- How to refresh, reset, or restore your PC
- Before you start to refresh or reset your PC
- Refresh, reset, or restore
- To refresh your PC
- To reset your PC
- To restore your PC to an earlier point in time
- How to restore a Windows 7-based computer to a previous Windows installation by using the Windows.old folder
- INTRODUCTION
- More Information
- Step 1: Determine whether there is a Windows.old folder and whether there is sufficient free space on the Windows hard disk
- Step 2: Start the Windows Recovery Environment
- Step 3: Move the Windows 7 folders to a new Win7 folder
- Step 4: Copy the contents or move the contents of the Windows.old folder
- Step 5: Restore the boot sector for the previous Windows installation
- Step 6: Restore the Boot.ini file for the previous Windows installation of Windows XP or of Windows 2000
- Step 7: Close the Command Prompt window, and then click Restart
- Recovery options in Windows 10
How to refresh, reset, or restore your PC
Note: For information about this topic in Windows 10, see Recovery options in Windows 10.
If you’re having problems with your PC, you can:
Refresh your PC to reinstall Windows and keep your personal files and settings. Refresh also keeps the apps that came with your PC and the apps you installed from the Microsoft Store.
Reset your PC to reinstall Windows but delete your files, settings, and apps—except for the apps that came with your PC.
Restore your PC to undo recent system changes you’ve made.
If you’re having trouble starting (booting) your PC, see Windows Startup Settings (including safe mode), and go to the “Get to Windows Startup Settings in the Windows Recovery Environment” section. You can refresh, reset, or restore your PC from the Windows Recovery Environment.
If you want to back up and restore your personal files using File History, see Set up a drive for File History.
Before you start to refresh or reset your PC
In most cases, once you start to refresh or reset your PC, it’ll finish on its own. However, if Windows needs missing files, you’ll be asked to insert recovery media, which is typically on a DVD disc or thumb drive. If that happens, what you’ll need depends on your PC.
If your PC came with Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1, you’ll need the discs or thumb drive that came with your PC. Check the info that came with your PC to see if your PC manufacturer provided these discs or media. In some cases, you might have created them when you first set up your PC.
If you don’t have either of those, you can make them if you have a USB thumb drive of 16 GB or larger. Having a recovery drive can help you troubleshoot and fix problems with your PC, even if it won’t start. For more info, see Create a USB recovery drive.
If you upgraded your PC to Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1 with a DVD, use that disc. If you don’t have Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1 media, contact Microsoft Support.
Refresh, reset, or restore
Select any of the following for more detailed info.
If your PC isn’t performing as well as it once did, and you don’t know why, you can refresh your PC without deleting any of your personal files or changing your settings.
Note: If you upgraded your PC from Windows 8 to Windows 8.1 and your PC has a Windows 8 recovery partition, refreshing your PC will restore Windows 8. You’ll need to upgrade to Windows 8.1 after the refresh has finished.
Warning: Apps you installed from websites and DVDs will be removed. Apps that came with your PC and apps you installed from Microsoft Store will be reinstalled. Windows puts a list of removed apps on your desktop after refreshing your PC.
To refresh your PC
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, tap Settings, and then tap Change PC settings.
(If you’re using a mouse, point to the upper-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer down, click Settings, and then click Change PC settings.)
Tap or click Update and recovery, and then tap or click Recovery.
Under Refresh your PC without affecting your files, tap or click Get started.
Follow the instructions on the screen.
If you want to recycle your PC, give it away, or start over with it, you can reset it completely. This removes everything and reinstalls Windows.
Note: If you upgraded your PC from Windows 8 to Windows 8.1 and your PC has a Windows 8 recovery partition, resetting your PC will restore Windows 8. You’ll need to upgrade to Windows 8.1 after the reset has finished.
Warning: All of your personal files will be deleted and your settings will be reset. All apps that you installed will be removed. Only apps that came with your PC will be reinstalled.
To reset your PC
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, tap Settings, and then tap Change PC settings.
(If you’re using a mouse, point to the upper-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer down, click Settings, and then click Change PC settings.)
Tap or click Update and recovery, and then tap or click Recovery.
Under Remove everything and reinstall Windows, tap or click Get started.
Follow the instructions on the screen.
Note: You’ll be asked to choose whether you want to erase data quickly or thoroughly. If you choose to erase data quickly, some data might be recoverable using special software. If you choose to erase data thoroughly, this will take longer but it makes recovering data less likely.
If you think an app or driver that you recently installed caused problems with your PC, you can restore Windows back to an earlier point in time, called a restore point. System Restore doesn’t change your personal files, but it might remove recently installed apps and drivers.
System Restore isn’t available for Windows RT 8.1.
Windows automatically creates a restore point when you install desktop apps and new Windows updates, if the last restore point is older than 7 days. You can also create a restore point manually at any time.
To restore your PC to an earlier point in time
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, and then tap Search.
(If you’re using a mouse, point to the upper-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer down, and then click Search.)
Enter Control Panel in the search box, and tap or click Control Panel.
Enter Recovery in the Control Panel search box, and then tap or click Recovery.
Tap or click Open System Restore, and then follow the instructions.
If you need additional help refreshing, resetting, or restoring your PC, check out the Repair and Recovery community pages in the Windows forum for solutions that other people have found for problems they’ve experienced.
How to restore a Windows 7-based computer to a previous Windows installation by using the Windows.old folder
INTRODUCTION
In certain scenarios you may need to restore your Windows 7 Computer back to the previous installation of Windows. This article walks you through the steps to manually restore your computer back to the previous version of Windows.
Note: To do this, you must use the command prompt, and you must type specific commands at the command prompt to rename and to move folders between the different versions of Windows.
Note: If you currently have Service Pack 1 for Windows 7 installed, the uninstall steps are the same as with Windows 7 without any service packs installed. If you are restoring back to a previous Windows 7 installation, you may need to Install Windows 7 Service Pack 1 to that installation.
This article is intended for a beginning to intermediate computer user.
More Information
To resolve this issue, follow the steps listed below to restore your computer back to a previous version of Windows using the Windows.OLD folder.
TIP: You may find it easier to follow the steps if you print this article first.
Step 1: Determine whether there is a Windows.old folder and whether there is sufficient free space on the Windows hard disk
Click Start 
On the View menu, click Details.
In the Free Space column, note how much space is available for Local Disk (C:) under the Hard Disk Drives area.
In the Hard Disk Drives area, double-click Local Disk (C:), and then determine whether the Windows.old folder exists.
Important If the Windows.old folder does not exist, you cannot follow the steps in this article to restore the previous Windows installation to this computer. You must backup and restore or transfer your files to the previous operating system.
Right-click the Windows.old folder.
Windows 7 will determine the size of the folder after several seconds.
Determine whether the Windows.old folder is smaller than the free space that is available for Local Disk (C:) in step 1.2.
Note If the Windows.old folder is two times as large as the free space that is available for the Local Disk (C:) entry, you may be unable to restore the previous Windows installation.
Step 2: Start the Windows Recovery Environment
Put the Windows 7 installation disc in the DVD drive, and then restart the computer.
Press a key when you are prompted to restart from the disc.
In the Install Windows window, select a language, a time, a currency, a keyboard input method or other input method, and then click Next.
In the Install Windows window, click Repair your computer.
In the System Recovery Options window, click the version of the Windows 7 operating system that you want to repair, and then click Next.
In the System Recovery Options window, click Command Prompt.
The Command Prompt window opens, and it displays the command prompt. The command prompt is where you will type the commands that are described in the following steps.
Step 3: Move the Windows 7 folders to a new Win7 folder
Note When you type one or more of the commands at the command prompt in the following steps and press ENTER, you may receive the following message:
The system cannot find the file specified.
If you receive this message, go to the next step in this section, and then type the command in that next step.
Type the following commands and press ENTER after each command:
Move Windows Win7\Windows
Move «Program Files» «Win7\Program Files»
Move Users Win7\Users
Attrib –h –s –r ProgramData
Move ProgramData Win7\ProgramData
Rd «Documents and Settings»
Step 4: Copy the contents or move the contents of the Windows.old folder
Note When you type one or more of the commands at the command prompt in the following steps and press ENTER, you may receive the following message:
The system cannot find the file specified.
If you receive this message, go to the next step in this section, and then type the command in the next step.
Type the following commands and press ENTER after each command:
move /y c:\Windows.old\Windows c:\
move /y «c:\Windows.old\Program Files» c:\
move /y c:\Windows.old\ProgramData c:\
move /y c:\Windows.old\Users c:\
move /y «c:\Windows.old\Documents and Settings» c:\
Step 5: Restore the boot sector for the previous Windows installation
Type one of the following commands at the command prompt, as appropriate for your situation.
Note In the following commands, D: represents the DVD drive. If the DVD drive on the computer is represented by a different letter, such as E:, use that letter in the command.
When the previous Windows installation was Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, or Microsoft Windows 2000
Type the following command, and then press ENTER:
D:\boot\bootsect /nt52 c:
When the previous Windows installation was Windows Vista
Type the following command, and then press ENTER:
D:\boot\bootsect /nt60 c:
Step 6: Restore the Boot.ini file for the previous Windows installation of Windows XP or of Windows 2000
Note Follow these steps only when the previous installation is Windows XP or Windows 2000.
Type the following commands and press ENTER after each command:
Attrib –h –s –r boot.ini.saved
Copy boot.ini.saved boot.ini
Step 7: Close the Command Prompt window, and then click Restart
Type the following command at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
Click Restart to restart your computer.
Note After you have verified that Windows XP is functional, you can remove the C:\Win7 folder if it is not needed for data recovery.
Recovery options in Windows 10
If you’re having problems with your PC, the following table can help you decide which recovery option to use.
See this section
Your PC isn’t working well and you recently installed an update.
Your PC isn’t working well and it’s been a while since you installed an app, driver, or update.
Your PC won’t start, you haven’t created a recovery drive, and resetting your PC didn’t work.
Your PC won’t start and you haven’t created a recovery drive.
Your PC won’t start and you’ve created a recovery drive.
You want to reinstall your previous operating system.
Your PC isn’t working well and you recently installed an app.
Click one of the recovery options below and follow the steps to try to get things working again.
If you’ve recently installed a Windows update, uninstall the update to try to resolve the issue.
Select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > View your update history > Uninstall updates.
View update history settings
Right-click the update you want to remove, and then select Uninstall.
Important: If you’ve encrypted your device, you’ll need your BitLocker key to reset your PC If you don’t know your BitLocker key, see Find my BitLocker recovery key.
Resetting reinstalls Windows 10, but lets you choose whether to keep your files or remove them, and then reinstalls Windows. You can reset your PC from Settings, the sign-in screen, or by using a recovery drive or installation media.
Reset your PC from Settings
Select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Recovery .
Open Recovery settings
Under Reset this PC, select Get started and then choose from the options and/or settings in the table below.
Keep my files > Change settings > Preinstalled apps On
Reinstalls Windows 10 and keeps your personal files.
Removes apps and drivers you installed.
Removes changes you made to settings.
Restores any apps your PC manufacturer installed if your PC came with Windows 10.
Keep my files > Change settings > Preinstalled apps Off
Reinstalls Windows 10 and keeps your personal files.
Removes apps and drivers you installed.
Removes changes you made to settings.
Removes any apps your PC manufacturer installed.
Reinstalls Windows 10 and removes your personal files.
Removes apps and drivers you installed.
Removes changes you made to settings.
Removes any apps your PC manufacturer installed. (If your PC came with Windows 10, apps from your PC manufacturer will be reinstalled.)
Note: Remove everything > Change settings gives you two options.
Data erasure On removes files and cleans the drive. If you’re planning to donate, recycle, or sell your PC, use this option. This might take an hour or two, but it makes it harder for other people to recover files you’ve removed.
Data erasure Off just removes files. It takes less time, but is less secure.
Reset your PC from the sign-in screen
If you can’t open Settings, you can reset your PC from the sign-in screen. Here’s how:
Press Windows logo key + L to get to the sign-in screen, and then restart your PC by pressing the Shift key while you select the Power button > Restart in the lower-right corner of the screen.
Your PC will restart in the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) environment.
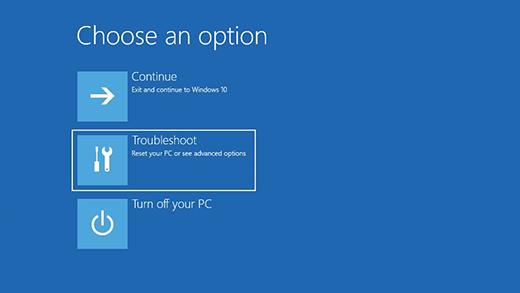
On the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot > Reset this PC, and then choose one of the options in the previous table.
Connect the installation media you created to your PC and reinstall Windows 10.
Open File Explorer and select the drive with the installation media.
From the root directory of the drive, double-click setup.exe, and then select Yes when asked if you’d like to allow the app to make changes to your device.
Select Change what to keep.
Select one of the following options, and then select Next:
Keep personal files and apps – This will preserve your personal data, apps, and settings.
Keep personal files only – This will preserve your personal data and settings, but all your apps will be removed.
Keep nothing – This will remove all personal data, settings, and apps.
Warning: You cannot undo a reinstallation of Windows 10. Be sure to back up your files first if you choose the Keep nothing option.
To finish, select Install to start reinstalling Windows 10 on your PC.
Your PC will restart several times during the resinstallation.
Important: If you’ve encrypted your device, you’ll need your BitLocker key to use a recovery drive to restore or reset your PC If you don’t know your BitLocker key, see Find my BitLocker recovery key.
If your PC won’t start and you haven’t created a recovery drive, download installation media and use it to restore from a system restore point or reset your PC.
Download the Windows 10 media creation tool and then run it.
Select Create installation media for another PC.
Choose a language, edition, and architecture (64-bit or 32-bit).
Follow the steps to create installation media, and then select Finish.
Connect the installation media you created to your nonfunctional PC, and then turn it on.
On the initial setup screen, enter your language and other preferences, and then select Next. If you don’t see the setup screen, your PC might not be set up to boot from a drive. Check your PC manufacturer’s website for info on how to change your PC’s boot order, and then try again.
Select Repair your computer.
On the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot. From there, you can:
Restore from a system restore point by selecting Advanced options > System Restore. This will remove recently installed apps, drivers, and updates that might be causing your PC problems. Restoring from a restore point won’t affect your personal files.
Important: If you’ve encrypted your device, you’ll need your BitLocker key to use a recovery drive to restore or reset your PC If you don’t know your BitLocker key, see Find my BitLocker recovery key.
If your PC won’t start, you can use a recovery drive to restore from a system restore point or recover your PC. For info on how to create a recovery drive on a working PC, see Create a recovery drive.
Note: If you are using a Surface, see Creating and using a USB recovery drive for Surface to download and create a USB recovery image specifically for your Surface device.
To restore or recover using the recovery drive:
Connect the recovery drive and turn on your PC.
Press Windows logo key + L to get to the sign-in screen, and then restart your PC by pressing the Shift key while you select the Power button> Restart in the lower-right corner of the screen.
Your PC will restart in the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) environment.
On the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot, and then select one of the following two options. (If you don’t see the Choose your option screen, your PC might not be set up to boot from a drive. Check your PC manufacturer’s website for info on how to change your PC’s boot order.)
To restore from a system restore point, select Advanced Options > System Restore. This won’t affect your personal files, but it will remove recently installed apps, drivers, and updates that might be causing your PC problems.
To reinstall Windows 10, select Advanced Options > Recover from a drive. This will remove your personal files, apps and drivers you installed, and changes you made to settings.
For a limited time after upgrading to Windows 10, you’ll be able to go back to your previous version of Windows by selecting the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Recovery and then selecting Get started under Go back to the previous version of Windows 10. This will keep your personal files, but it’ll remove apps and drivers installed after the upgrade, as well as any changes you made to settings. In most cases, you’ll have 10 days to go back.
Open Recovery settings
To go back, you’ll need to:
Keep everything in the windows.old and $windows.
bt folders after the upgrade.
Remove any user accounts you added after the upgrade.
Know the password you used to sign in to Windows 7 or Windows 8.1 (if you used one).
Have the USB drive you used to upgrade to Windows 10 (if you used one).
Note: If you go back to Windows 8.1, some apps that came with Windows, like Mail and People, might not work anymore. To fix the apps, reinstall them from the Microsoft Store.
Note: The option in Settings to go back to your previous version of Windows is only available for a limited time after upgrading.
Info for Windows Insiders
If you’re an Insider and the current preview build isn’t working for you, select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Recovery . Under Go back to the previous version of Windows 10, select Get Started. This won’t remove your personal files, but it’ll remove recently installed apps and drivers, and change settings back to their defaults.
Going back to an earlier build won’t remove you from the Insider Program. When the next preview build is ready, it’ll be installed on your PC.
This option takes your PC back to an earlier point in time, called a system restore point. Restore points are generated when you install a new app or driver, and when you create a restore point manually. Restoring won’t affect your personal files, but it will remove apps, drivers, and updates installed after the restore point was made.
In the search box on the taskbar, type control panel,andthen choose it from the list of results
In the Control Panel search box, type recovery.
Select Recovery > Open System Restore.
In the Restore system files and setting box, select Next.
Select the restore point that you want to use in the list of results, and then select Scan for affected programs.
If you don’t see the restore point that you want to use, select the Show more restore points check box to see more restore points.
If you’re not seeing any restore points, it might be because system protection isn’t turned on. Here’s how to check:
In the search box on the taskbar, type control panel,andthen choose it from the list of results.
In the Control Panel search box, type recovery.
Select Recovery > Configure System Restore > Configure and see if the Turn on system protection option is selected.
If the Turn on system protection option is not selected, system protection isn’t turned on and there aren’t any restore points. In this scenario, you won’t be able to recovery your PC using a system restore point and will need to use one of the other recovery options listed on this page.
If the Turn on system protection option is selected, continue with step 6.
You’ll see a list of items that will be deleted if you remove this restore point. If you’re OK with the deletions, select Close> Next > Finish.