- ИТ База знаний
- Полезно
- Навигация
- Серверные решения
- Телефония
- Корпоративные сети
- Как запустить, остановить и перезапустить сервисы в Linux
- Базовый синтаксис команды systemctl
- Как проверить, работает ли служба в Linux
- Как перезапустить сервис
- Как перезагрузить конфигурационные файлы сервиса
- Как запустить сервис
- Как остановить сервис
- Как включить сервис при загрузке
- Как отключить сервис при загрузке
- Полезно?
- Почему?
- Ubuntu Linux: Start, Stop, Restart, Reload OpenSSH Server
- Start / Stop / Restart / Reload OpenSSH Server on Ubuntu
- Ubuntu Linux: Start OpenSSH Server
- Ubuntu Linux: Stop OpenSSH server
- Ubuntu Linux: Restart OpenSSH server
- Reboot Linux System Command
- Linux system restart
- Reboot Linux system command
- How do I reboot remote Linux server?
- A note about systemctl command when using systemd
- Conclusion
- How to Restart Your Linux Server (3 Easy Methods)
- When Should You Not Restart a Linux Server?
- Your Website or Email Doesn’t Work Correctly
- You Installed Something
- The Server Hasn’t Been Restarted in Awhile
- When Should I Stop or Restart a Linux Server?
- Critical Updates
- Test Server Restart Feature
- Save Money with a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- How to Restart a Linux Server
- How to Restart Your VPS in AMP
- How to Restart Your Linux Server in WHM
- How to Restart Your Linux Server via SSH
ИТ База знаний
Курс по Asterisk
Полезно
— Узнать IP — адрес компьютера в интернете
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Калькулятор инсталляции IP — АТС Asterisk
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Как запустить, остановить и перезапустить сервисы в Linux
Start — Stop — Restart — Reload
3 минуты чтения
Linux обеспечивает детальный контроль над системными службами через systemd с помощью команды systemctl. Службы могут быть включены, выключены, перезапущены, перезагружены или даже включены или отключены при загрузке. Если вы используете Debian, CentOSили Ubuntu, ваша система, вероятно, использует systemd.
Мини — курс по виртуализации
Знакомство с VMware vSphere 7 и технологией виртуализации в авторском мини — курсе от Михаила Якобсена
Это руководство покажет вам, как использовать основные команды для запуска, остановки и перезапуска служб в Linux.
Базовый синтаксис команды systemctl
Основной синтаксис для использования команды systemctl:
Как правило, вам нужно запускать это как суперпользователь поэтому команды будут начинаться с sudo.
Как проверить, работает ли служба в Linux
Чтобы проверить, активна ли служба или нет, выполните следующую команду:
Замените SERVICE_NAME на нужный сервис.
В нашем случае мы будем брать за пример веб-сервер Apache.
Интересный факт: в Ubuntu и других дистрибутивах на основе Debian служба Apache называется apache2. В CentOS и других дистрибутивах RedHat служба Apache называется httpd или httpd.service
Так мы проверили состояние Apache. Выходные данные показывают, что служба активна (работает), как на рисунке ниже:

Как перезапустить сервис
Чтобы остановить и перезапустить службу в Linux, используйте команду:
Где SERVICE_NAME — имя вашего сервиса.
После выполнения команды ваш сервис должен снова заработать. Вы можете проверить состояние с помощью команды status
Для перезапуска нашего сервера Apache используем:
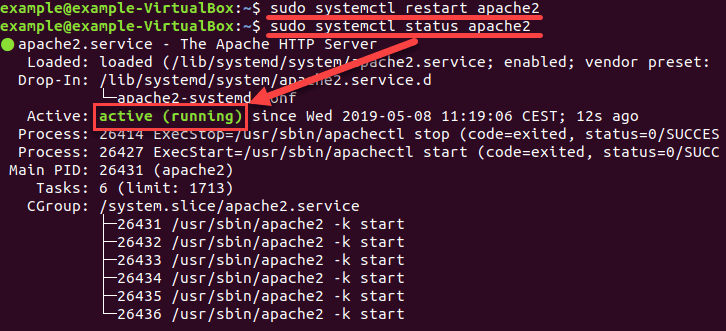
Как перезагрузить конфигурационные файлы сервиса
Чтобы служба перезагрузила свои файлы конфигурации, введите в терминале следующую команду:
После перезагрузки проверьте ее состояние командой status для подтверждения.
В нашем примере мы перезагрузили Apache, используя:

Как запустить сервис
Чтобы запустить службу в Linux вручную, введите в терминале следующее:
Например, команда для запуска службы Apache:
Как остановить сервис
Чтобы остановить активную службу в Linux, используйте следующую команду:
Для нашего апача используем команду
Проверьте, остановился ли сервис с помощью команды status . Вывод должен показать, что сервис неактивен — inactive (dead)
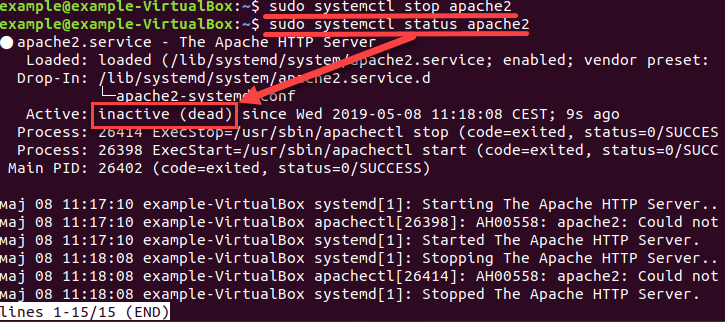
Как включить сервис при загрузке
Чтобы настроить службу для запуска при загрузке системы, используйте команду:
Чтобы включить Apache при загрузке системы, выполните команду:

Как отключить сервис при загрузке
Вы можете запретить запуск службы при загрузке с помощью команды:
Мини — курс по виртуализации
Знакомство с VMware vSphere 7 и технологией виртуализации в авторском мини — курсе от Михаила Якобсена
Полезно?
Почему?
😪 Мы тщательно прорабатываем каждый фидбек и отвечаем по итогам анализа. Напишите, пожалуйста, как мы сможем улучшить эту статью.
😍 Полезные IT – статьи от экспертов раз в неделю у вас в почте. Укажите свою дату рождения и мы не забудем поздравить вас.
Источник
Ubuntu Linux: Start, Stop, Restart, Reload OpenSSH Server
I need to provide a remote access to my Ubuntu Linux based server. How do I start / stop, OR restart the ssh server under Ubuntu Linux operating system using command line options?
You need to run a script called /etc/init.d/ssh to stop, start, and restart the OpenSSH server. You can also use the service command to control a System V init script. If you are using the latest version of Ubuntu such as 12.04 LTS or 13.04+, you need to use upstart job based commands as listed below.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Ubuntu Linux with sudo command |
| Est. reading time | 3 mintues |
Start / Stop / Restart / Reload OpenSSH Server on Ubuntu
Latest version of Ubuntu such as Ubuntu Linux 16.04 LTS or 18.04 LTS and others use the systemctl command to control ssh server on Ubuntu. Older version use the service command. To find out your Ubuntu Linux version, type:
lsb_release -a
cat /etc/*release*
Sample outputs:
Ubuntu Linux: Start OpenSSH Server
Type the following command:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start
OR
$ sudo service ssh start
For systemd based Ubuntu Linux 16.04/18.04/20.04 LTS or above servers, run:
$ sudo systemctl start ssh
Ubuntu Linux: Stop OpenSSH server
Type the following command:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh stop
OR
$ sudo service ssh stop
Again for systemd based Ubuntu Linux 16.04/18.04/20.04 LTS or above server, enter:
$ sudo systemctl stop ssh
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Ubuntu Linux: Restart OpenSSH server
Type the following command:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
OR
$ sudo service ssh restart
For systemd based Ubuntu Linux 16.04/18.04/20.04 LTS or above server, execute:
$ sudo systemctl restart ssh
systemctl command in action on Ubuntu Linux desktop
Источник
Reboot Linux System Command
Linux system restart
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux |
| Est. reading time | 1m |
To reboot Linux using the command line:
- To reboot the Linux system from a terminal session, sign in or “su”/”sudo” to the “root” account.
- Then type “ sudo reboot ” to reboot the box.
- Wait for some time and the Linux server will reboot itself
Reboot Linux system command
You must login as root user to reboot the system. Open the terminal application (or login to remote box using ssh client) and type any one of the following command to reboot the system immediately:
# /sbin/reboot
OR
# /sbin/shutdown -r now
You can also use sudo command under Ubuntu/Debian/Fedora and other Linux based distros:
$ sudo reboot
It is a good idea to provide notification to all logged-in users that the system is going down and, within the last five minutes of TIME, new logins are prevented. Type the following command:
# shutdown -r +5
Sample output:
TIME may have different formats, the most common is simply the word “ now ” which will bring the system down immediately. Other valid formats are +m, where m is the number of minutes to wait until shutting down and hh:mm which specifies the time on the 24hr clock.
How do I reboot remote Linux server?
Simply login as the root user using ssh command:
$ ssh root@remote-server-com /sbin/reboot
OR
$ ssh root@remote-server-com /sbin/shutdown -r now
Sample outputs:
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Get notification using the ping command when remote-server-com comes online:
ping -a remote-server-com
It is possible to use sudo command along with normal user over ssh session too. The syntax is:
$ ssh -t vivek@remote-server-com /sbin/reboot
Without the -t you will seen an error “sudo: no tty present and no askpass program specified“, hence you must pass the -t to the ssh command.
A note about systemctl command when using systemd
Are you using systemd as init on your Linux distro? Most modern Linux distro such as Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, Arch, and many uses systemd, and we can use the following command to reboot the system:
sudo systemctl reboot
Conclusion
This page demonstrated how to use reboot command on Linux to reboot the server or desktop for software and kernel updates.
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How to Restart Your Linux Server (3 Easy Methods)
5 Minutes, 48 Seconds to Read
Instead of skipping to how to restart your Linux server, read the entirety of the guide for better understanding of the pros and cons.
A demonstration on how to restart your Linux server in WHM and AMP
When a PC slows down, we all know restarting it as a quick solution. This is good enough for users who don’t audit system logs to investigate the matter. Usually, the best solution is to investigate running processes and better secure the system. With server hosting, this is especially important because it’s always online and you can’t disconnect it from the internet to work on it locally. Logs are your best friend during incident response procedures after a cyber attack.
Managed VPS , Cloud Server, and Dedicated Server hosting customers have the option to restart their Linux server in multiple ways. There are times when this is necessary. It shouldn’t be often, though. Below we’ll cover:
When Should You Not Restart a Linux Server?
When a server is in use, there are always disk writes to a database, server log, or application. You may already know not to halt a system during an SSH connection with activity. Whatever you’re doing in the server terminal will end abruptly unless you started the process with screen or tmux . Here are other specific cases where you DO NOT want to restart your server immediately, and what you should do instead.
Your Website or Email Doesn’t Work Correctly
Each popular content management system (CMS) has common errors, hopefully with well documented solutions. Performance demands climb every year with new technologies like HTTP/3 and NVMe drives. And of course, cyber attacks are always on the rise. Any of these situations can affect website and server performance. Instead of restarting your server, check if:
- Your website loads properly on another device and for other countries with web apps like GeoPeeker and ShotSherpa
- Your hosting provider has noted outage issues
- You’re receiving a lot of orders from your eCommerce store
- Your web analytics application or social media indicates posts that may be viral
- Error logs indicate database, misconfiguration, denial of service (DoS), or other malicious issues
If this is a constant issue, consider one or more of the following:
When you have email issues, usually you receive some type of bounceback error. Restarting the server won’t fix those errors.
Check your email client settings if you can’t send email.
Check local firewall settings if you can’t send email while using a virtual private network (VPN).
If your emails deliver to spam / junk folders, improve your email authentication settings.
You Installed Something
Many installation guides for server level software instruct you to “restart your VPS” at some point. Popular examples include Apache modules, new PHP versions, and SSH port changes. Most times, you only need to restart the web server application.
WebHost Manager (WHM) can do this as well under Restart Services.
The Server Hasn’t Been Restarted in Awhile
Going back to restarting PCs, Linux servers normally have log optimization methods already in place to save disk space. Usually, it’s compressing older logs in tar files and deleting them after a certain amount of time.
When Should I Stop or Restart a Linux Server?
The most common situations when you DO want to restart your server:
Critical Updates
Some major update, installation, and uninstallation processes require rebooting the server. Read the instructions carefully to ensure it states to restart the server instead of just the web server application.
Test Server Restart Feature
You should be sure that all installed applications will start without issue after a reboot. You don’t know when you or your hosting provider may need to apply critical updates which require a reboot while you’re sleeping.
For VPS administrators, if your hosting provider starts disaster recovery procedures for their cloud infrastructure, your virtual server may be restarted as part of a node. Remember, a VPS or cloud server (cloud VPS) shares a physical server with other customers. In some instances, you may have a temporary issue due to something outside of your control.
Save Money with a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Unlike a VPS, a virtual private cloud (VPC) can expand to meet peaking resource demands and is pay-per-usage in seconds/hours online instead of a monthly subscription. If you don’t need your VPC on, shut it off. But ensure installed applications will start correctly before doing so.
How to Restart a Linux Server
Managed VPS, Cloud Server, and Dedicated Server hosting customers can restart your Linux server in AMP , WHM, or SSH. Remember, rebooting the server restarts Apache, MySQL, and email as well.
You can’t restart a shared server because you don’t have a virtual system and root access. You have a cPanel account on a shared physical server. Shared servers rarely need to be restarted unless our system administrators see an issue requiring it. If you have website issues which you believe result from the server, contact technical support for further assistance.
How to Restart Your VPS in AMP
You do not need root access for this.
- Log into AMP.
- Locate the server hosting account and select Restart VPS.
- Read the warnings. If you’re sure, select Restart VPS.
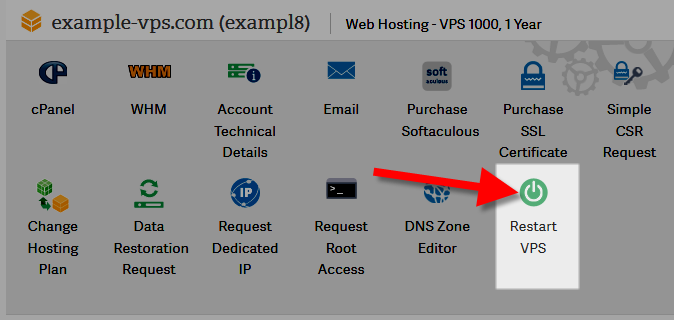
How to Restart Your Linux Server in WHM
You may need root access for this, depending on your cPanel user privileges in WHM.
- Log into WHM.
- On the left under System Reboot, select Graceful Server Reboot or Forceful Server Reboot. Use the graceful method because it prompts cPanel to finish user-level processes and not start anything new, preventing data corruption. The forceful method is the hard reset option you should only use if the graceful option doesn’t work.
You can restart individual services in WHM under Restart Services.
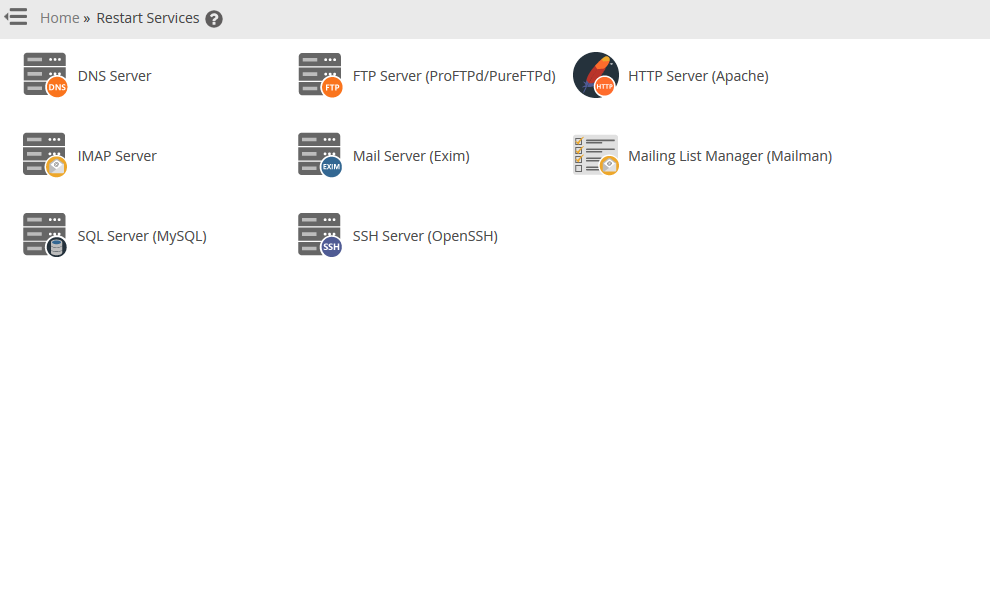
How to Restart Your Linux Server via SSH
You will need root access to execute the following commands in SSH or WHM Terminal.
It’s generally best to use AMP or WHM to do this on cPanel servers to prevent data loss.
Restart your server:
Shutdown your server:
Learn more about managing your Linux server hosting from our VPS Hosting Product Guide.
Источник





