- Запуск Python и python-скрипт на компьютере
- Где запускать Python-скрипты и как?
- Запуск Python-кода интерактивно
- Интерактивный режим в Linux
- Интерактивный режим в macOS
- Интерактивный режим в Windows
- Запуск Python-скриптов в интерактивном режиме
- Как выполняются Python-скрипты?
- Блок-схема выполнения кода интерпретатором
- Как запускать Python-скрипты?
- Как запускать скрипт в командной строке?
- Запуск python скрипта в Linux
- Запуск python скрипта в Linux
- How to Run bash scripts Using Python?
- Executing Bash Commands
- subprocess.run()
- subprocess.run() – input
- subprocess.Popen()
- communicate
- subprocess.Popen() – input
- Executing Bash Scripts
- Conclusion
Запуск Python и python-скрипт на компьютере
Код, написанный на языке Python, может храниться в редакторе кода, IDE или файле. И он не будет работать, если не знать, как его правильно запускать.
В этом материале рассмотрим 7 способов запуска кода, написанного на Python. Они будут работать вне зависимости от операционной системы, среды Python или местоположения кода.
Где запускать Python-скрипты и как?
Python-код можно запустить одним из следующих способов:
- С помощью командной строки операционной системы (shell или терминал);
- С помощью конкретной версии Python или Anaconda;
- Использовать Crontab;
- Запустить код с помощью другого Python-скрипта;
- С помощью файлового менеджера;
- Использовать интерактивный режим Python;
- Использовать IDE или редактор кода.
Запуск Python-кода интерактивно
Для запуска интерактивной сессии нужно просто открыть терминал или командную строку и ввести python (или python3 в зависимости от версии). После нажатия Enter запустится интерактивный режим.
Вот как запустить интерактивный режим в разных ОС.
Интерактивный режим в Linux
Откройте терминал. Он должен выглядеть приблизительно вот так :
После нажатия Enter будет запущен интерактивный режим Python.
Интерактивный режим в macOS
На устройствах с macOS все работает похожим образом. Изображение ниже демонстрирует интерактивный режим в этой ОС.
Интерактивный режим в Windows
В Windows нужно открыть командную строку и ввести python . После нажатия Enter появится приблизительно следующее:
Запуск Python-скриптов в интерактивном режиме
В таком режиме можно писать код и исполнять его, чтобы получить желаемый результат или отчет об ошибке. Возьмем в качестве примера следующий цикл.
Этот код должен выводить целые числа от 0 до 5. В данном случае вывод — все, что появилось после print(i) .
Для выхода из интерактивного режима нужно написать следующее:
И нажать Enter. Вы вернетесь в терминал, из которого и начинали.
Есть и другие способы остановки работы с интерактивным режимом Python. В Linux нужно нажать Ctrl + D, а в Windows — Ctrl + Z + Enter.
Стоит отметить, что при использовании этого режима Python-скрипты не сохраняются в локальный файл.
Как выполняются Python-скрипты?
Отличный способ представить, что происходит при выполнении Python-скрипта, — использовать диаграмму ниже. Этот блок представляет собой скрипт (или функцию) Python, а каждый внутренний блок — строка кода.
При запуске скрипта интерпретатор Python проходит сверху вниз, выполняя каждую из них. Именно таким образом происходит выполнение кода.
Но и это еще не все.
Блок-схема выполнения кода интерпретатором
- Шаг 1: скрипт или .py-файл компилируется, и из него генерируются бинарные данные. Готовый файл имеет расширение .pyc или .pyo.
- Шаг 2: генерируется бинарный файл. Он читается интерпретатором для выполнения инструкций.
Это набор инструкций, которые приводят к финальному результату.
Иногда полезно изучать байткод. Если вы планируете стать опытным Python-программистом, то важно уметь понимать его для написания качественного кода.
Это также пригодится для принятия решений в процессе. Можно обратить внимание на отдельные факторы и понять, почему определенные функции/структуры данных работают быстрее остальных.
Как запускать Python-скрипты?
Для запуска Python-скрипта с помощью командной строки сначала нужно сохранить код в локальный файл.
Возьмем в качестве примера файл, который был сохранен как python_script.py. Сохранить его можно вот так:
- Создать Python-скрипт из командной строки и сохранить его,
- Создать Python-скрипт с помощью текстового редактора или IDE и сохранить его. Просто создайте файл, добавьте код и сохраните как «python_script.py»
Сохранить скрипт в текстовом редакторе достаточно легко. Процесс ничем не отличается от сохранения простого текстового файла.
Но если использовать командную строку, то здесь нужны дополнительные шаги. Во-первых, в самом терминале нужно перейти в директорию, где должен быть сохранен файл. Оказавшись в нужной папке, следует выполнить следующую команду (на linux):
После нажатия Enter откроется интерфейс командной строки, который выглядит приблизительно следующим образом:
Теперь можно писать код и с легкостью сохранять его прямо в командной строке.
Как запускать скрипт в командной строке?
Скрипты можно запустить и с помощью команды Python прямо в интерфейсе терминала. Для этого нужно убедиться, что вы указали путь до него или находитесь в той же папке. Для выполнения скрипта (python_script.py) откройте командную строку и напишите python3 python_script.py .
Замените python3 на python , если хотите использовать версию Python2.x.
Источник
Запуск python скрипта в Linux
Python — очень популярный язык программирования для написания различных системных скриптов в Linux. В Windows, там где не хватает возможностей командной оболочки используется PowerShell. В Linux же, когда возможностей Bash не хватает используется язык Python.
На этом языке написано огромное количество системных программ, среди них пакетный менеджер apt, видеоредактор OpenShot, а также множество скриптов, которые вы можете установить с помощью утилиты pip. В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим как запустить Python скрипт в Linux с помощью терминала различными способами.
Запуск python скрипта в Linux
Для примера нам понадобится Python скрипт. Чтобы не брать какой-либо из существующих скриптов, давайте напишем свой:
print(«Hello from losst!»)
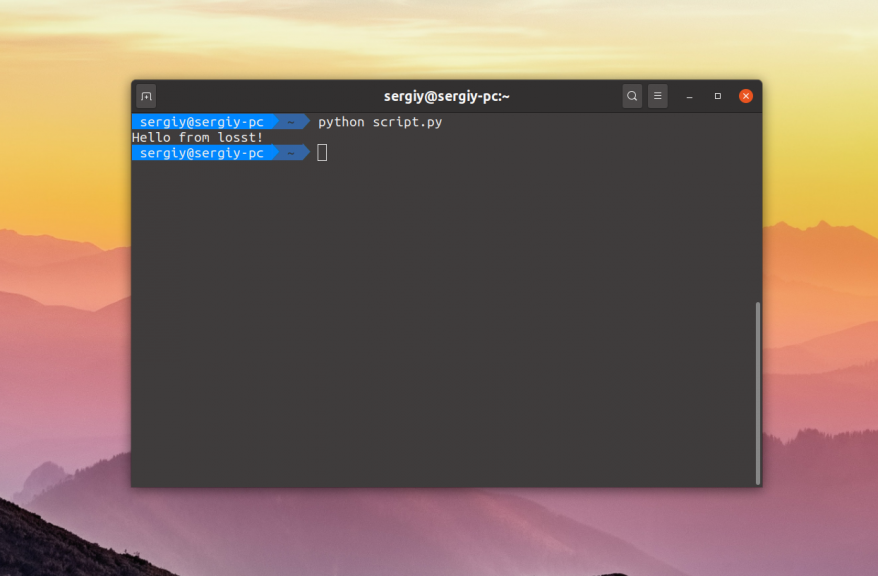
Для того чтобы запустить скрипт необходимо передать его интерпретатору Python. Для этого просто откройте терминал с помощью сочетания клавиш Ctrl + Alt + T, перейдите в папку со скриптом и выполните:
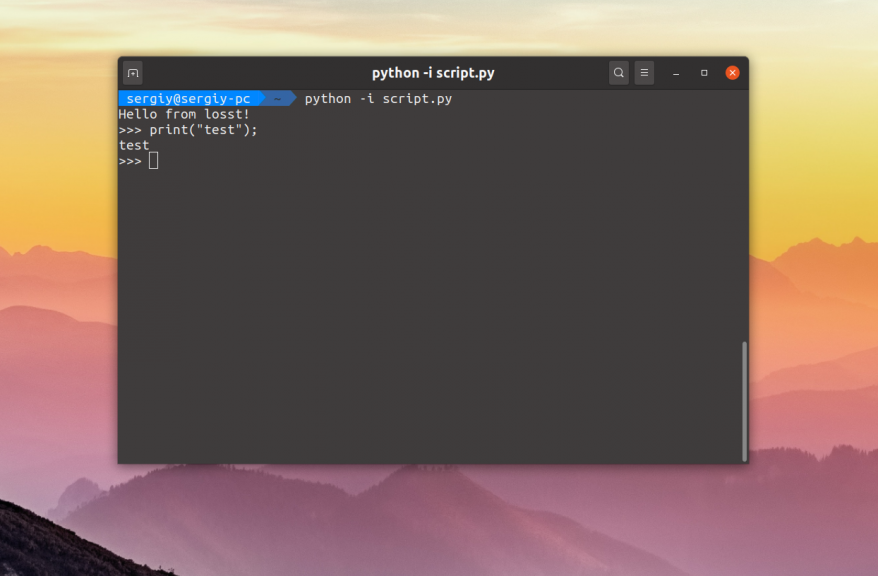
Если вы хотите, чтобы после выполнения скрипта открылась консоль, в которой можно интерактивно выполнять команды языка Python используйте опцию -i:
python -i script.py
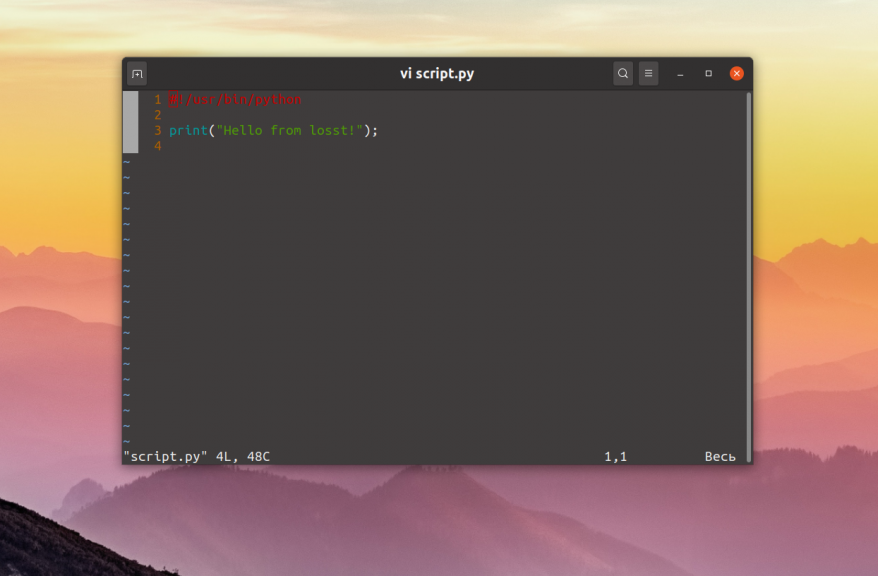
Но как вы могли заметить, при запуске apt или openshot не надо писать слово python. Это намного удобнее. Давайте разберемся как это реализовать. Если вы не хотите указывать интерпретатор в командной строке, его надо указать в самом скрипте. Для этого следует в начало скрипта добавить такую строчку:
Сохраните изменения, а затем сделайте файл скрипта исполняемым с помощью такой команды:
chmod ugo+x script.py
После этого можно запустить скрипт Python просто обращаясь к его файлу:
Если убрать расширение .py и переместить скрипт в каталог, находящийся в переменной PATH, например /usr/bin/, то его можно будет выполнять вот так:
Как видите, запуск команды python Linux выполняется довольно просто и для этого даже есть несколько способов. А каким способом пользуетесь вы? Напишите в комментариях!
Источник
How to Run bash scripts Using Python?
Geekflare is supported by our audience. We may earn affiliate commissions from buying links on this site.
If you are using Linux, then you would definitely love the shell commands.
And if you are working with Python, then you may have tried to automate things. That’s a way to save time. You may also have some bash scripts to automate things.
Python is handy to write scripts than bash. And managing Python scripts are easy compared to bash scripts. You will find it difficult to maintain the bash scripts once it’s growing.
But what if you already have bash scripts that you want to run using Python?
Is there any way to execute the bash commands and scripts in Python?
Yeah, Python has a built-in module called subprocess which is used to execute the commands and scripts inside Python scripts. Let’s see how to execute bash commands and scripts in Python scripts in detail.
Executing Bash Commands
As you may have already seen the module subprocess is used to execute the bash commands and scripts. It provides different methods and classes for the same.
There are mainly one method and one class to know about from the subprocess module. They are run and Popen. These two help us to execute the bash commands in Python scripts. Let’s see them one by one.
subprocess.run()
The method subprocess.run() will take a list of strings as a positional argument. This is mandatory as it has the bash command and arguments for it. The first item in the list is the command name and the remaining items are the arguments to the command.
Let’s see a quick example.
The above script list all the items in the current working directory as the script lies. There are no arguments to the command in the above script. We have given only the bash command. We can provide additional arguments to the ls command like -l , -a , -la , etc.
Let’s see a quick example with command arguments.
The above command displays all the files including hidden files along with the permissions. We have provided the argument la which displays files and directories extra information and hidden files.
We may end up making some mistakes while writing the commands. Errors will raise according to the mistakes. What if you want to capture them and use them later? Yeah, we can do that using the keyword argument stderr.
Let’s see an example.
Make sure you don’t have the file with the name sample.txt in the working directory. The value to the keyword argument stderr is PIPE which helps to return the error in an object. We can access it later with the same name. And the keyword argument text helps to tell that the output should be a string.
Similarly, we can capture the output of the command using the stdout keyword argument.
subprocess.run() – input
You can give input to the commands using the input keyword argument. We will give inputs in a string format. So, we need to set the keyword argument text to True . By default, it takes it in bytes.
Let’s look at an example.
In the above program, the Python script add.py will take two numbers as input. We have given the input to the Python script using the input keyword argument.
subprocess.Popen()
The class subprocess.Popen() is advanced than the method subprocess.run(). It gives us more options to execute the commands. We will create an instance of the subprocess.Popen() and use it for various things like knowing the status of the command execution, getting output, giving input, etc.
There are several methods of the class subprocess.Popen() that we need to know. Let’s see them one by one along with the code examples.
It is used to wait until the completion of the execution of the command. The next lines of the Python script won’t execute until the completion of the previous command that is written after the wait method. Let’s see the example.
Run the above code and observe the output. You will see that the message Completed! is printed before the execution of the command. We can avoid it using the wait method. Let’s wait till the completion of the command.
If you see the output for the above code, then you will realize that wait is actually working. The print statement is executed after the completion of the command execution.
communicate
The method communicate is used to get the output, error and give input to the command. It returns a tuple containing output and error respectively. Let’s see an example.
subprocess.Popen() – input
We can’t pass the input to the class Popen directly. We need to use the keyword argument called stdin to give the input to the command. The instance of the class Popen will provide us stdin object. It has a method called write which is used to give the input to the command.
As we discussed earlier, it will take inputs as bytes-like objects by default. So, don’t forget to set the keyword argument text to True while creating the instance of Popen .
Let’s see an example.
The method poll is used to check whether the execution of the command is completed or not. This method will return None if the command is still executing. Let’s see an example.
In the above code, we have used the ping command with 5 requests. There is an infinite loop that iterates until the completion of the command execution. We have used the method poll to check the status of the command execution. If the method poll returns code other than None , then the execution completes. And the infinite loop breaks.
Executing Bash Scripts
We have seen two ways to execute the commands. Now, let’s see how to execute the bash scripts in Python scripts.
The subprocess has a method called call. This method is used to execute the bash scripts. The method returns the exit code from the bash script. The default exit code for the bash scripts is 0. Let’s see an example.
Create a bash script with the name practice.sh as follows.
Now, write a Python script execute the above bash script.
You will get the following output once you run the above Python script.
Conclusion
We have seen how to execute bash commands and scripts in Python. You can use them to automate things more efficiently.
Источник