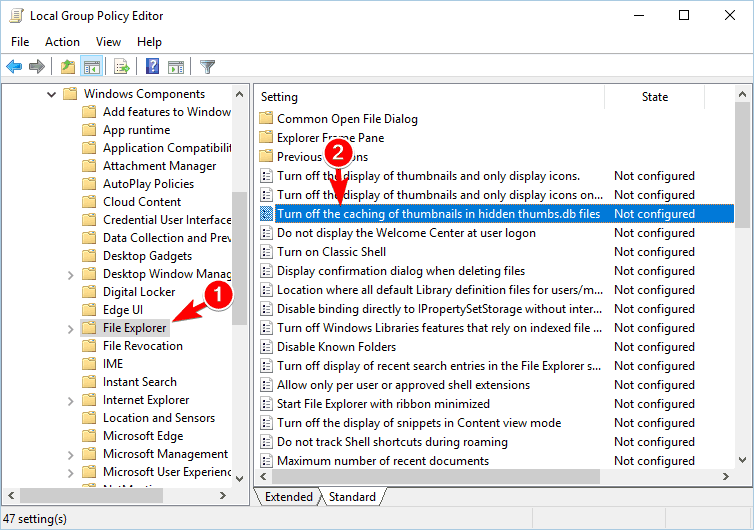
- Press Windows Key + R and enter gpedit.msc. Click OK or press Enter.
- When theGroup Policy Editor opens, navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > File Explorer in the left pane.
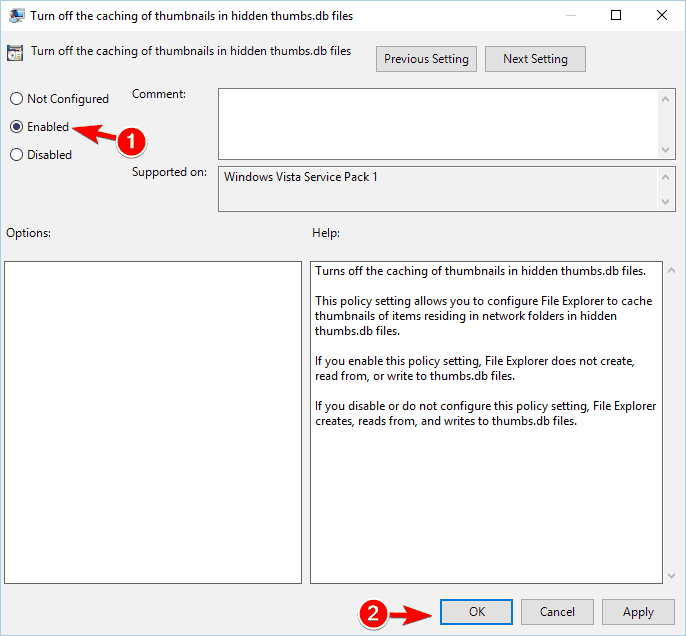
- In the right pane double click on Turn off caching of thumbnails in hidden thumbs.db files.
- Select the Enabled option and clickApply and OK to save changes.
If you can’t access Group Policy Editor, you can disable thumbnail generation using Registry Editor. To do that, follow these steps:
- Press Windows Key + R and enter regedit. Press Enter or click OK.
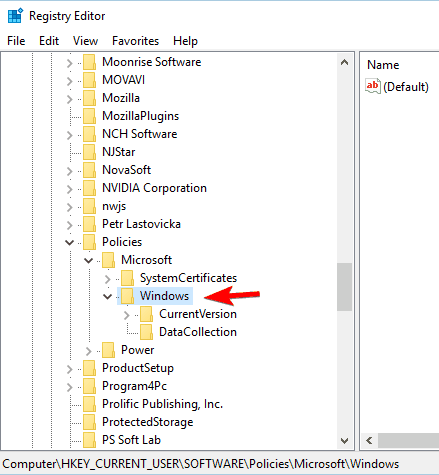
- When the Registry Editor opens, navigate to HKEY_CURRENT_USERSOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindows key in the left pane.
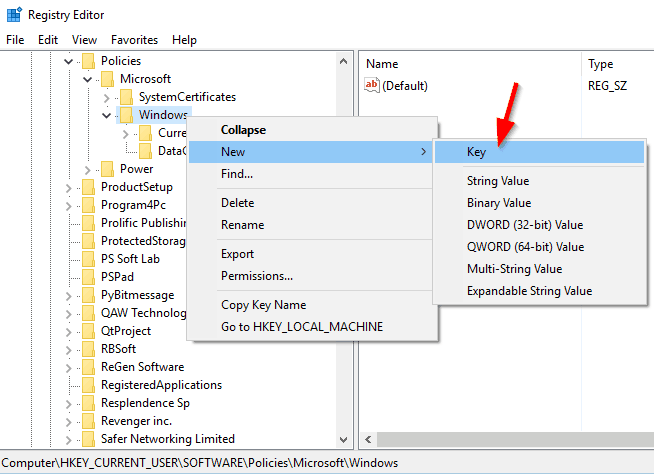
- Right-click the Windows key and choose New > Key. Enter Explorer as the name of the new key.
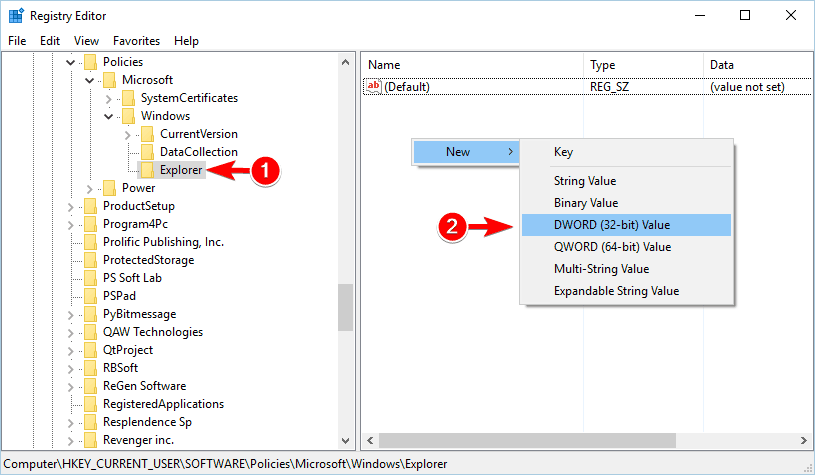
- Navigate to the Explorer key and right-click the empty space in the right pane.
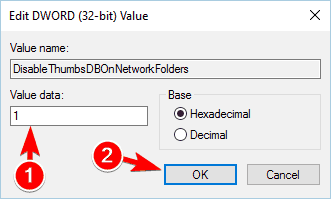
- Choose New > DWORD (32-bit) Value. Enter DisableThumbsDBOnNetworkFolders as the name of the new DWORD.
- Double-click newly created DisableThumbsDBOnNetworkFolders DWORD to open its properties.
- Set Value data to 1 and click OK to save changes.
- After you’re done, close Registry Editor and check if the problem is resolved.
If you’re having problems with this error, you might be able to fix it by disabling thumbnail generation. You can do that by using the Group Policy Editor. This solution applies to network drives, but it might work for your local drive as well.
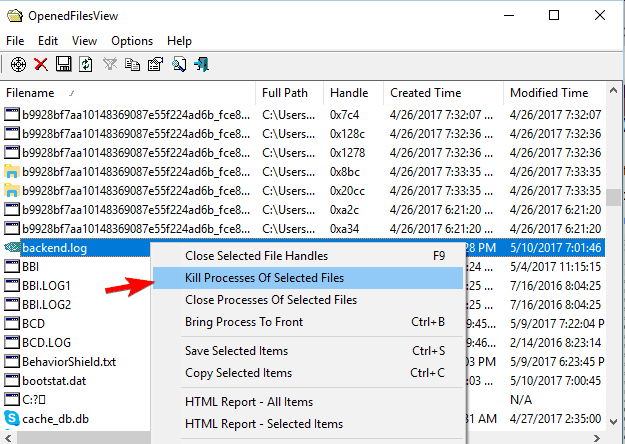
1.9. Use OpenFilesView tool
- Download OpenFilesView tool.
- Start the application. A list of active files will now appear.
- Locate the problematic file on the list, right-click it and choose Kill Processes of Selected Files. By doing so, you’ll terminate processes that are associated with that file.
- After doing that, try to delete the file again.
Another third-party application that can help you with this problem is OpenFilesView tools. The application is simple to use.
This is a simple application that allows you to close all processes related to a specific file. If the problematic file isn’t available on the list, you might have to try a different solution.
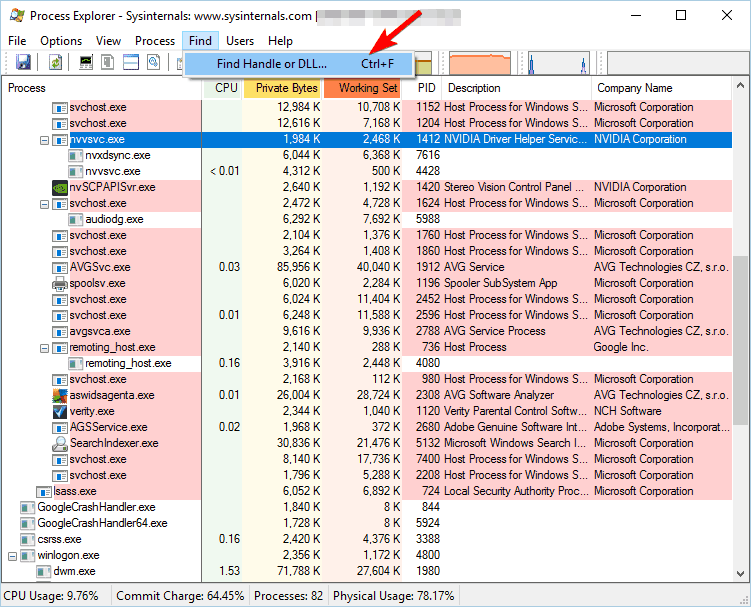
1.10. Use Process Explorer
- Download Process Explorer.
- When the application opens, go to Find > Find Handle or DLL.
- In the Handle or DLL substring field, enter the name of the problematic file and click the Search button.
- A list of associated applications and DLLs should appear. Locate the application associated with the file, right-click it and choose the Close Handle option.
Several users reported that you might be able to fix the problem by using Process Explorer.
Keep in mind that you might have to repeat this process few times in order to close all related applications. We have to mention that Process Explorer is an advanced tool, so you might find it hard to use if you’re a novice user.
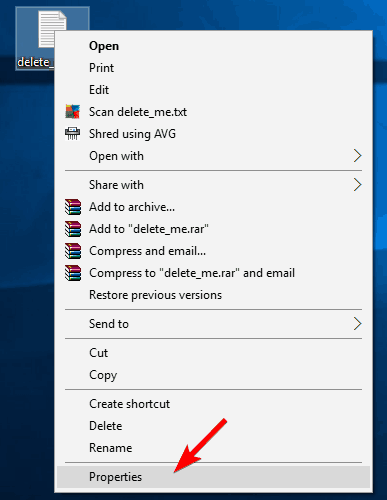
1.11. Make sure that file isn’t blocked
- Right-click the problematic file and choose Properties from the menu.
- Go to the General tab and click the Unblock button in Security section. Click OK and Apply to save changes.
Sometimes, the File in use error can appear if the file you’re trying to delete is blocked. Windows sometimes blocks downloaded files in order to protect you from malware. Although this feature can be useful, it can also prevent you from removing certain files.
After unblocking the file, try to delete it again. If you can’t find the Unblock button in the Properties window, it means that the file is already unblocked, so you should try a different solution.
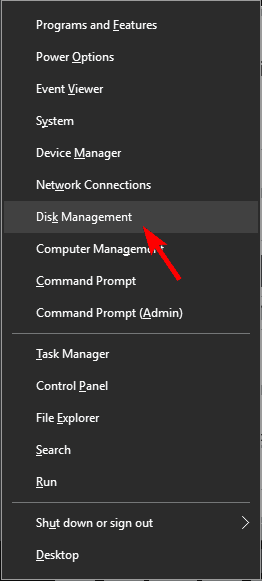
1.12. Remove the virtual hard drive
- Press Windows Key + X and choose Disk Management from the list.
- The Disk Management tool will now appear. Locate your virtual hard drive, right-click it and choose Detach VHD.
- A confirmation message will now appear. Click OK. After you detach the drive, it will disappear from Disk Management tool.
- After doing that, close Disk Management and try to delete the .vhdx file again.
A few users reported that the File in use error appears while trying to remove a virtual hard drive .vhdx file. To fix this problem, you need to remove the virtual hard drive from your PC.
Keep in mind that this solution only applies when deleting virtual hard drive files. If you have this problem with any other type of file, you should try a different solution.
1.13. Use Resource Monitor
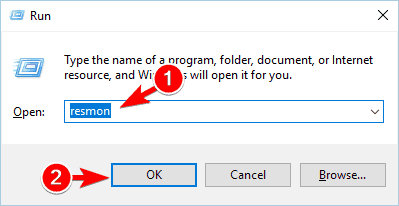
- Press Windows Key + R and enter resmon. Press Enter or click OK.
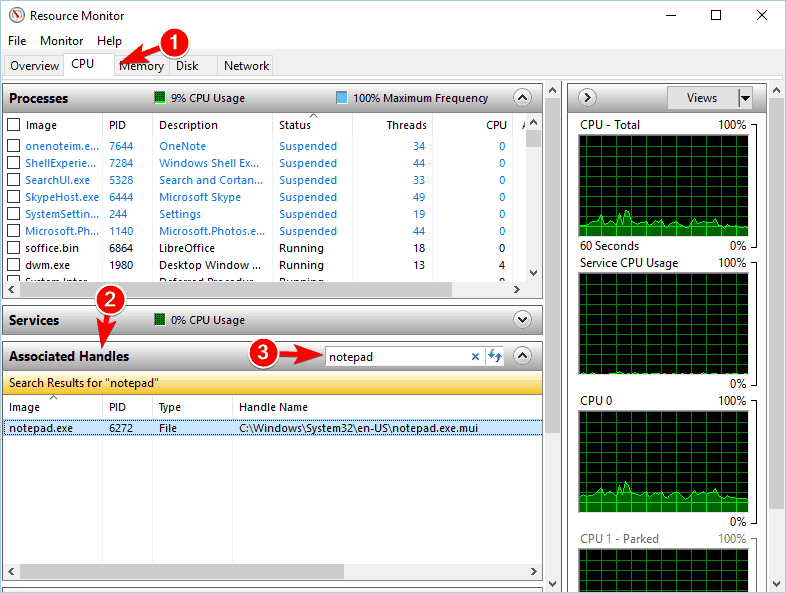
- When Resource Monitor starts, go to the CPU tab. Now, expand the Associated Handles section and in the Search Handles field, enter the name of the problematic file. A list of associated applications will now appear.
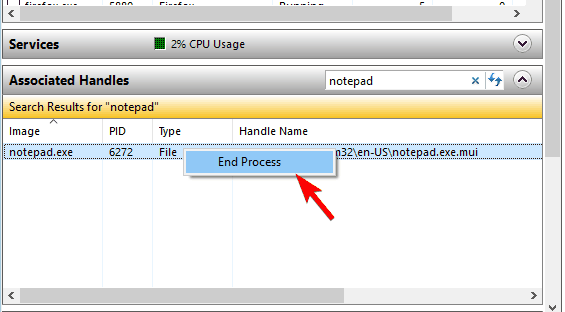
- Right-click the associated application and choose End Process from the menu.
If you can’t delete a specific file, you might be able to solve the problem by using Resource Monitor, a Windows application that can give you a lot of information about open applications and files.
Keep in mind that sometimes you won’t be able to find the problematic file using Resource Monitor. If that happens, you might have to check each process one by one and check the list of all associated handles.
If you manage to find the folder that has the problematic file, you’ll be able to determine which application is using it. Resource Monitor is an advanced tool, so it might take you a while to get used to it especially if you’re a first time user.
2. How do I fix the File in use error in Excel?
2.1. Create a registry file and add it to your registry
- Open Notepad.
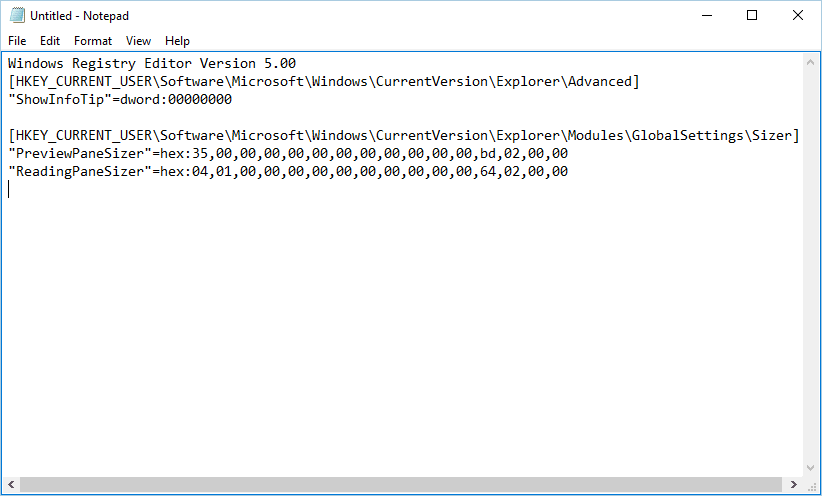
- Paste the following text:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerAdvanced]
«ShowInfoTip»=dword:00000000[HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerModulesGlobalSettingsSizer] «PreviewPaneSizer»=hex:35,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,bd,02,00,00«ReadingPaneSizer»=hex:04,01,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,00,64,02,00,00 - Go to File and click Save as.
- Set Save as type to All Files. Enter fix.reg as the File name and click the Save button.
- Close Notepad and locate the fix.reg file. Double-click it and choose Yes when the warning message appears.
According to users, you might be able to fix the File in use error while opening Excel files by creating a .reg file and adding it to your registry.
Keep in mind that this solution will modify your registry, therefore it’s advised to create a backup or System Restore point.
2.2. Disable the preview pane
Users claim you can fix this problem simply by disabling the preview pane in File Explorer. We already explained how to do that in one of our previous solutions, so be sure to check it out.
2.3. Check the file name
The File in use error can appear if the file name of your Excel document is too long. If the file name is too long, Excel can’t create the lock file.
To fix the issue, you need to locate your Excel file and shorten its name. After renaming the file, you should be able to access it without issues.
2.4. Delete the hidden lock file
- Navigate to the folder where problematic Excel file is saved.
- Click View and check the Hidden items option.
- Locate the lock file. (It should have the same name as your Excel document.)
- Delete the lock file.
Excel usually creates a temporary lock file alongside your Excel document. According to users, you simply have to locate and remove the lock file in order to fix this error.
After removing the lock file, you should be able to access your Excel document without any issues.
2.5. Check the personal.xlsb file
- Navigate to C:Usersyour_usernameAppDataRoamingMicrosoftExcelXLSTART folder.
- If this folder isn’t available, navigate to C:Usersyour_usernameAppDataLocalMicrosoftExcelXLSTART folder instead.
- If you can’t find any of these folders, you’ll need to reveal hidden files. We already showed you how to do that in our previous solution, so be sure to check it out.
- Keep in mind that personal.xlsb is a hidden file, so you’ll need to reveal hidden files in order to see it.
- Once you locate personal.xlsb file, delete it if you don’t plan to use it.
- Optional: If you need the personal.xlsb file, right-click it and choose Properties from the menu.
- Navigate to General tab and check the Read-only option. Click Apply and OK to save changes.
According to users, the File in use error in Excel appears after adding macros to the personal.xlsb file. To fix the problem, you need to find and delete that file.
After doing that, you should be able to start Excel without any problems.
The File in use error is an annoying problem that will prevent you from accessing your files. If you have this error on your PC, be sure to try some of our solutions and let us know how it works out for you!








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tim-fisher-5820c8345f9b581c0b5a63cf.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ryanperiansquare-de5f69cde760457facb17deac949263e-180a645bf10845498a859fbbcda36d46.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/disk-cleanup-windows-10-5c3f45ddc9e77c000196fc5b.png)