Start your PC in safe mode in Windows 10
Safe mode starts Windows in a basic state, using a limited set of files and drivers. If a problem doesn’t happen in safe mode, this means that default settings and basic device drivers aren’t causing the issue. Observing Windows in safe mode enables you to narrow down the source of a problem, and can help you troubleshoot problems on your PC.
There are two versions of safe mode: Safe Mode and Safe Mode with Networking. Safe Mode with Networking adds the network drivers and services you’ll need to access the Internet and other computers on your network.
Select from the following sections to find out how to start your PC in safe mode from Settings, from the sign-in screen, or from a black or blank screen.
Press Windows logo key + I on your keyboard to open Settings. If that doesn’t work, select the Start button, then select Settings .
Under Advanced startup, select Restart now.
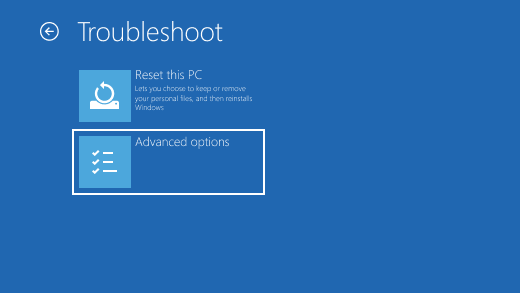
After your PC restarts to the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. You may be asked to enter your BitLocker recovery key.
After your PC restarts, you’ll see a list of options. Select 4 or press F4 to start your PC in Safe Mode. Or if you’ll need to use the Internet, select 5 or press F5 for Safe Mode with Networking.
When you can’t open Settings to get into safe mode, restart your device from the Windows sign-in screen.
On the Windows sign-in screen, press and hold the Shift key while you select the Power > Restart .
After your PC restarts to the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. You may be asked to enter your BitLocker recovery key.
After your PC restarts, you’ll see a list of options. Select 4 or F4 to start your PC in safe mode. Or if you’ll need to use the Internet, select 5 or F5 for Safe Mode with Networking.
Note: If you’ve encrypted your device, you’ll need your BitLocker key to start in safe mode.
Before you enter safe mode, you need to enter the Windows Recovery Environment (winRE). To do this, you will repeatedly turn your device off, then on:
Hold down the power button for 10 seconds to turn off your device.
Press the power button again to turn on your device.
On the first sign that Windows has started (for example, some devices show the manufacturer’s logo when restarting) hold down the power button for 10 seconds to turn off your device.
Press the power button again to turn on your device.
When Windows restarts, hold down the power button for 10 seconds to turn off your device.
Press the power button again to turn on your device.
Allow your device to fully restart. You will enter winRE.
Now that you are in winRE, you will follow these steps to take you to safe mode:
On the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
After your device restarts, you’ll see a list of options. Select option 5 from the list or press F5 for Safe Mode with Networking.
If you need more info on a black or blank screen error, see Troubleshoot black or blank screen errors.
Notes: If you need to exit safe mode, simply restart your device, or:
Press the Windows logo key + R.
Type msconfig in the Open box and then select OK.
Select the Boot tab.
Under Boot options, clear the Safe boot checkbox.
Advanced startup options (including safe mode)
The Advanced Boot Options screen lets you start Windows in advanced troubleshooting modes. You can access the menu by turning on your computer and pressing the F8 key before Windows starts.
Some options, such as safe mode, start Windows in a limited state, where only the bare essentials are started. If a problem doesn’t reappear when you start in safe mode, you can eliminate the default settings and basic device drivers and services as possible causes. Other options start Windows with advanced features intended for use by system administrators and IT professionals. For more information, go to the Microsoft website for IT professionals.
Repair Your Computer
Shows a list of system recovery tools you can use to repair startup problems, run diagnostics, or restore your system. This option is available only if the tools are installed on your computer’s hard disk. If you have a Windows installation disc, the system recovery tools are located on that disc.
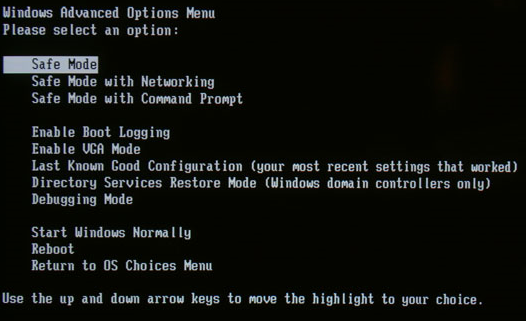
Safe Mode
Starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services.
To start in safe mode:
Remove all floppy disks, CDs, and DVDs from your computer, and then restart your computer. Click the Start button , click the arrow next to the Shut Down button (or the arrow next to the Lock button), and then click Restart.
Do one of the following:
If your computer has a single operating system installed, press and hold the F8 key as your computer restarts. You need to press F8 before the Windows logo appears. If the Windows logo appears, you’ll need to try again by waiting until the Windows logon prompt appears, and then shutting down and restarting your computer.
If your computer has more than one operating system, use the arrow keys to highlight the operating system you want to start in safe mode, and then press F8.
On the Advanced Boot Options screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the safe mode option you want, and then press Enter.
Log on to your computer with a user account that has administrator rights.
Safe Mode with Networking. Starts Windows in safe mode and includes the network drivers and services needed to access the Internet or other computers on your network.
Safe Mode with Command Prompt. Starts Windows in safe mode with a command prompt window instead of the usual Windows interface. This option is intended for IT professionals and administrators.
Enable Boot Logging. Creates a file, ntbtlog.txt, that lists all the drivers that are installed during startup and that might be useful for advanced troubleshooting.
Enable low-resolution video (640×480). Starts Windows using your current video driver and using low resolution and refresh rate settings. You can use this mode to reset your display settings. For more information, see Change your screen resolution.
Last Known Good Configuration (advanced). Starts Windows with the last registry and driver configuration that worked successfully.
Directory Services Restore Mode. Starts Windows domain controller running Active Directory so that the directory service can be restored. This option is intended for IT professionals and administrators.
Debugging Mode. Starts Windows in an advanced troubleshooting mode intended for IT professionals and system administrators.
Disable automatic restart on system failure. Prevents Windows from automatically restarting if an error causes Windows to fail. Choose this option only if Windows is stuck in a loop where Windows fails, attempts to restart, and fails again repeatedly.
Disable Driver Signature Enforcement. Allows drivers containing improper signatures to be installed.
Start Windows Normally. Starts Windows in its normal mode.
How to Restart Windows in Safe Mode
Troubleshoot booting problems in Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8.1 and Windows 10
Need to get into Safe Mode on your Windows PC? If you’re not able to boot your computer normally, you can try to enter safe mode, a diagnostic mode for Windows that lets you troubleshoot problems that prevent normal booting.
In Safe Mode, Windows only loads the most essential services and drivers in order for it to run. All other normal Windows settings and start up programs are disabled in order to allow the user to fix the problem with their computer.
In this guide, I am going to go through the steps to get into Safe Mode in Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8.1 and Windows 10.
Note that if you installed a driver or just recently made a configuration change to your computer, you may want to try the “Last Known Good Configuration” before going into safe mode in Windows 7, Vista and XP.
Last Known Good Configuration loads the last working version of Windows. However, it is replaced each time you log into the computer, so if a problem has occurred, make sure to try this option BEFORE logging onto the computer again.
In Windows 8 and Windows 10, the Last Known option is no longer included. Instead, they have other options like Refresh, Reset (Reinstall), Restore, etc. I’ll go into more details below in the Windows 8/10 section.
Also note that there are three types of Safe Mode, so read the descriptions below to figure out which one is best for you.
Safe Mode – The basic option that loads Windows with a GUI interface and is usually what most people should choose when troubleshooting their computer.
Safe Mode with Networking – If you need access to the Internet or the network while in Safe mode, then this is the option to choose. This mode is useful when you need to fix a problem that requires an Internet connection so that you can download updates, drivers, or other files to help fix your problem.
Safe Mode with Command Prompt – This mode will load with just the MS DOS command line prompt. This is useful if you need to run a DOS command like fixboot or chkdsk.
Safe Mode in Windows XP/Vista/7
To get into the Safe Mode in Windows XP, Vista or 7, re-boot the computer and then press and hold the “F8 Key” which will then bring up the “Windows Advanced Options Menu“. Scroll down to “Safe Mode” using the arrow keys and press Enter.
Note that sometimes if you press and hold the F8 key, some computers will start to beep annoyingly, so in that case, simply hold the F8 key continuously during the boot up period.
If you are still not able to get into Safe Mode, you can try to kill the power on the computer to turn it off and then turn it back on. If Windows shuts down unexpectedly, it will usually bring up the Advanced Boot Options menu automatically. If that doesn’t work, you can read my previous post on getting into Safe Mode if F8 is not working. This method, however, requires you to be able to log into Windows in order to tell it to boot into safe mode on the next restart.
Safe Mode in Windows 8/10
In Windows 8 and Windows 10, the process of getting into safe mode is completely different. The F8 key no longer works because the boot process is too fast.
The only way to get into safe mode is to boot into System Recovery Options, which is where you can perform various troubleshooting tasks including starting in safe mode.
I’ve already written about how to boot to the Windows 8 System Recovery Options screen, but the process is slightly different for Windows 10, so I’ll mention it here. In Windows 10, there are two ways to get to the recovery options screen. Firstly, you can click on the new Start button, which is back again in a different form, and then hold down the SHIFT key and click on the power button.
While still holding down the SHIFT key, click on Restart. The other way is the same as Windows 8, but it just looks a bit different. Click on the Start button and then click on Settings as shown above.
This will bring up a new Settings dialog that basically replaces the PC Settings dialog in Windows 8. Here you will click on Update & recovery.
Now you’ll see the options to refresh your PC, reinstall everything or restart in advanced startup mode.
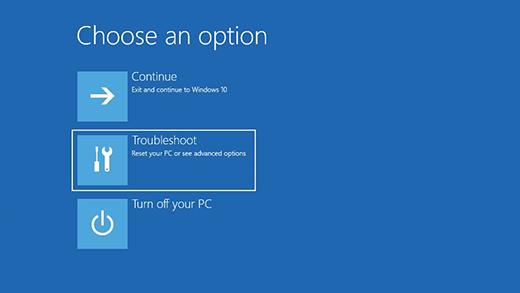
At this point, the process to get into Safe Mode in Windows 8 or Windows 10 is the same. You’ll now see three options: Continue, Troubleshoot and Turn off your PC.
Now just follow the instructions on my article on booting to safe mode in Windows 8. You basically click on Troubleshoot and go from there. Windows 8 and Windows 10 are also a lot smarter than previous versions and will normally bring up the recovery options automatically if a problem is detected while booting.
If you have any questions about getting into safe mode on any version of Windows, feel free to post a comment. Enjoy!
Founder of Online Tech Tips and managing editor. He began blogging in 2007 and quit his job in 2010 to blog full-time. He has over 15 years of industry experience in IT and holds several technical certifications. Read Aseem’s Full Bio