- Управление службами Windows с помощью PowerShell
- Основные командлеты PowerShell для управления службами Windows
- Остановка, запуск, приостановка и перезапуск служб из PowerShell
- Set-Service – изменение настроек службы Windows
- Создание и удаление служб Windows c помощью PowerShell
- Изменение учетной записи для запуска службы
- Start, stop, pause, resume, restart SQL Server services
- Identify the service
- Database Engine service
- SQL Server Agent service
- SQL Server Browser service
- Additional Information
- Security
- Permissions
- SQL Server Configuration Manager
- Starting SQL Server Configuration Manager
- To start, stop, pause, resume, or restart an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine
- To start, stop, pause, resume, or restart the SQL Server Browser or an instance of the SQL Server Agent
- SQL Server Management Studio
- To start, stop, pause, resume, or restart an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine
- To start, stop, or restart an instance of the SQL Server Agent
- Command Prompt Window using net Commands
- To start the default instance of the Database Engine
- To start a named instance of the Database Engine
- To start the Database Engine with startup options
- To start the SQL Server Agent on the default instance of SQL Server
- To start the SQL Server Agent on a named instance of SQL Server
- To start the SQL Server Browser
- To pause or stop services from the Command Prompt window
- Transact-SQL
- To stop the Database Engine using Transact-SQL
- PowerShell
- To start and stop Database Engine services
- Using Service Controller Class
- Manage the SQL Server service on Linux
- To start, stop, or restart an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine
Управление службами Windows с помощью PowerShell
В Windows вы можете управлять службами не только из графической консоли services.msc или утилиты командной строки Sc.exe (первоначальна включалась в пакет ресурсов Resource Kit), но и с помощью PowerShell. В этой статье мы смотрим различные сценарии управления службами Windows с помощью PowerShell.
Основные командлеты PowerShell для управления службами Windows
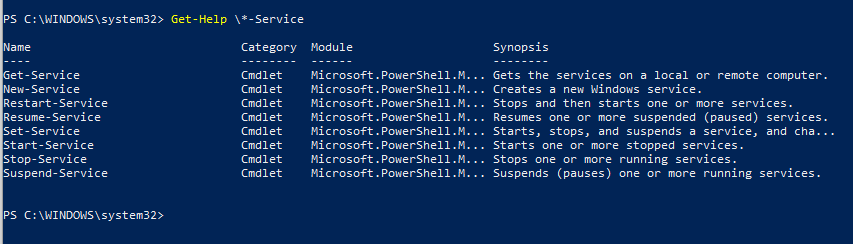
Существует восемь основных командлетов Service, предназначенных для просмотра состояния и управления службами Windows.
Чтобы получить весь список командлетов Service, введите команду:
- Get-Service — позволяет получить службы на локальном или удаленном компьютере, как запущенные, так и остановленные;
- New-Service – создать службу. Создает в реестре и базе данных служб новую запись для службы Windows;
- Restart-Service – перезапустить службу. Передает сообщение об перезапуске службы через Windows Service Controller
- Resume-Service – возобновить службы. Отсылает сообщение о возобновлении работы диспетчеру служб Windows;
- Set-Service — изменить параметры локальной или удаленной службы, включая состояние, описание, отображаемое имя и режим запуска. Этот командлет также можно использовать для запуска, остановки или приостановки службы;
- Start-Service – запустить службу;
- Stop-Service – остановить службу (отсылает сообщение об остановке диспетчеру служб Windows);
- Suspend-Service приостановить службу. Приостановленная служба по-прежнему выполняется, однако ее работа прекращается до возобновления работы службы, например с помощью командлета Resume-Service.
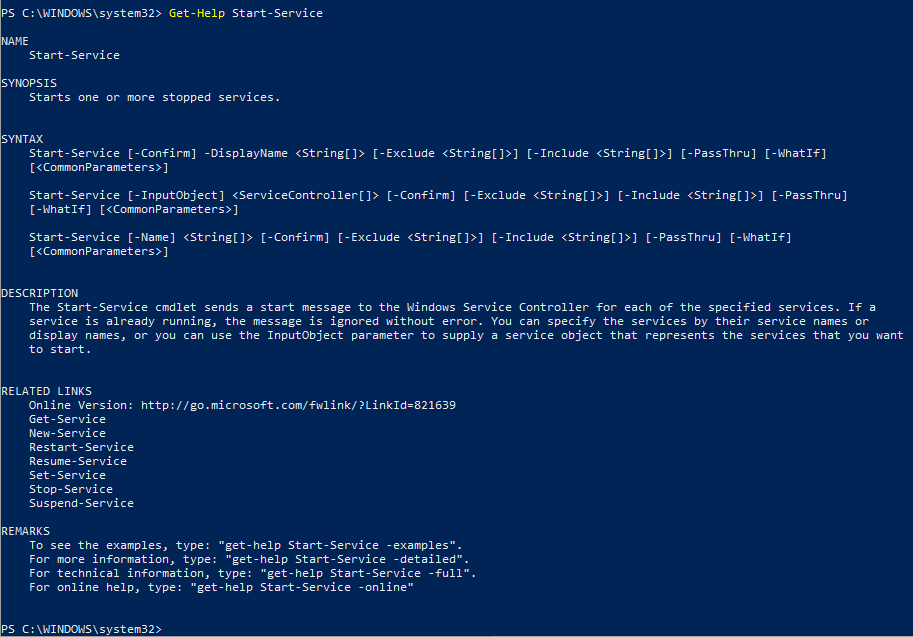
Получить подробное описание и примеры использования конкретного командлета можно через Get-help:
Get-Service: получаем список служб и их состояние
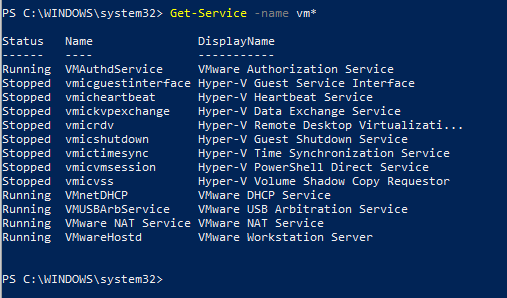
Получить список и состояние (Running/Stopped) службы на локальном или удаленном компьютере можно с помощью командлета Get-Service. Параметр -Name позволяет делать отбор по имени службы. Имя службы можно задать с использованием подстановочного символа *.
Если вы не знаете точное имя службы, есть возможность найти службы по отображаемому имени с помощью параметра –DisplayName. Можно использовать список значений и подстановочные знаки.
Командлет Get-Service можно использовать для получения состояния служб на удаленных компьютерах, указав параметр -ComputerName. Можно опросить статус службы сразу на множестве удаленных компьютеров, их имена нужно перечислить через запятую. Например, приведенная ниже команда получает состояние службы Spooler на удаленных компьютерах RM1 и RM2.
Get-Service spooler –ComputerName RM1,RM2
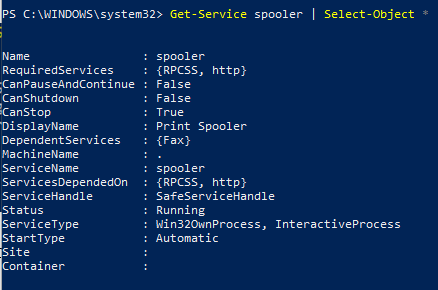
Вывести все свойства службы позволит командлет Select-Object:
Get-Service spooler | Select-Object *
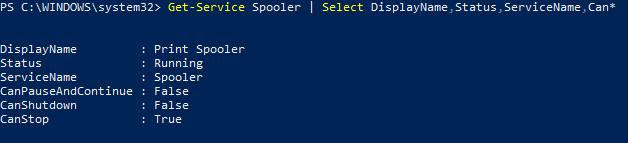
Командлет Select-Object позволит вывести определенные свойства службы. Например, нам нужно вывести имя, статус и доступные возможности службы Spooler:
Get-Service Spooler | Select DisplayName,Status,ServiceName,Can*
Командлет Get-Service имеет два параметра, которые позволяют получить зависимости служб:
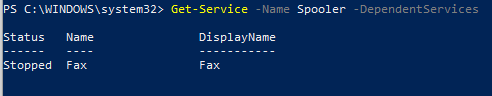
- Параметр -DependentServices позволяет вывести службы, которые зависят от данной службы;
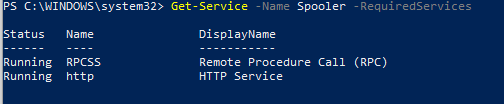
- Параметр -RequiredServices позволяет вывести службы, от которых зависит данная служба.
Приведенная ниже команда выводит службы, необходимые для запуска службе Spooler:
Get-Service –Name Spooler -RequiredServices
Следующая команда выводит службы, которые зависят от службы Spooler:
Get-Service –Name Spooler -DependentServices
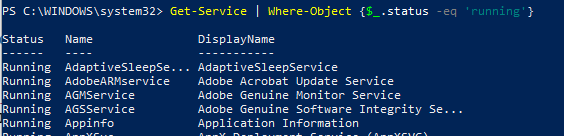
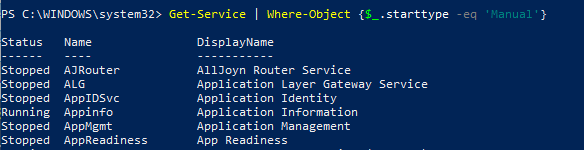
При необходимости найти службы с определенным состоянием или параметрами, используйте командлет Where-Object. Например, получим список запущенных служб со статусом Running:
Для вывода служб с типом запуска Manual, выполните команду
Проверить, что в системе имеется указанная служба:
if (Get-Service «ServiceTest» -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)
<
Write-host «ServiceTest exists»
>
Остановка, запуск, приостановка и перезапуск служб из PowerShell
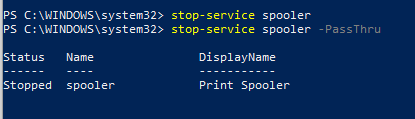
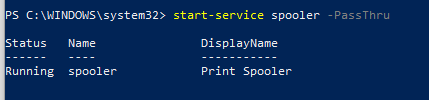
Остановить службу можно с помощью командлета Stop-Service. Чтобы остановить службу печати, выполните команду:
Stop-Service -Name spooler
Командлет Stop-Service не выводит никаких данных после выполнения. Чтобы увидеть результат выполнения команды, используйте параметр -PassThru.
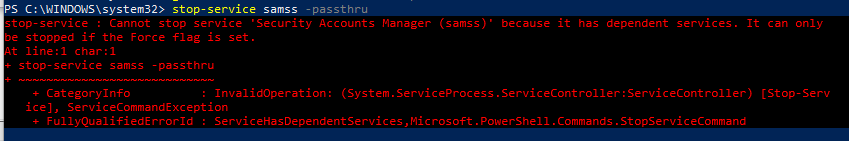
Обратите внимание, что не каждую службу можно остановить. Если есть зависимые службы, то получите ошибку
Для принудительной остановки используйте параметр –Force. Вы должны помнить, что остановятся также все зависимые службы:
Stop-Service samss –Force -Passthru
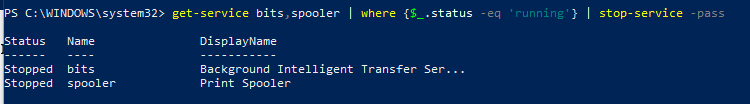
Следующая команда остановит перечисленные службы (bits,spooler) со статусом ”Running”:
get-service bits,spooler | where <$_.status -eq 'running'>| stop-service –passthru
Командлет Start-Service запускает остановленные службы:
Start-Service -Name spooler -PassThru
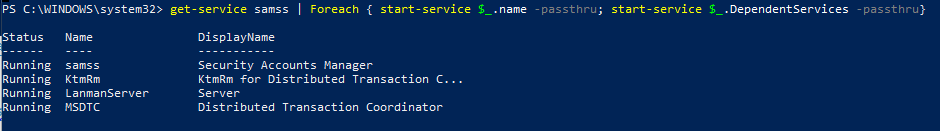
Служба не запустится, если есть остановленные зависимые службы. Чтобы их найти и включить:
get-service samss | Foreach
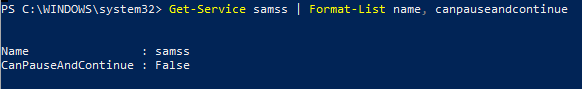
Командлет Suspend-Service может приостанавливать службы, допускающие временную приостановку и возобновление. Для получения сведений о возможности временной приостановки конкретной службы используйте командлет Get-Service со свойством «CanPauseAndContinue«.
Get-Service samss | Format-List name, canpauseandcontinue
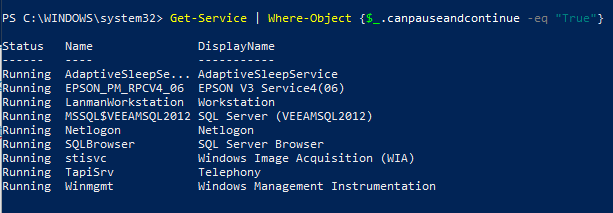
Чтобы отобразить список всех служб, работа которых может быть приостановлена, введите команду:
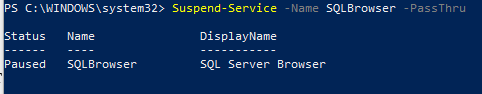
Приостановим службу SQLBrowser:
Suspend-Service -Name SQLBrowser
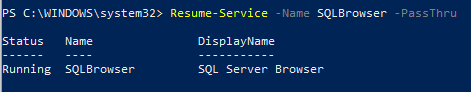
Для возобновления работы приостановленной службы служит командлет Resume-service:
Resume-Service -Name SQLBrowser
Следующая команда возобновляет работу всех приостановленных служб:
get-service | where-object <$_.Status -eq "Paused">| resume-service
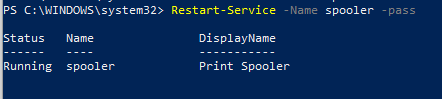
Командлет Restart-Service перезапускает службу:
Restart-Service -Name spooler
Эта команда запускает все остановленные сетевые службы компьютера:
get-service net* | where-object <$_.Status -eq "Stopped">| restart-service
Параметр —ComputerName у этих командлетов отсутствует, но их можно выполнить на удаленном компьютере с помощью командлета Invoke-Command или через пайп:
Например, чтобы перезапустите очередь печати на удаленном компьютере RM1, выполните команду:
Get-Service Spooler -ComputerName RM1 | Start-Service
Set-Service – изменение настроек службы Windows
Командлет Set-Service позволяет изменить параметры или настройки служб на локальном или удаленном компьютере. Так как состояние службы является свойством, этот командлет можно использовать для запуска, остановки и приостановки службы. Командлет Set-Service имеет параметр -StartupType, позволяющий изменять тип запуска службы.
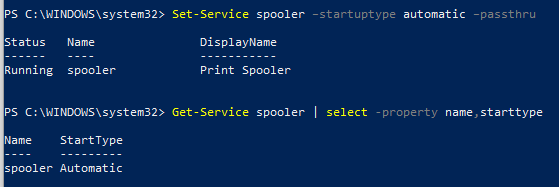
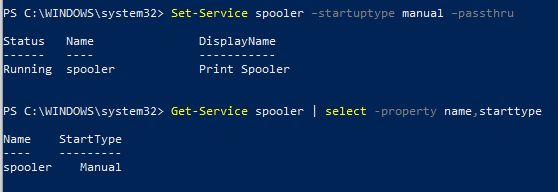
Изменим тип запуска службы spooler на автоматический:
Set-Service spooler –startuptype automatic –passthru
Можно перевести службу на ручной (manual) запуск:
Set-Service spooler –startuptype manual –passthru
Создание и удаление служб Windows c помощью PowerShell
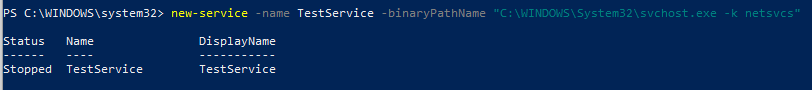
New-Service – командлет для создания новой службы в Windows. Для новой службы требуется указать имя и исполняемый файл (вы можете запустить PowerShell скрипт как службу Windows).
В примере создадим новую службу с именем TestService.
new-service -name TestService -binaryPathName «C:\WINDOWS\System32\svchost.exe -k netsvcs»
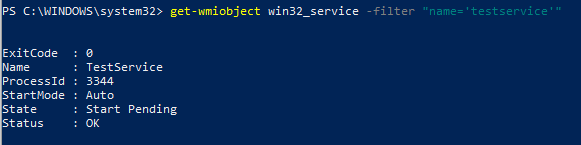
С помощью параметра Get-WmiObject получим информацию о режиме запуска и описание службы
get-wmiobject win32_service -filter «name=’testservice'»
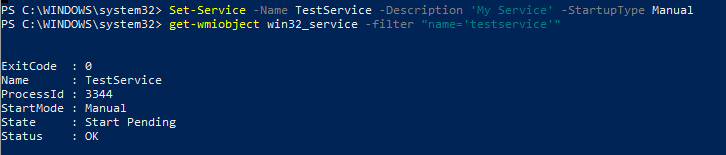
Изменить параметры новой службы можно командой
Set-Service -Name TestService -Description ‘My Service’ -StartupType Manual
Чтобы удалить службу используйте команду
(Get-WmiObject win32_service -Filter ″name=′TestService′″).delete()
Изменение учетной записи для запуска службы
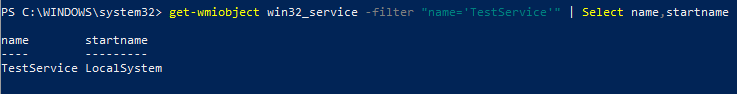
Вы можете изменить учетную запись, из-под которой запускается служба. Получим имя учетной записи, которая используется для запуска службы TestService
get-wmiobject win32_service -filter «name=’TestService'» | Select name,startname
Для изменения имени и пароля учетной записи выполняем команды.
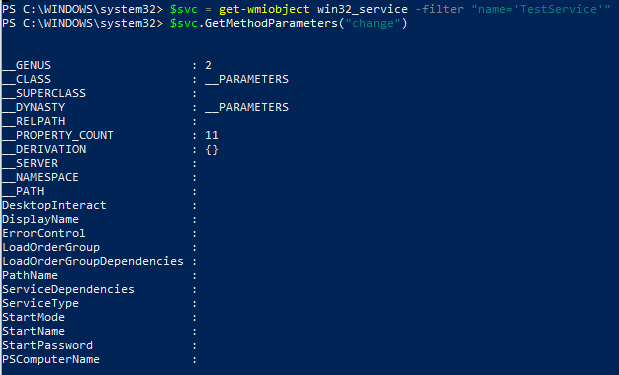
$svc = get-wmiobject win32_service -filter «name=’TestService'»
$svc.GetMethodParameters(«change»)
В результате получаем список параметров метода Change(). Считаем на каком месте находятся параметры StartName и StartPassword – 20 и 21 место соответственно.
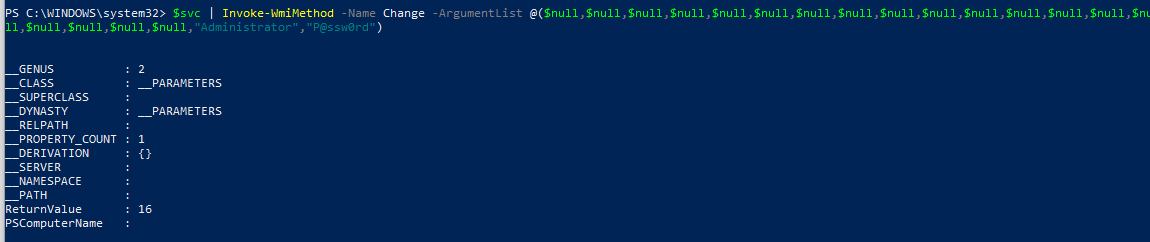
$svc | Invoke-WmiMethod -Name Change –ArgumentList @ ($null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null, $null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null, $null,$null,$null,»Administrator»,»P@ssw0rd»)
Либо вы можете указать имя gMSA аккаунта. Пароль при этом не указывается.
Как видите, PowerShell позволяет легко управлять службами Windows. Можно создавать, останавливать, запускать и возобновлять службы, менять их свойства. Большинство командлетов позволяют управлять службами на удаленных компьютерах.
Start, stop, pause, resume, restart SQL Server services
Applies to: SQL Server (all supported versions)
This topic describes how to start, stop, pause, resume, or restart the SQL Server Database Engine, the SQL Server Agent, or the SQL Server Browser service by using SQL Server Configuration Manager, SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), net commands from a command prompt, Transact-SQL, or PowerShell.
Identify the service
SQL Server components are executable programs that run as a Windows service. Programs that run as a Windows service can continue to operate without displaying any activity on the computer screen.
Database Engine service
The executable process that is the SQL Server Database Engine. The Database Engine can be the default instance (limit one per computer) or can be one of many named instances of the Database Engine. Use SQL Server Configuration Manager to determine which instances of the Database Engine are installed on the computer. The default instance (if you install it) is listed as SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER). Named instances (if you install them) are listed as SQL Server ( ). By default, SQL Server Express is installed as SQL Server (SQLEXPRESS).
SQL Server Agent service
A Windows service that executes scheduled administrative tasks, which are called jobs and alerts. For more information, see SQL Server Agent. SQL Server Agent is not available in every edition of SQL Server. For a list of features that are supported by the editions of SQL Server, see Features Supported by the Editions of SQL Server 2019.
SQL Server Browser service
A Windows service that listens for incoming requests for SQL Server resources and provides clients information about SQL Server instances installed on the computer. A single instance of the SQL Server Browser service is used for all instances of SQL Server installed on the computer.
Additional Information
Pausing the Database Engine service prevents new users from connecting to the Database Engine, but users who are already connected can continue to work until their connections are broken. Use pause when you want to wait for users to complete work before you stop the service. This enables them to complete transactions that are in progress. Resume allows the Database Engine to accept new connections again. The SQL Server Agent service cannot be paused or resumed.
The SQL Server Configuration Manager and SSMS display the current status of services by using the following icons.
SQL Server Configuration Manager
A green arrow on the icon next to the service name indicates that the service is started.
A red square on the icon next to the service name indicates that the service is stopped.
Two vertical blue lines on the icon next to the service name indicate that the service is paused.
When restarting the Database Engine, a red square indicates that the service stopped, and then a green arrow indicates that the service started successfully.
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
A white arrow on a green circle icon next to the service name indicates that the service is started.
A white square on a red circle icon next to the service name indicates that the service is stopped.
Two vertical white lines on a blue circle icon next to the service name indicate that the service is paused.
When using SQL Server Configuration Manager or SSMS, only options that are possible are available. For example, if the service is already started, Start is unavailable.
When running on a cluster, the SQL Server Database Engine service is best managed by using Cluster Administrator.
Security
Permissions
By default, only members of the local administrators group can start, stop, pause, resume, or restart a service. To grant non-administrators the ability to manage services, see How to grant users rights to manage services in Windows Server 2003. (The process is similar on other versions of Windows Server.)
Stopping the Database Engine by using the Transact-SQL SHUTDOWN command requires membership in the sysadmin or serveradmin fixed server roles, and is not transferable.
SQL Server Configuration Manager
Starting SQL Server Configuration Manager
On the Start menu, point to All Programs, point to Microsoft SQL Server, point to Configuration Tools, and then click SQL Server Configuration Manager.
Because the SQL Server Configuration Manager is a snap-in for the Microsoft Management Console program and not a stand-alone program, SQL Server Configuration Manager does not appear as an application in newer versions of Windows. Here are the paths to the last four versions when Windows is installed on the C drive.
| Version | Path |
|---|---|
| SQL Server 2019 | C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager15.msc |
| SQL Server 2017 | C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager14.msc |
| SQL Server 2016 | C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager13.msc |
| SQL Server 2014 | C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager12.msc |
| SQL Server 2012 | C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager11.msc |
To start, stop, pause, resume, or restart an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine
Start SQL Server Configuration Manager, using the instructions above.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, click Yes.
In SQL Server Configuration Manager, in the left pane, click SQL Server Services.
In the results pane, right-click SQL Server (MSSQLServer) or a named instance, and then click Start, Stop, Pause, Resume, or Restart.
Click OK to close the SQL Server Configuration Manager.
To start an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine with startup options, see Configure Server Startup Options (SQL Server Configuration Manager).
To start, stop, pause, resume, or restart the SQL Server Browser or an instance of the SQL Server Agent
Start SQL Server Configuration Manager, using the instructions above.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, click Yes.
In SQL Server Configuration Manager, in the left pane, click SQL Server Services.
In the results pane, right-click SQL Server Browser, or SQL Server Agent (MSSQLServer) or SQL Server Agent ( ) for a named instance, and then click Start, Stop, Pause, Resume, or Restart.
Click OK to close the SQL Server Configuration Manager.
SQL Server Agent cannot be paused.
SQL Server Management Studio
To start, stop, pause, resume, or restart an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine
In Object Explorer, connect to the instance of the Database Engine, right-click the instance of the Database Engine you want to start, and then click Start, Stop, Pause, Resume, or Restart.
Or, in Registered Servers, right-click the instance of the Database Engine you want to start, point to Service Control, and then click Start, Stop, Pause, Resume, or Restart.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, click Yes.
When prompted if you want to act, click Yes.
To start, stop, or restart an instance of the SQL Server Agent
In Object Explorer, connect to the instance of the Database Engine, right-click SQL Server Agent, and then click Start, Stop, or Restart.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, click Yes.
When prompted if you want to act, click Yes.
Command Prompt Window using net Commands
The Microsoft SQL Server services can be started, stopped, or paused by using Microsoft Windows net commands.
To start the default instance of the Database Engine
From a command prompt, enter one of the following commands:
net start «SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER)»
net start MSSQLSERVER
To start a named instance of the Database Engine
From a command prompt, enter one of the following commands. Replace with the name of the instance you want to manage.
net start «SQL Server ( instancename )»
net start MSSQL$ instancename
To start the Database Engine with startup options
Add startup options to the end of the net start «SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER)» statement, separated by a space. When started using net start, startup options use a slash (/) instead of a hyphen (-).
net start «SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER)» /f /m
net start MSSQLSERVER /f /m
For more information about startup options, see Database Engine Service Startup Options.
To start the SQL Server Agent on the default instance of SQL Server
From a command prompt, enter one of the following commands:
net start «SQL Server Agent (MSSQLSERVER)»
net start SQLSERVERAGENT
To start the SQL Server Agent on a named instance of SQL Server
From a command prompt, enter one of the following commands. Replace instancename with the name of the instance you want to manage.
net start «SQL Server Agent( instancename )»
net start SQLAgent$ instancename
For information about how to run SQL Server Agent in verbose mode for troubleshooting, see sqlagent90 Application.
To start the SQL Server Browser
From a command prompt, enter one of the following commands:
net start «SQL Server Browser»
net start SQLBrowser
To pause or stop services from the Command Prompt window
To pause or stop services, modify the commands in the following ways.
To pause a service, replace net start with net pause.
To stop a service, replace net start with use net stop.
Transact-SQL
The Database Engine can be stopped by using the SHUTDOWN statement.
To stop the Database Engine using Transact-SQL
To wait for currently running Transact-SQL statements and stored procedures to finish, and then stop the Database Engine, execute the following statement.
To stop the Database Engine immediately, execute the following statement.
For more information about the SHUTDOWN statement, see SHUTDOWN (Transact-SQL).
PowerShell
To start and stop Database Engine services
In a Command Prompt window, start SQL Server PowerShell by executing the following command.
At a SQL Server PowerShell command prompt, by executing the following command. Replace computername with the name of your computer.
Identify the service that you want to stop or start. Pick one of the following lines. Replace instancename with the name of the named instance.
To get a reference to the default instance of the Database Engine.
To get a reference to a named instance of the Database Engine.
To get a reference to the SQL Server Agent service on the default instance of the Database Engine.
To get a reference to the SQL Server Agent service on a named instance of the Database Engine.
To get a reference to the SQL Server Browser service.
Complete the example to start and then stop the selected service.
Using Service Controller Class
You can use ServiceController class to control SQL server service or any other Windows service. For an example on how to do this, see ServiceController Class.
Manage the SQL Server service on Linux
To start, stop, or restart an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine
The following shows how to start, stop, restart, and check the status of the SQL Server service on Linux.
Check the status of the SQL Server service using this command:
You can stop, start, or restart the SQL Server service as needed using the following commands: